Application of CO2 in increasing activity of endogenous and exogenous digestive enzymes in intestinal tracts of termites
A technology for digestive enzymes and termites, applied in the field of insects, can solve problems such as affecting the degradation of lignocellulose and increasing the activity of endogenous and exogenous digestive enzymes of termites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
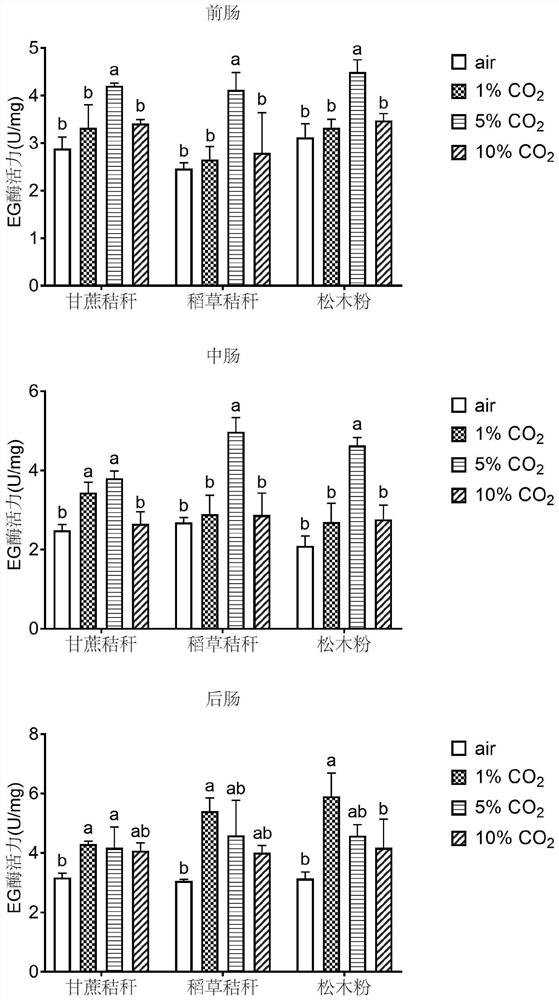
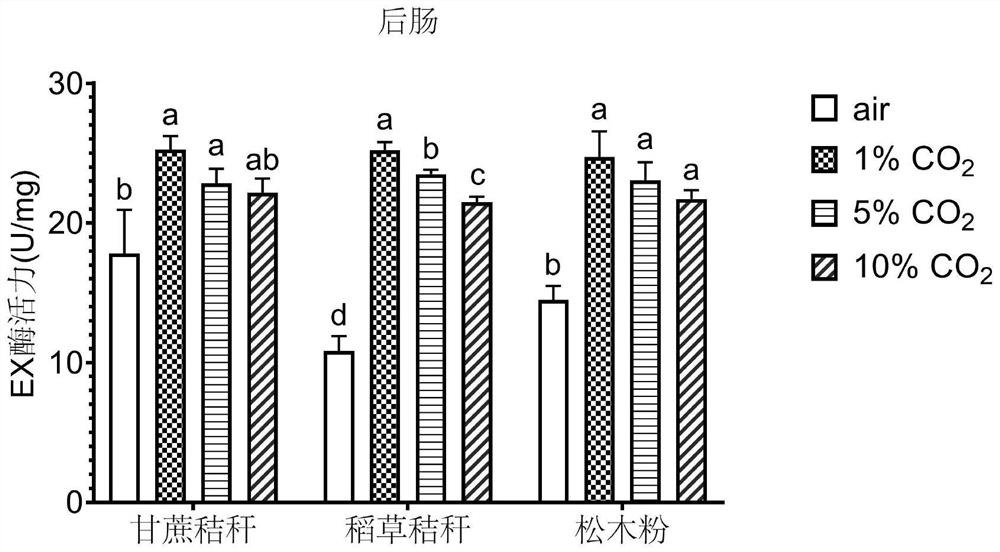
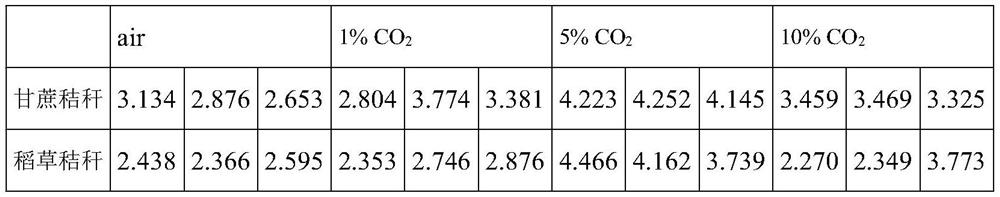
[0018] 1. Experimental method
[0019] 1. Food handling
[0020] Sugarcane straw, straw straw and pine sawdust were ground into powder, sterilized in an autoclave at 121°C for 30 minutes, dried, and pressed into a solid powder for feeding termites.
[0021] 2. Feeding treatment of test termites
[0022] The test workers were fed after starvation for 24 hours, and 50 sterile fine sand, corresponding food powder and healthy workers were placed in a petri dish with a diameter of 35 mm. The petri dishes were placed in a carbon dioxide artificial climate incubator with a temperature of 30 ± 1 °C and a relative humidity of 70 ± 5%, and the above three kinds of food were fed to L. taiwanae for 10 days. The air treatment group did not set CO. 2 Concentration (CO 2 concentration is about 0.04%), CO 2 The concentrations of the treatment groups were set at 1%, 5% and 10%, respectively.
[0023] 3. Determination of enzyme activity
[0024] Select 20 worker ants, in SAB solution (ace...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com