Patents
Literature
58 results about "Unit of length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A unit of length refers to any discrete, pre-established length or distance having a constant magnitude which is used as a reference or convention to express linear dimension. The most common units in modern use are U.S. customary units in the United States and metric units elsewhere. British Imperial units are still used for some purposes in the United Kingdom and some other countries. The metric system is sub-divided into SI and non-SI units.
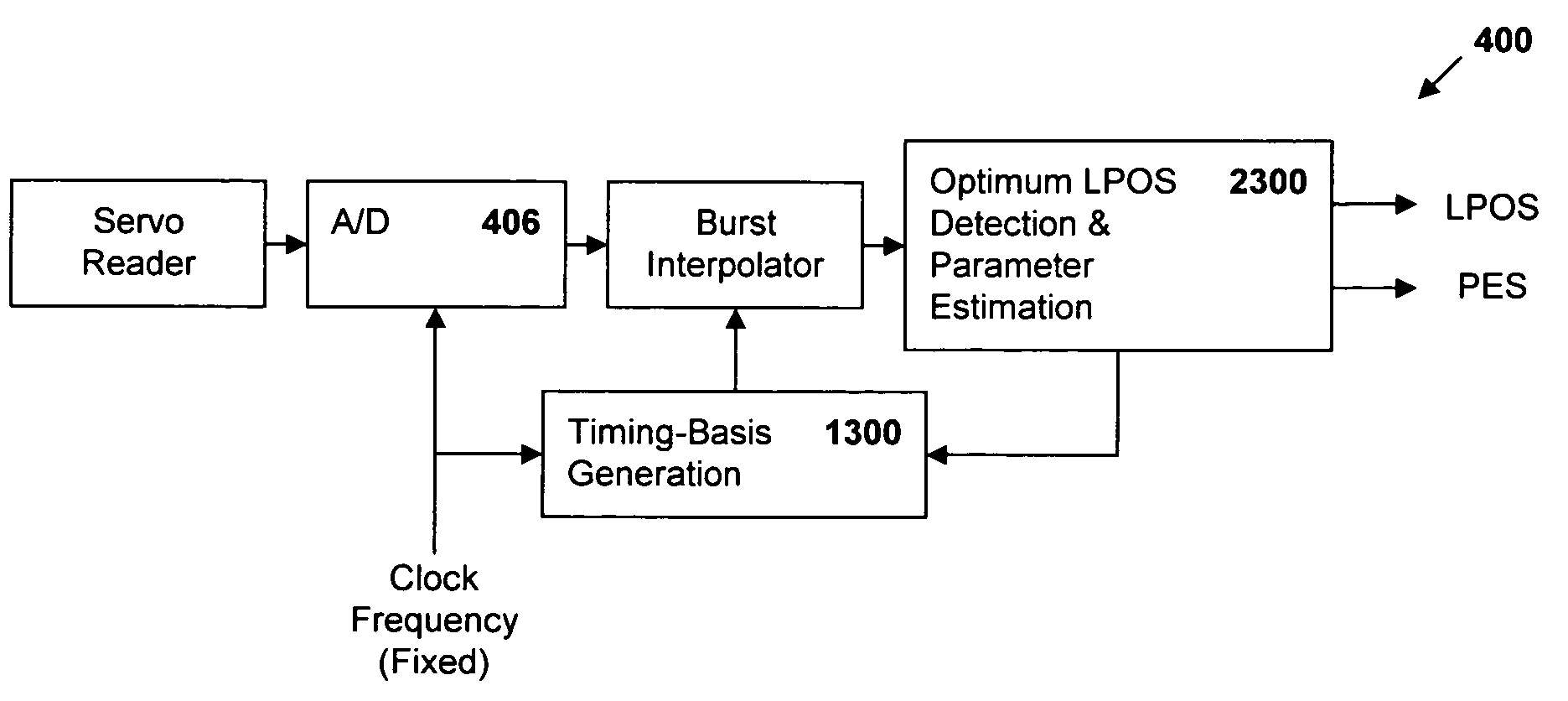
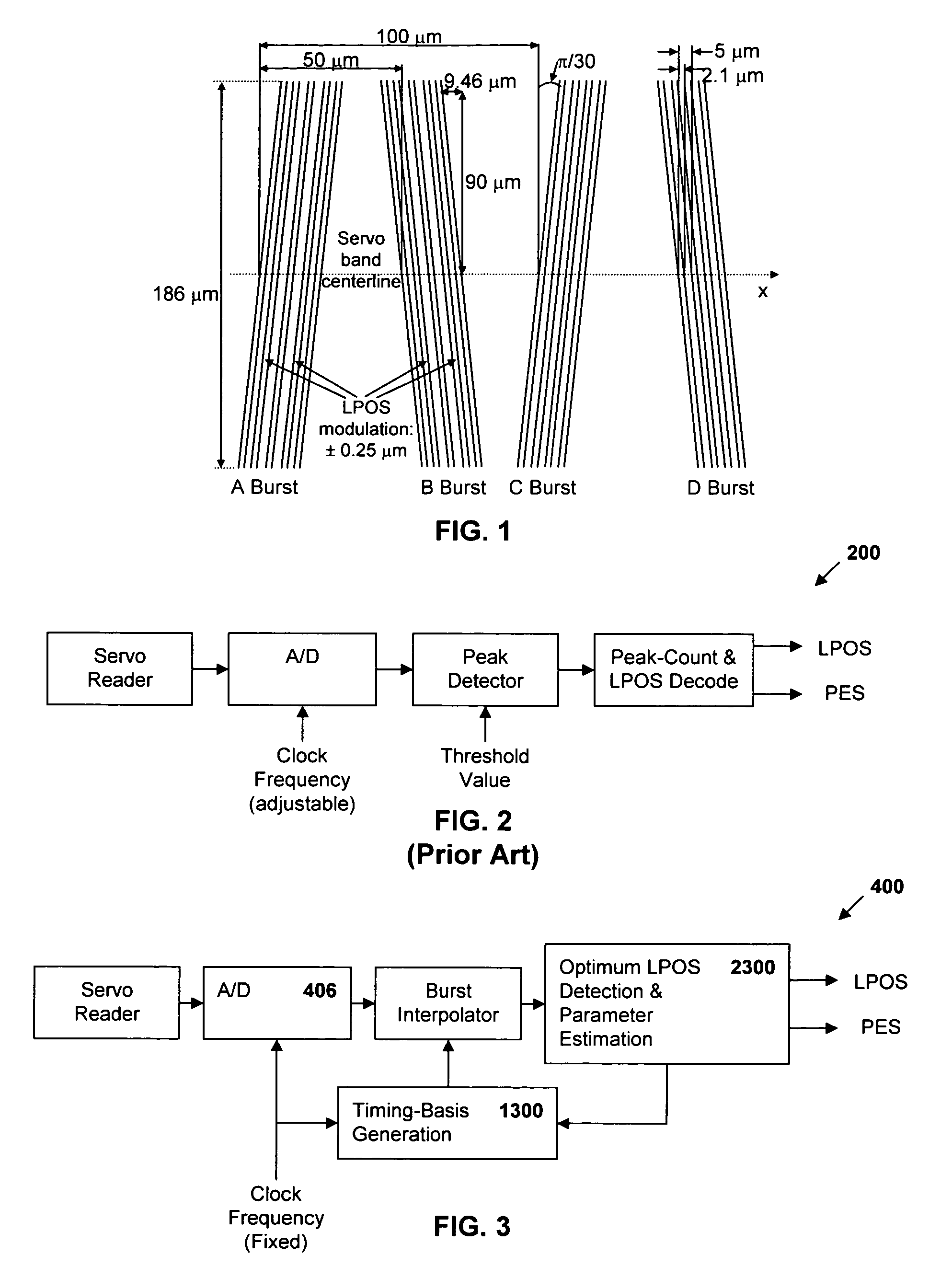
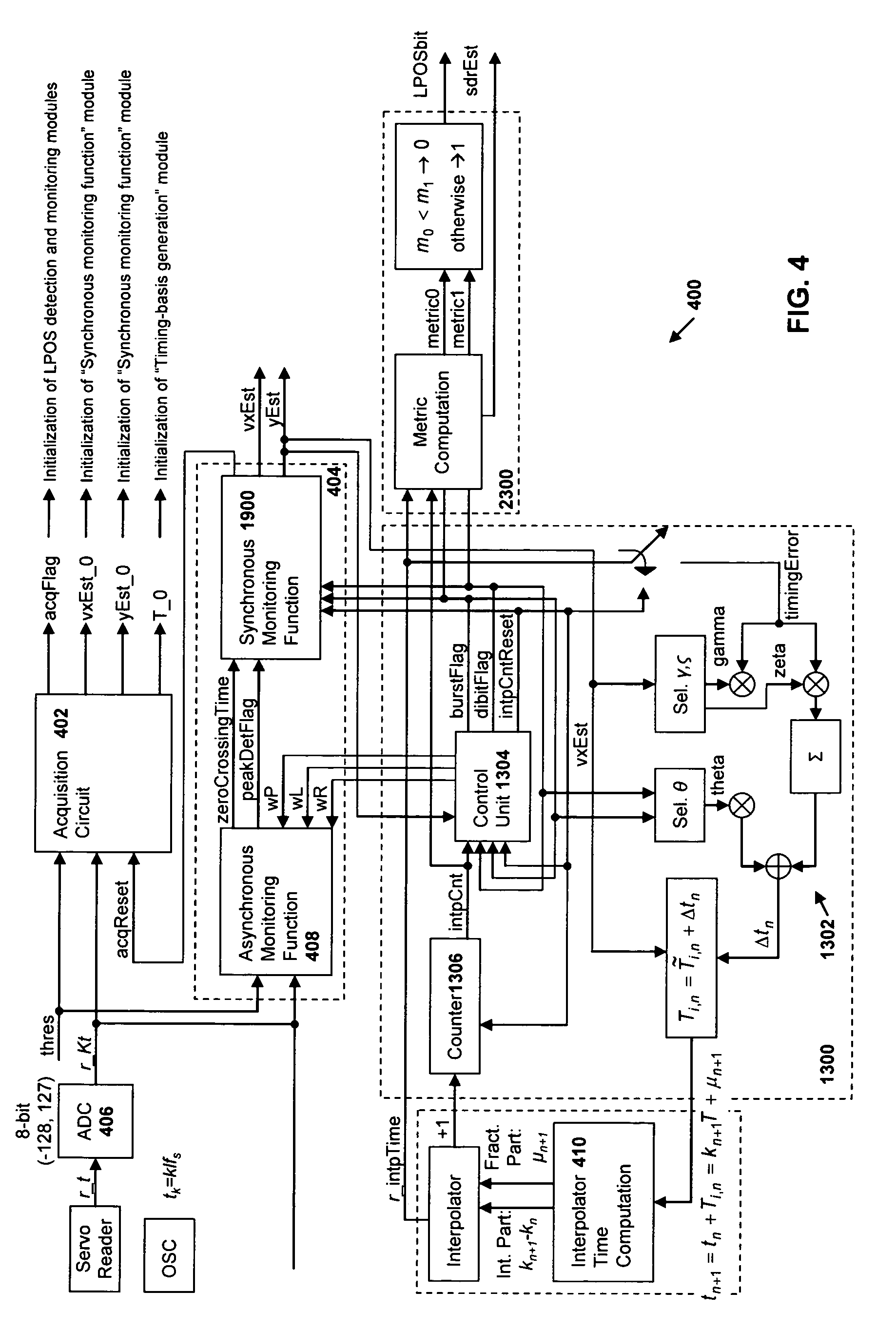
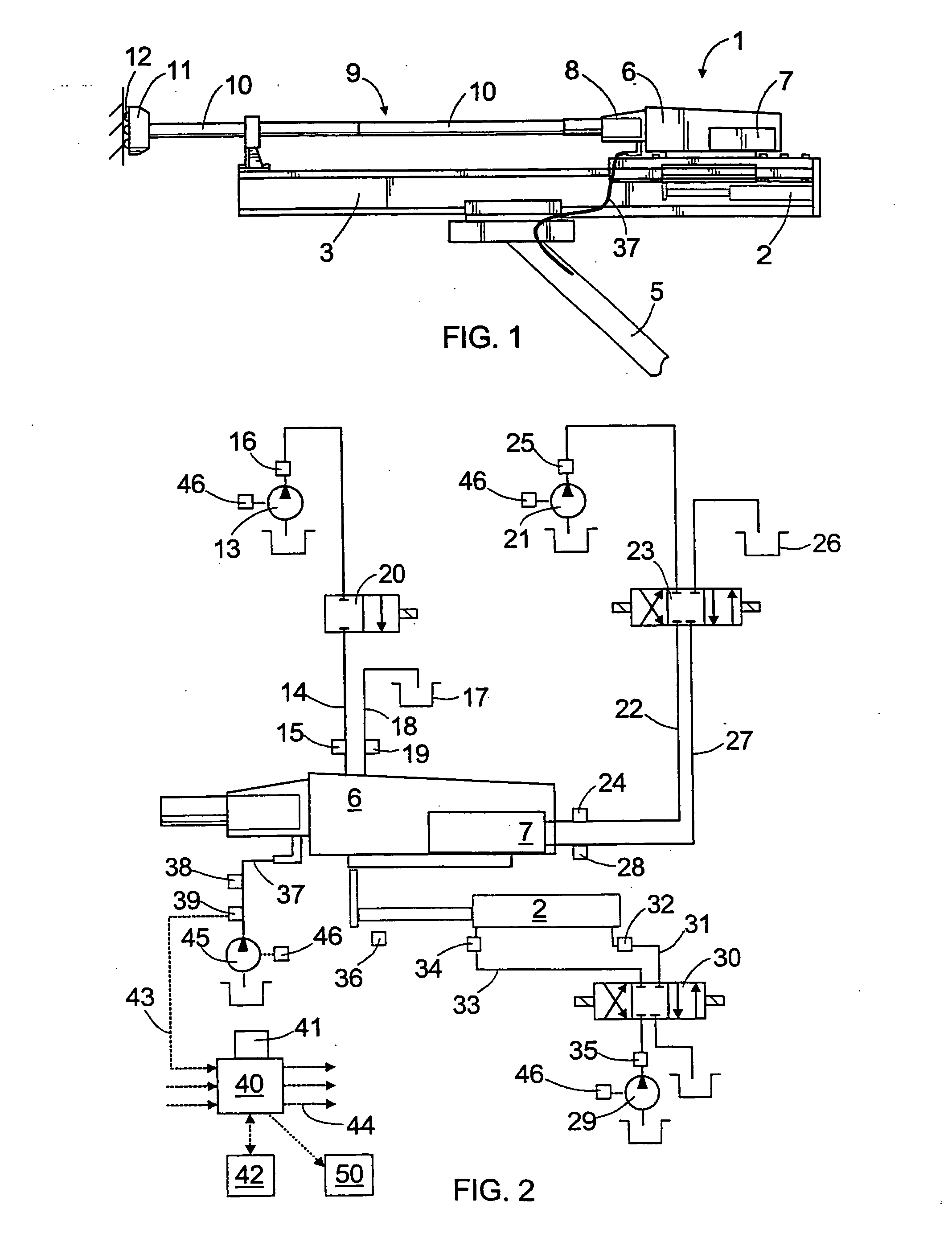
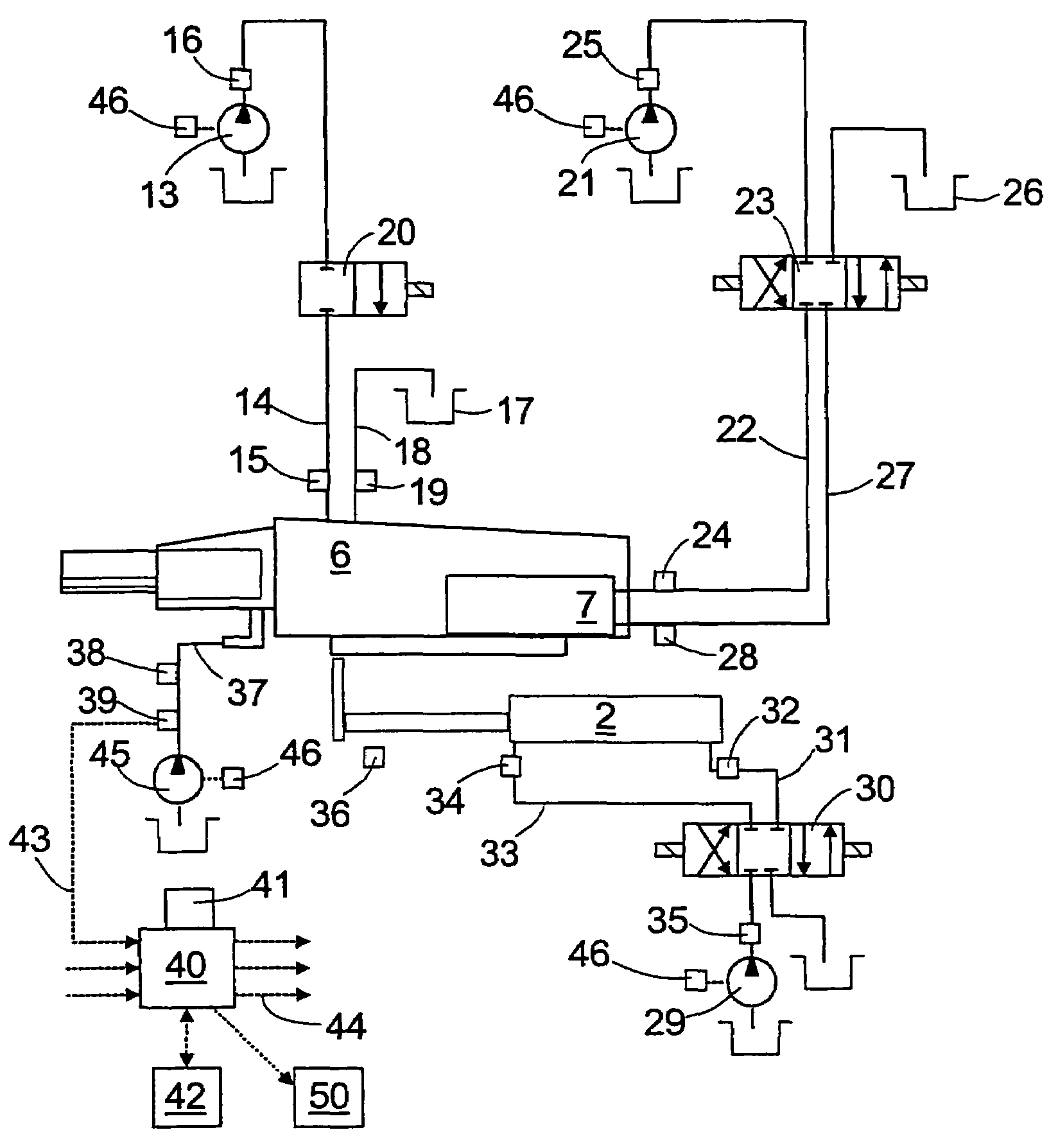
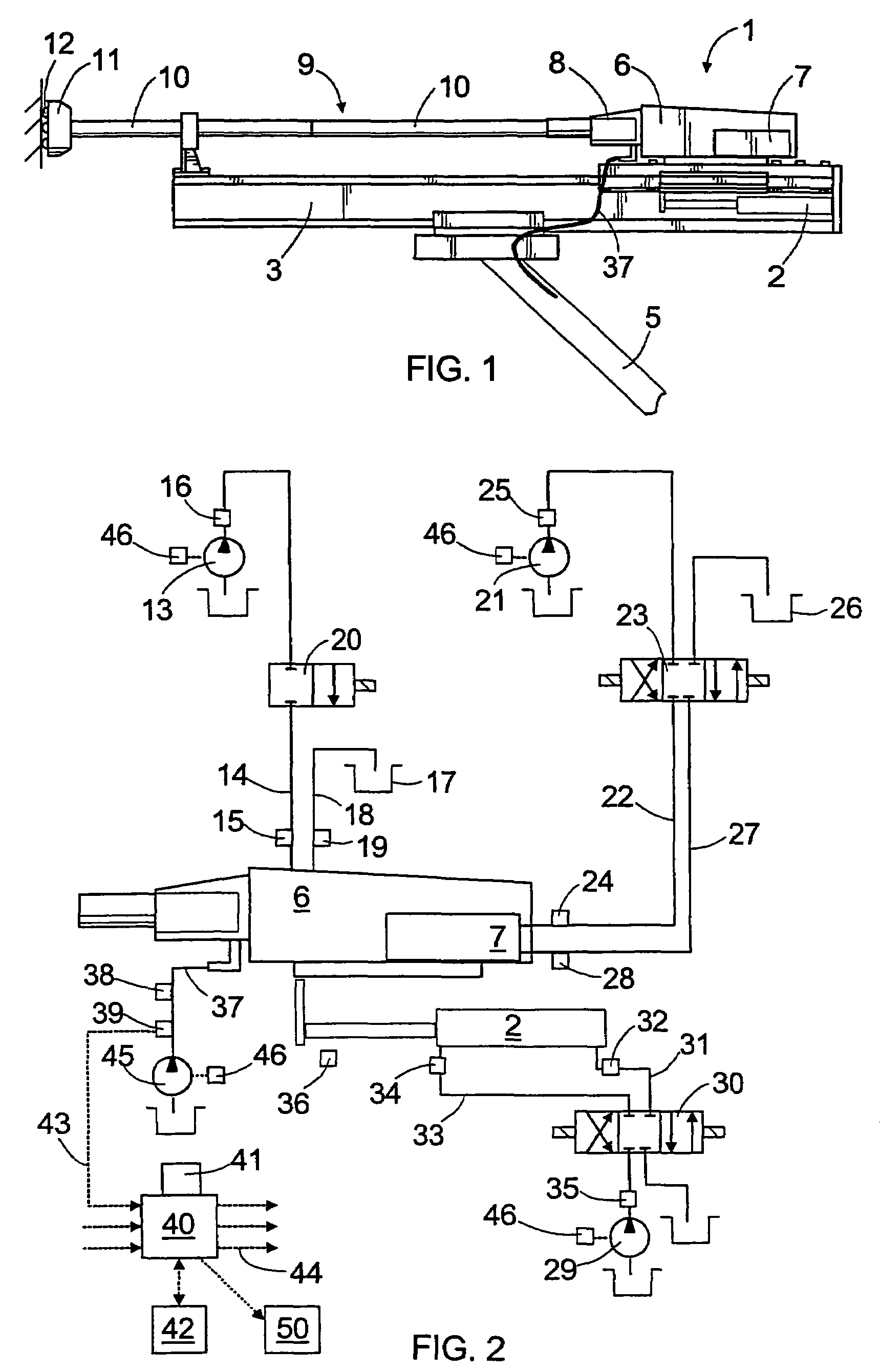
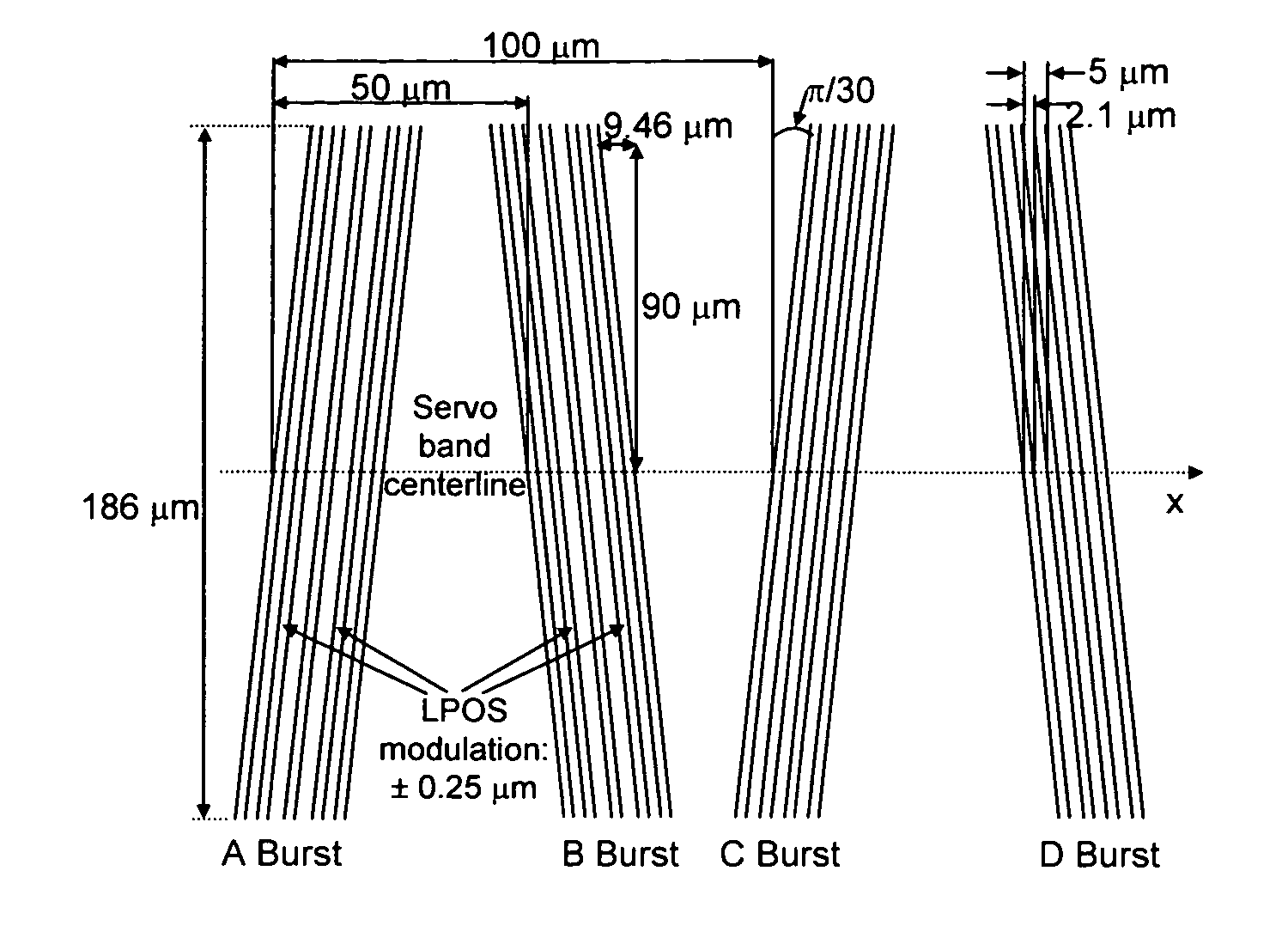
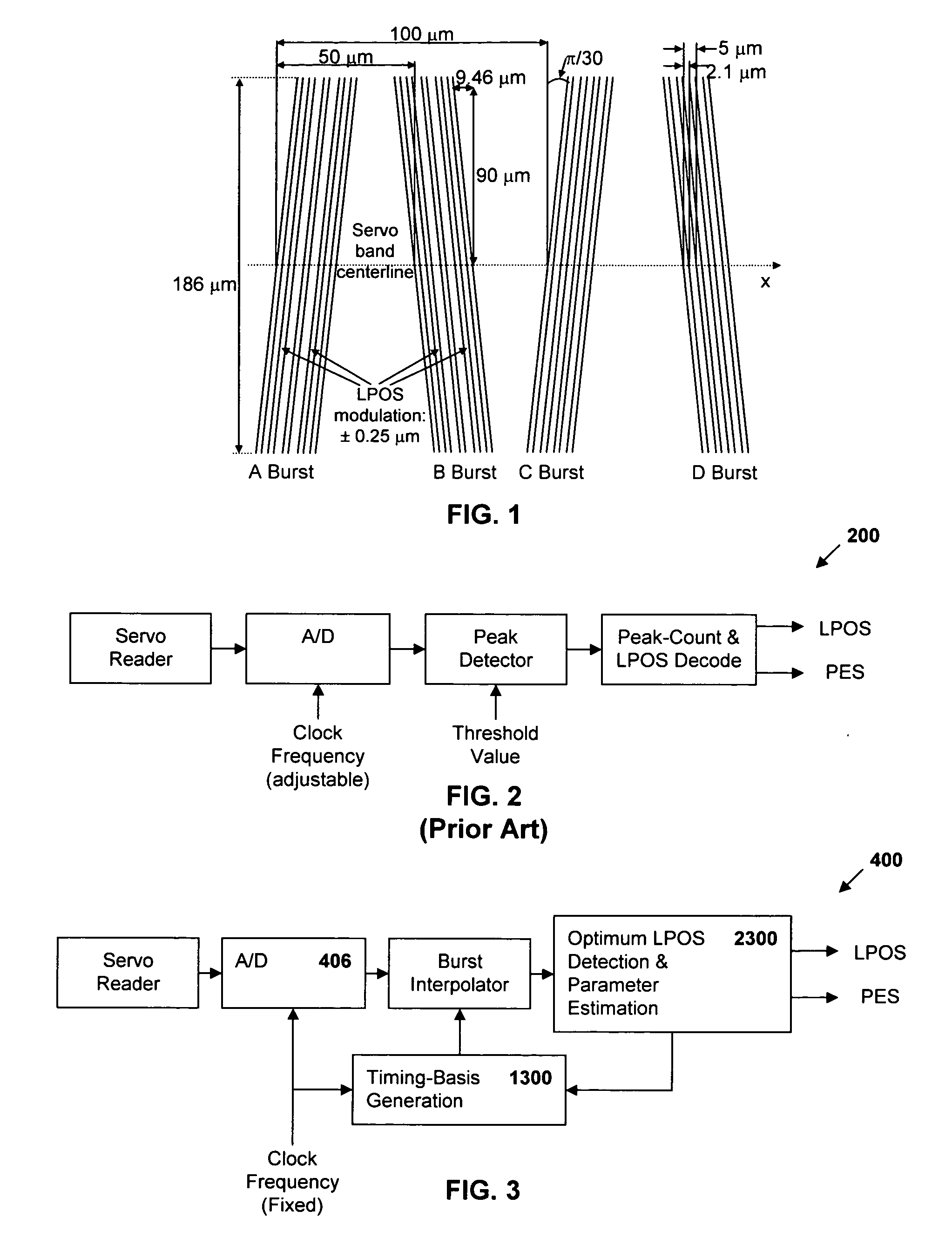
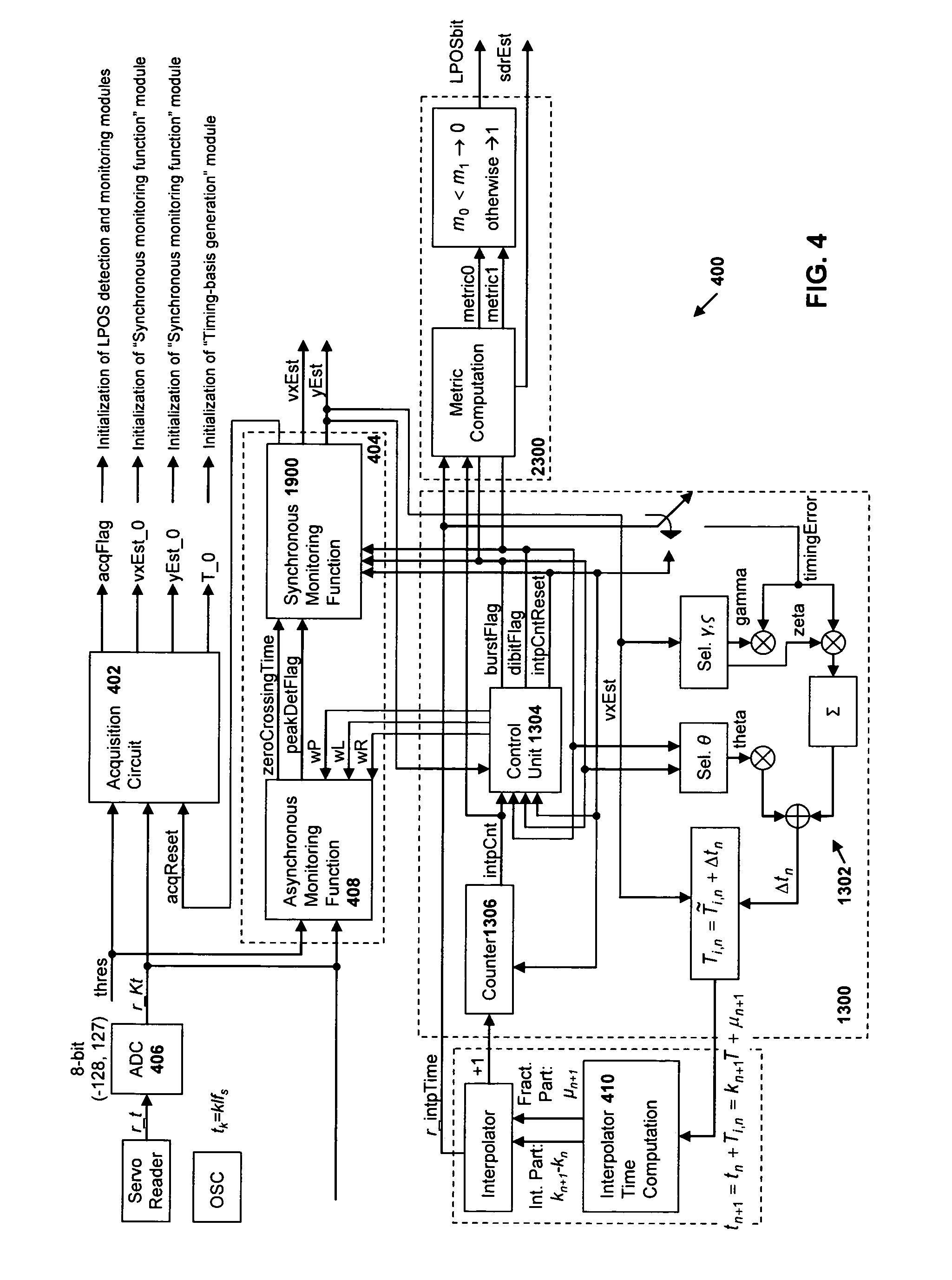
Synchronous servo channel for longitudinal position detection and position error signal generation in tape drive systems
InactiveUS7245450B1Improve reliabilityFilamentary/web record carriersAlignment for track following on tapesTape speedUnit of length
A fully synchronous longitudinal position (LPOS) detection system is provided for improving the reliability of servo channels in tape systems. The system is based on the interpolation of the servo channel output signal, which is sampled by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) at a fixed sampling rate, using a clock at a nominal frequency, so that interpolated signal samples are obtained at a predetermined fixed rate, independent of tape velocity. This predetermined fixed rate is defined in terms of samples per unit of length, as opposed to samples per unit of time, which is the measure of the ADC sampling rate. The resolution with which the servo channel signal is obtained at the interpolator output is thus determined by the step interpolation distance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Display device
ActiveUS20080048934A1Frame area can be reducedSimple designStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDriver circuitUnit of length
In a display device of built-in driver circuit type including a non-rectangular image display area, the frame area surrounding the display area is reduced and the wiring delay is reduced. The image display device includes a plurality of pixels arranged in an orthogonal matrix form, a plurality of scanning wiring lines connected to the plural pixels, a plurality of signal wiring lines connected to the plural pixels, the signal wiring lines being disposed to construct an orthogonal matrix form with the plural scanning wiring lines; signal wiring internal circuits for driving the plural signal wiring lines, and an image display area including a plurality of pixels, the image display area having a non-rectangular outer contour. The signal wiring internal circuits are separated from each other in an extending direction of the signal wiring lines in a unit of length of the pixel.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Method and device for producing thin glass panes
InactiveUS20080184741A1Quality improvementImprove productivityBlowing machine gearingsRibbon machinesUnit of lengthGlass sheet
The method of making thin glass panes includes conveying a glass melt through a vertical inlet to a drawing tank with a slit nozzle; drawing a glass ribbon downward from the slit nozzle; setting a total throughput by setting length and cross section of the inlet and by heating and cooling the inlet to control glass melt viscosity so that pressure in the inlet decreases; and setting a throughput per unit of length in a lateral direction along the glass ribbon via nozzle system geometry and by heating and cooling of the drawing tank and slit nozzle to control melt viscosity, so that glass does not wet an underside of the slit nozzle near a breaking edge. The setting of the total throughput and the throughput per unit length are largely decoupled to simplify process control. An inventive apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method for determining geomechanical parameters of a rock sample
InactiveUS20150068292A1Efficient methodRapid determinationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEarth material testingUnit of lengthYoung's modulus
The present invention relates to a method for determining geomechanical parameters of a rock sample, including a searching step, during which the horizontal and vertical forces provided to a blade advancing at a constant speed and at a constant cutting depth along the sample are measured, in order to destroy a constant volume per unit of length at the surface of the rock sample; a micro-indentation step, during which mechanical features of the rock are determined by micro-indentation; a step of determining the geological parameters of the sample, during which at least one parameter chosen from the uniaxial compressive strength, the angle of friction, internal cohesion, Brinell hardness and Young's modulus of the rock is estimated by means of measurements taken during the scratching and micro-indentation steps.
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR
Method and arrangement for controlling percussion rock drilling
The invention relates to a rock drilling arrangement and a method and program for controlling rock drilling on the basis of specific energy consumption. The specific energy of drilling is the quantity of energy used per a unit of length of the drilled hole. Not only the used impact energy, but also the energy used by at least one other sub-process is taken into account when determining the specific energy. Rotation energy is typically included, but feeding energy and flushing energy can also be considered. Drilling variables are adjusted so that the specific energy is of a predetermined size.
Owner:SANDVIK TAMROCK
Method and arrangement for controlling percussion rock drilling
The invention relates to a rock drilling arrangement and a method and program for controlling rock drilling on the basis of specific energy consumption. The specific energy of drilling is the quantity of energy used per a unit of length of the drilled hole. Not only the used impact energy, but also the energy used by at least one other sub-process is taken into account when determining the specific energy. Rotation energy is typically included, but feeding energy and flushing energy can also be considered. Drilling variables are adjusted so that the specific energy is of a predetermined size.
Owner:SANDVIK TAMROCK
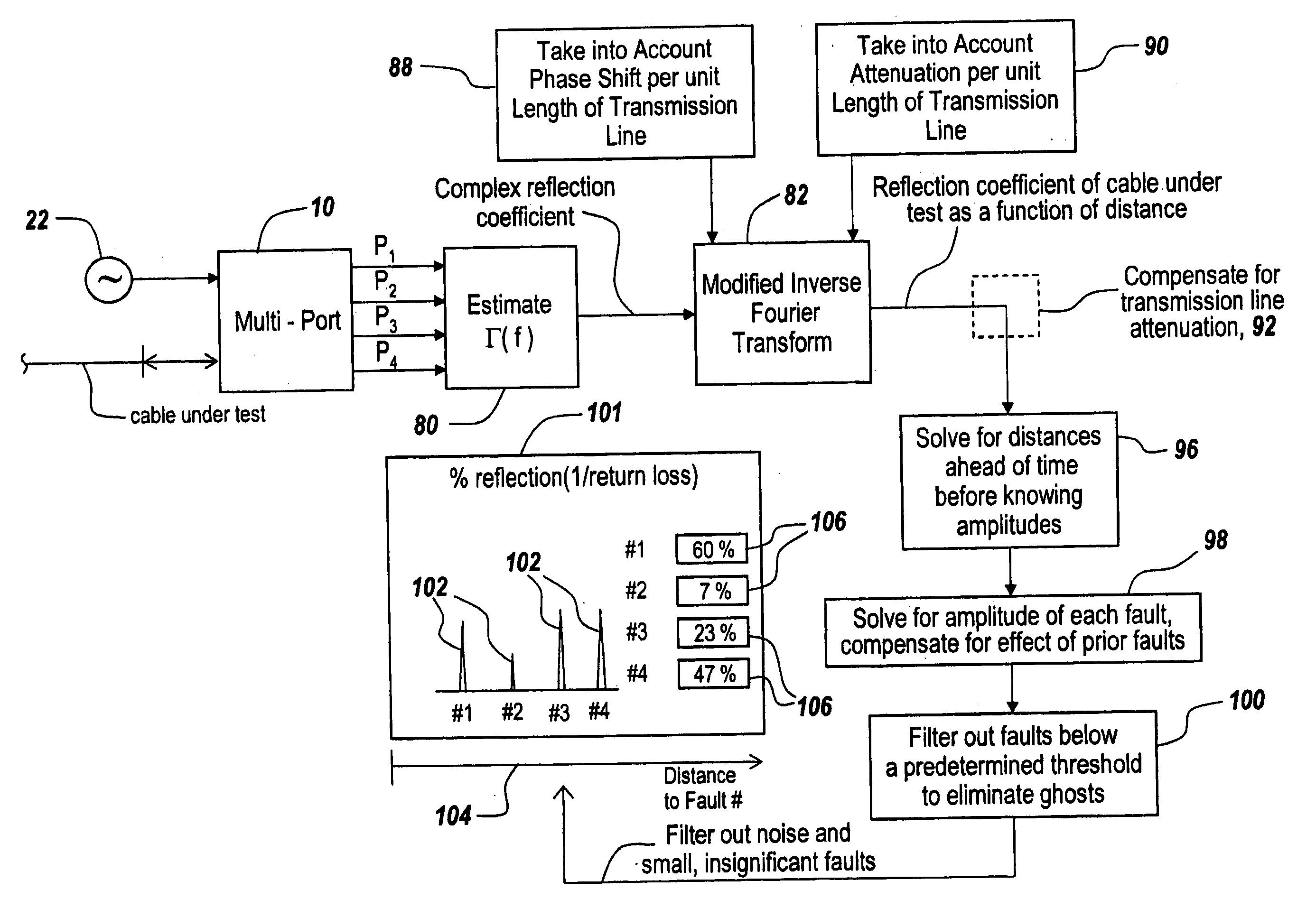
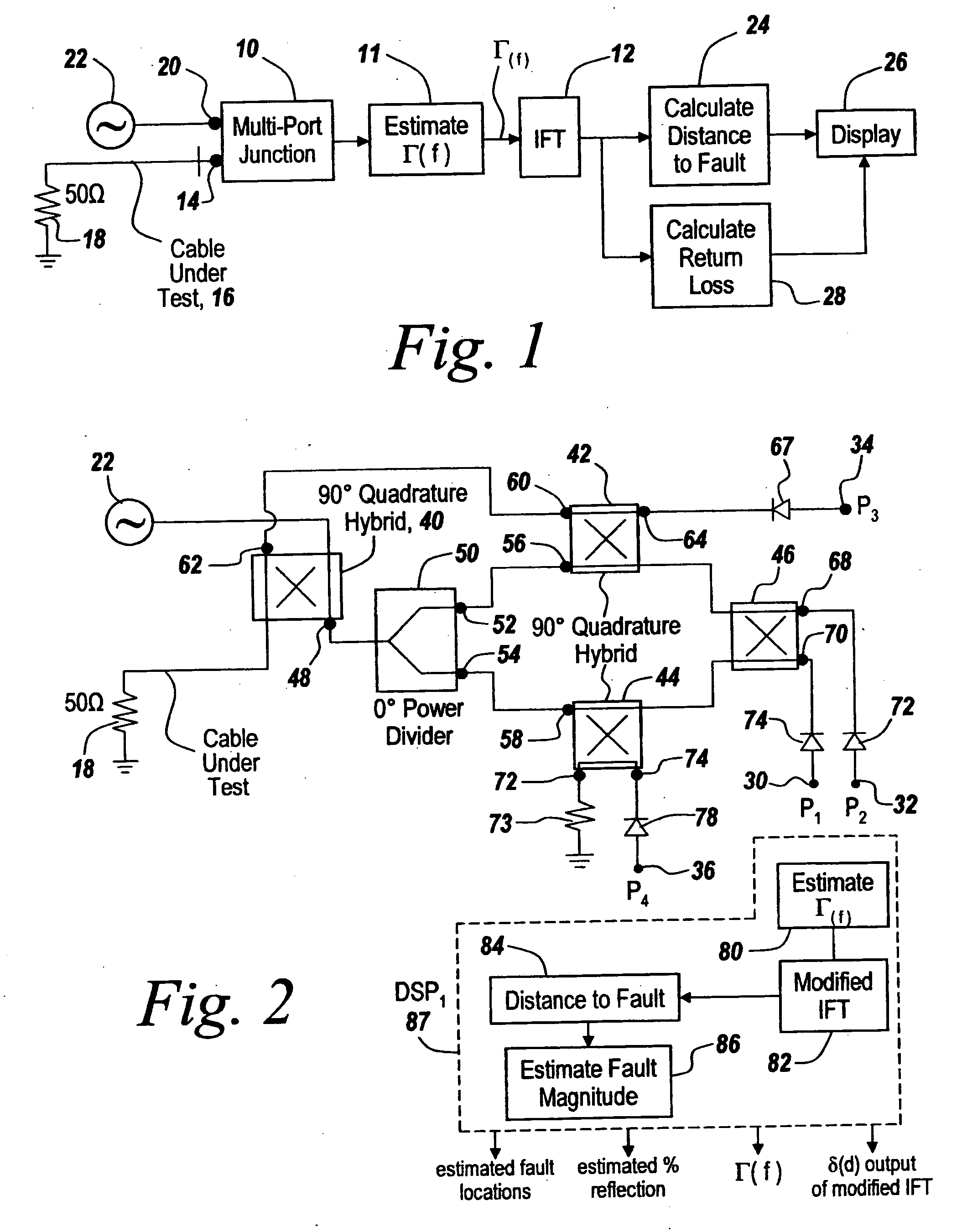
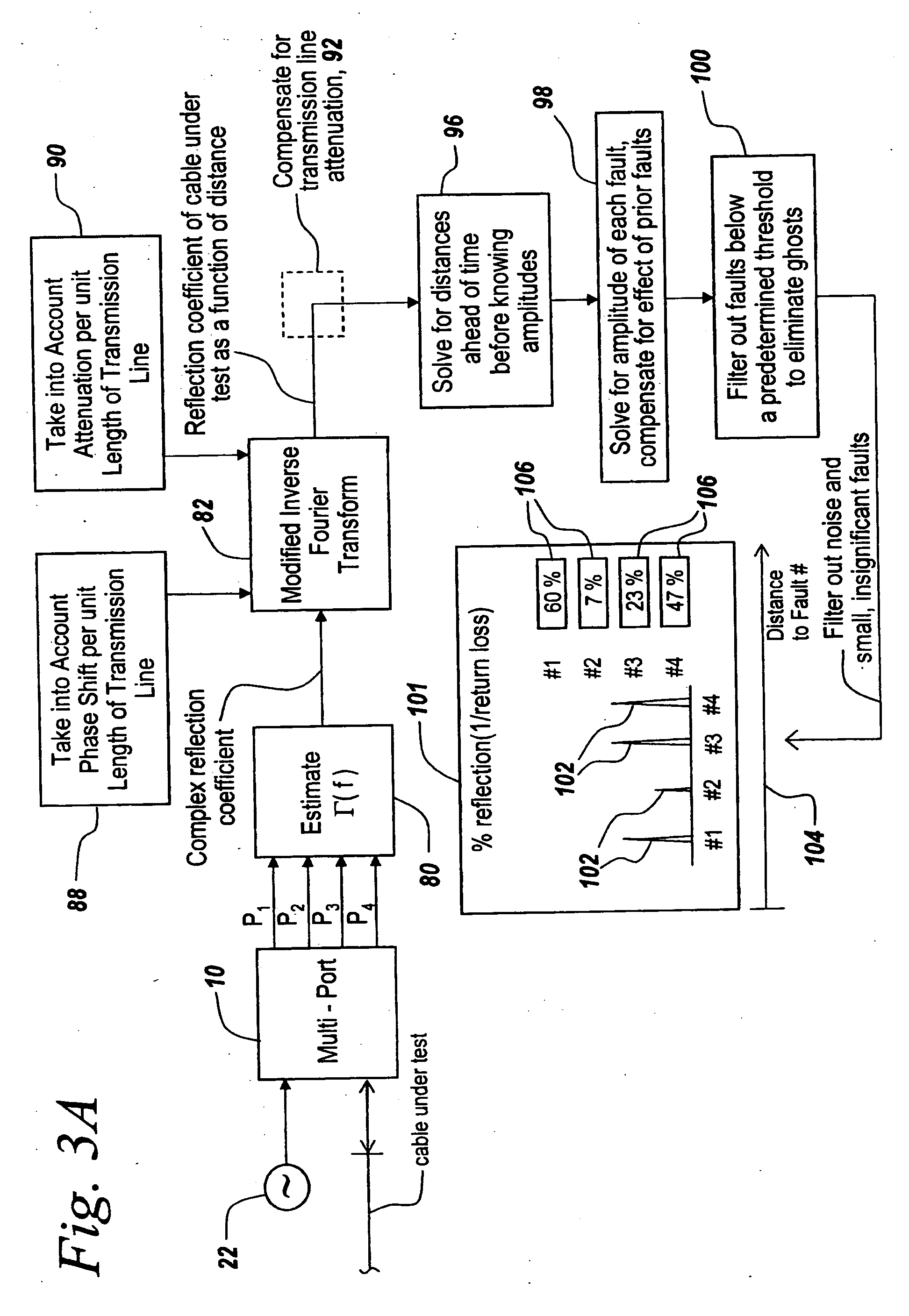
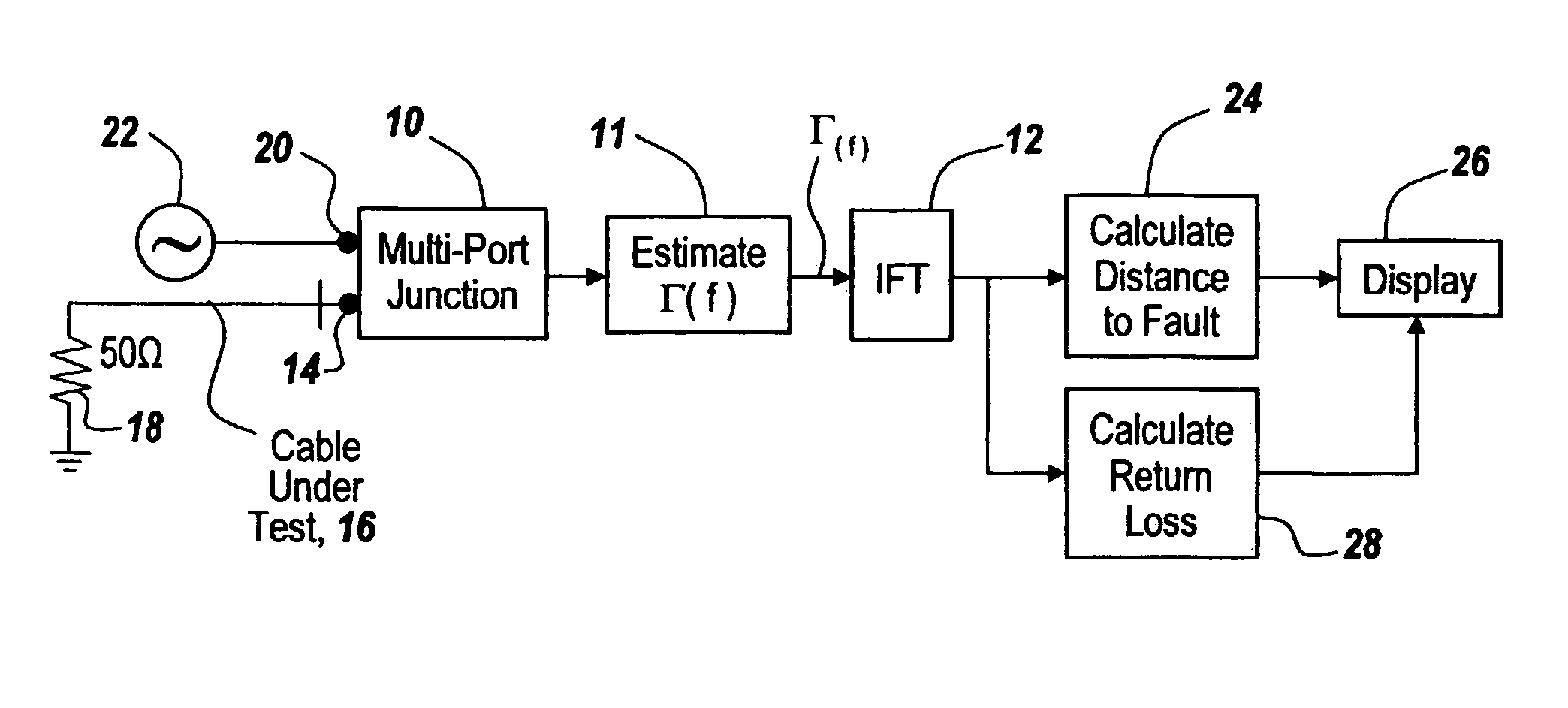
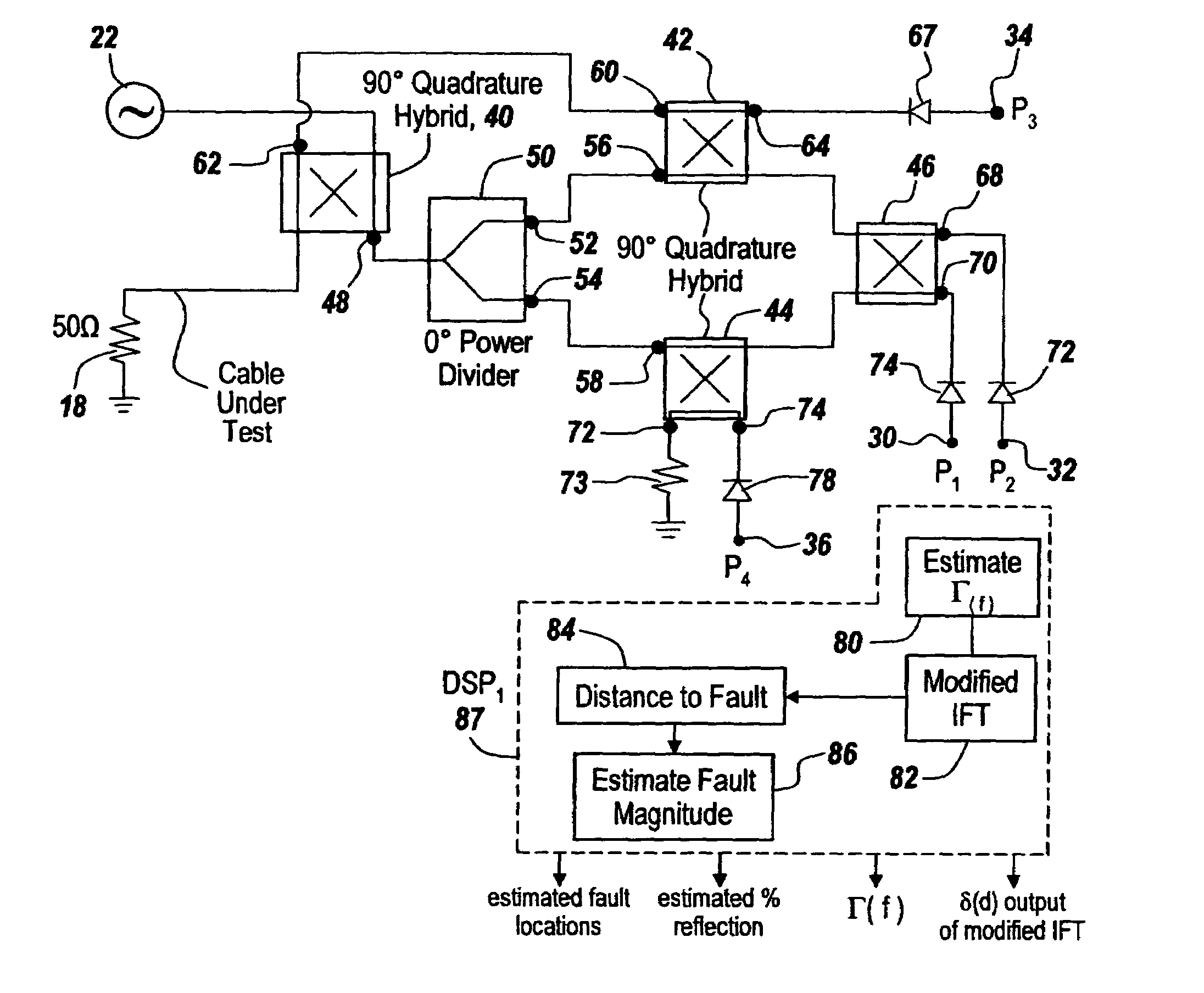
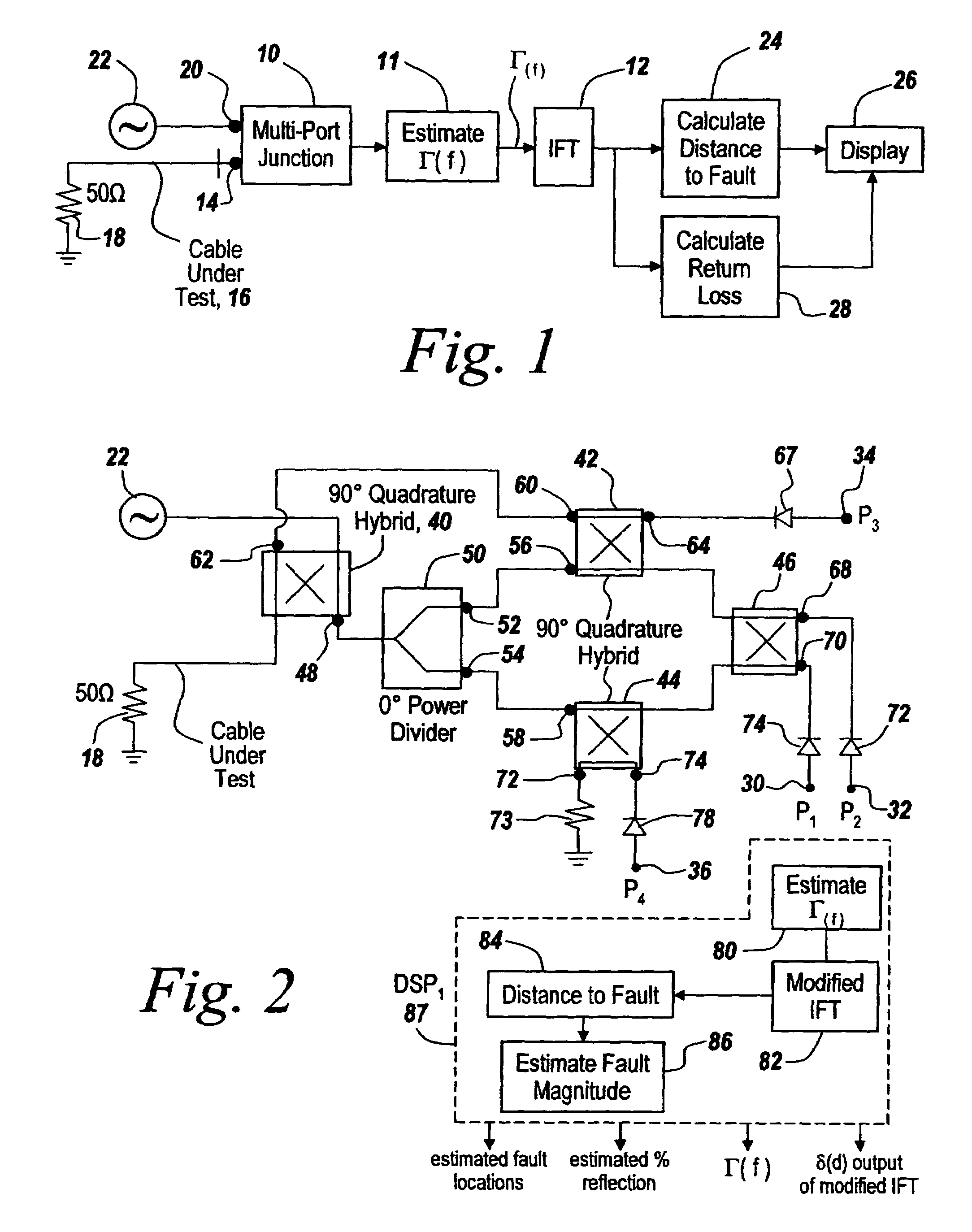
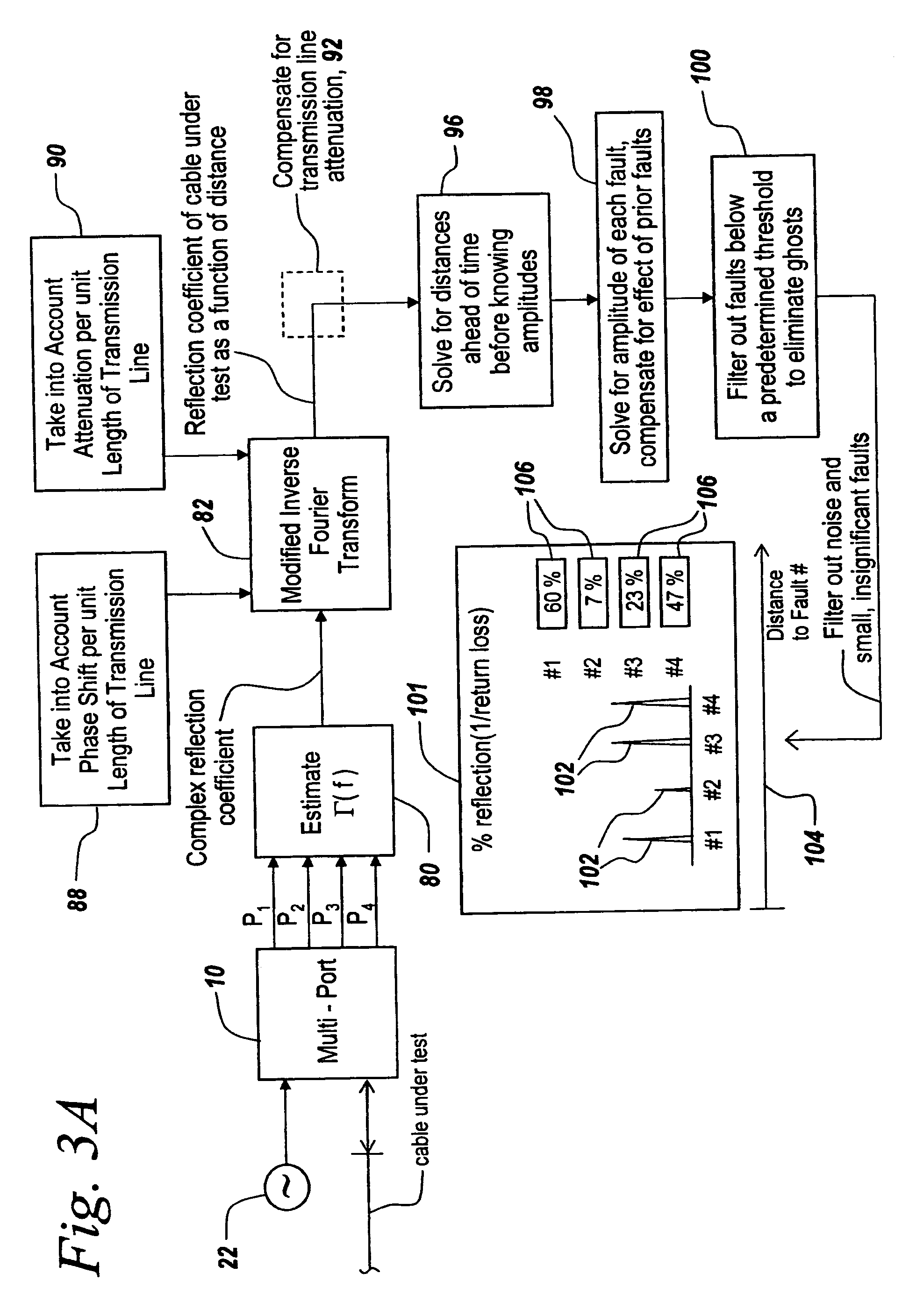
Method and apparatus for transmission line and waveguide testing
InactiveUS20050234666A1Accurately measure the magnitude of each faultCompensation effectTransmitters monitoringResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringPeak value
A multi-port junction is used in combination with an Inverse Fourier Transform to detect distance to fault in an RF transmission line or waveguide without the use of heterodyne down-conversion circuits. To provide an ultra-wide bandwidth frequency domain reflectometer the output ports of the multi-port junction are used to calculate distance to fault and return loss. The Inverse Fourier Transform algorithm is modified to take into account both phase shift per unit length of the transmission line and attenuation per unit of length in the transmission line, with the output of the modified Inverse Fourier Transform being applied to a module that subtracts out the effect of previous faults by solving for the distances ahead of time before knowing amplitudes and for solving for amplitude at each prior fault starting with the first fault. The output of this module is then used thresholded to remove the effects of noise, secondary reflections and inconsequential peaks. The result is a time domain waveform in which peak positions indicate the distance to real faults and in which return loss or percent reflection is calculated for each of the faults. Moreover, internal calibration loads and specialized processing are used to effortlessly calibrate the reflectometer in the field.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and device for producing thin glass panes
InactiveUS7735338B2Quality improvementImprove productivityBlowing machine gearingsRibbon machinesUnit of lengthGlass sheet
The method of making thin glass panes includes conveying a glass melt through a vertical inlet to a drawing tank with a slit nozzle; drawing a glass ribbon downward from the slit nozzle; setting a total throughput by setting length and cross section of the inlet and by heating and cooling the inlet to control glass melt viscosity so that pressure in the inlet decreases; and setting a throughput per unit of length in a lateral direction along the glass ribbon via nozzle system geometry and by heating and cooling of the drawing tank and slit nozzle to control melt viscosity, so that glass does not wet an underside of the slit nozzle near a breaking edge. The setting of the total throughput and the throughput per unit length are largely decoupled to simplify process control. An inventive apparatus for performing the method is also disclosed.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
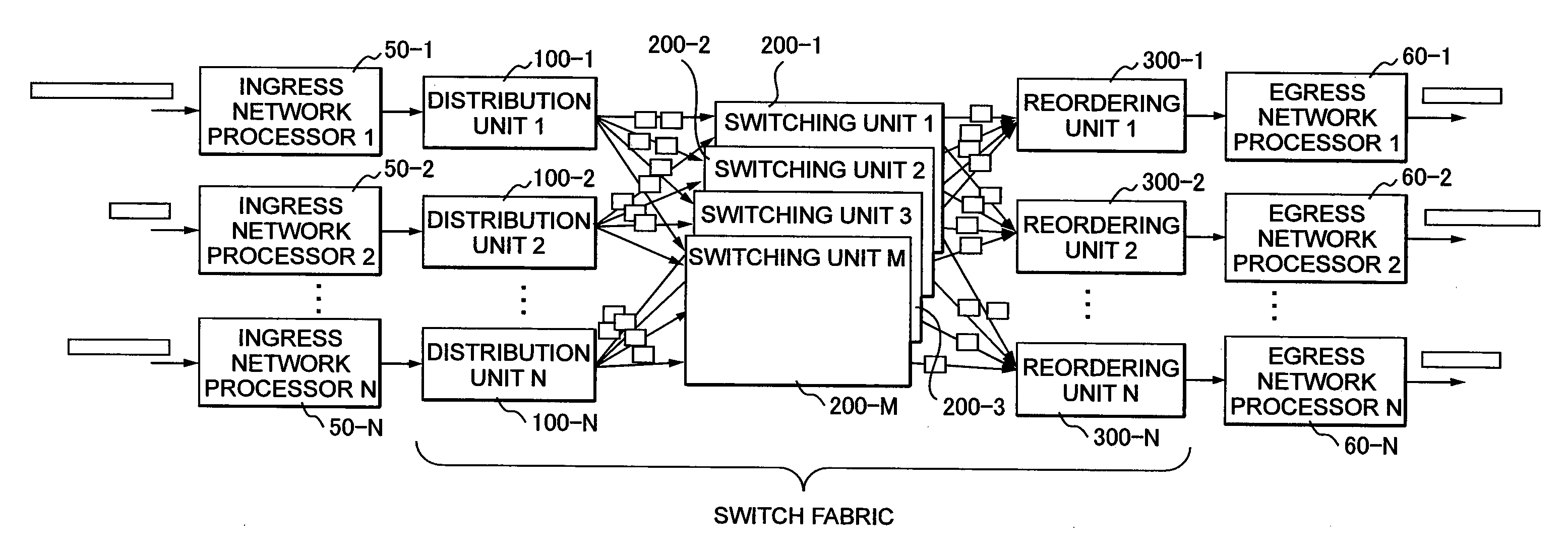
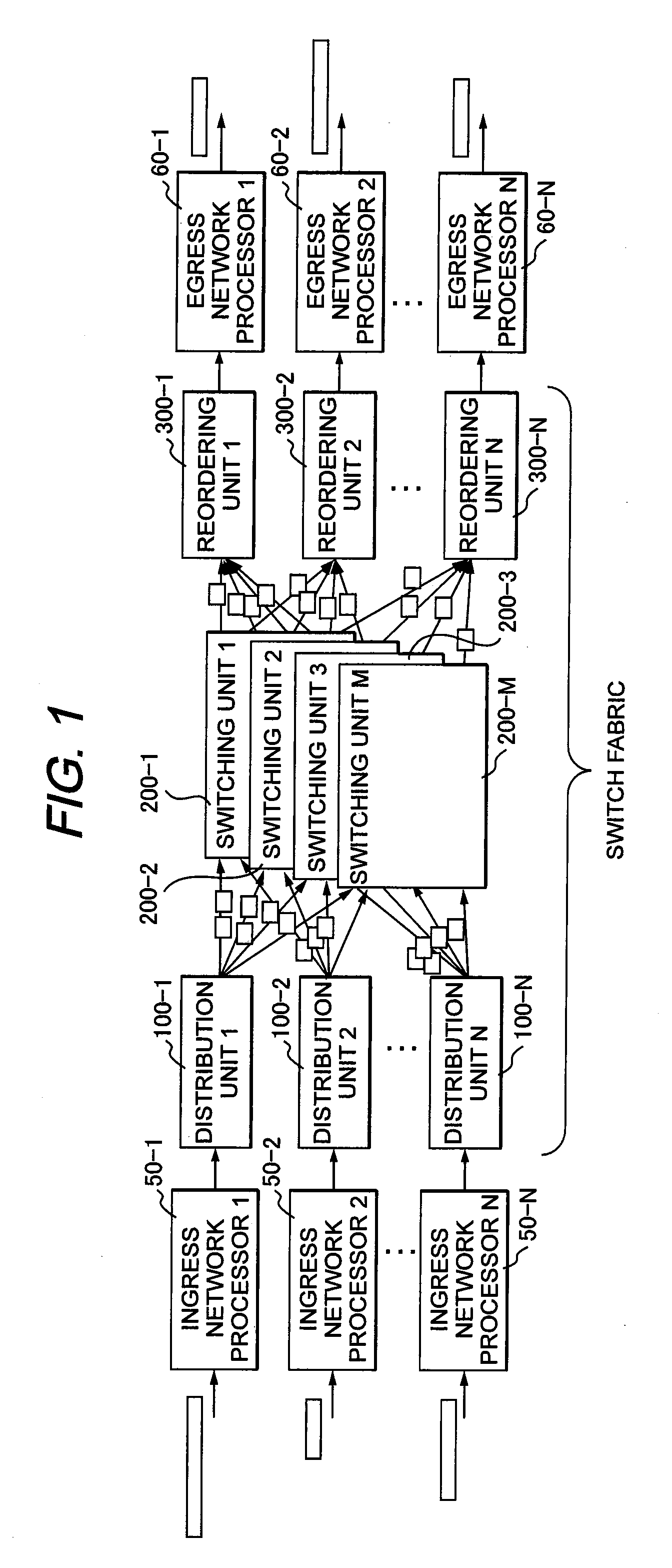
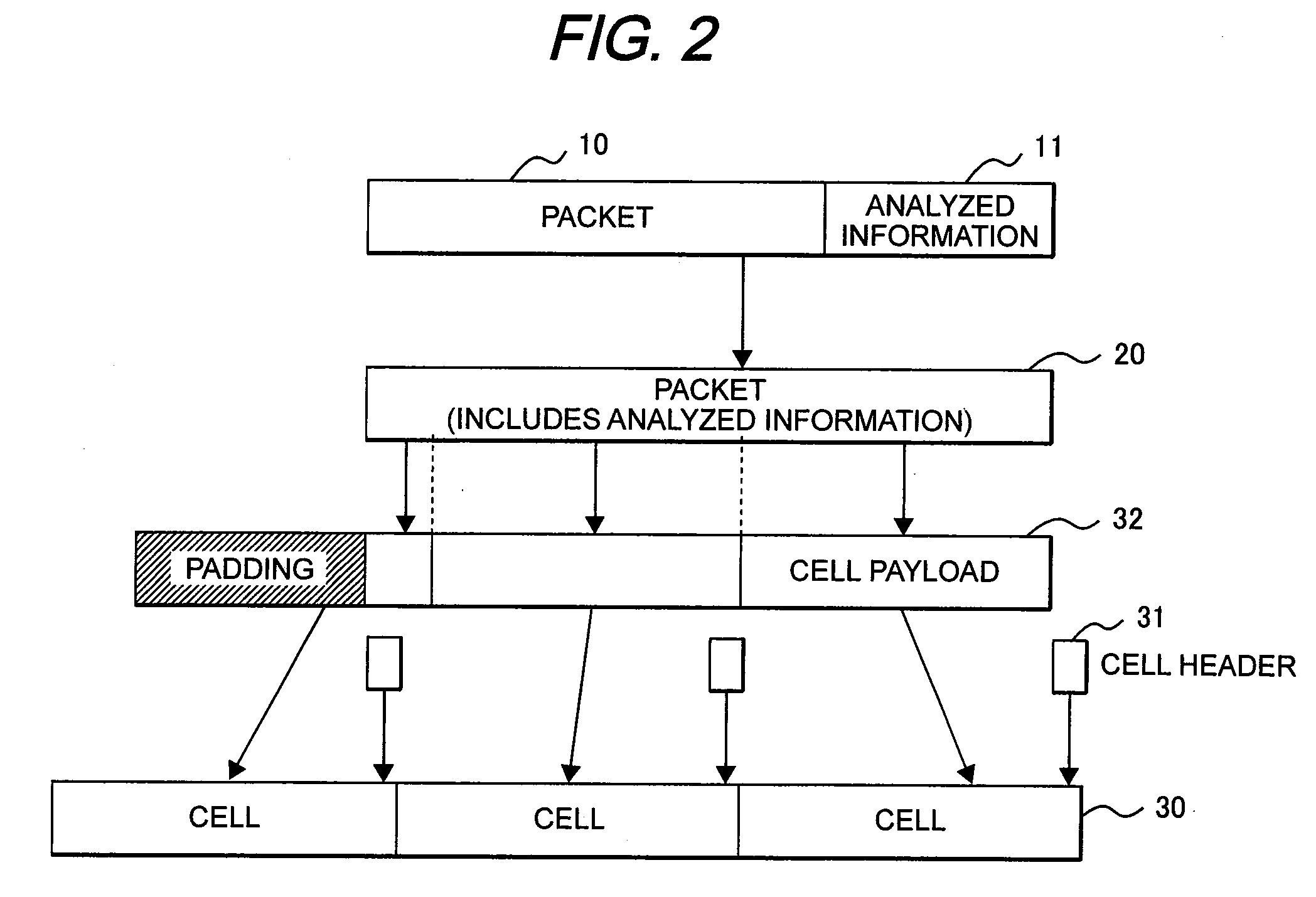
Multi-plane cell switch fabric system
ActiveUS20090252168A1Insufficient areaRealize switchingMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationUnit of lengthEngineering
A multi-plane cell switch fabric system prevents a decrease of the effective switching capacity when switching the variable-length packets. Distribution units classify input variable-length packets for each address, arranges the packets by a first division length unit, divides the packets into fixed-length cell payloads by a second division length unit that is an integer multiple being twice or more as large as the first division length unit, and forms a fixed-length cell by providing destination information, a source ID, a sequential number, and packet head tail information to each of the cell payloads. The cells are distributed to all the switching units one by one whenever the cells are collected to be the same number as the plural switching units. The reordering units classify the cells, reorder the sequential number in an original order, and reassemble the packets by the packet head tail information of the cell.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
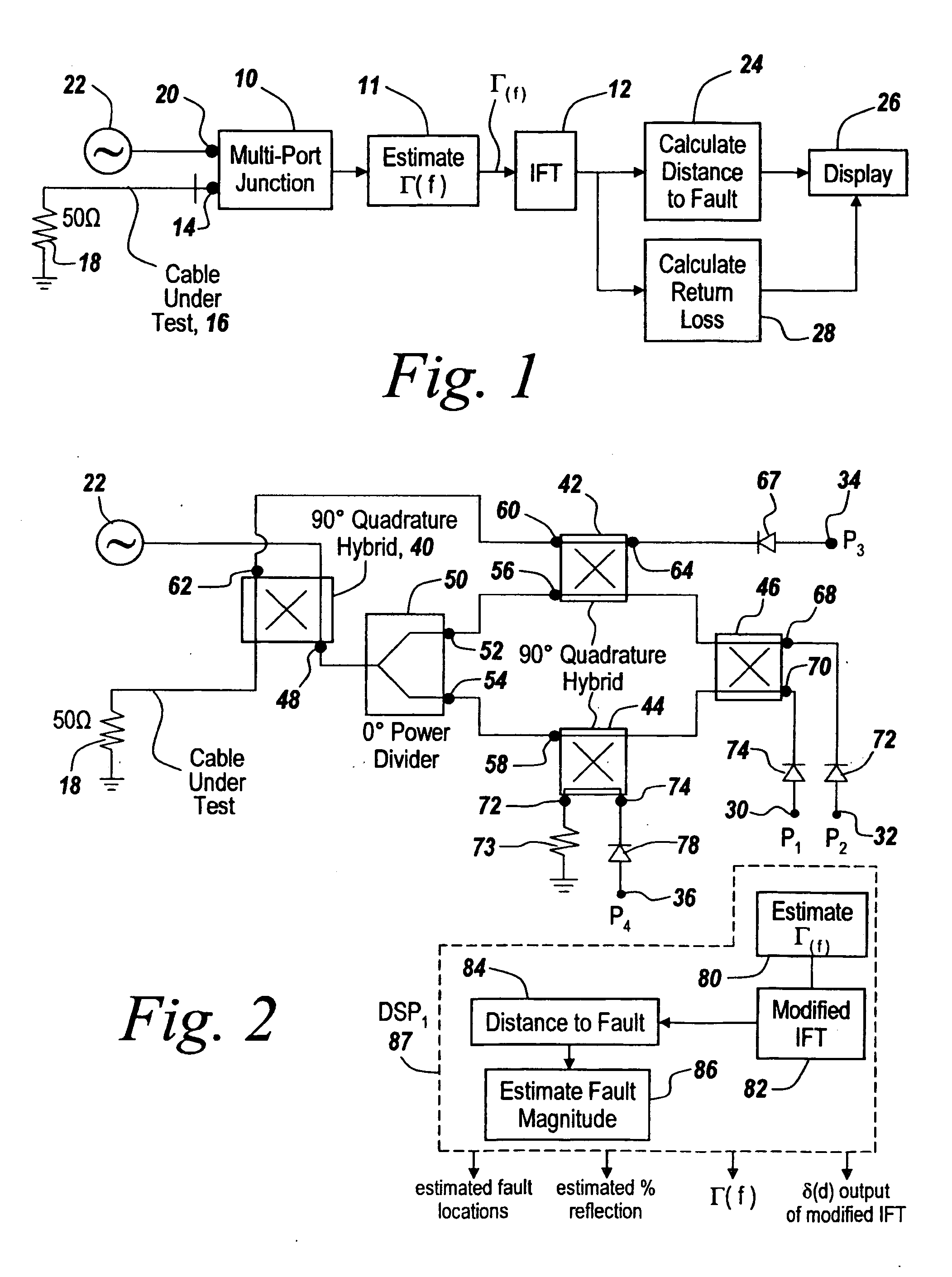
Method and apparatus for transmission line and waveguide testing
InactiveUS20050203711A1Accurately measure the magnitude of each faultCompensation effectSpectral/fourier analysisSystems using filtering and bypassingPeak valueMulti port
A multi-port junction is used in combination with an Inverse Fourier Transform to detect distance to fault in an RF transmission line or waveguide without the use of heterodyne down-conversion circuits. To provide an ultra-wide bandwidth frequency domain reflectometer the output ports of the multi-port junction are used to calculate distance to fault and return loss. The Inverse Fourier Transform algorithm is modified to take into account both phase shift per unit length of the transmission line and attenuation per unit of length in the transmission line, with the output of the modified Inverse Fourier Transform being applied to a module that subtracts out the effect of previous faults by solving for the distances ahead of time before knowing amplitudes and for solving for amplitude at each prior fault starting with the first fault. The output of this module is then used thresholded to remove the effects of noise, secondary reflections and inconsequential peaks. The result is a time domain waveform in which peak positions indicate the distance to real faults and in which return loss or percent reflection is calculated for each of the faults. Moreover, internal calibration loads and specialized processing are used to effortlessly calibrate the reflectometer in the field.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
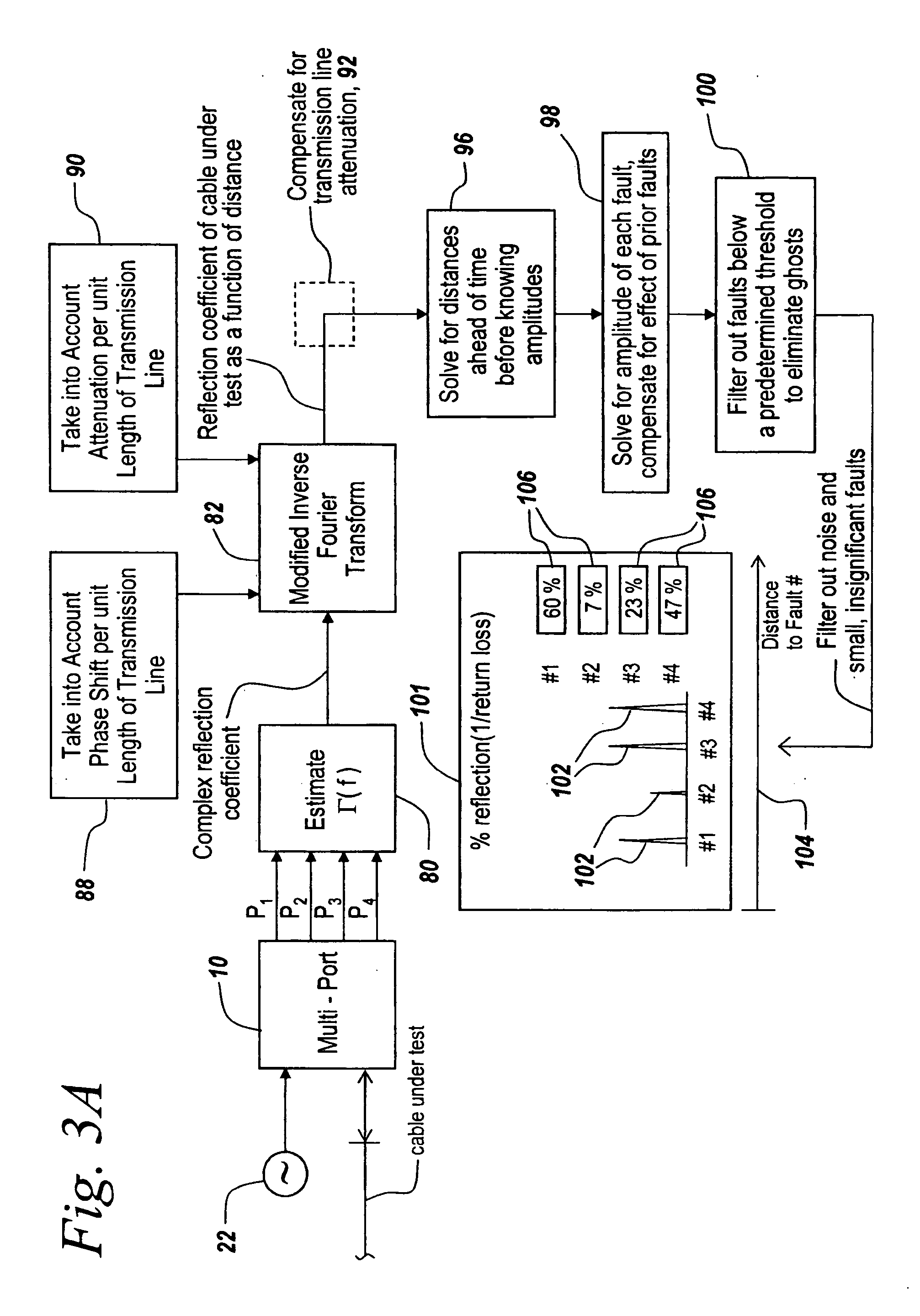
Method and apparatus for transmission line and waveguide testing
InactiveUS7061251B2Accurately measure the magnitude of each faultCompensation effectTransmitters monitoringResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringPeak value
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and device for inspecting a traveling wire cable
ActiveUS20120294506A1Facilitate cognitionInspecting textilesCharacter and pattern recognitionUnit of lengthImage segmentation
Owner:WIRECO GERMANY GMBH
Method for quality monitoring of longitudinally moving yarn at workplace of textile machine
ActiveCN101648660AFlexible and automatic adjustmentLow winding qualityFilament handlingTextiles and paperYarnLower limit
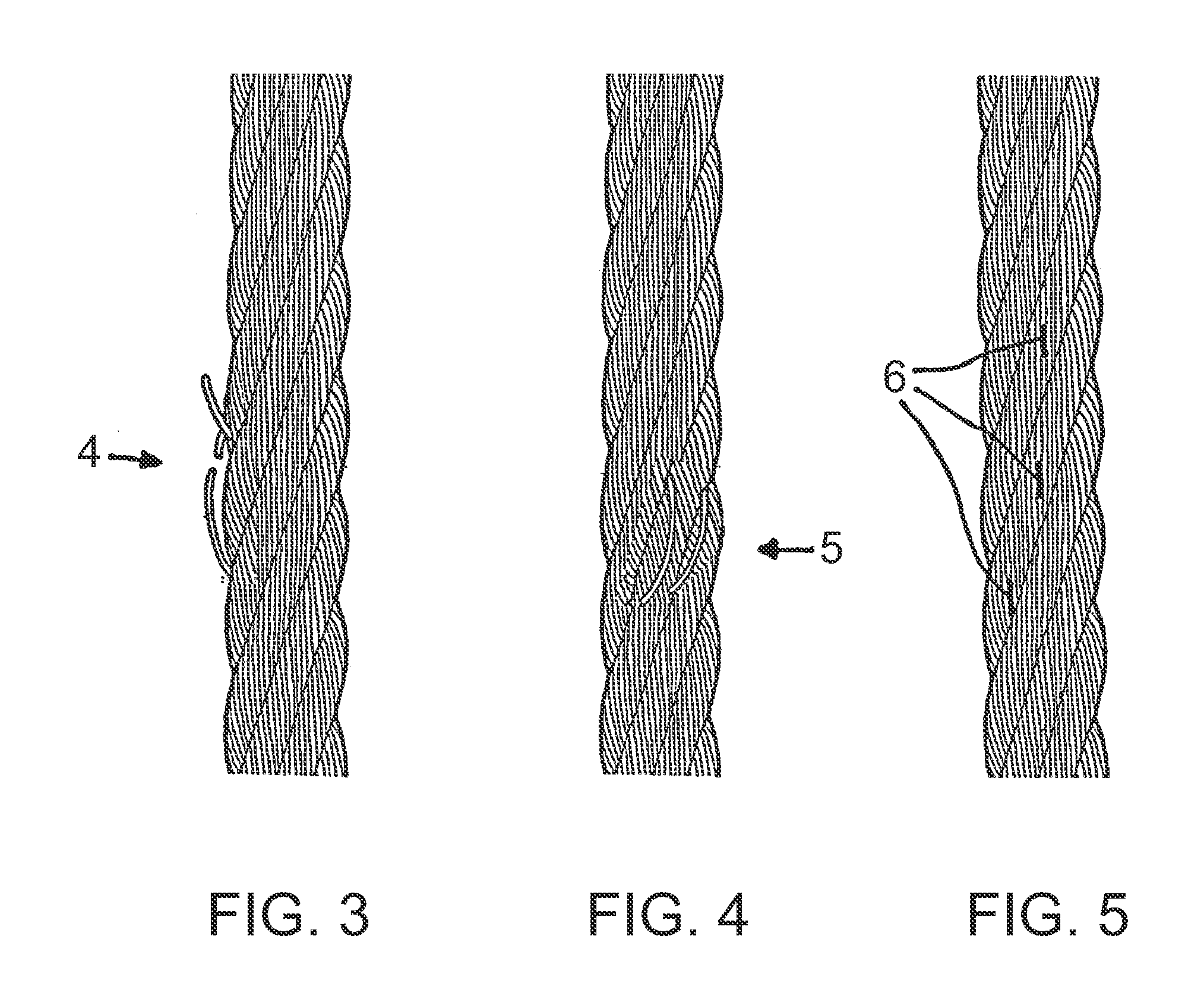
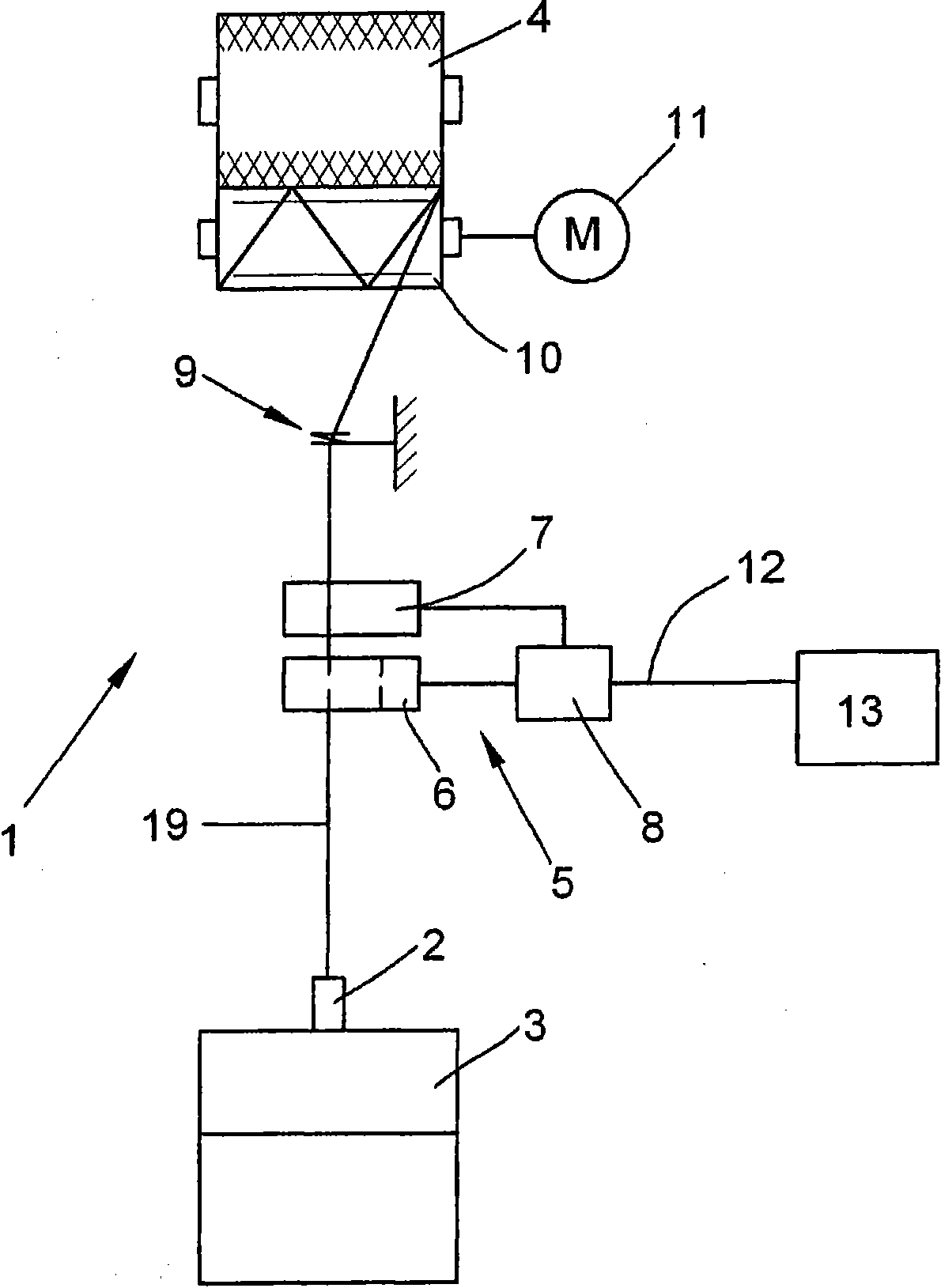
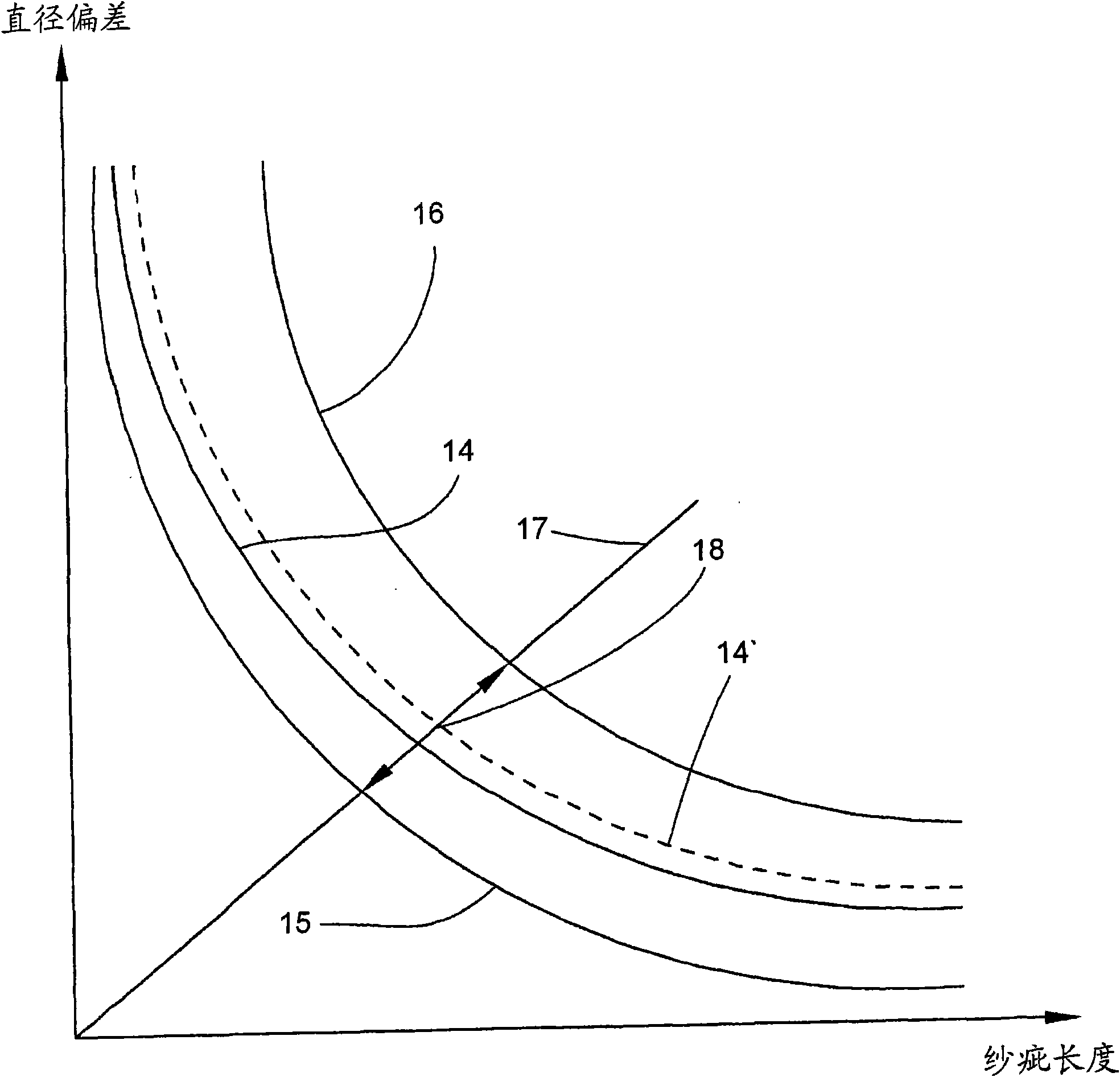
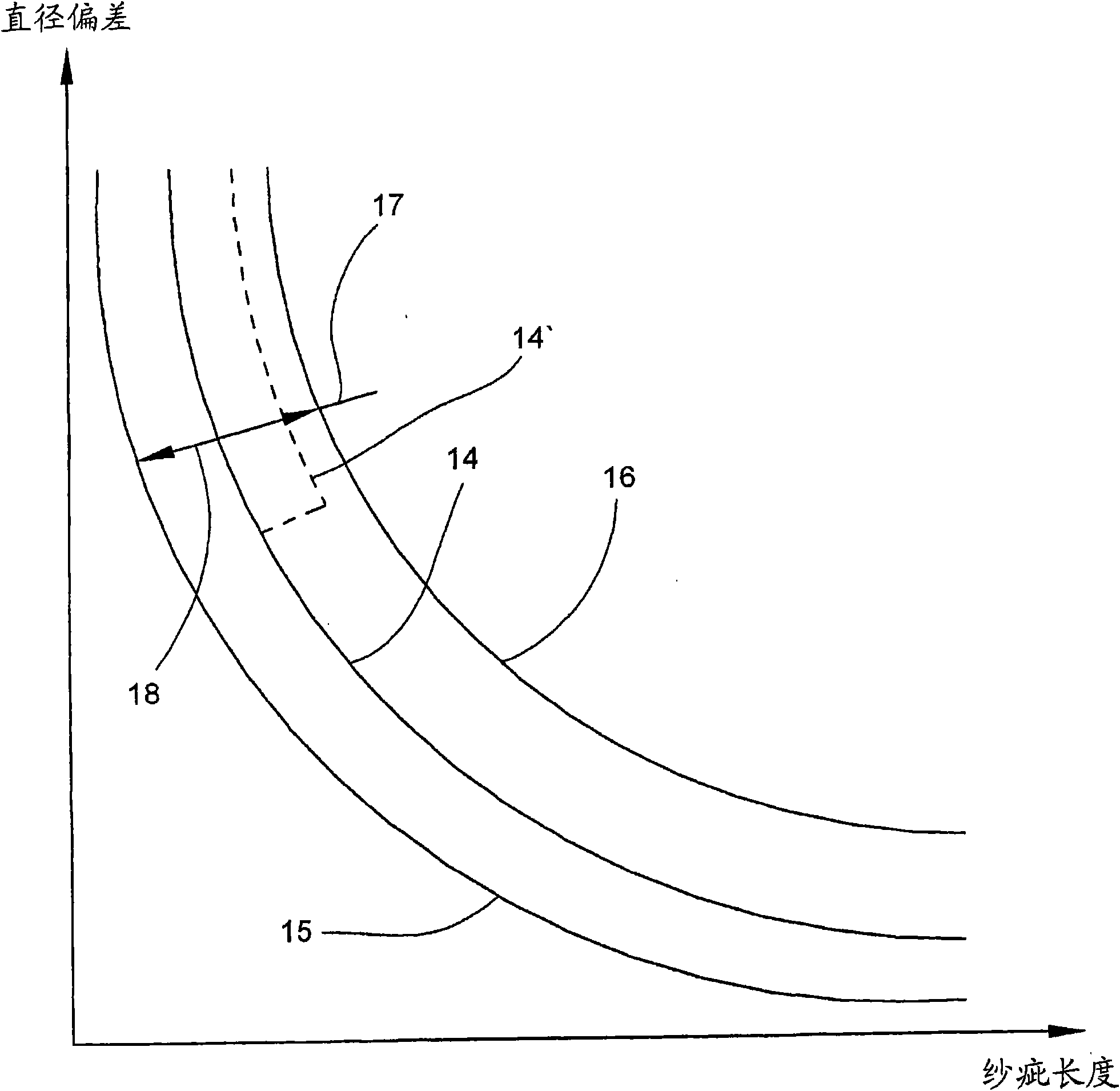
The invention relates to a method for quality monitoring of longitudinally moving yarn at workplace of textile machine manufacturing cross-coil, wherein, the yarn fault is, related to the diameter deviation and longitudinal length of the yarn, estimated in the yarn by aid of an inspecting apparatus and an estimating apparatus, which is realized by comparing the diameter deviation with the clearing threshold value and removing the deviations positioned over the clearing threshold value, wherein, a width is set in a coordinate system for the position of the clearing threshold value and definedby an upper limit and a lower limit, wherein, the fluctuation of the diameter under the lower limit can not be estimated into the yarn fault, while each yarn fault over the upper limit is removed, andbased on the given yarn quality each time on the station, the clearing threshold value is changed in the way that the amount of the yarn fault located between the clearing threshold value and the lower limit and therefore being retained in the yarn can not exceed that of the predetermined yarn fault in the yarn in a unit of length or plane fabric in a unit of length made of the yarn dependent onthe quality.
Owner:SAURER GERMANY GMBH & CO KG
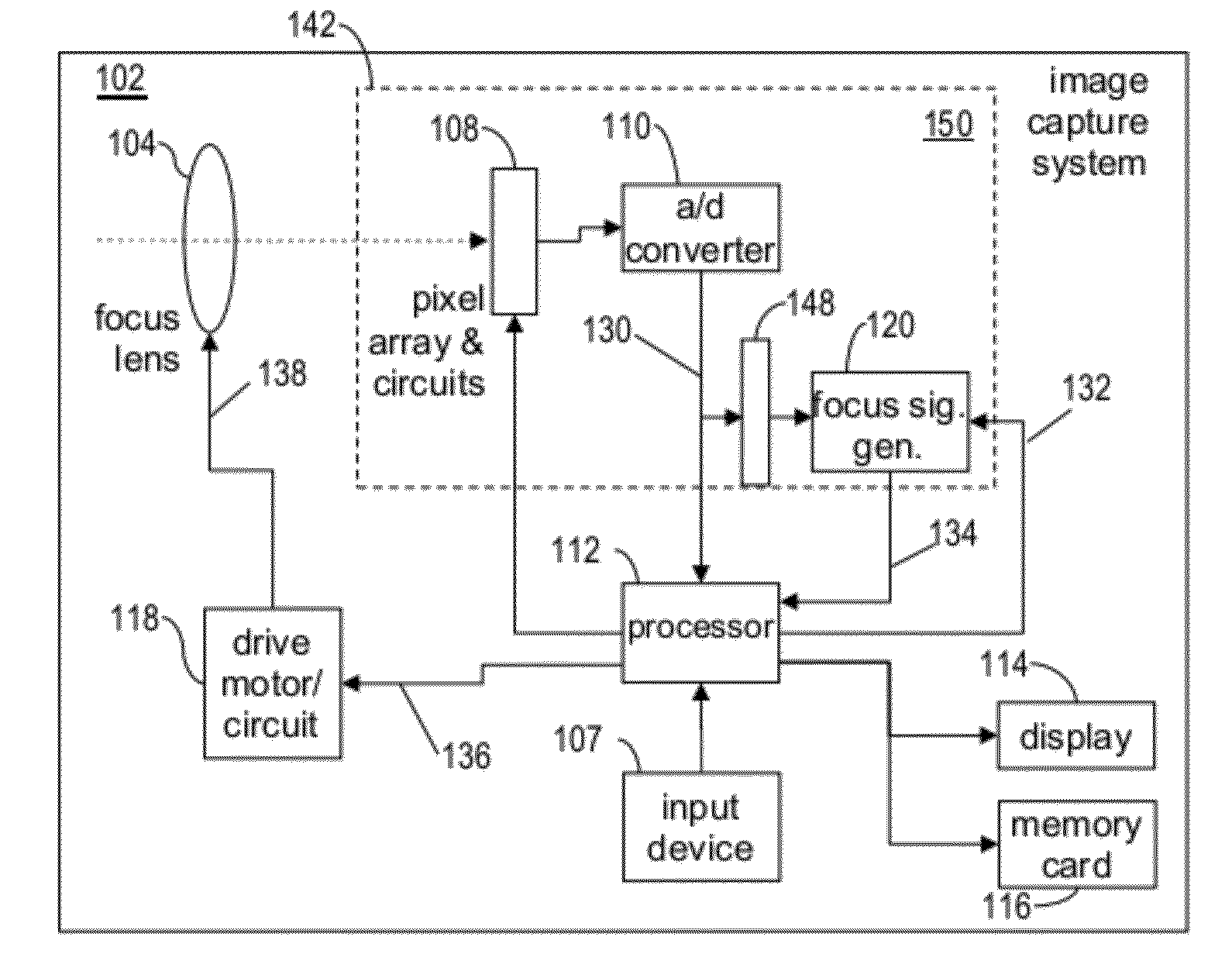
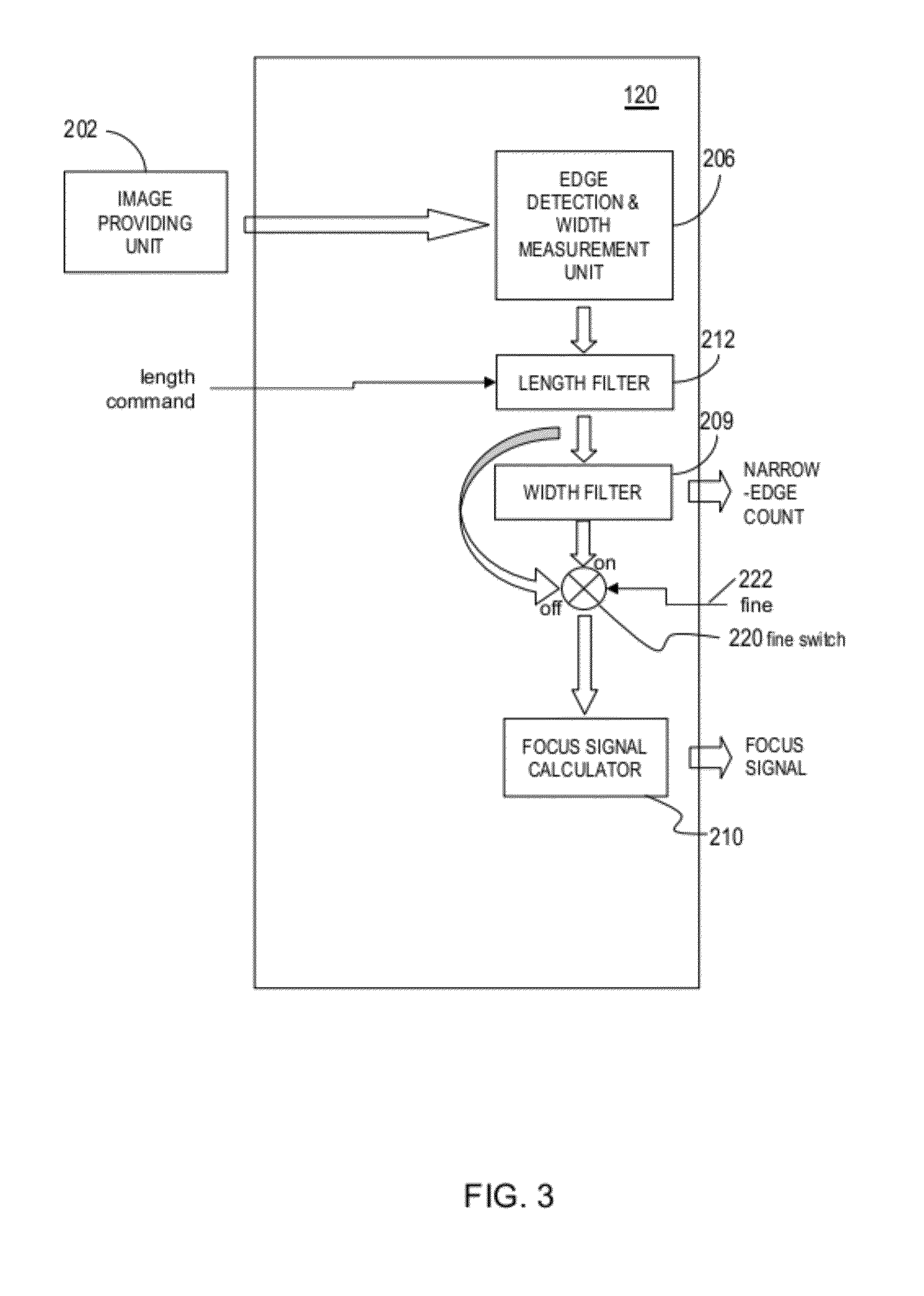
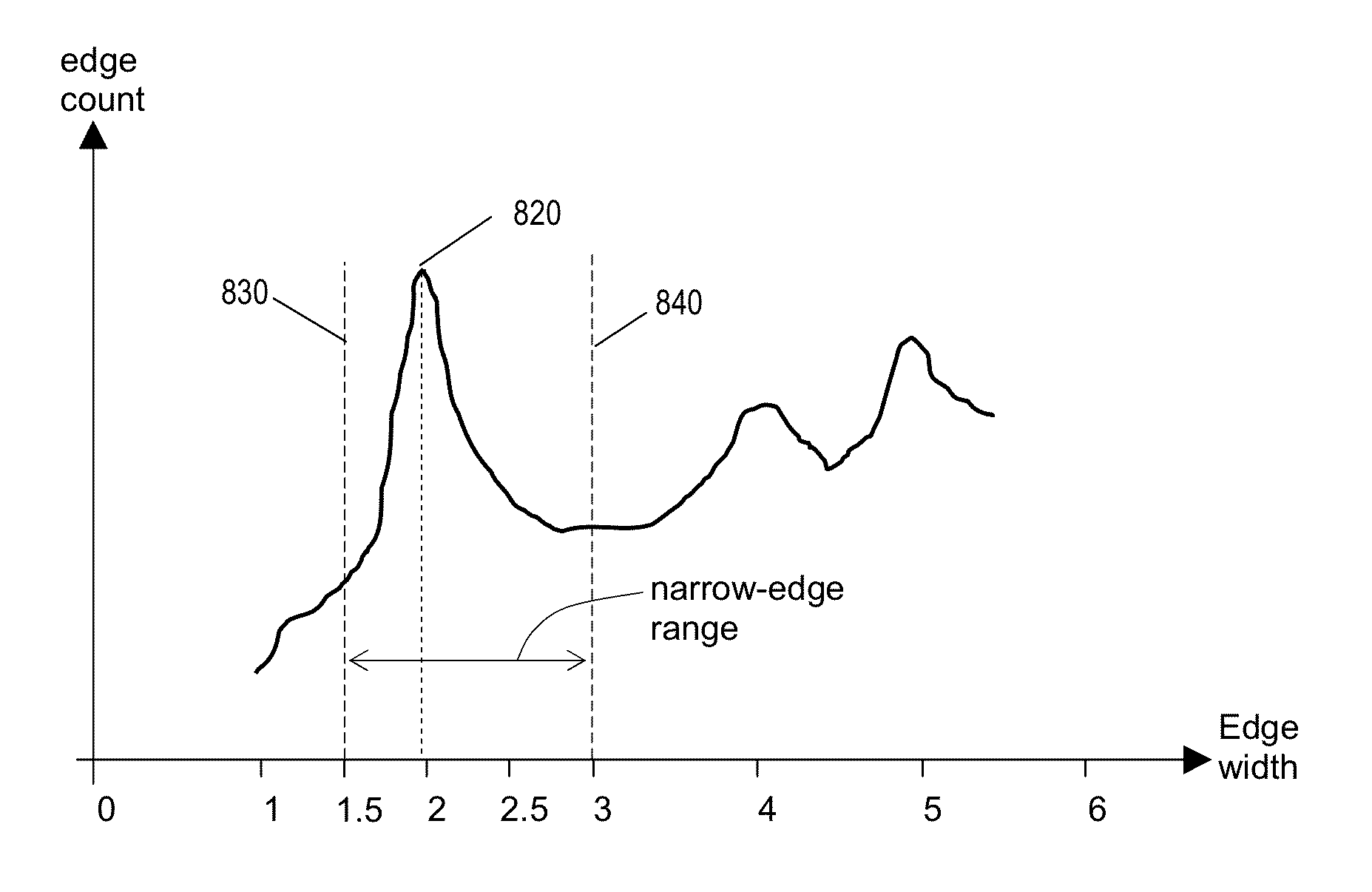
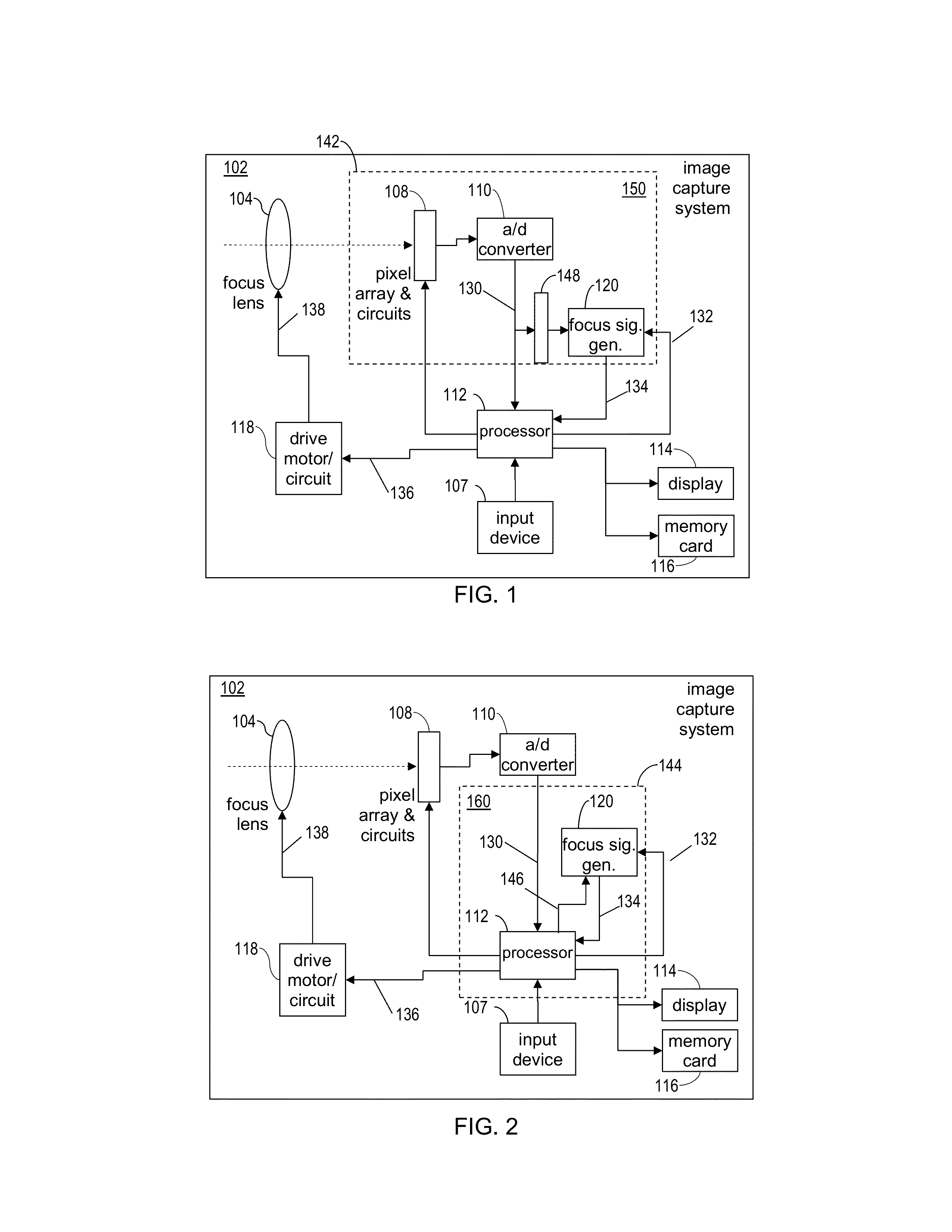
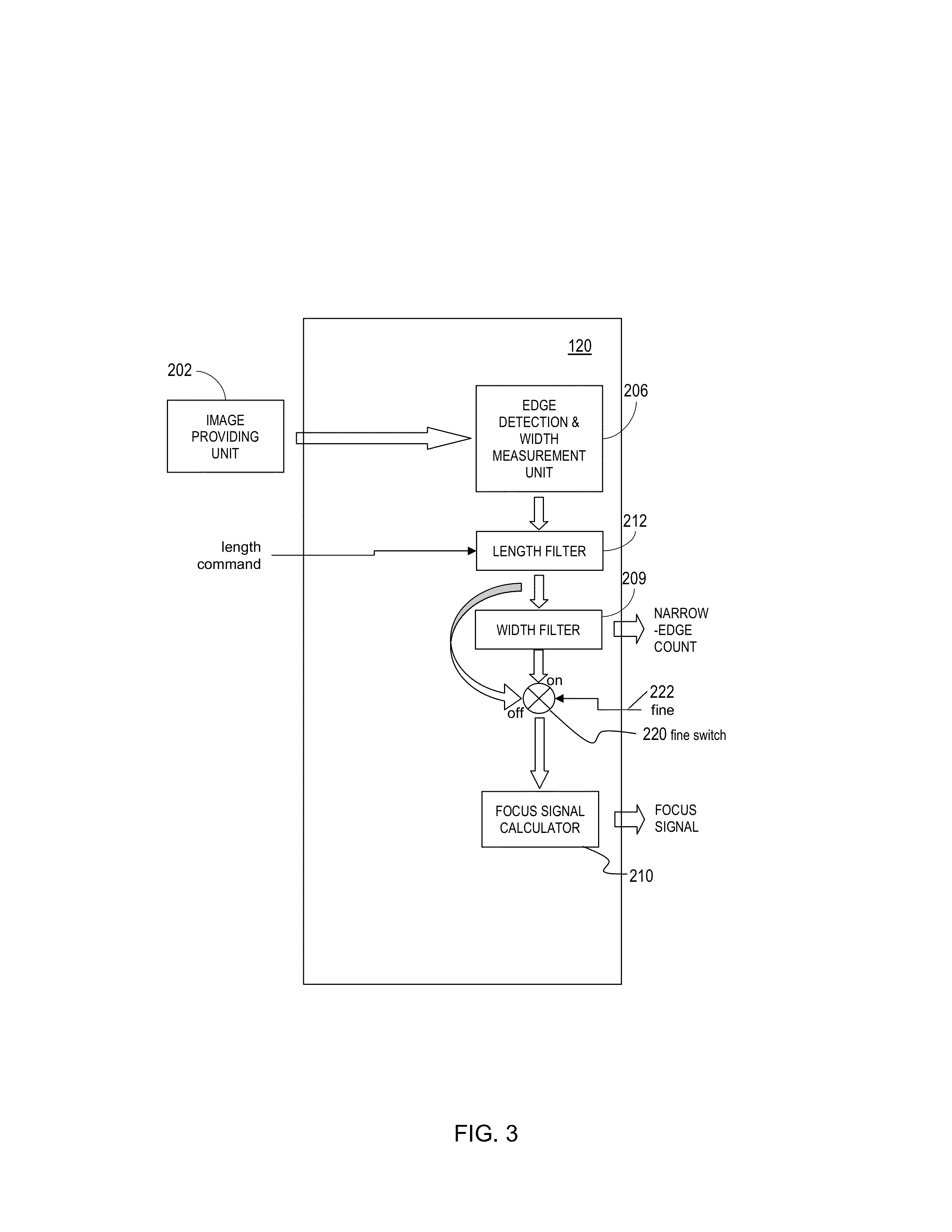
Auto-focus image system
An auto focus image system that includes a pixel array coupled to a focus signal generator. The pixel array captures an image that has a plurality of edges. The generator generates a focus signal that is a function of a plurality of edge-sharpness measures for the plurality of edges. The generator compares a sequence of gradients across the edge with one or more reference sequences of gradients and / or reference curves defined by data retrieved from a non-volatile memory. The generator may reject or de-emphasize the edge using result of the comparison. The edge sharpness measure is a quantity whose unit is a positive or negative, integer or non-integer power of a unit of length. It may be measured from the edge and / or a reference sequence / curve matched to the edge, or may be retrieved for the matched reference sequence / curve from a non-volatile memory.
Owner:TAY HIOK NAM
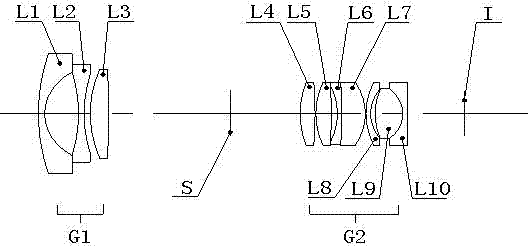
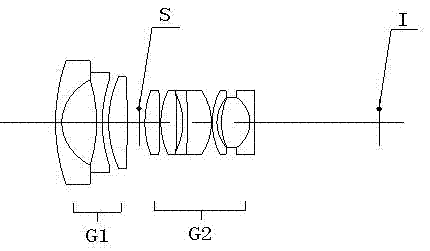
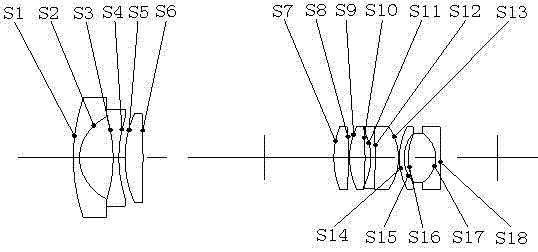
High-resolving force optical zoom lens with large target surface
The invention relates to a high-resolving force optical zoom lens with a large target surface, and belongs to the field of optical and mechanical integration. The high-resolving force optical zoom lens with the large target surface sequentially comprises a first lens group G1 with negative power, a diaphragm and a second lens group G2 with positive power from an object side to an image side. The focal length of the lens is charged through moving the second lens group G2, and the change of the position of the zoomed image surface is compensated through moving the first lens group G1 to ensure that the position of the inner image surface within the whole zooming range is unchangeable. The target surface of the optical zoom lens is 1 / 2 cun, wherein the cun is a unit of length. In the whole focal length section, values of an optical modulation transfer function (MTF) of the lens are all more than 0.3 at a place of 1301p / mm, which ensures that the resolving force can realize high definition corresponding to mega pixel within the whole focal length section, thereby adapting to the development tendency of a security industry, and having wide market prospects.
Owner:FUZHOU DEV ZONE HONGFA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
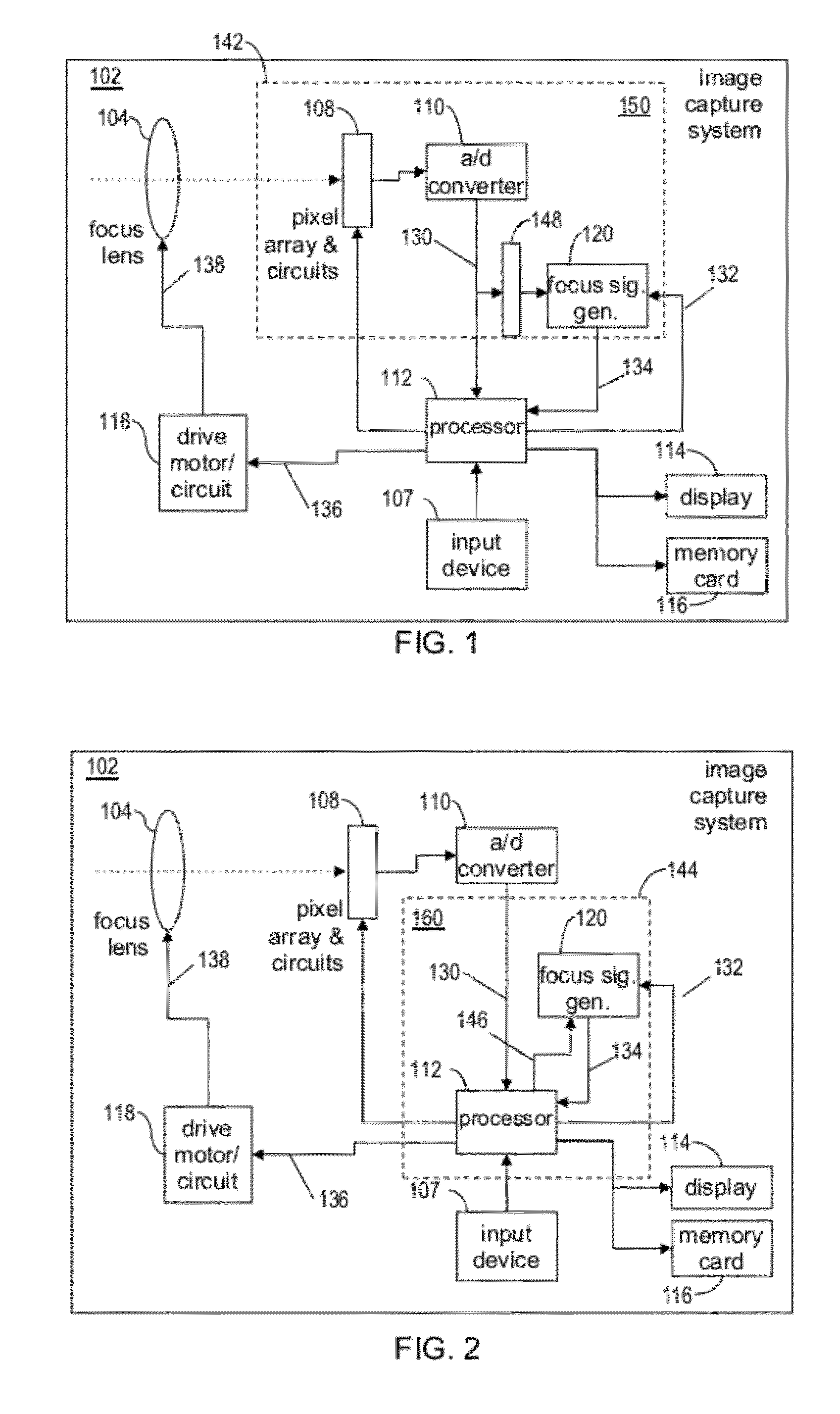
Auto-focus image system
An auto-focus image system includes a focus signal generator and a pixel array coupled thereto that captures an image that includes a plurality of edges. The generator computes a focus signal from a plurality of edge-sharpness measures, each measured from and contributed by a different edge as a quantity with a unit that is a power of a unit of length. The generator reduces a relative weight of the contribution of an edge depending on a shape of a normalized gradient profile of the edge as identified by an n-tuple of values of n different shape measures (n≧2). Each shape measure varies across normalized gradient profiles of different shapes. One shape measure may be the edge-sharpness measure itself. The weight may be zero if the n-tuple falls outside a predetermined region. At least one symmetrical shape that has perfect reflection symmetry receives reduced weight.
Owner:TAY HIOK NAM
Display device having particular pixels and signal wiring internal circuits
ActiveUS8023087B2Reduce degradationSimple designStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDriver circuitUnit of length
In a display device of built-in driver circuit type including a non-rectangular image display area, the frame area surrounding the display area is reduced and the wiring delay is reduced. The image display device includes a plurality of pixels arranged in an orthogonal matrix form, a plurality of scanning wiring lines connected to the plural pixels, a plurality of signal wiring lines connected to the plural pixels, the signal wiring lines being disposed to construct an orthogonal matrix form with the plural scanning wiring lines; signal wiring internal circuits for driving the plural signal wiring lines, and an image display area including a plurality of pixels, the image display area having a non-rectangular outer contour. The signal wiring internal circuits are separated from each other in an extending direction of the signal wiring lines in a unit of length of the pixel.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Continuous roll of optical function film, method of manufacture of liquid crystal display element employing same, and optical function film laminating device
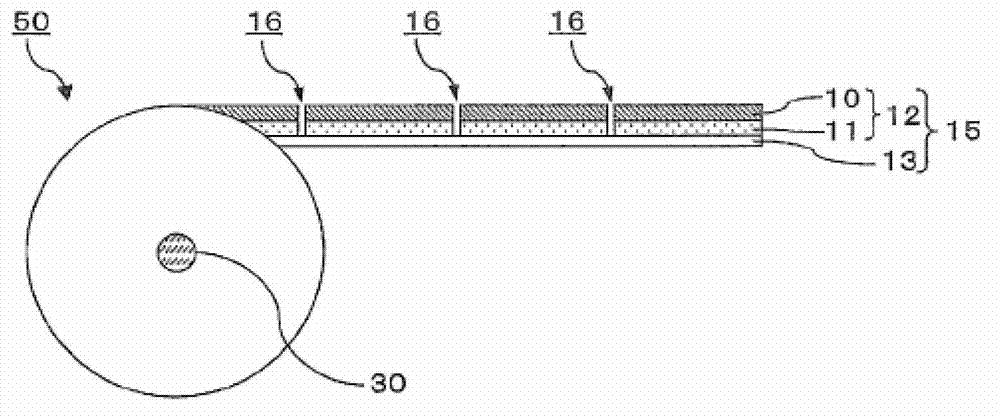
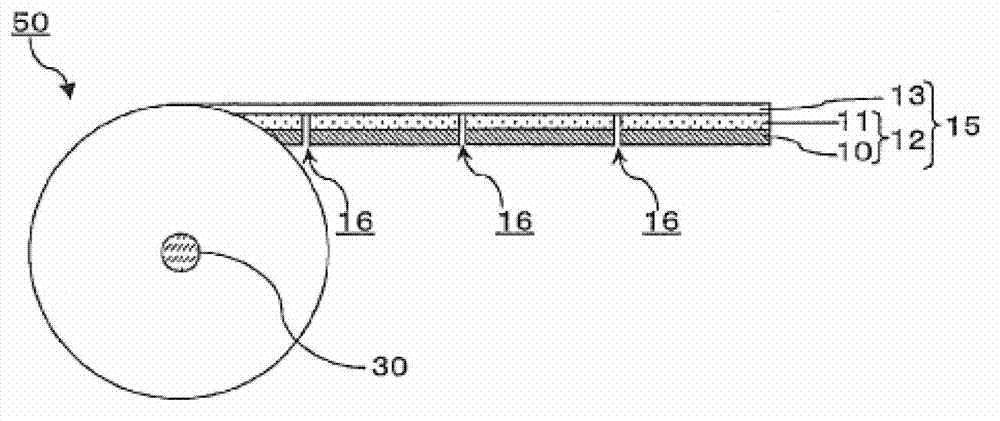
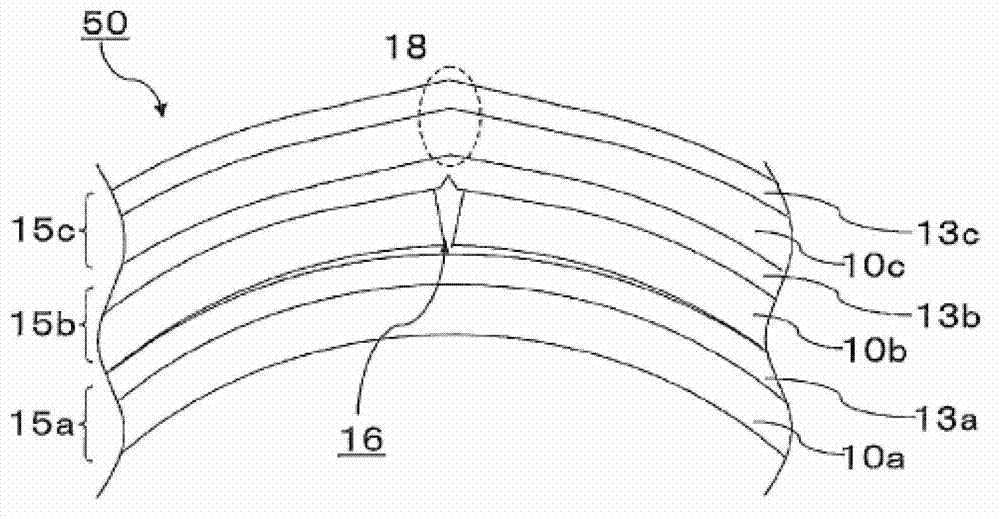
ActiveCN103080788AReduce processing timeCurb bendingPolarising elementsOptical articlesLiquid-crystal displayUnit of length
An objective of the present invention is to alleviate striped display distortion that occurs in liquid crystal display elements when taking optical function film from a continuous optical function film roll having cutting lines in the width direction thereof and laminating the optical function film on a liquid crystal panel. This continuous roll has an optical function film layered body (15) in a continuous web shape rolled thereupon, said layered body (15) including at least an optical function film (10) and a carrier film (13) that is detachably layered on the optical function film. The optical film (10) is cut into a plurality of optical function film sheets by cut lines (16) being formed along the width direction of the optical film layered body (15). It is possible to resolve the problem by making the resilience to bending per unit of length of the optical function film in the length direction fall within a prescribed range.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Dunnage conversion system and method for expanding pre-slit sheet stock material
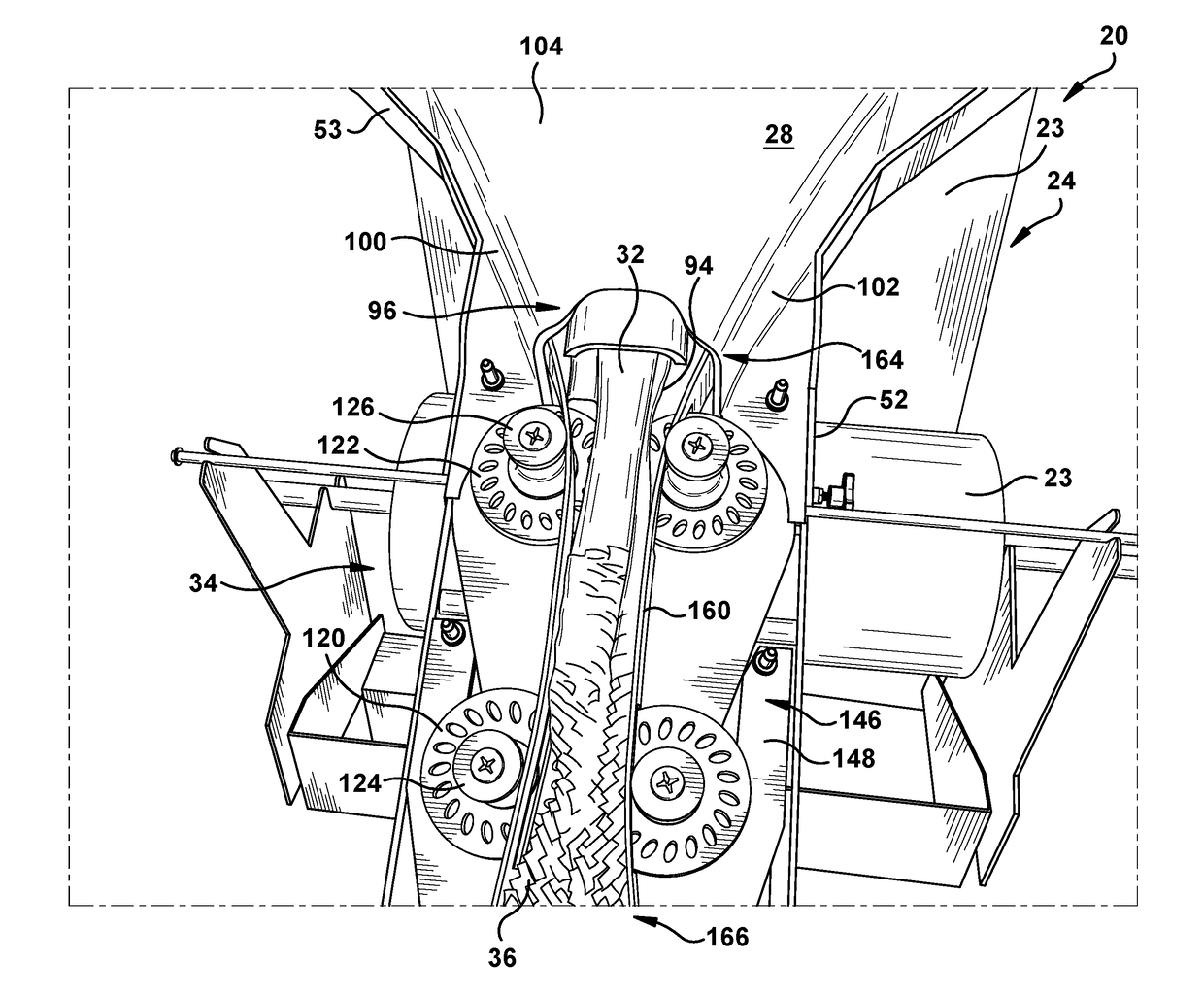
ActiveUS20180079161A1Easy loadingHigh ratio of volume per unitPaper/cardboard articlesUnit of lengthDunnage
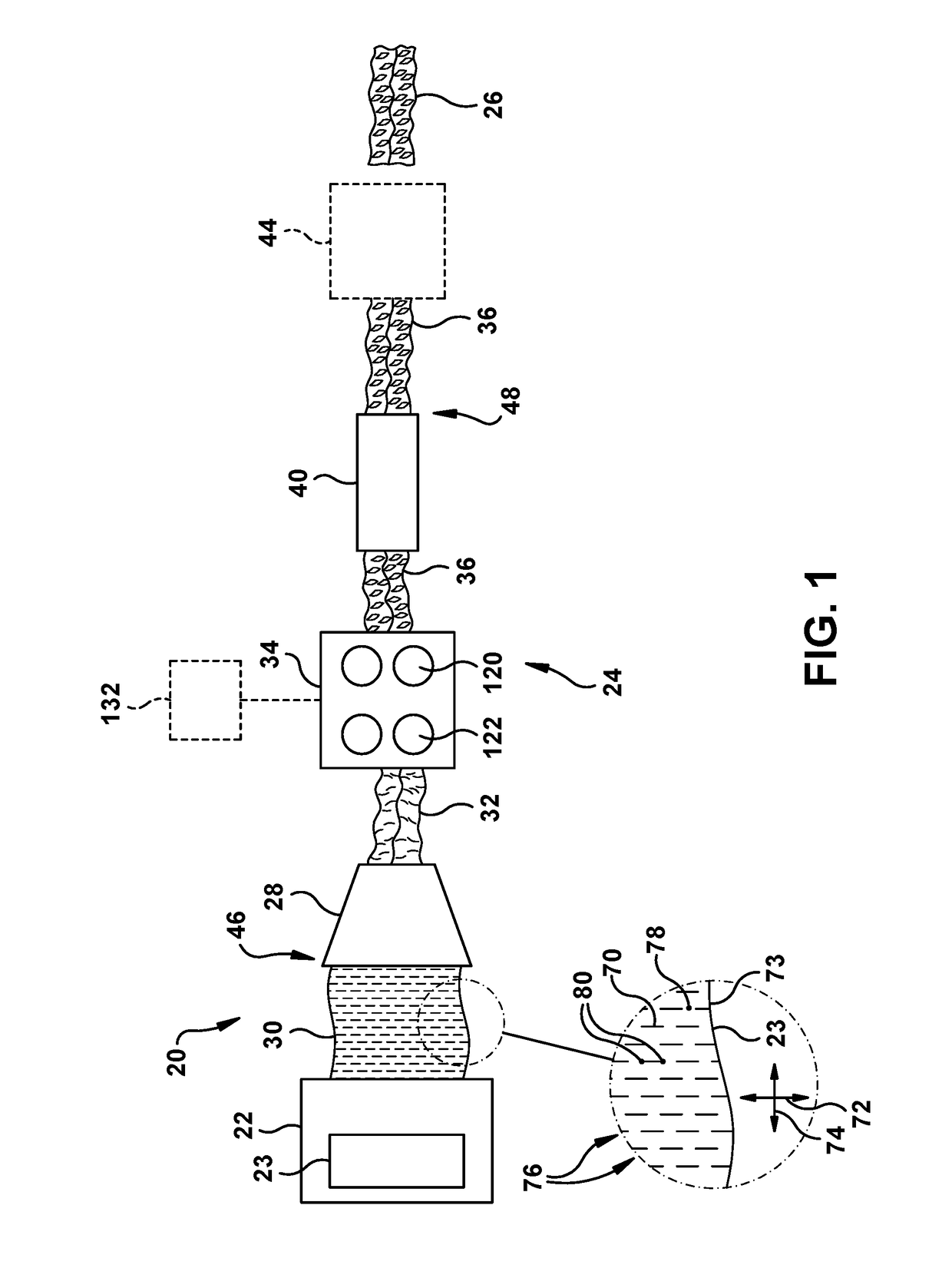
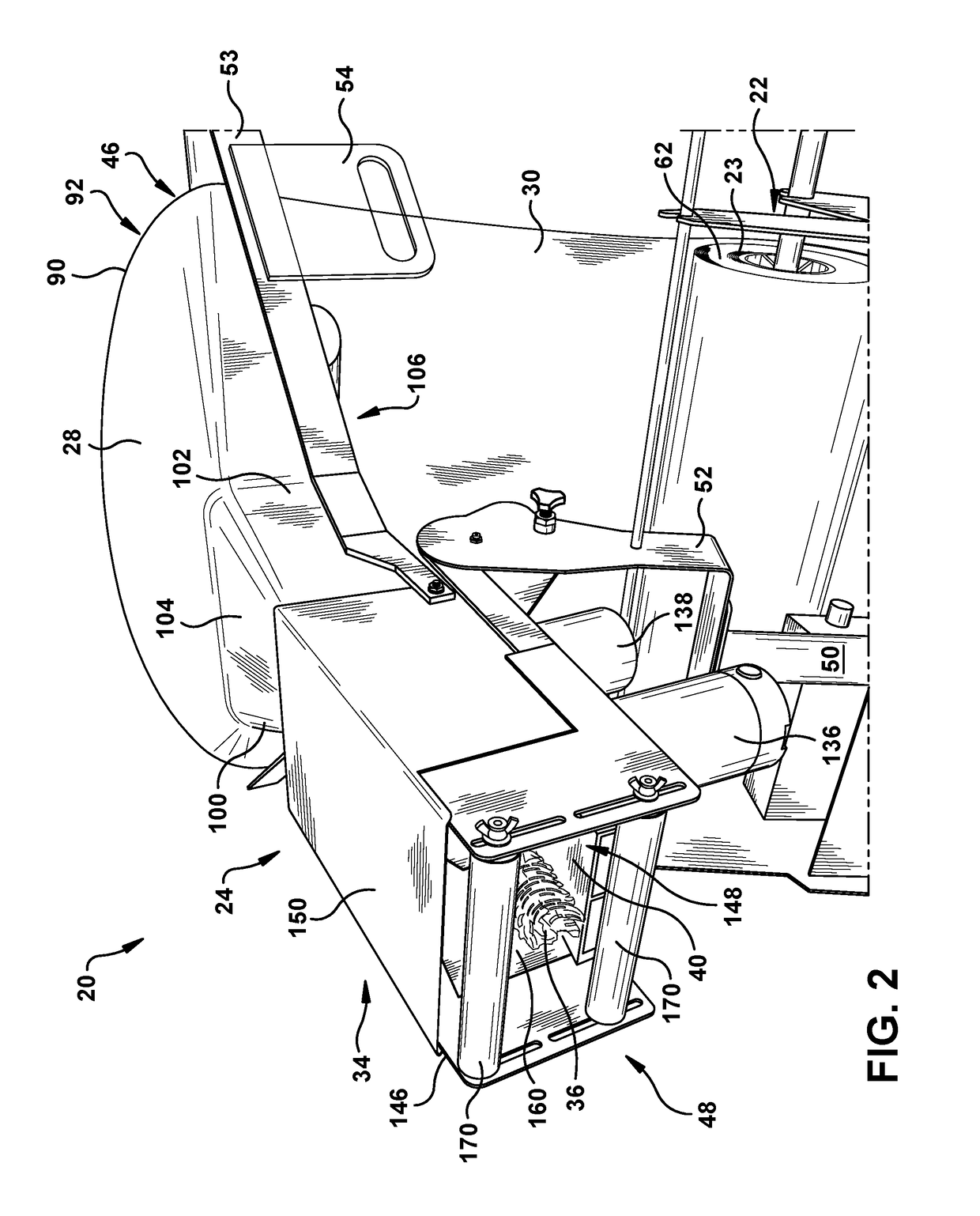
A dunnage conversion system (20) for expanding an unexpanded slit sheet stock material (23) to form an expanded dunnage product (26). The dunnage conversion system includes a converging chute (28) to inwardly gather laterally-extending edges of sheet stock material towards one another, causing random crumpling of the sheet stock material to form a modified ply. The conversion system also includes feed wheels (120) that advance the modified ply through the converging chute and pinch rollers (122) that cooperate with the feed wheels to expand the modified ply traveling between the feed wheels and the pinch rollers to form a dunnage product. The expanded dunnage product is expanded both in a longitudinal feed direction and in thickness as compared to the unexpanded slit sheet stock material, and thus is a three-dimensional product having increased volume and lower density per unit of length as compared to the unexpanded slit sheet stock material.
Owner:RANPAK CORP
Method and device for inspecting a traveling wire cable
InactiveUS8254660B2Simple methodInspecting textilesCharacter and pattern recognitionUnit of lengthEngineering
Owner:CASAR DRAHTSEILWERK SAAR GMBH
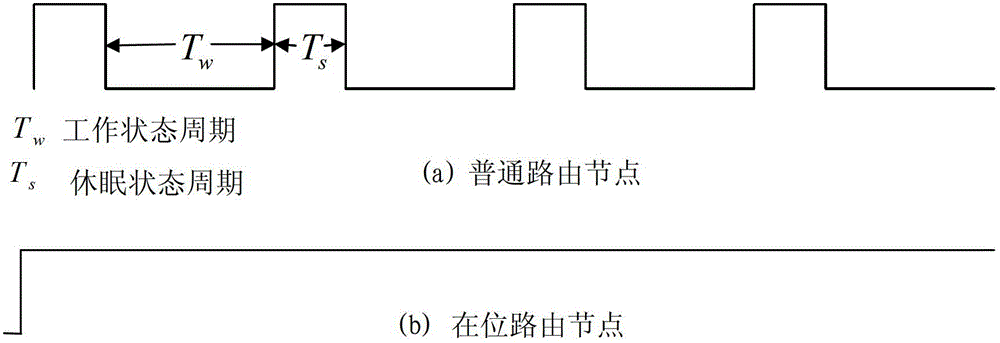
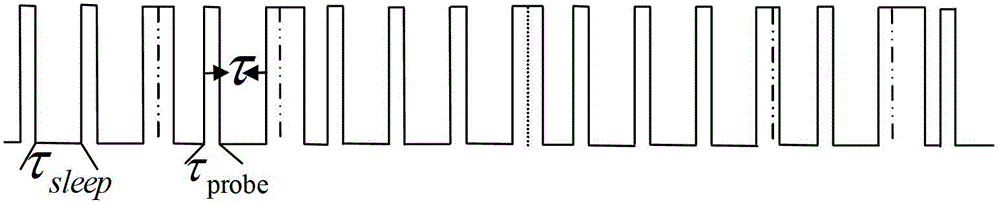
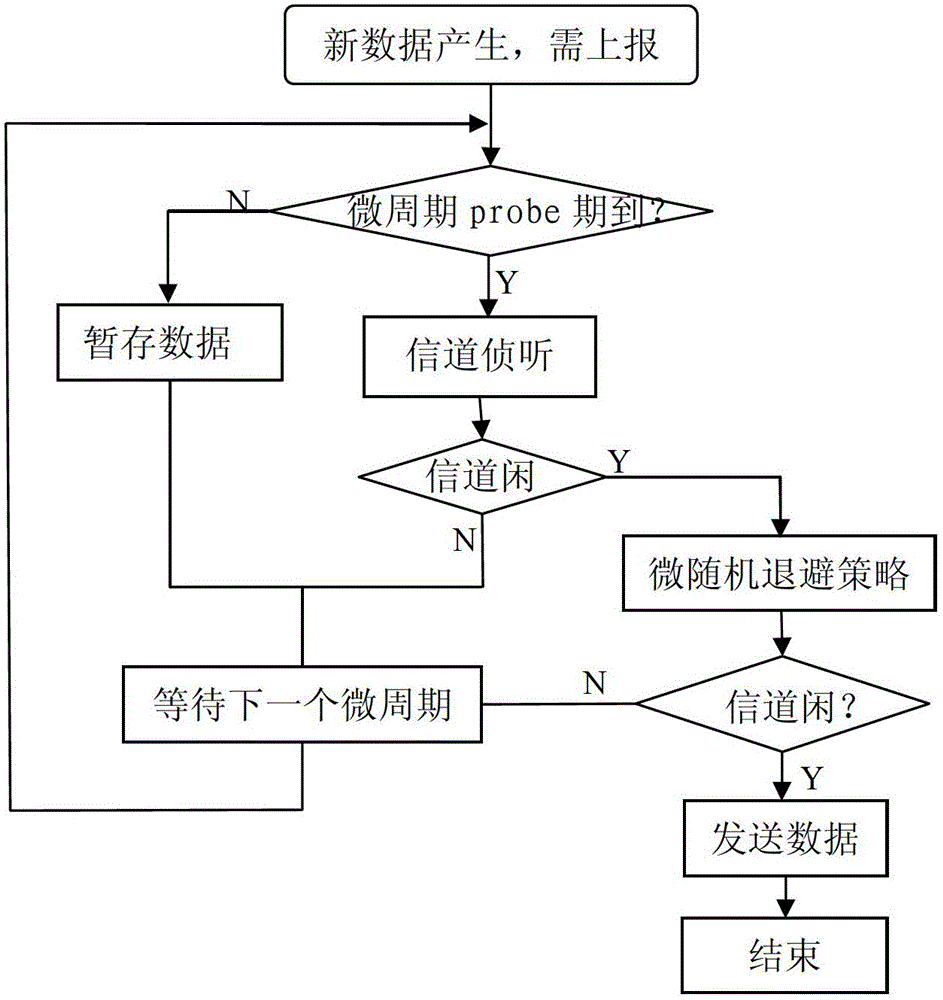
Micro-cycle-based sleep method adapted to routing nodes in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102724741AReduce node energy consumptionProlong lifeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMobile wireless sensor networkSleep time
The invention provides a micro-cycle-based sleep method adapted to routing nodes in a wireless sensor network. The method comprises the following steps of: synchronizing global clocks of all nodes in the entire wireless sensor network; dividing the time into a micro-cycle taking t as the unit of length at bit routing nodes according to the global clocks, and the bit routing nodes going to sleep by taking t as a unit periodically; the bit routing nodes being routing nodes being responsible for relaying tasks in the current period of time; and the micro-cycle t consisting of detection time and sleep time, and the bit routing nodes receiving and sending data within the detection time and being in a sleep state in the sleep time. According to the method, the energy consumption of the nodes in the network can be effectively reduced, and the network lifetime is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Synchronous servo channel for longitudinal position detection and position error signal generation in tape drive systems
InactiveUS20070171565A1Improve reliabilityAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageTape speedUnit of length
A fully synchronous longitudinal position (LPOS) detection system is provided for improving the reliability of servo channels in tape systems. The system is based on the interpolation of the servo channel output signal, which is sampled by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) at a fixed sampling rate, using a clock at a nominal frequency, so that interpolated signal samples are obtained at a predetermined fixed rate, independent of tape velocity. This predetermined fixed rate is defined in terms of samples per unit of length, as opposed to samples per unit of time, which is the measure of the ADC sampling rate. The resolution with which the servo channel signal is obtained at the interpolator output is thus determined by the step interpolation distance.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Gliding board
InactiveUS20060181061A1High densityImprove reinforcementSki bindingsSki-brakesUnit of lengthEngineering
The invention relates to a snow gliding board (1) having a sidecut (2) that widens from the middle area (3) of the board towards at least one of its ends to a point of maximum width (4) and of which the structure includes a reinforcing fibre mat (10) comprising yarns (11) that extend in the longitudinal direction of the board. It is characterised in that the number of yarns (11) per unit of length, measured across the board, varies from the middle area (3) towards the point of maximum width (4) of the board.
Owner:SKIS ROSSIGNOL +1
Row unit for a planter, planter and method for planting
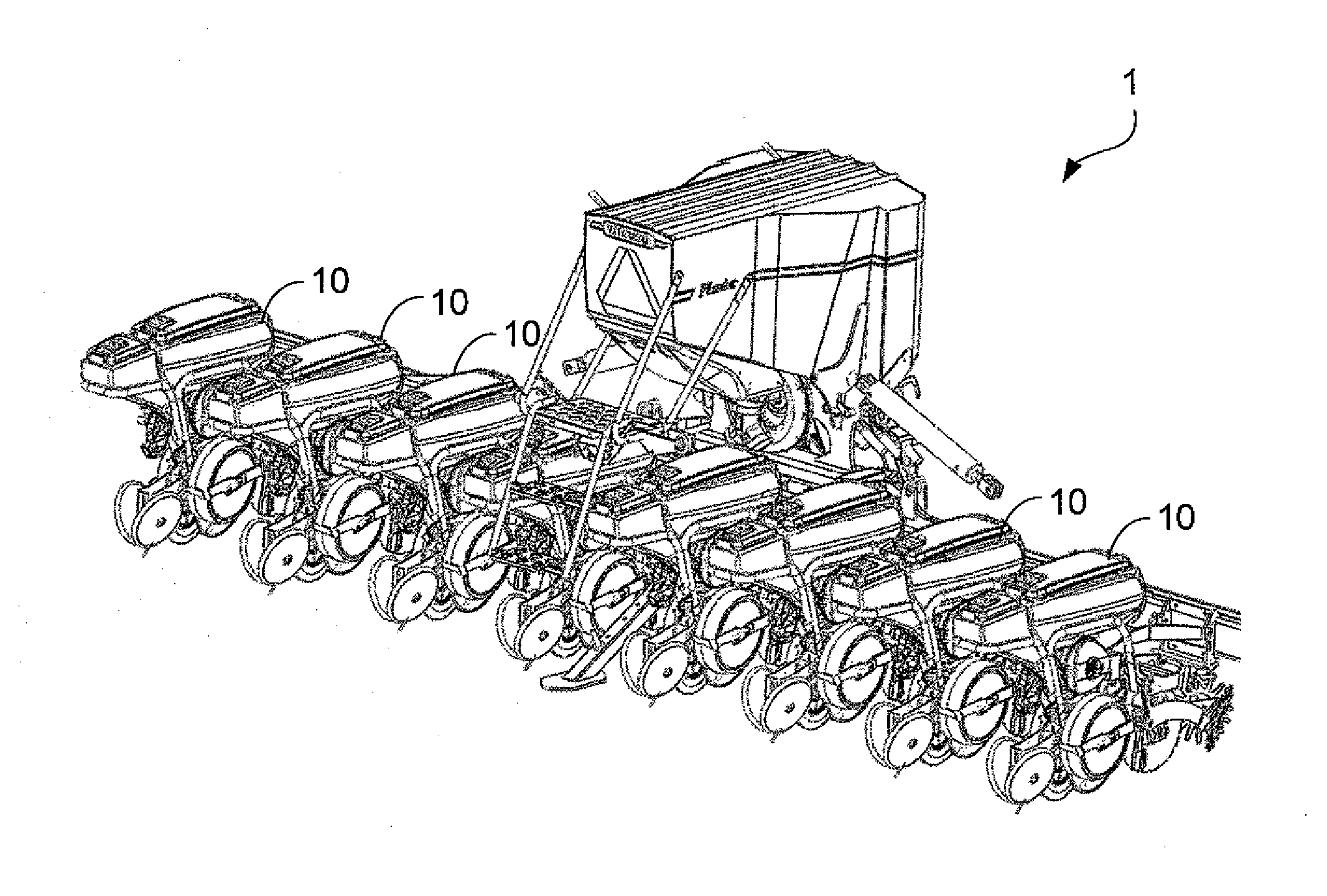
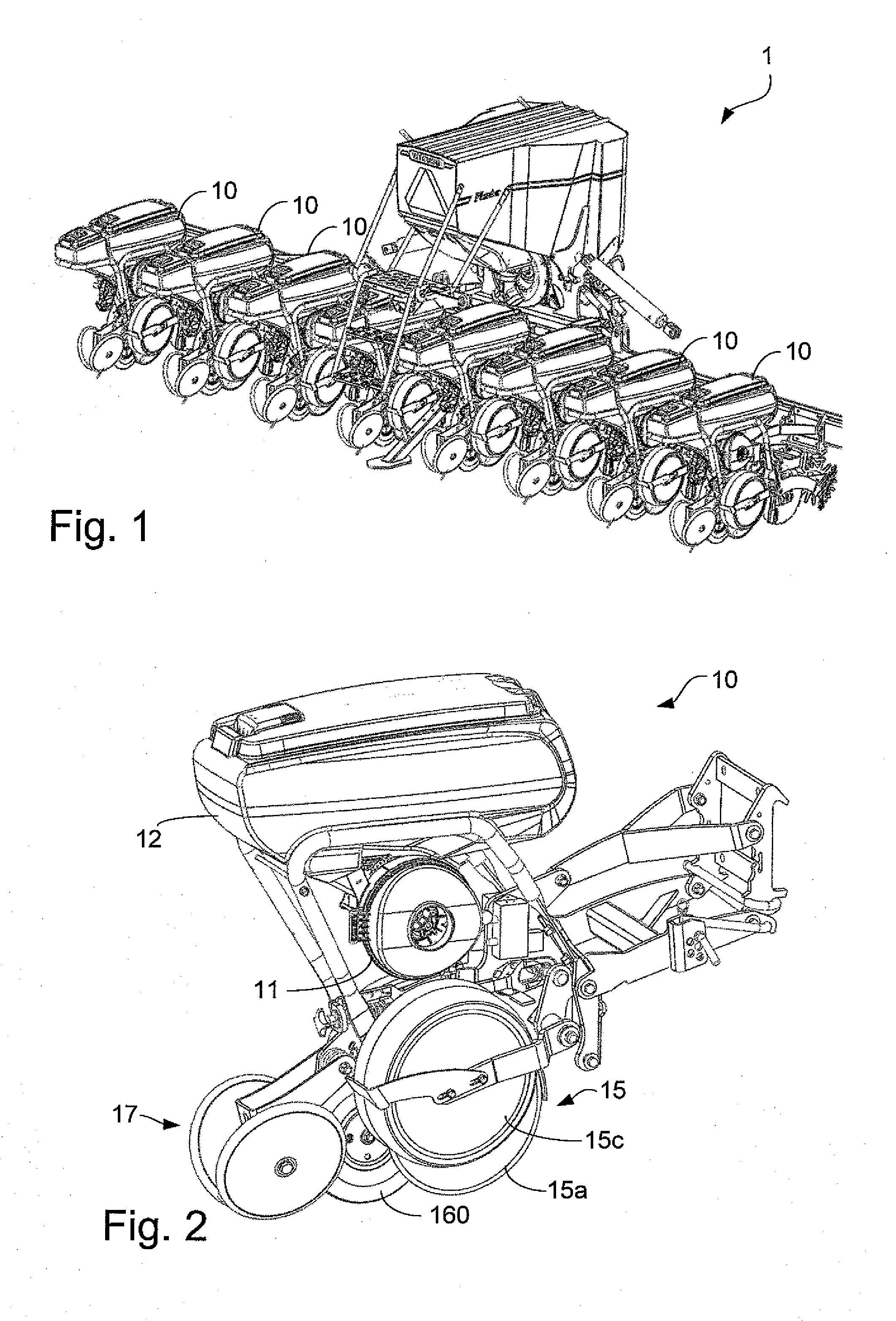
ActiveUS20130118393A1Eliminates and reduces drawbackEliminates and reduces problemPlantingFurrow making/coveringSeederUnit of length
A precision seeder for sowing seeds to obtain a predetermined number of plants per unit of length includes a seed discharging tube adapted to feed the seed by an excess air pressure from a seed distributing device to a seed outlet, a seed furrow opener including two sowing discs arranged at an angle relative to each other, and a resilient press surface for pressing the seed into the soil. The press surface is configured such that a direction of flow of the seeds at the seed outlet intersects or is substantially tangent to at least a portion of the press surface. The seed outlet is located between the sowing discs and, as seen in the transverse direction, inside or immediately adjacent to the periphery of at least one of the sowing discs.
Owner:VADERSTAD HLDG
Plate dipole antenna
InactiveUS6937204B2Reduce disadvantagesEasy to harvestAntenna arraysAntenna feed intermediatesUnit of lengthDipole antenna
Owner:AERIAL SCI
Gliding board
The invention relates to a snow gliding board (1) having a sidecut (2) that widens from the middle area (3) of the board towards at least one of its ends to a point of maximum width (4) and of which the structure includes a reinforcing fiber mat (10) comprising yarns (11) that extend in the longitudinal direction of the board.It is characterised in that the number of yarns (11) per unit of length, measured across the board, varies from the middle area (3) towards the point of maximum width (4) of the board.
Owner:SKIS ROSSIGNOL +1
Method and device for inspecting a traveling wire cable
ActiveUS8526706B2Facilitate cognitionInspecting textilesCharacter and pattern recognitionUnit of lengthImage segmentation
Owner:WIRECO GERMANY GMBH
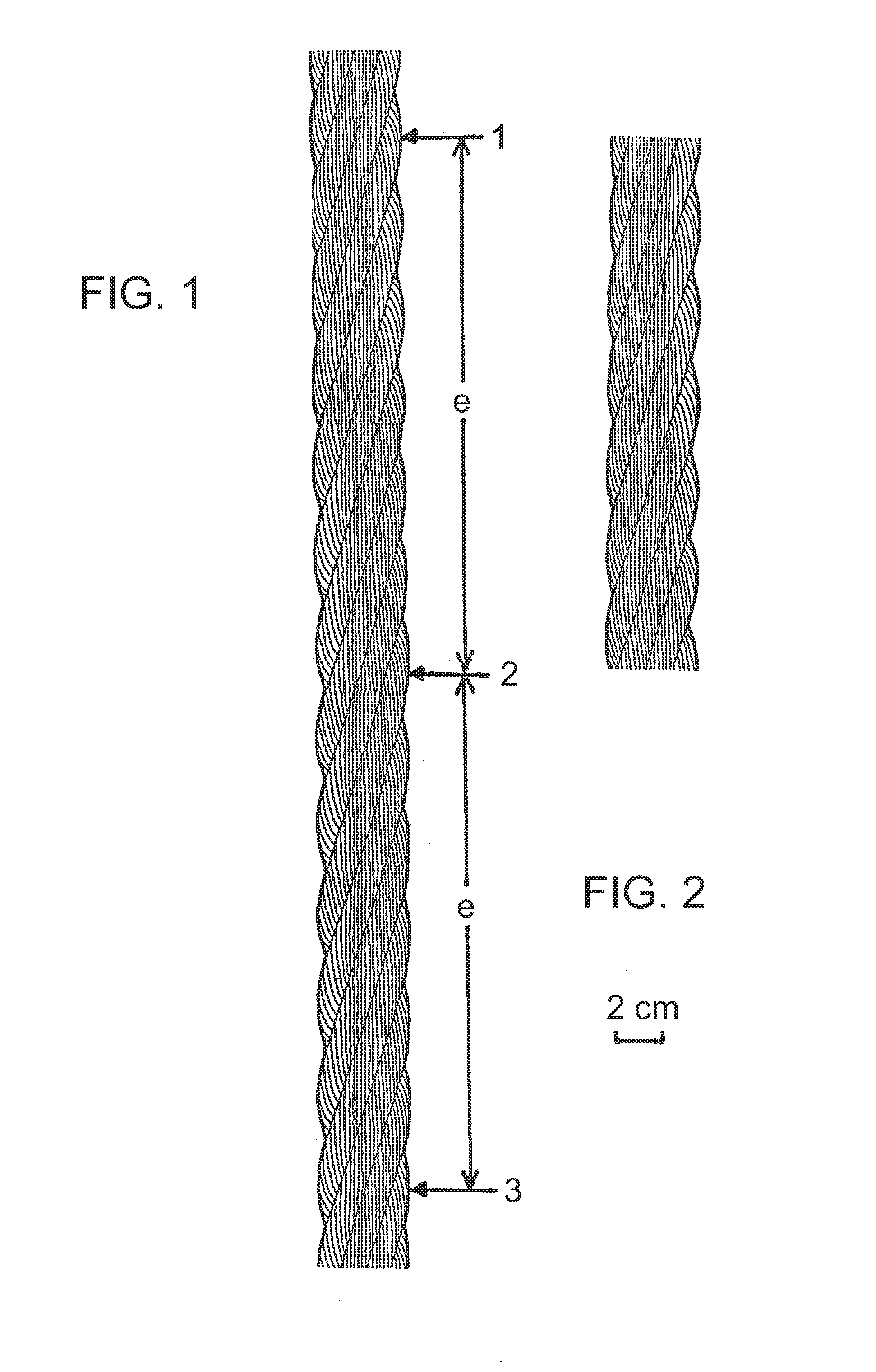
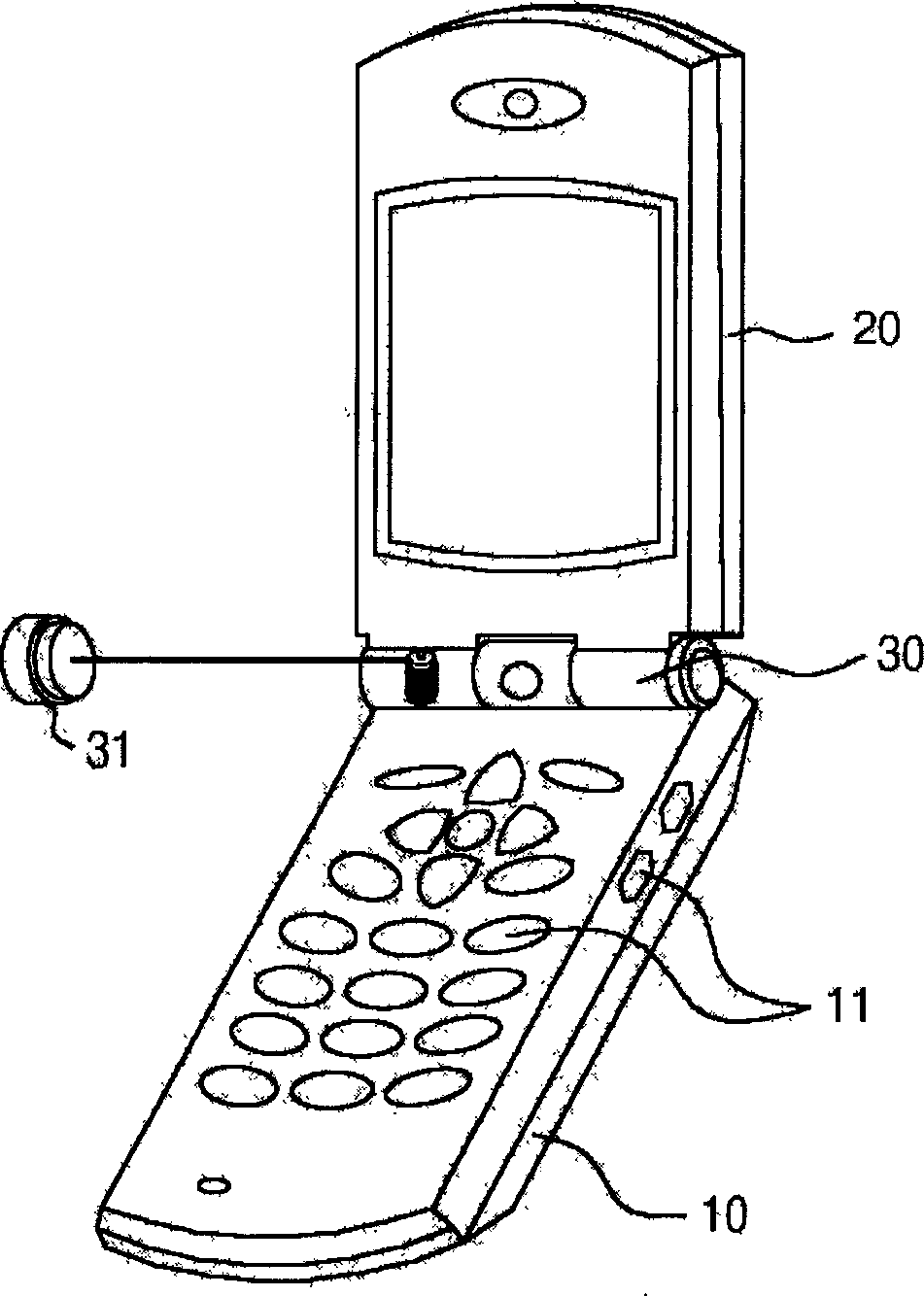
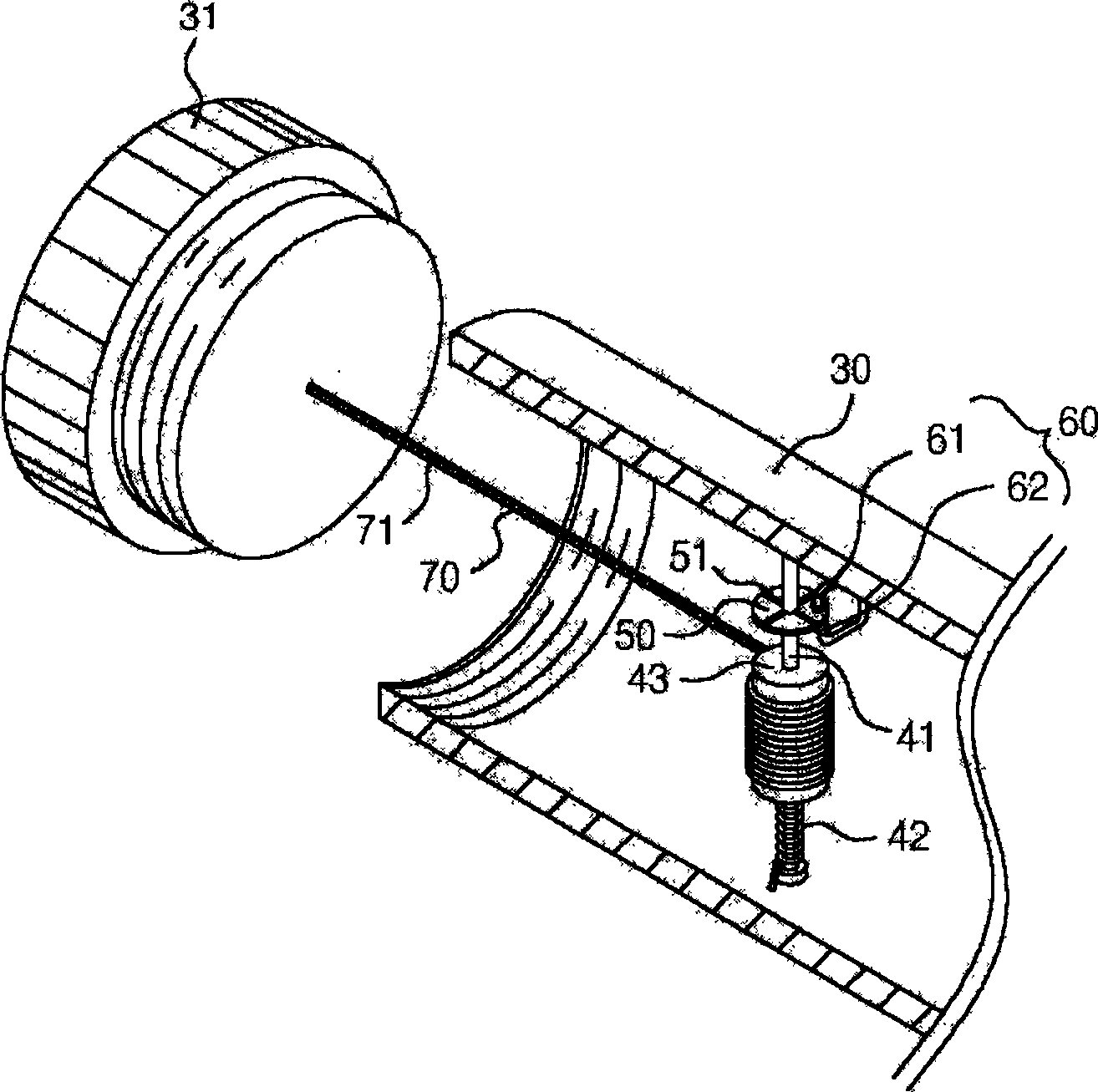
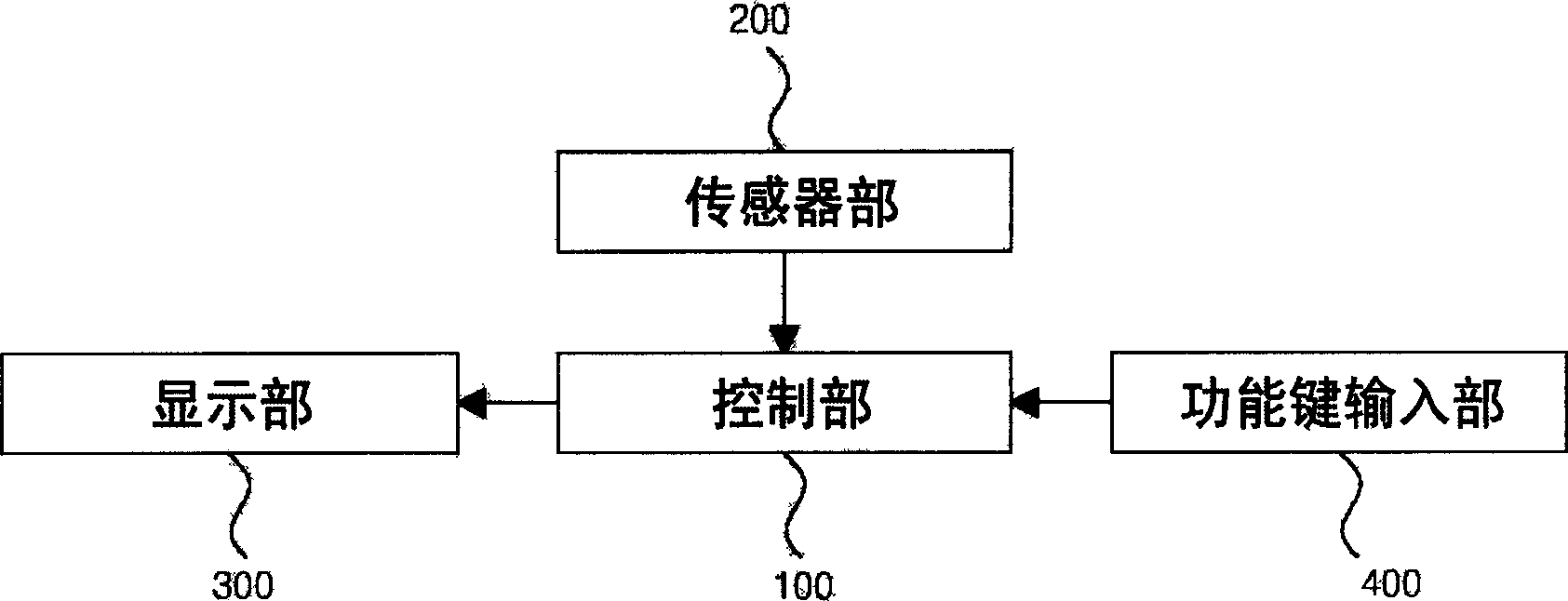
Mobile communication terminal with length measurer
The invention discloses a mobile communication terminal with a length measuring device belonging to a mobile communication device. Contains the following parts: the sensor part for detecting the number of revolutions of the rotating disk; the display part for displaying the reference length unit detected by the sensor part; the function key input part for controlling the operation of the sensor part; and the control part for measuring and displaying the length detected by the sensor part. It also includes: connecting the clamshell and the body of the mobile communication terminal, and installing a detection reference member and a rotatable rotating body at one end of the inner hollow hinge shaft; a rotating disk with engraved lines on either side of the upper and lower sides of the rotating body; The sensor part is installed adjacent to the rotating disk; one end is fixed on the rotating body, and the other end is fixed on a metal wire on the measurement reference member. Therefore, adding the function of a tape measure as a daily necessities to a mobile communication terminal can be used for assembly operations and precise measurement of the size or error of parts on a production line, or as a general household daily necessities.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (CHINA) R&D CENT CO LTD
Measurement Devices and Methods
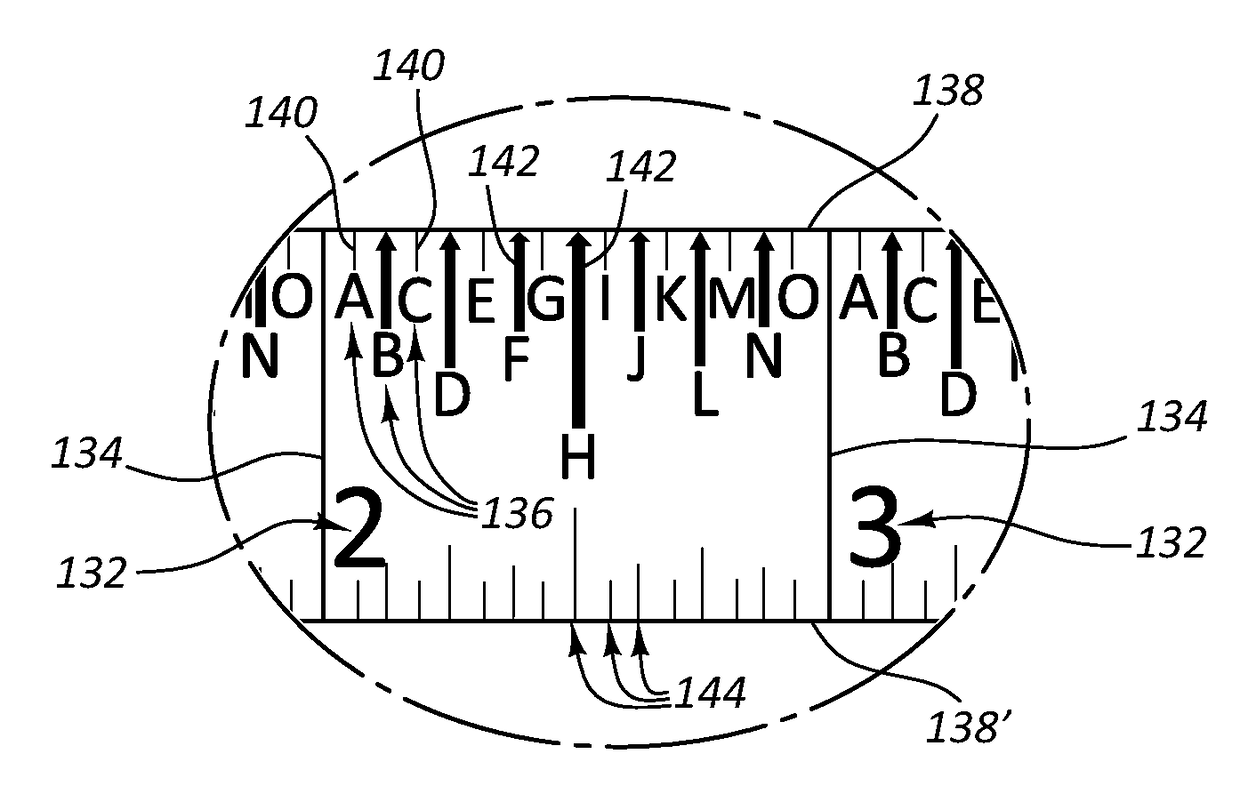
ActiveUS20170322006A1Frustration and wasteImproper lengthRulers for direct readingMeasuring tapesMeasurement deviceUnit of length
A measurement device includes first and second measurement indicia. First indicia (e.g., on the tape) may include numerals regularly spaced to mark inches or other units of length (e.g., 1, 2, 3, etc,). Also included are second indicia, that are non-numeric (e.g., letters, such as A, B, C, etc.) where the second indicia are regularly spaced to mark fractions of inches or other units of length indicated by the first indicia. The second indicia are positioned between adjacent first indicia. For example, the letters (A, B, C, etc.) may he spaced every sixteenth or other fraction of an inch between the “1” and “2” (adjacent first indicia). Where sixteenths are used, the letters A-O are equally spaced, between the adjacent first indicia (e.g., between the “1”P′ and the “2”). The A-O may repeat between each integral number—between “1” and “2”, between “2” and “3” and so forth.
Owner:MJ STEWART INVESTMENTS LLC
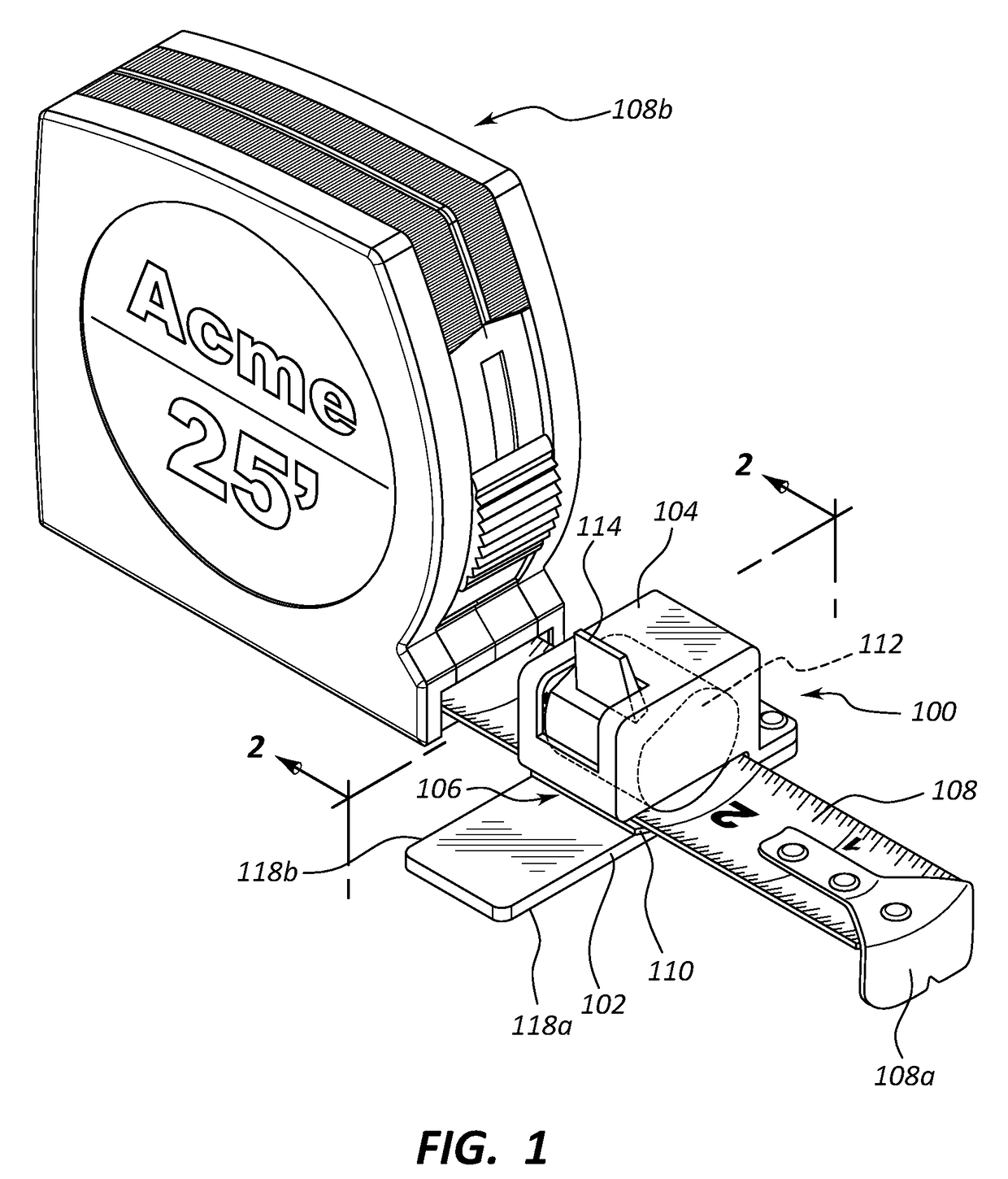
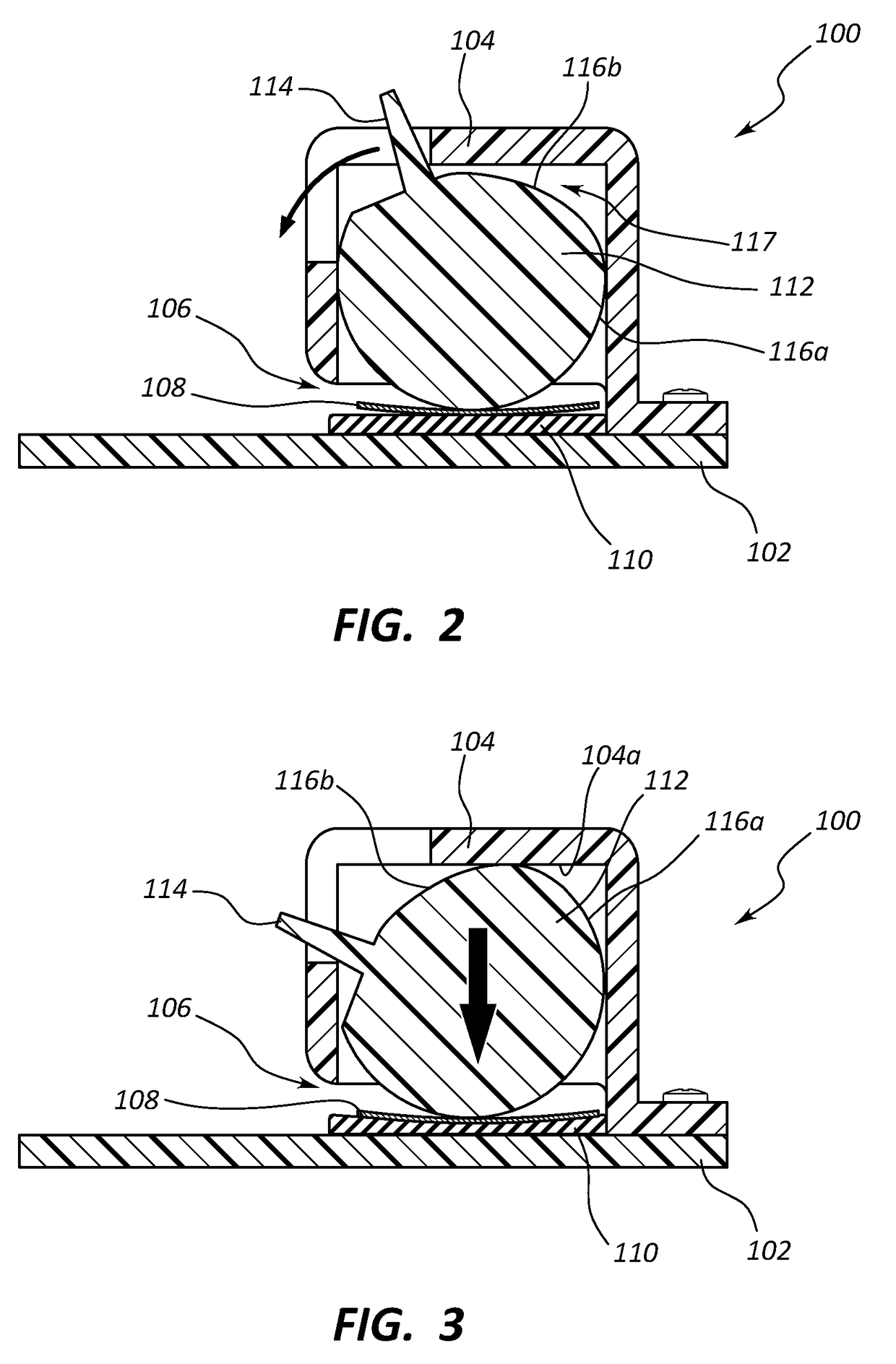
Tape rule accessory
A tape rule accessory with a receiving slot that is shaped conformally to the curvature of a tape rule for receiving a tape rule side edge into the receiving slot. The upper flange has a window with opposed and aligned alignment pointers for aligning to demarcations on the tape rule when the tape rule is installed in the receiving slot. The alignment pointers are positioned an integer number of units of length (for example, inches or centimeters) from an end of the accessory. Exterior marking guides are aligned to the alignment pointers. One or more level indicators, such as spirit levels, may be attached, preferably by being snap fit into housings. Friction ridges may be used within the receiving slot to prevent accidental movement while maintaining ease of use. A thermally bonded, two-part embodiment is disclosed.
Owner:HIGGINBOTHAM SCOTT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com