Method for improving strength of (Ce + Yb) composite modified hypoeutectic Al-Si-Mg-Cu-Cr alloy
A technology of al-si-mg-cu-cr and compound modification, which is applied in the field of improving the strength of compound modified hypoeutectic Al-Si-Mg-Cu-Cr alloy, can solve the problem that synergy cannot be fully exerted, strength, Problems such as limited improvement of plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
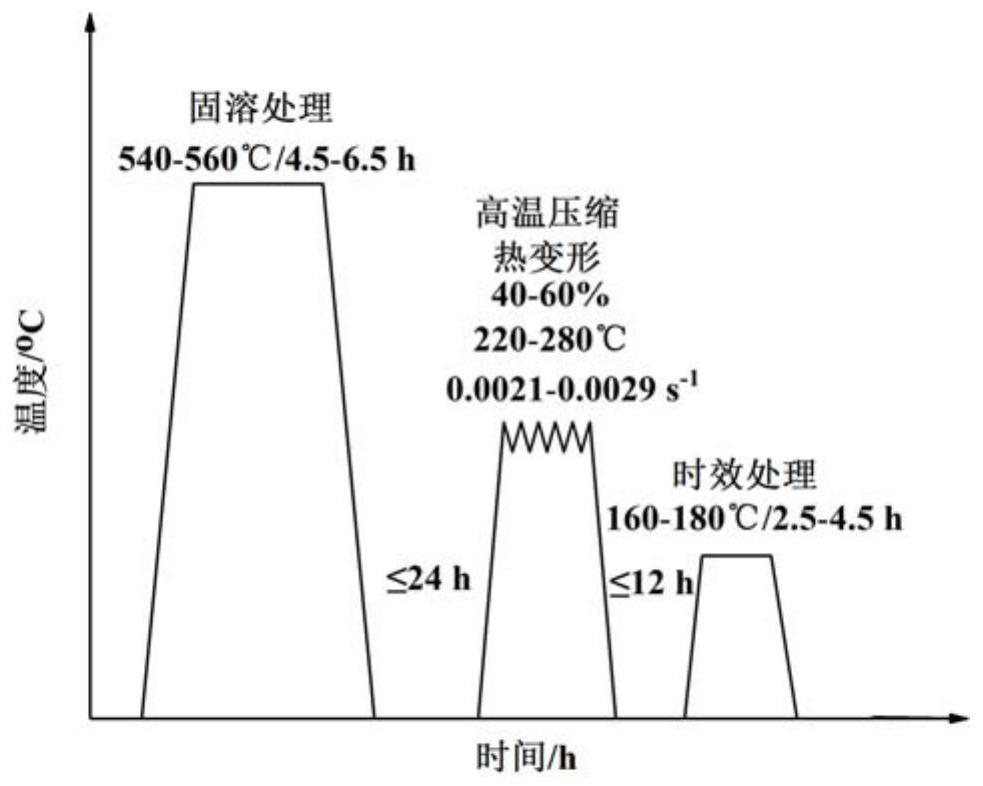
[0035] step one:.
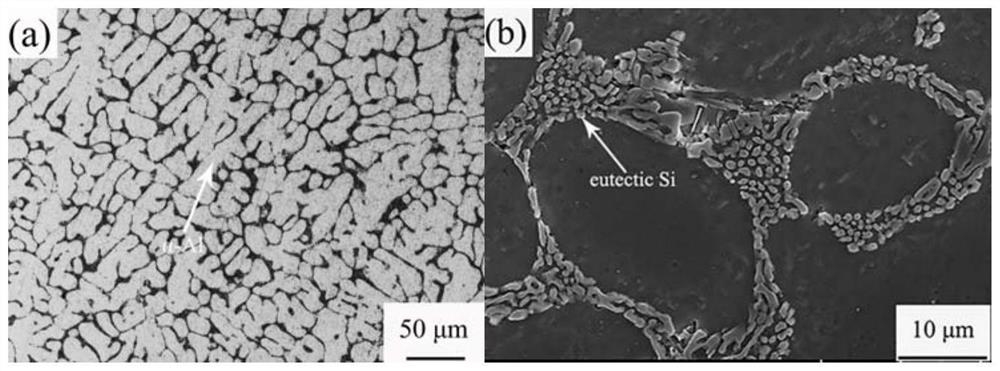
[0036] Carry out solid solution treatment with Al-6Si-0.6Mg-0.6Cu-0.2Cr-0.2Ce-0.2Yb (wt.%) as-cast alloy cylindrical sample in electric resistance furnace, take out after solid solution time (stay in air Time ≤ 10s) Quenching with warm water at 60°C;
[0037] Step two:
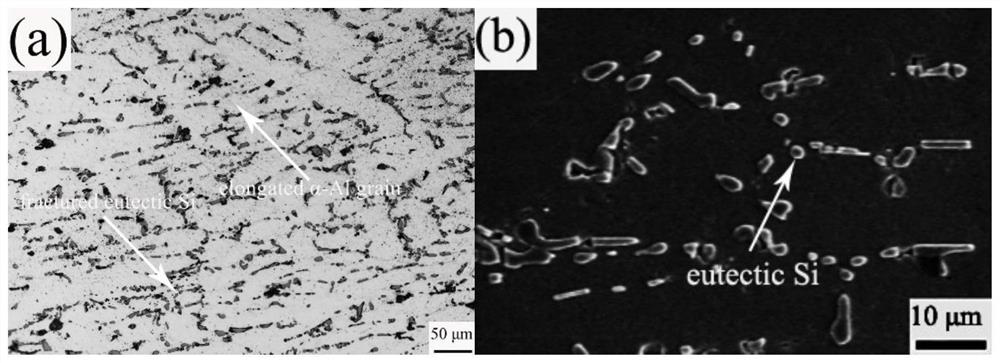
[0038] The interval time does not exceed 24 hours, and the solid solution alloy sample is subjected to high-temperature compression and thermal deformation on a hydraulic press that can control the strain rate until the deformation reaches the set deformation amount, and immediately cools down with room temperature water to retain the thermally deformed structure;
[0039] Step three:
[0040] The interval time does not exceed 12h, and the high-temperature compression heat-deformation alloy sample is subjected to aging treatment in a resistance furnace, and after the aging time is up, it is taken out and air-cooled.
[0041] The alloy sample after the "solid solution-high temperature com...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Step 1, Step 2 and Step 3 in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that the process parameters of "solid solution-high temperature compression thermal deformation-aging" treatment are different, as shown in Table 1. The alloy sample after the "solid solution-high temperature compression thermal deformation-aging" treatment was tested for tensile properties at room temperature, and the results were: the ultimate tensile strength of the alloy in this example was 353.1 MPa, and the uniform elongation was 14.3%. In this embodiment, the strength of the alloy is increased by 9.2%, and the elongation is increased by 134.4%.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Step 1, Step 2 and Step 3 in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that the process parameters of "solid solution-high temperature compression thermal deformation-aging" treatment are different, as shown in Table 1. The alloy sample after the "solid solution-high temperature compression thermal deformation-aging" treatment was tested for tensile properties at room temperature, and the results were: the ultimate tensile strength of the alloy in this example was 346.3 MPa, and the uniform elongation was 13.4%. In this embodiment, the strength of the alloy is increased by 7.1%, and the elongation is increased by 119.7%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ultimate tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| ultimate tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com