Ceramic nano injection molding polyamide and preparation method thereof
A technology for injection molding polyamide and polyamide, which is applied in the field of composite laser forming materials, can solve problems such as the difficulty of taking into account the bonding force and mechanical properties, and achieves the effect of simple and easy preparation method and improved mechanical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] The preparation of the plastic-ceramic testing monolith used in the present invention:
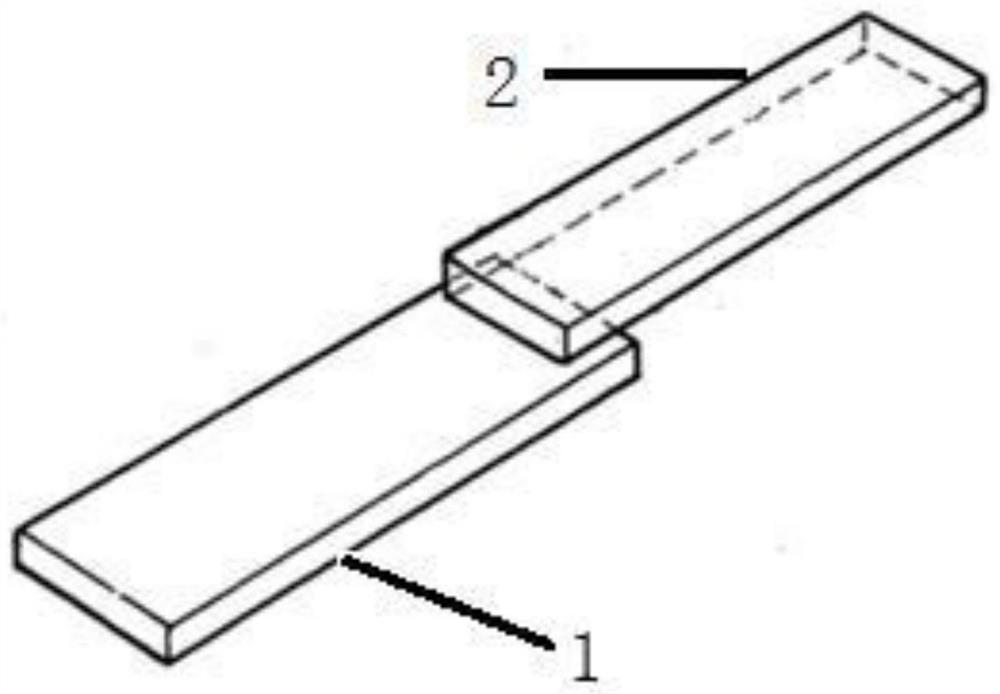
[0030] In the present invention, the overall plastic ceramic test piece is prepared with reference to the related patent method of Japanese Dacheng nano injection molding. The details are as follows: figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the ceramic plastic test piece. The size of the ceramic piece is 18mm×45mm×1.6mm, the size of the plastic part is 10mm×45mm×3mm, and the combined area of plastic and ceramic is 0.5cm 2 . In all experiments, the injection molding kept the same injection molding conditions, the barrel temperature was 300-320 °C, and the mold temperature was 140 °C.
[0031] Plastic ceramic bonding performance test:
[0032] The test standard for the adhesion between ceramics and plastics used in the present invention refers to the standard in Japan's Taisei Chemical Patent, and the bonding area between plastics and ceramics is 0.5cm 2 , ...
Embodiment 1
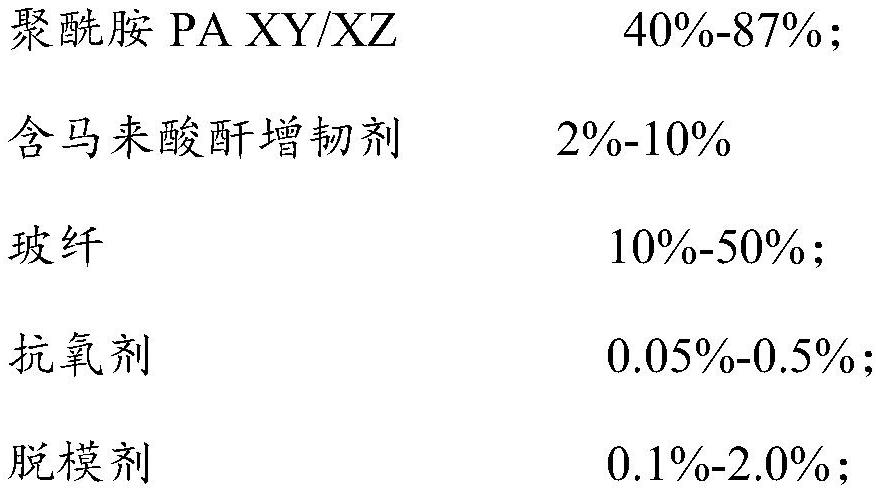
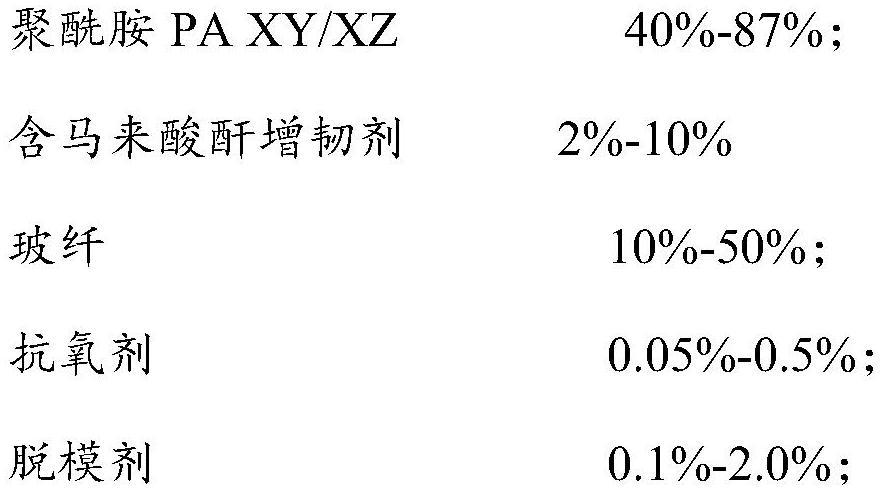
[0035] This example discusses the effects of different proportions of PA106 / 10T, PA106, and common PA66 materials on the performance of polyamide composites, and provides 5 groups of test examples (Test Example 1 to Test Example 5) and 2 groups of comparative examples (Comparative Example 1 / 2), according to the above preparation method to prepare a polyamide composite, the proportions of its components and the corresponding properties of the obtained polyamide composite are shown in Table 1.
[0036] Table 1 Component ratio and performance data table of each polyamide compound in Example 1
[0037]
[0038] From the data in Table 1, it can be seen that compared with PA66, PA106 and PA106 / 10T with different composition ratios have higher binding capacity. In the ceramic NMT process, it is generally considered that a material with a binding force of more than 30 MPa is usable, and a binding force of more than 35 MPa indicates that the material has a wide range of applicabilit...
Embodiment 2
[0040]This example discusses the effect of toughening agents on the properties of polyamide composites, and provides 1 group of comparative examples (comparative example 3) and 10 groups of test examples (2, 6-14), and polyamides are prepared according to the above preparation method. The composite, the proportion of each component and the corresponding properties of the obtained polyamide composite are shown in Table 2.
[0041] Table 2 Component ratio and performance data table of each polyamide compound in Example 2
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] It can be seen from Table 2 that, first, both toughening agents can significantly improve the ceramic bonding force of the material. Secondly, under different glass fiber content, the ratio of the two toughening agents has a significant effect on the ceramic bonding force of the material. When maleic anhydride is not contained in copolymerized polyethylene methyl acrylate, although the binding force of the material is improved, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com