Power semiconductor device
A technology for power semiconductors and devices, applied in the field of power semiconductor devices, can solve problems such as poor turn-off uniformity of chips, and achieve the effects of improving cathode area utilization, reducing process difficulty, and improving turn-off capability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
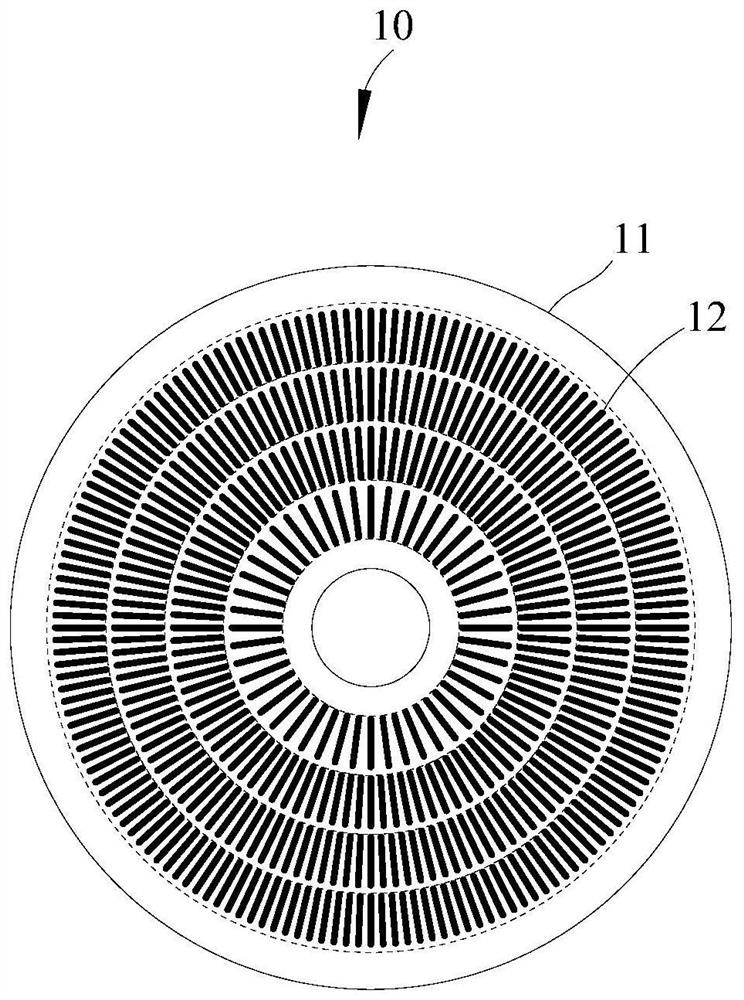
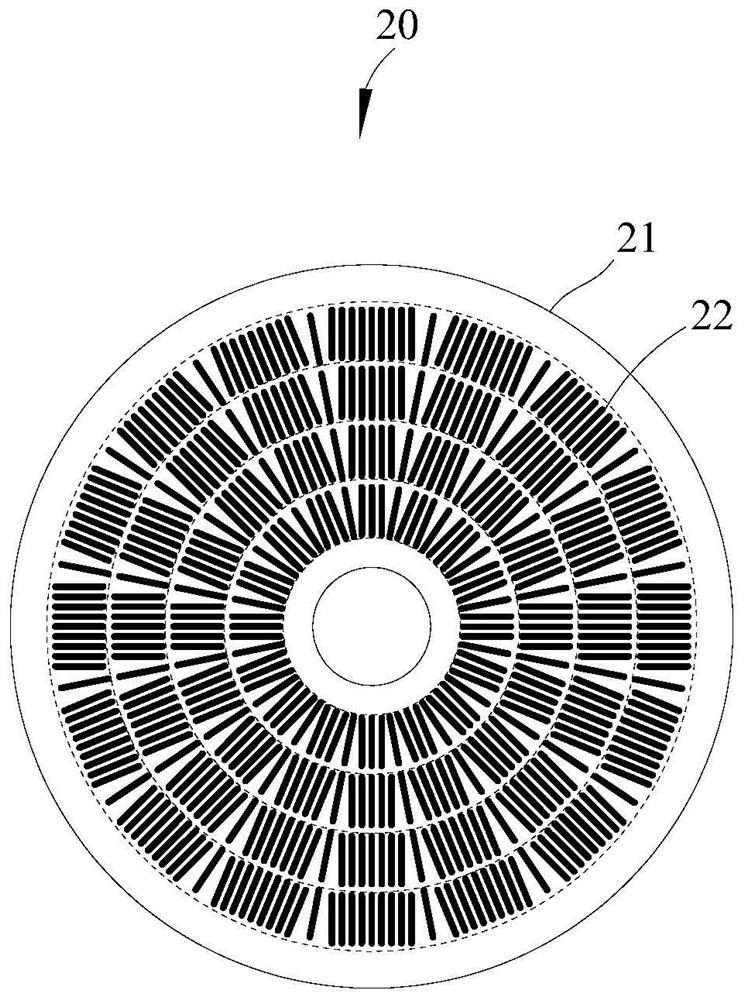
[0062] An embodiment of the present application provides a power semiconductor device 40 , including a wafer 41 and a plurality of first cathode combs 42 and gates 45 disposed on the surface of the wafer 41 .
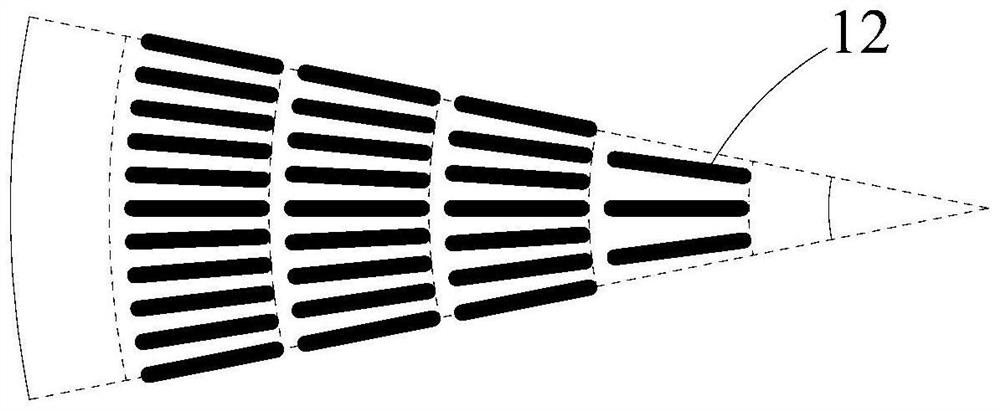
[0063] Among them, such as Figure 4 As shown, the surface of the wafer 41 is divided into a plurality of concentric ring regions 411 and a plurality of concentric sector regions 412 with the same center O, and a plurality of concentric ring regions 411 and a plurality of concentric sector regions 412 overlap to define a plurality of The graphic area 413, that is, the overlapping area of multiple concentric circular ring areas 411 and multiple concentric fan-shaped areas 412 is a basic graphic unit.
[0064] The number of annular areas 411 can be between 1 and 18, and the number of sectoral areas 412 can be between 30 and 144, wherein the number of annular areas 411 is related to the diameter of the wafer 41 and the size of the first cathode comb bar 42 . The radial...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Based on the first embodiment, this embodiment provides a specific application example of a power semiconductor device.
[0107] In this embodiment, the power semiconductor device is a 4-inch GCT chip. The arrangement of the first cathode comb 42 adopts 32 sectors (the central angle of each sector is 11.25°) and is matched with the design scheme of the edge gate 45. The schematic diagram of the design effect is as follows Figure 7a , Figure 7b with Figure 7c shown. The central position of the surface of the wafer is also provided with a central spacer bar 46 . The radial width of the edge gate 45 is designed to be 4.23 mm, and the radial distance between the side of the edge gate 45 away from the circle and the circle-cutting edge line of the wafer is 3.00 mm, which are respectively located in two adjacent ring areas. The radial spacing of the first cathode comb strips 42 is 0.28mm. The various parameters of the layout design of the cathode combs are shown in Ta...
Embodiment 3
[0115] On the basis of the first embodiment, this embodiment provides another specific application example of a power semiconductor device.
[0116] In this embodiment, the power semiconductor device is a 6-inch RC-GCT (reverse conduction gate commutated thyristor) chip. The arrangement of the first cathode comb 42 adopts 64 sectors (the central angle of each sector is 5.625°) and is matched with the design scheme of the edge gate 45. The schematic diagram of the design effect is as follows Figure 8a , Figure 8b with Figure 8c shown. A fast recovery diode FRD with a radius of 40 mm is also arranged at the center of the surface of the wafer. The radial width of the edge gate 45 is designed to be 4.6 mm, and the radial distance between the first cathode comb strips 42 located in two adjacent ring regions is 0.28 mm. The various parameters of the layout design of the cathode combs are shown in Table 2.
[0117] Table 2 Design parameters of cathode sliver arrangement in 6-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com