Method for detecting bubble effect in oil paper insulation based on initial temperature envelope
A technology of oil-paper insulation and initial temperature, applied in the field of electrical equipment insulation, can solve the problems of increasing the risk of air bubbles and reducing the electrical strength of the transformer insulation system, and achieves the effects of fast calculation speed, rapid calculation and simple calculation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
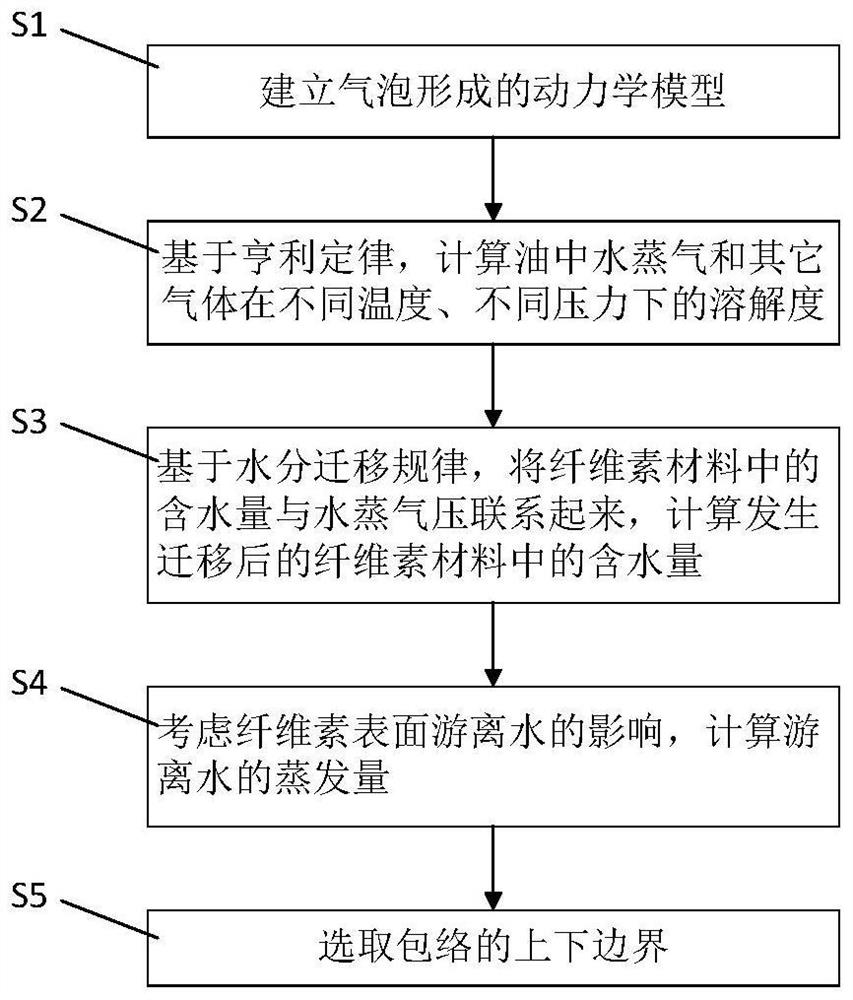
[0065] The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for detecting bubble effect in oil-paper insulation based on the initial temperature envelope, based on the dynamic model of bubble evolution, taking into account the effects of gas solubility in oil, water migration law and free water on the envelope. It can be widely used in oil-paper insulation systems with the same dynamic description. The calculated envelope can cover the onset temperature of the bubble effect obtained under different test conditions, and can adapt to water in the oil, gas saturation, and free cellulose on the surface of the oil. Extreme conditions such as water are of great significance to the study of the temperature limit of the transformer, which provides an important method basis for reducing the risk of bubble formation during the operation of the transformer.
[0066] like figure 1 As shown, the invention provides a method for detecting the bubble effect in the oil-paper insulation ...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Different from Embodiment 1, Process A and Process C and Process D are included.
[0114] Process C, based on the law of water migration, connect the water content in the cellulose material with the water vapor pressure, and calculate the water content in the cellulose material after migration;
[0115] Process D, consider the effect of free water on the surface of cellulose, and calculate the evaporation of free water.
[0116] Moisture content Z of paperboard at time t in step 8 described in Example 1 0 for Z water (t), which is calculated as:
[0117] Z water (t)=Z 0 -Z(t) (17)
[0118] Z(t)=(P vap (t) / 133·e -21.92+6850 / T(t) ) 0.75 (18)
[0119] At time t, the actual moisture content Z(t) of the board after migration cannot exceed the initial moisture content Z of the board 0 , the actual moisture content of the cardboard after migration is:
[0120] Z(t)=min(Z(t), Z 0 ) (19)
[0121] In the step 8, the amount of water vapor in the bubble at time t is n...
Embodiment 3
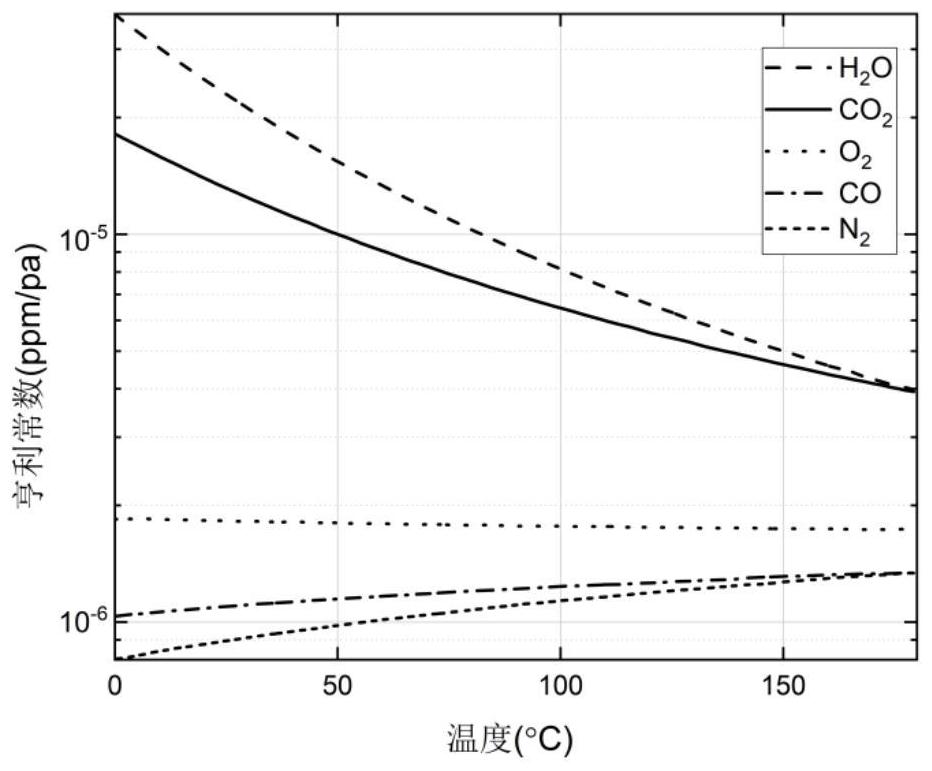
[0151] like figure 2 As shown in the figure, the graph is a graph of the Henry constant of different gases in mineral oil measured by W.J.McNutt and W.A.Fessler through experiments, which is generally recognized in the profession. The amount of water vapour species n after dissolution can be calculated from this graph vap and the quantity n of gaseous substances other than water vapour gas .
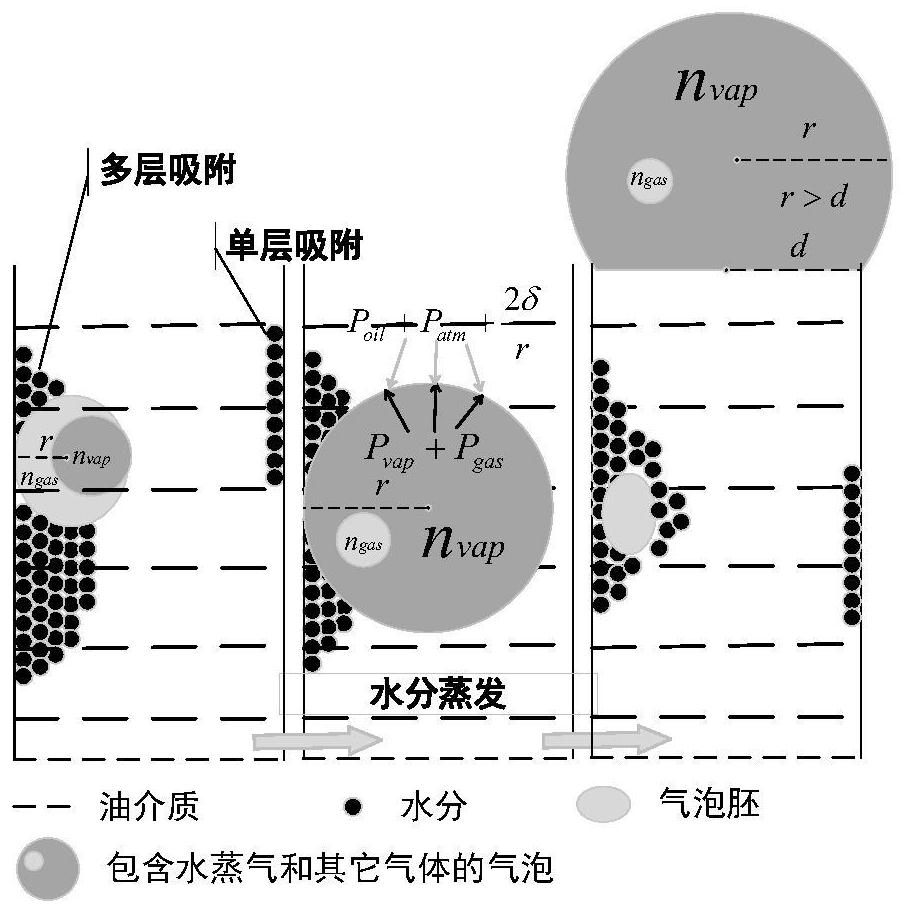
[0152] like image 3 As shown, for oil-immersed transformers, the cellulosic materials in it are: a "thick structure" for support, a "thin hot structure" wrapped around the windings, and a "thin cold structure" at normal oil temperature . When the local oil temperature rises, moisture is transferred from the "thin thermal structure" cellulose insulation to the "thick structure" monolithic insulation. As the overall temperature in the transformer increases, the surface moisture of the insulating material will begin to migrate into the oil. During the temperature rise, the migration...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com