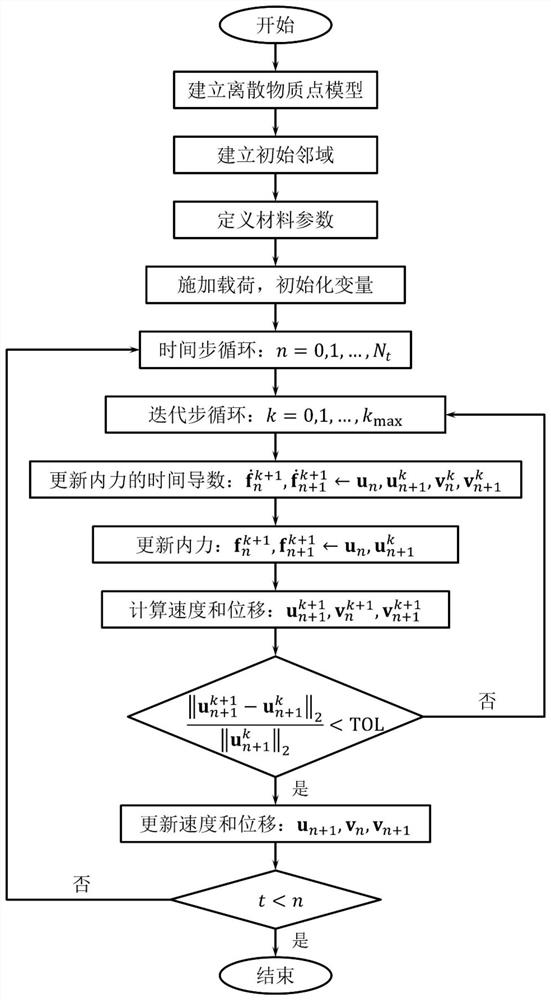
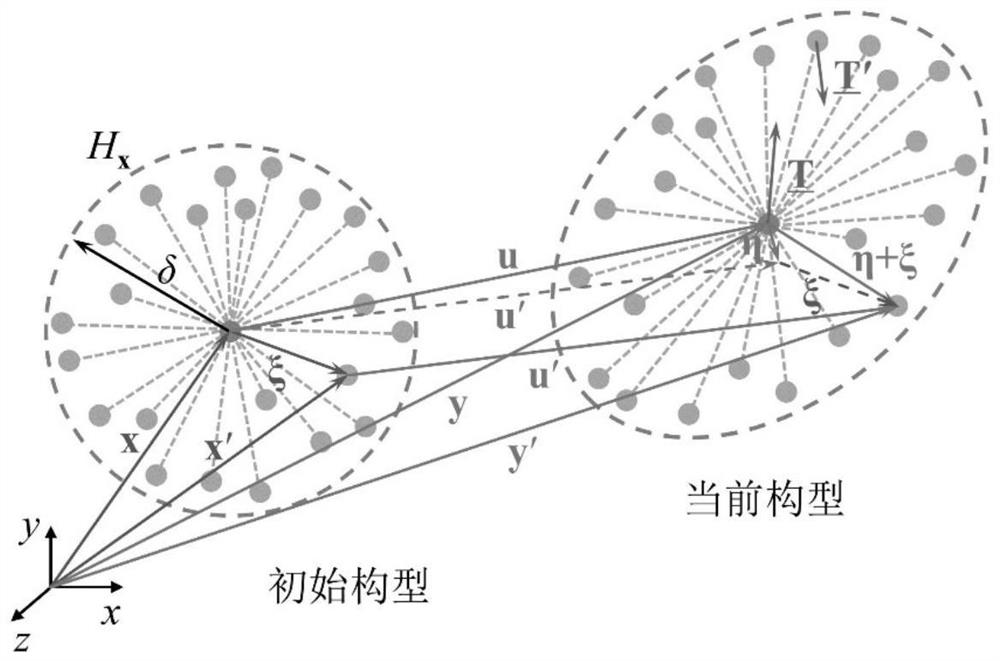
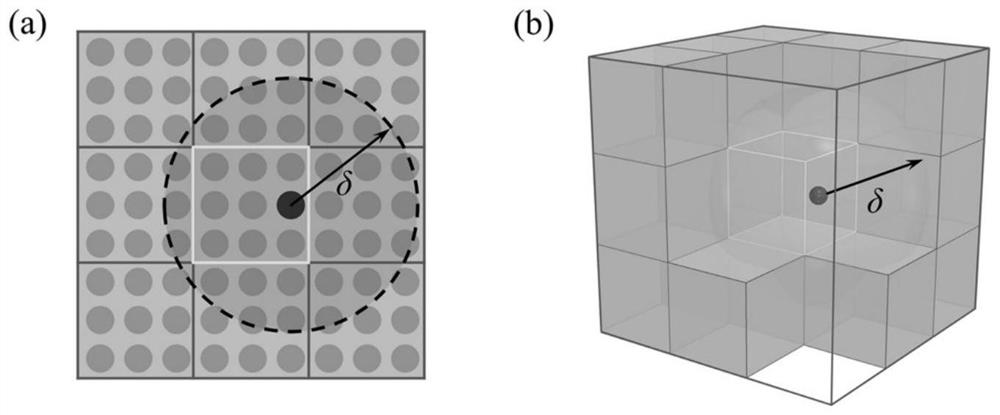
Time discontinuous state-based near-field dynamics method for structure impact elastic-plastic fracture analysis
A technology of structural impact and elastoplasticity, applied in the field of computational mechanics, can solve problems such as reducing the difficulty of numerical implementation, reducing numerical accuracy, reducing the complexity of fracture mechanics damage representation, etc., achieving the goal of simple numerical simulation method, reducing complexity and reducing difficulty Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0149] Example 1: Propagation of Stress Waves in Elastoplastic Rods (attached Figure 4~5 )
[0150] This example is a standard numerical example, considering the propagation of stress waves in a one-dimensional structure, the structure size and boundary conditions are as follows Figure 4 shown. The length of the rod is 10m, which is discretized into 5000 material points. The right end of the rod is free, and its left end is subject to impact load,
[0151]
[0152] Using Johnson-Cook constitutive model, Young's modulus E=10000Pa, Poisson's ratio ν=0, mass density ρ=1kg / m 3 . The material constants of the Johnson-Cook model are A=5Pa, B=600Pa, m 1 =0.7, C=0. Figure 5 Illustrated at t a = 0.055s and t b = 0.135s Stress wave distributions obtained using time-discontinuous state-based peridynamics SBPD-TD and peridynamics-coupled central difference method SBPD-CDM, respectively. Since the plastic modulus varies with the stress state, the propagation of the stress wa...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Embodiment 2: the prediction of elastoplastic rod fracture position (attachment Figure 6~7 )
[0154] This embodiment is an example of predicting the fracture position of an elastoplastic rod under impact load. Peridynamics, as a non-local theory, can overcome the singularity problems encountered in traditional continuum mechanics damage research to a certain extent. Therefore, peridynamics has a significant advantage in dealing with fracture problems. In the following, a numerical example is used to illustrate the advantages and necessity of time-discontinuous state-based peridynamics in predicting crack locations. First consider a bar that can be compressed but can only bear a low tensile stress. The dimensions of the model and the boundary conditions are as follows Figure 4 shown. The length of the rod is 10m, which is discretized into 5000 material points. The right end of the rod is free, and the left end is subjected to impact load as shown in formula (44)....
Embodiment 3
[0157] Embodiment 3: the impact fracture problem of two-dimensional elastoplastic plate (attachment Figure 8-10 )
[0158] This example is a verification example of a two-dimensional impact fracture test, which was completed by Zhou et al. Figure 8 For the model size and boundary conditions (the unit of length is mm), the plate is evenly divided into 100×200 material points. Its elastic modulus E=192GPa, Poisson's ratio ν=0.3, mass density ρ=7830kg / m 3 . Using a linear hardening model, the initial yield stress σ y0 =2GPa, plastic modulus E p = 200 GPa. Impact velocity v=25m / s. According to the experimental observation, when the impact velocity is 20m / s Figure 9 It can be seen that the SBPD-TD method effectively suppresses the serious numerical oscillation caused by SBPD-CDM. The final damage morphology of the plate is as follows Figure 10 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com