Moisture-permeable composite material for blocking bacteriophage and preparation method thereof
A composite material and phage technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve problems such as antibacterial properties and moisture permeability that cannot meet the needs of use, and achieve the effects of improving user experience, improving mechanical properties and stability, and uniform thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
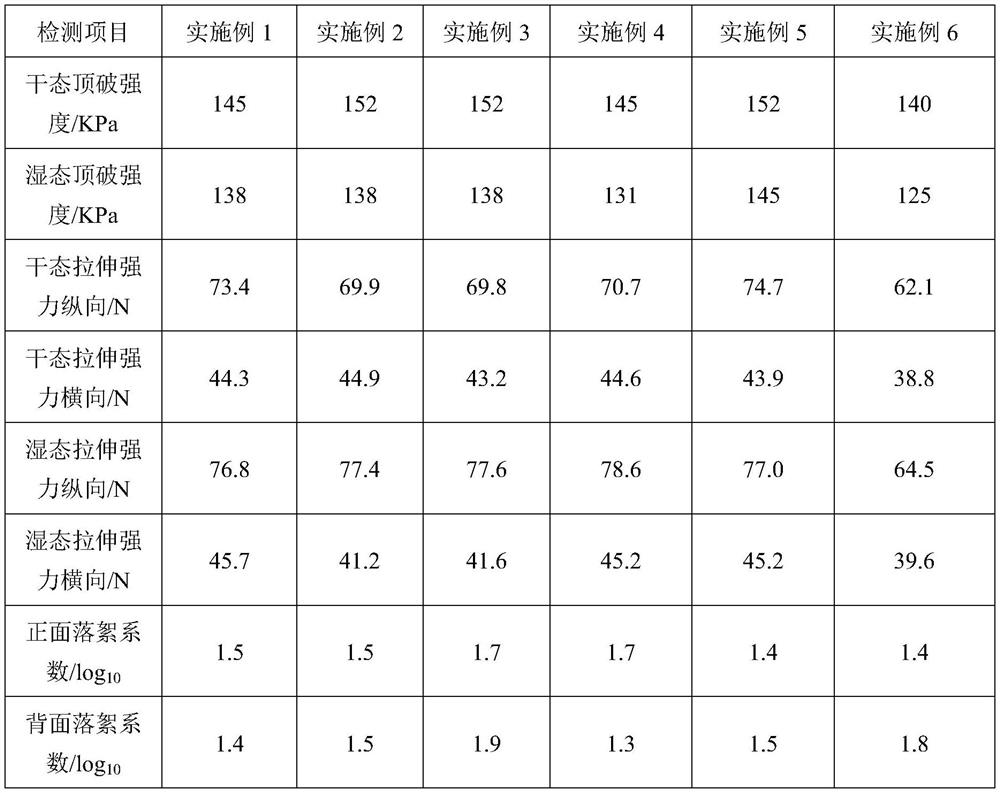
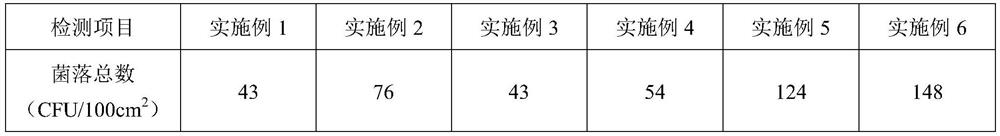
Embodiment 1
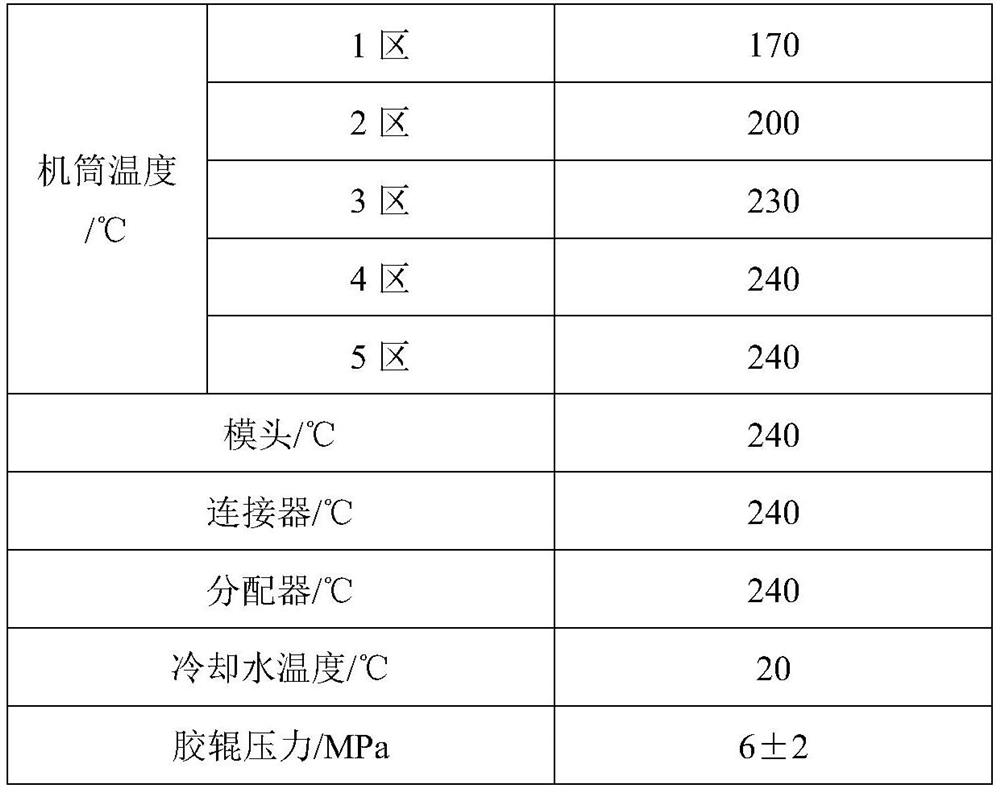
[0023] S1. Preparation of moisture-permeable film: 80 parts of KHTS-140 and 20 parts of erucamide are heated, mixed and pressurized by the extruder, and continuously passed through the die in a flowing state;
[0024] S2, prepare flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric:
[0025] Melt 80 parts of polypropylene, 1 part of nano-zinc oxide, 0.1 part of antioxidant, and 0.2 part of polyethyleneimine-polyethylene glycol copolymer, melt, filter, spin, stretch into filaments, lay a net, coat a film, roll A flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric was prepared.
[0026] S3. Heat the hot melt adhesive through the glue spraying compound machine, and apply the glue sprayed into a mesh shape by a high-pressure nozzle between the flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric, the moisture-permeable film, and the wear-resistant PP cloth, and heat Pressing and bonding, and winding to obtain the composite material.
Embodiment 2
[0028] S1. Preparation of moisture-permeable film: 120 parts of KHTS-140 and 40 parts of erucamide are heated, mixed and pressurized by the extruder, and continuously passed through the die in a flowing state;
[0029] S2, prepare flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric:
[0030] 100 parts of polypropylene, 3 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 0.5 parts of antioxidant, and 0.5 parts of polyethyleneimine-polyethylene glycol copolymer are melted, filtered, spun, stretched into silk, laid, coated, rolled A flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric was prepared.
[0031] S3. Heat the hot melt adhesive through the glue spraying compound machine, and apply the glue sprayed into a mesh shape by a high-pressure nozzle between the flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric, the moisture-permeable film, and the wear-resistant PP cloth, and heat Pressing and bonding, and winding to obtain the composite material.
Embodiment 3
[0033] S1. Preparation of moisture-permeable film: 85 parts of KHTS-140 and 25 parts of erucamide are heated, mixed and pressurized by the extruder, and continuously passed through the die in a flowing state;
[0034] S2, prepare flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric:
[0035] 95 parts of polypropylene, 2.5 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 0.4 parts of antioxidant, and 0.4 parts of polyethyleneimine-polyethylene glycol copolymer are melted, filtered, spun, stretched into silk, laid, coated, rolled A flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric was prepared.
[0036] S3. Heat the hot melt adhesive through the glue spraying compound machine, and apply the glue sprayed into a mesh shape by a high-pressure nozzle between the flexible hydrophilic non-woven fabric, the moisture-permeable film, and the wear-resistant PP cloth, and heat Pressing and bonding, and winding to obtain the composite material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com