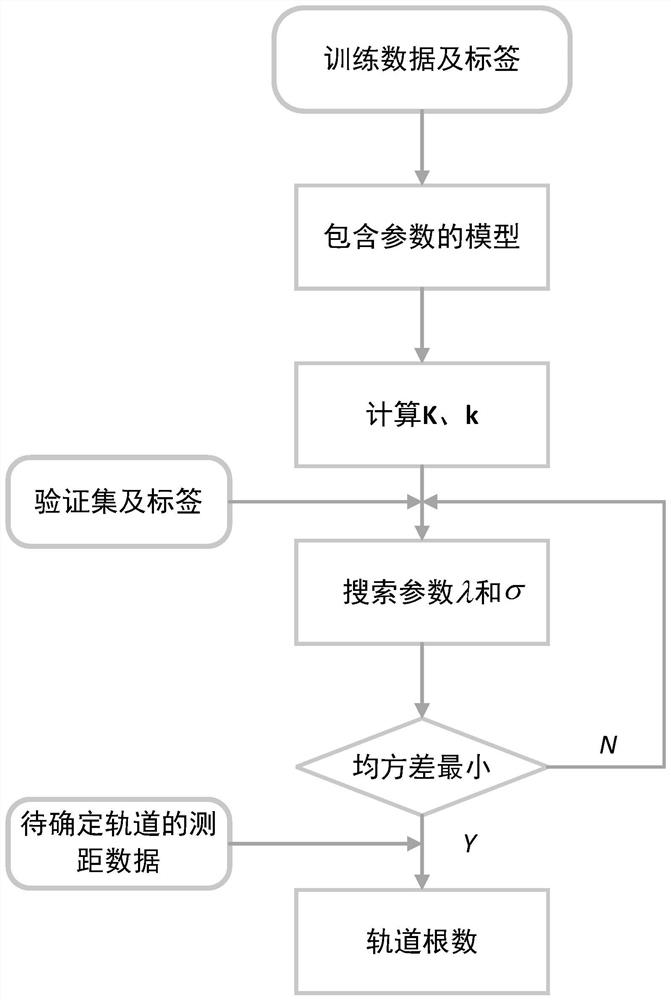
Spacecraft orbit determination method, system, device and medium
A technology for spacecraft and target spacecraft, applied in the aerospace field, can solve problems such as inability to guarantee convergence, and achieve the effect of improving robustness and robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047]This embodiment discloses a method for quickly determining a spacecraft orbit based on nuclear techniques, which can provide a direct mapping relationship from ranging data to orbital elements without relying on prior orbital distribution and dynamic models. To verify the method, simulation verification is carried out in this embodiment. Orbit determination of geostationary satellites is carried out using ranging-only data from three ground measurement and control stations. The coordinates of the three stations are (46.8, 130.32, 0.101), (39.505, 75.929, 1.255), (18.313, 109.311, 0.018) corresponding to latitude (deg), longitude (deg), elevation (km), set GEO The prior distribution of satellite orbit parameters is:
[0048] a~U(42160.7,42170.7)km
[0049] e~U(0.0001,0.001)
[0050] i~U(0,0.05)deg
[0051] Ω~U(220,230)deg
[0052] ω~U(0,10)deg
[0053] M~U(45,50)deg
[0054] It should be stated here that the prior distribution of orbital parameters given here is on...
Embodiment 2
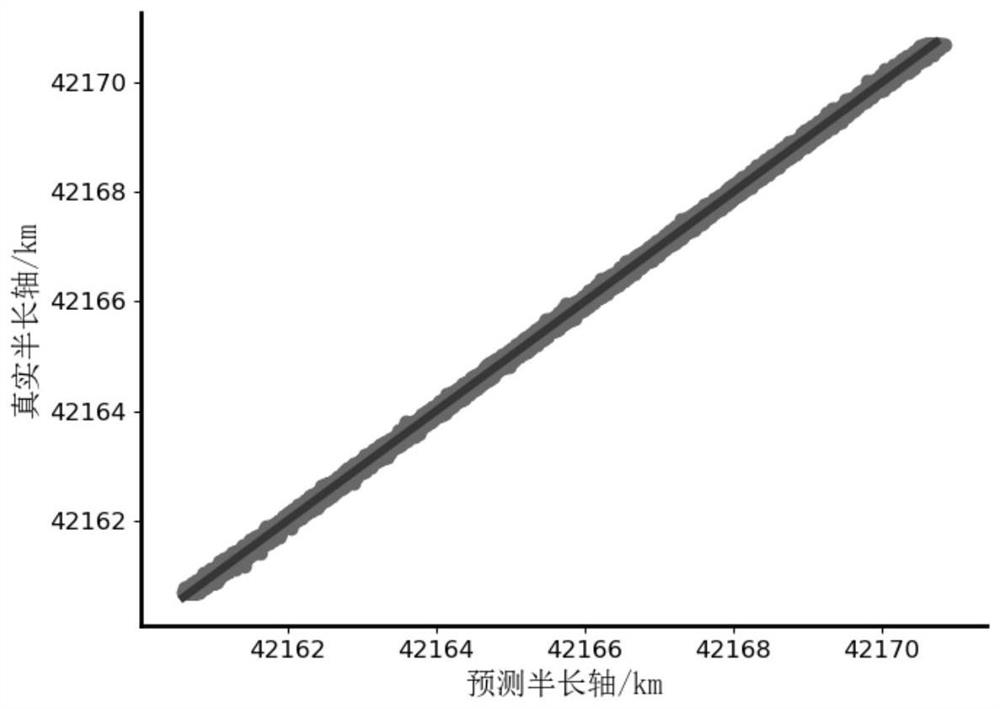
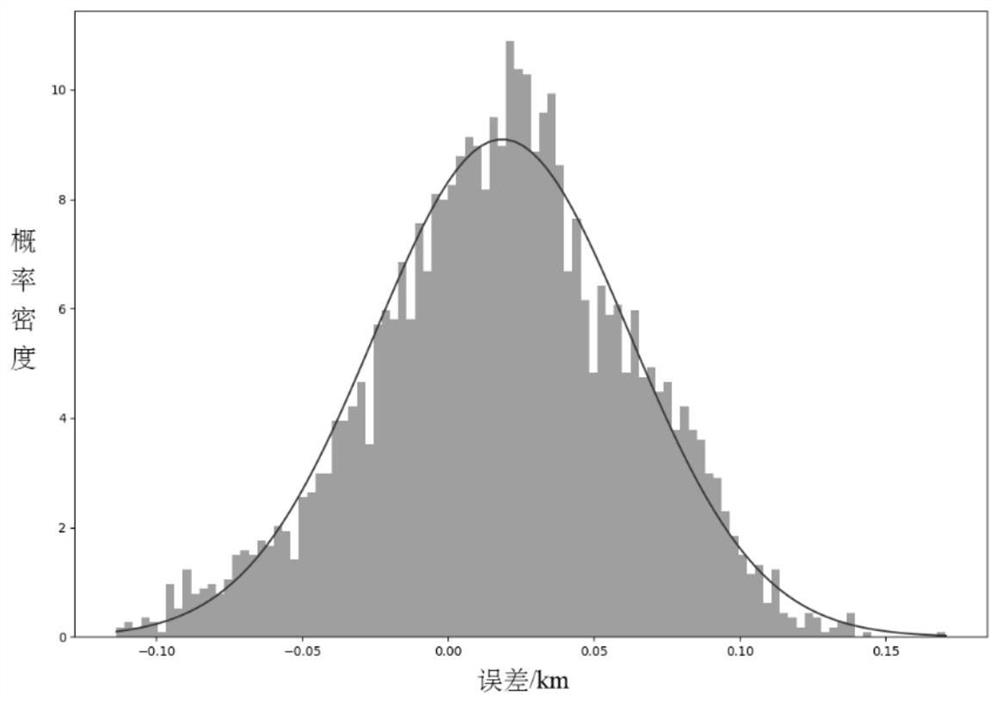
[0082] In order to verify the prediction results of the algorithm for sparse observation data, under the same conditions as in Example 1, modify the station to observe an observation point on each track for 12 hours, so that for the case of extrapolating the simulated track for one day, each track The orbit is equivalent to only two sampling points, so the format of the three-station ranging training data becomes (1200, 2, 3), which cannot be solved in the traditional orbit determination method. The probability distribution of prediction error of semi-major axis under the condition of 5m system noise and 10m random noise is as follows: figure 2 . Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that when using sparse data for orbit determination, the prediction error of the semi-major axis is about 20m, which is a problem that cannot be solved by traditional orbit determination methods. At the same time, in image 3 , the predicted error peak is on the right side of 0, that is, there is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com