Ferrite blank sintering process
A ferrite and blank technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve the problems of large size, different upper and lower end faces, deformation of ferrite core blanks, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing deformation, increasing stacking height, and improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
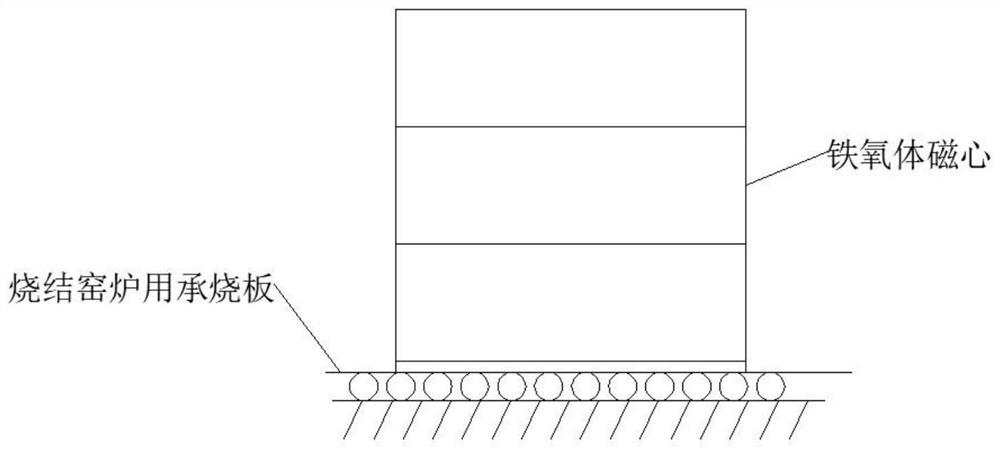
[0038] This embodiment provides a ferrite core blank sintering process, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0039] According to the predetermined placement position of multiple ferrite core blanks, use soft wool brush and other tools that will not damage the surface of ferrite core blanks, and according to the size and volume of ferrite core blanks, The contact surface of the oxygen body blank is coated with an appropriate amount of anti-adhesion coating; the anti-adhesion coating is a paste made by mixing and stirring water and corundum sand in a mass ratio of 2 to 3:1, and the particle size of the corundum sand is preferably ≤ 80 orders; What sintered in the present embodiment is the circular ferrite magnetic core;
[0040] After the multiple ferrite core blanks are coated and stacked in place, they are immediately sintered to avoid deformation of the ferrite core blanks due to moisture absorption due to excessive storage time. This embodiment adopts the form...
Embodiment 2
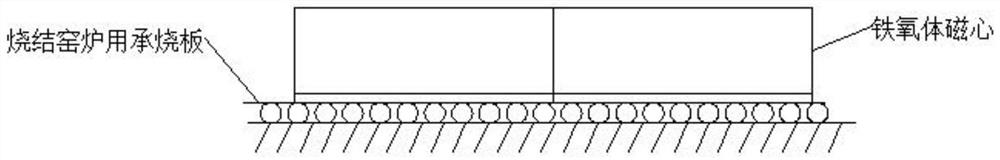
[0044] This embodiment provides a ferrite core blank sintering process, the operation steps of which are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the ferrite core blanks in this embodiment are sintered by placing them side by side. Situation such as figure 2 shown. When sintering side by side, you also need to pay attention to the amount of coating. As mentioned above, too much will easily cause product deformation and cracking, and too little will not solve the problem of magnetic core adhesion and deformation; when placed side by side, the coating thickness is 0.8mm ~0.9mm is suitable, and 0.8mm is the best. The placement of the ferrite core blank in this embodiment is as follows figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
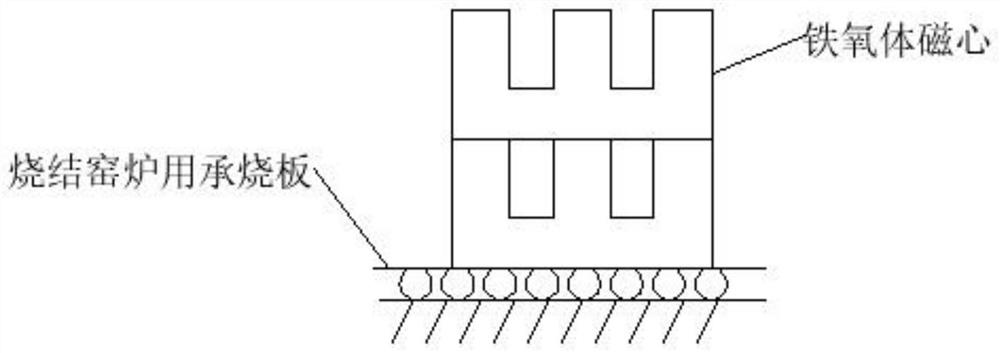
[0046] This embodiment provides a ferrite core blank sintering process, the operation steps of which are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the E-type ferrite core blank is used in this embodiment. The placement of the E-type ferrite core blank in the present embodiment is as follows image 3 shown. The finished ferrite core obtained after sintering is as follows: Figure 5 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com