Liposome drug in-vivo biological analysis method
A technology of bioanalysis and liposome, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of not effectively reflecting the bioavailability of drugs, and achieve the effect of precise release degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
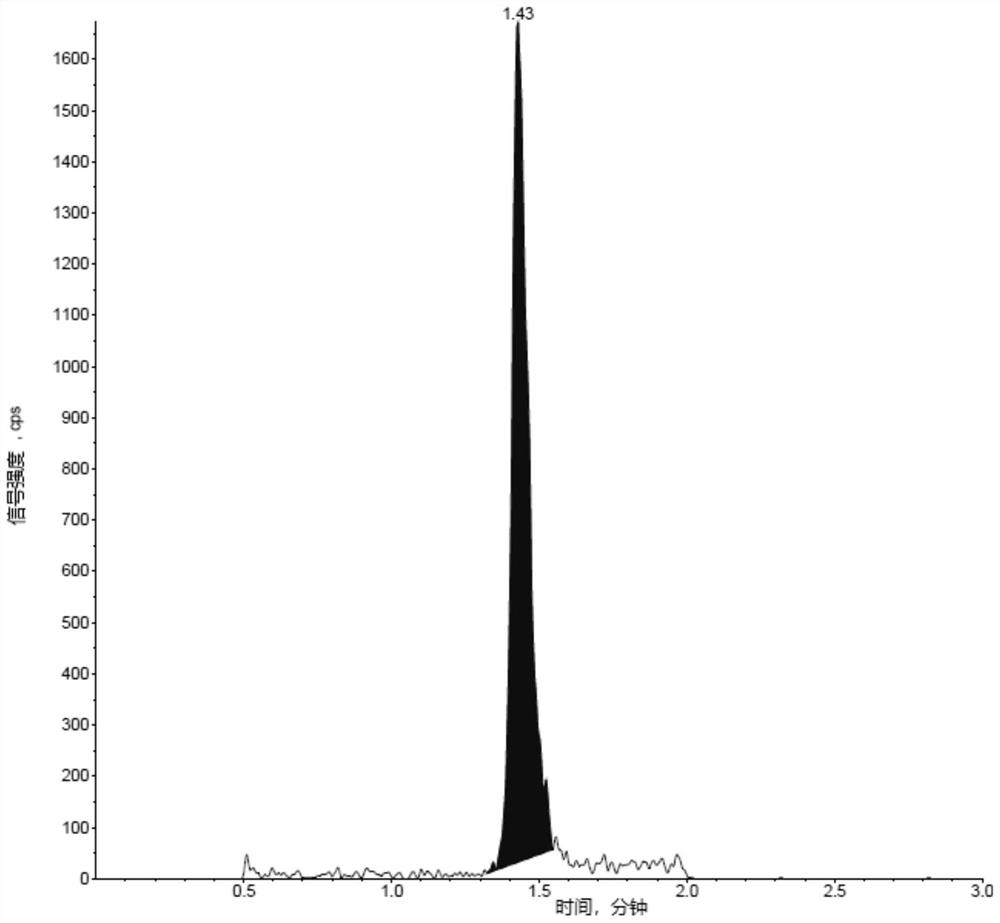
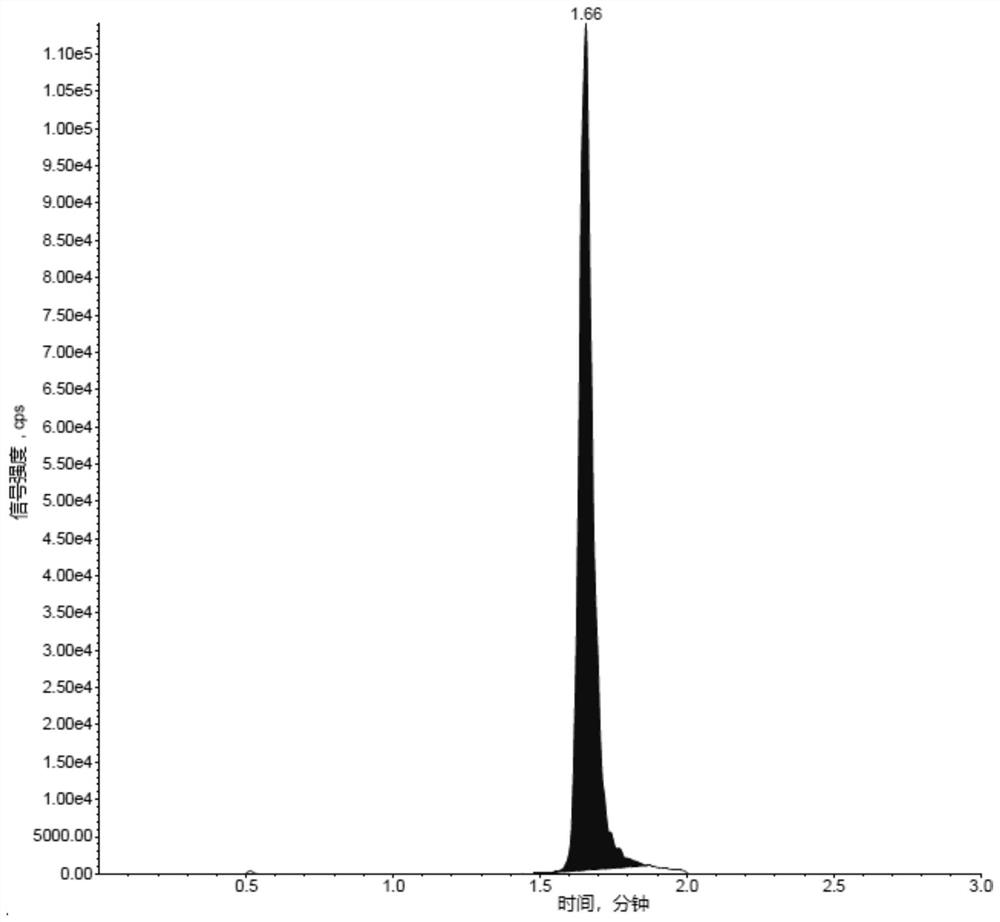
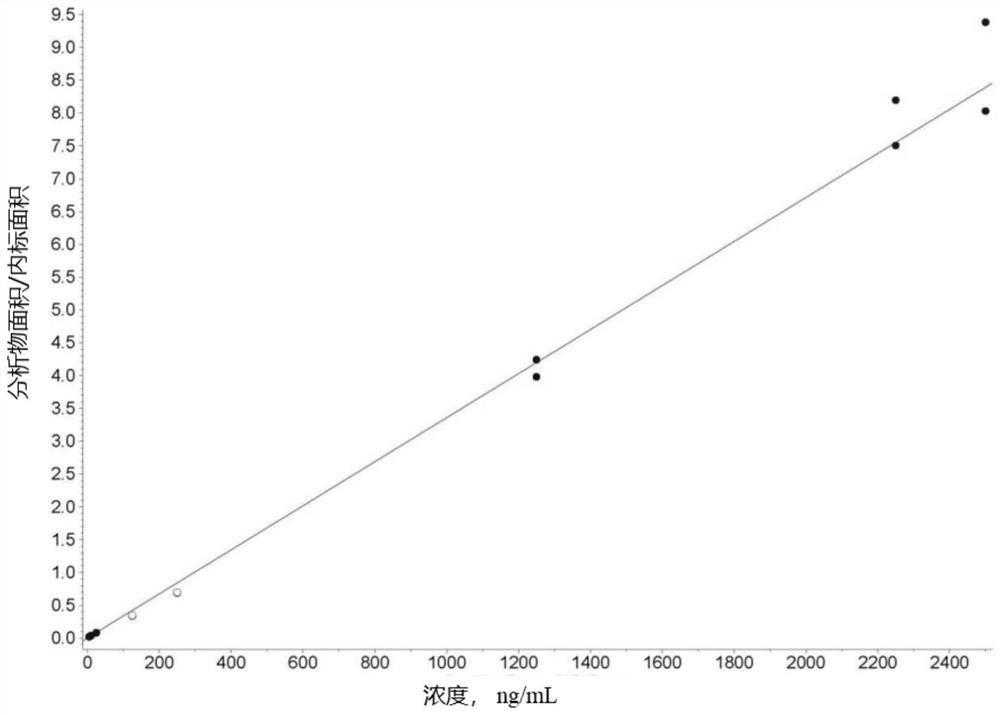
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: the extraction process of total doxorubicin (low concentration quantitative range)
[0037] 1. After all the samples to be tested are completely melted, mix for 10-30 seconds.
[0038] 2. Pipette 50 μL of the sample to be tested into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 50 μL of IS solution with a concentration of 100 ng / mL, mix well, and obtain a sample to be tested containing an internal standard; pipette 50 μL of a blank sample (that is, 50 μL of blank plasma) to 1.5 Add 50 μL of IS solution with a concentration of 100 ng / mL to a mL centrifuge tube, mix well to obtain a blank internal standard control; pipette 50 μL of a blank sample (i.e. 50 μL of blank plasma) into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 50 μL of methanol:water (1 : 1), mix well, obtain blank control.
[0039]3. Add 800 μL of chloroform to the test sample containing internal standard, blank internal standard control, and blank control respectively, vortex for 3 minutes, and centrifuge at 10,000×g, 4°...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: the extraction process of total doxorubicin (high concentration quantitative range)
[0044] 1. After all the samples to be tested are completely melted, mix for 10-30 seconds.
[0045] 2. Pipette 50 μL of the sample to be tested into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 50 μL of IS solution with a concentration of 500 ng / mL, mix well, and obtain a sample to be tested containing an internal standard; pipette 50 μL of a blank sample (that is, 50 μL of blank plasma) to 1.5 Add 50 μL of IS solution with a concentration of 500 ng / mL into a mL centrifuge tube, mix well to obtain a blank internal standard control; pipette 50 μL of a blank sample (i.e. 50 μL of blank plasma) into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, add 50 μL of methanol:water (1 : 1), mix well, obtain blank control.
[0046] 3. Add 800 μL of chloroform to the test sample containing internal standard, blank internal standard control, and blank control respectively, vortex for 3 minutes, and centrifuge at 10,000×g...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: the extraction process of the doxorubicin of liposome encapsulation (low concentration quantitative range)
[0051] 1. After all the samples to be tested are completely melted, mix for 10-30 seconds.
[0052] 2. Add 100 μL of water to 50 μL of the sample to be tested and mix well to obtain a mixed sample.
[0053] 3. Sequentially add 1 mL of methanol and water to activate the SPE solid phase extraction plate (Strata C18-E).
[0054] 4. Transfer the above-mentioned mixed sample and 150 μL of water to the activated solid phase extraction plate in sequence, and collect the effluent.
[0055] 5. Add 50 μL of IS solution with a concentration of 100 ng / mL to the effluent, mix well, and obtain the test sample containing internal standard. Replace 50 μL of the blank sample (i.e. 50 μL of blank plasma) with the 50 μL of the sample to be tested in step 2 of this example and proceed to step 5 to obtain a blank internal standard control; replace the step of this exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com