Polarized light rays separating device and combining device
A beam splitter and combiner technology, used in polarization elements, coupling of optical waveguides, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increased insertion loss, compensation of optical path length difference, optical path length difference, etc., and achieve the effect of overcoming the manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
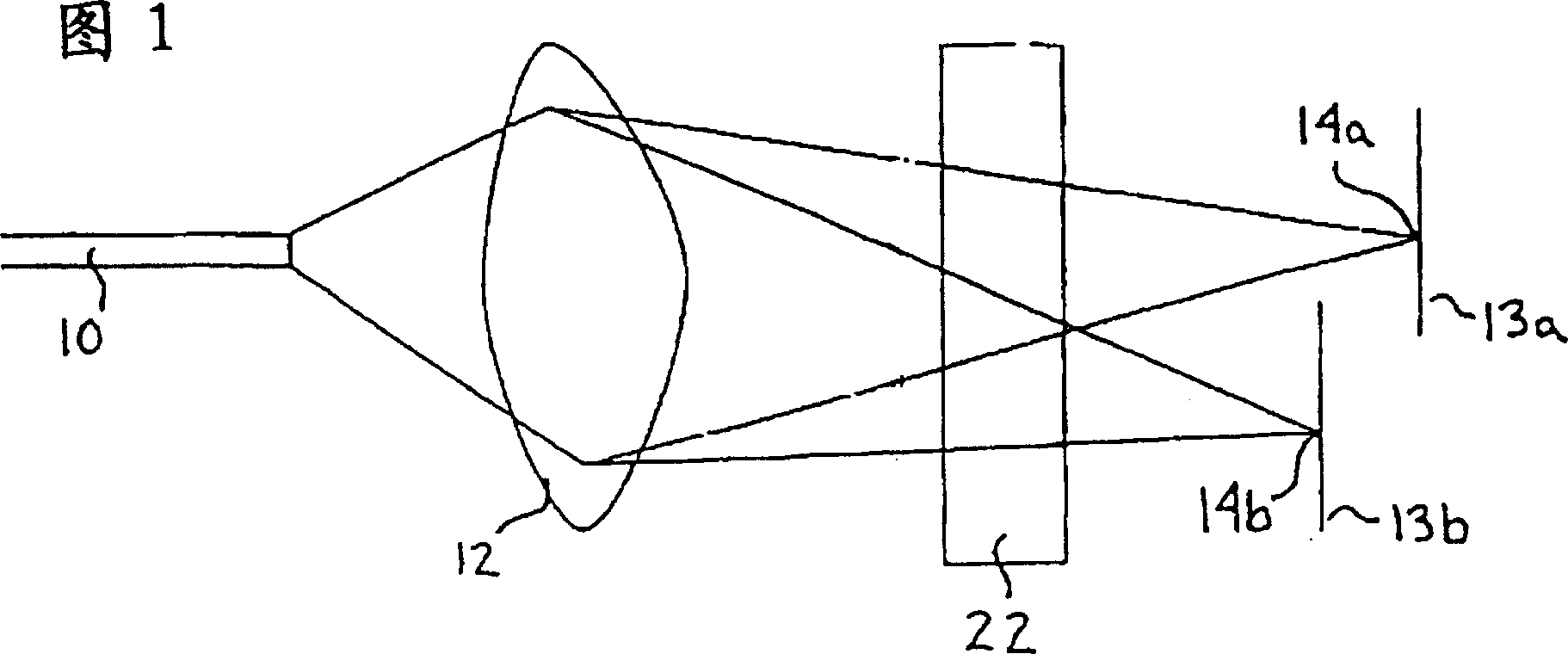
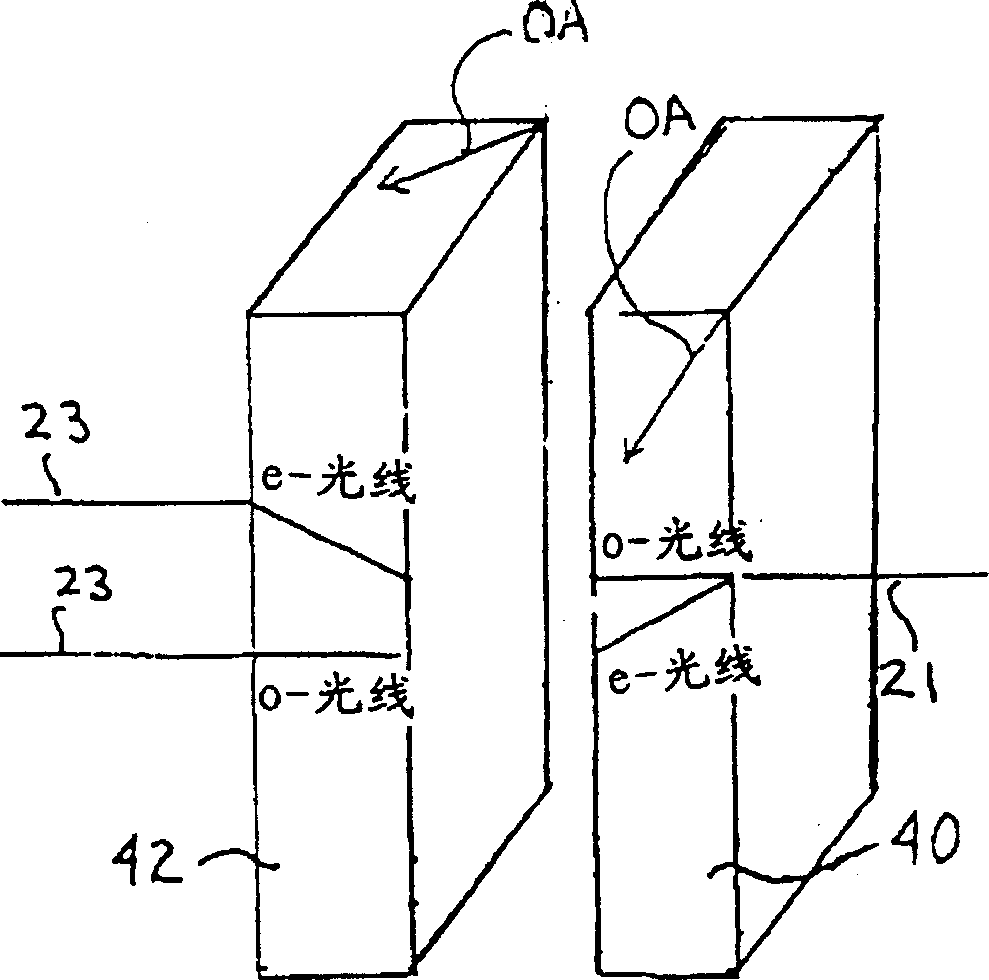
[0036]Returning now to FIG. 1, it is shown that an uncollimated light beam emerges from an optical fiber 10 through a lens 12 and passes through a small birefringent crystal 22, and two focal points 14a and 14b are shown at different focal planes 13a and 13b . To couple the two orthogonal, spatially separated sub-beams into the fiber, a focusing lens is required between the birefringent crystal 22 and the two fibers. Since the sub-beam corresponding to the o-ray of one of the sub-beams follows a longer optical path length than the other sub-beam corresponding to the e-ray, the focal planes of the two sub-beams are different. This difference in focal plane should result in poor coupling if the two fibers are separated by the same distance from the lens.
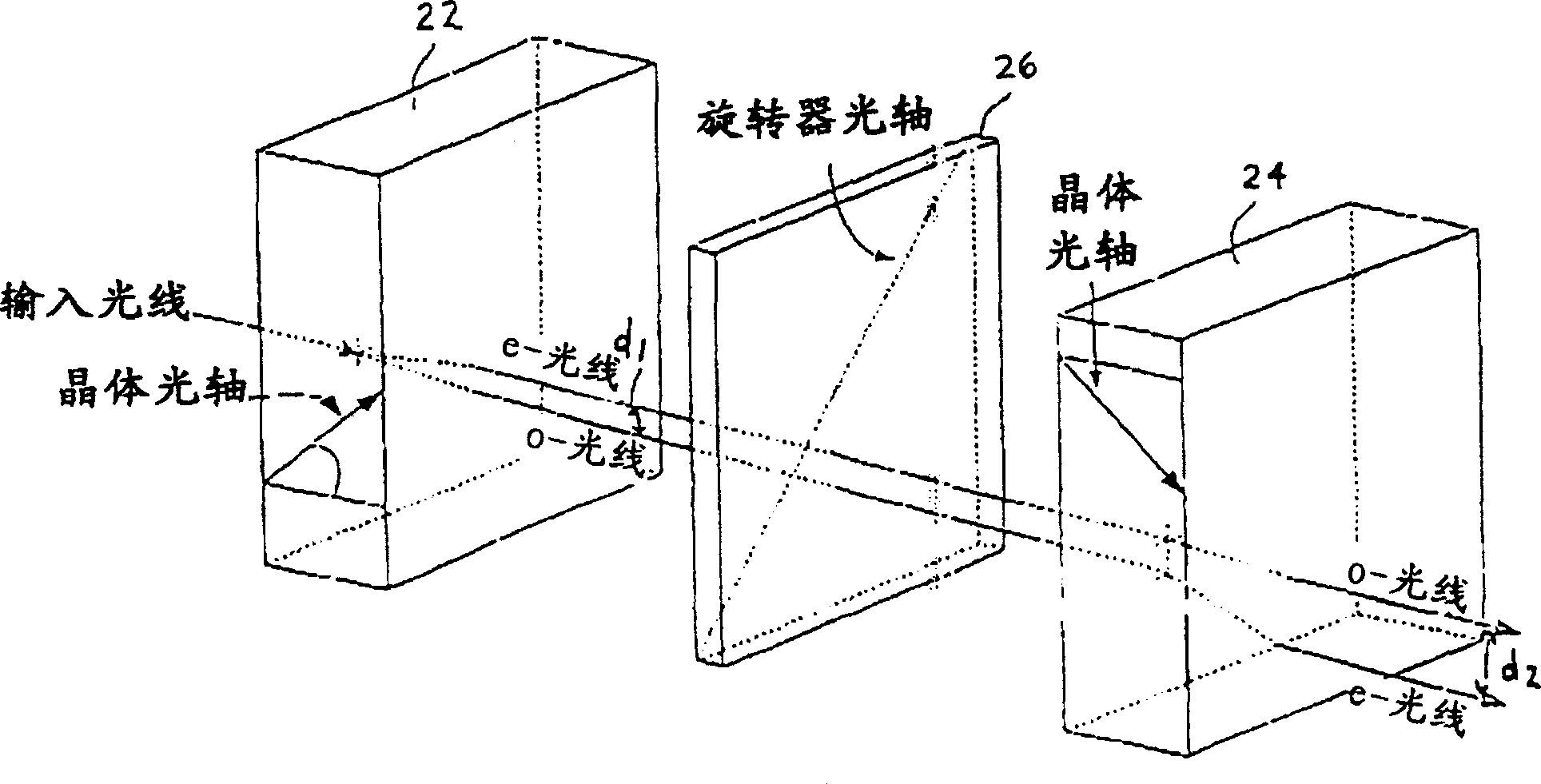
[0037] see now figure 2 , according to an embodiment of the invention, a first uniaxial beam splitter / combiner in the form of a birefringent rutile crystal 22 is shown optically coupled to a second rutile crystal 24 of equal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com