Method for increasing permeability of cytoplasmic membrane and structure suitable for same
A cytoplasmic membrane and structure technology, applied in the field of increasing the permeability of cytoplasmic membrane, can solve problems such as limiting molecular efficiency, and achieve the effect of avoiding fragmentation or release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
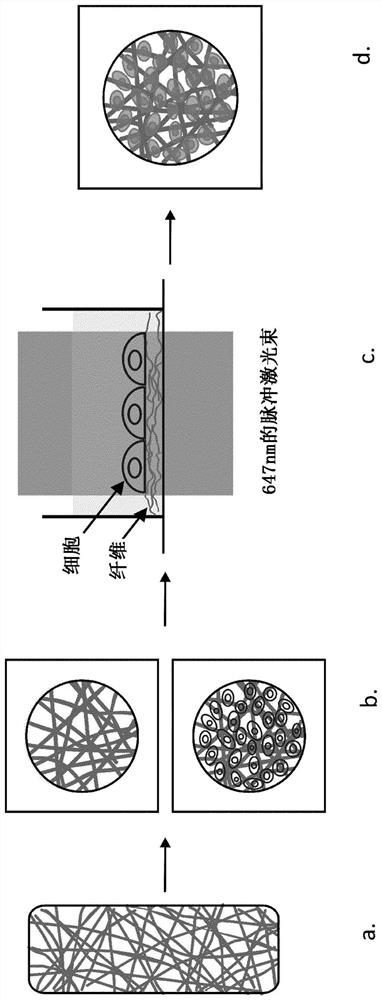
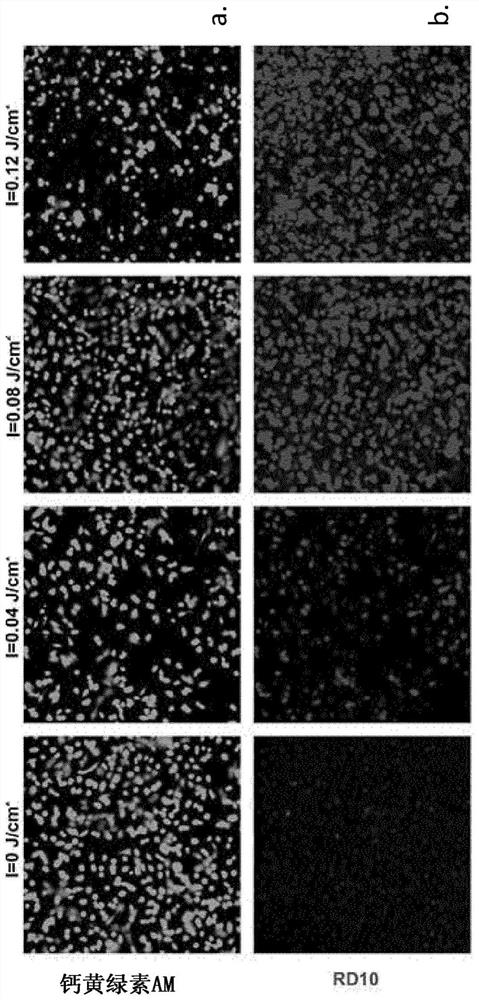
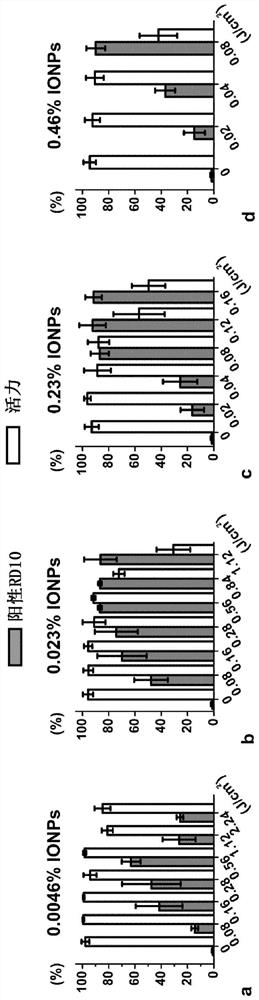
[0141] Example 1 Porous structure comprising nanofiber web and particles embedded in nanofibers
[0142] A second embodiment of the structure of the present invention includes a porous structure comprising nanofibers and particles capable of absorbing electromagnetic radiation embedded in the nanofibers. The examples described below include polycaprolactone as a structural material and iron oxide nanopowders as particles capable of absorbing electromagnetic radiation. Obviously, other materials and other particles are also contemplated.
[0143] 1.a Synthesis and characterization of photothermal electrospun nanofibers
[0144] The following materials were used to synthesize nanofiber webs:
[0145] Polycaprolactone (PCL, Mw≈70,000g / mol);
[0146] ·N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF);
[0147] Tetrahydrofuran (THF);
[0148] Iron oxides (Fe 3 O 4 ) Nanopowder (IONP) (#MKBW3262, Sigma-Aldrich, Belgium);
[0149] Poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH, Mw=17,560 g / mol, #MKBZ2824V, S...
Embodiment 2
[0203] Example 2 Non-porous structure comprising polymeric material and nanoparticles
[0204] Figure 21a A schematic diagram of an embodiment of the structure 1 of the present invention is shown. Figure 21b shown Figure 21a Structure 1 is shown in cross section along line AA'. The structure 1 comprises a polymer sheet comprising a polymer material 2 and particles 3 capable of absorbing electromagnetic radiation. The particles 3 include, for example, carbon particles or iron oxide particles or a combination of carbon particles and iron oxide particles. The particles 3 are embedded in the material 2 and have an average equivalent spherical diameter d of, for example, 1000 nm.
[0205] The structure has a thickness t of 0.1 μm to 100 μm, for example a thickness of 1 μm, 2 μm or 5 μm.
[0206] The ratio of the free area surface S of the structure to the volume V of the structure, ie the ratio S / V, is 1 / t.
[0207] The polymer sheet preferably comprises a polymer comprisi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com