Fractionation and processing of oilseed meal
A seed, rapeseed technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Isolation of unroasted Canadian canola flakes
[0044] Oil-extracted canola flakes with hexane were obtained from industrial crushing equipment. This material has not been desolvated or roasted. The flakes were stored in burlap bags and kept in the open air for a minimum of 7 days to allow the hexane to evaporate. The desolvated flakes were crushed to break up larger clumps in the flakes.
[0045] Table 1 : Protein and dry matter content during extraction-dehydration of canola flakes
Embodiment 2
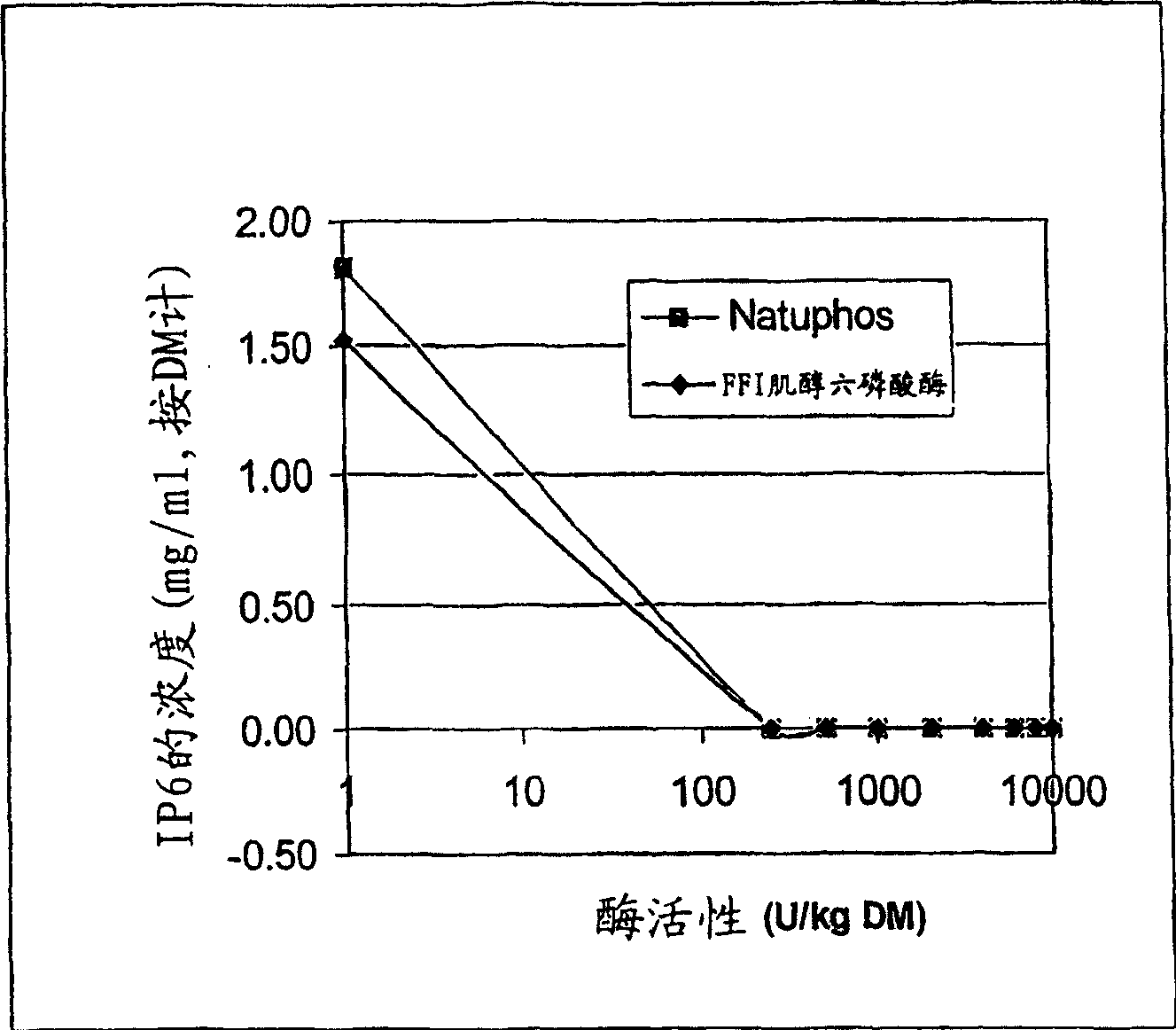
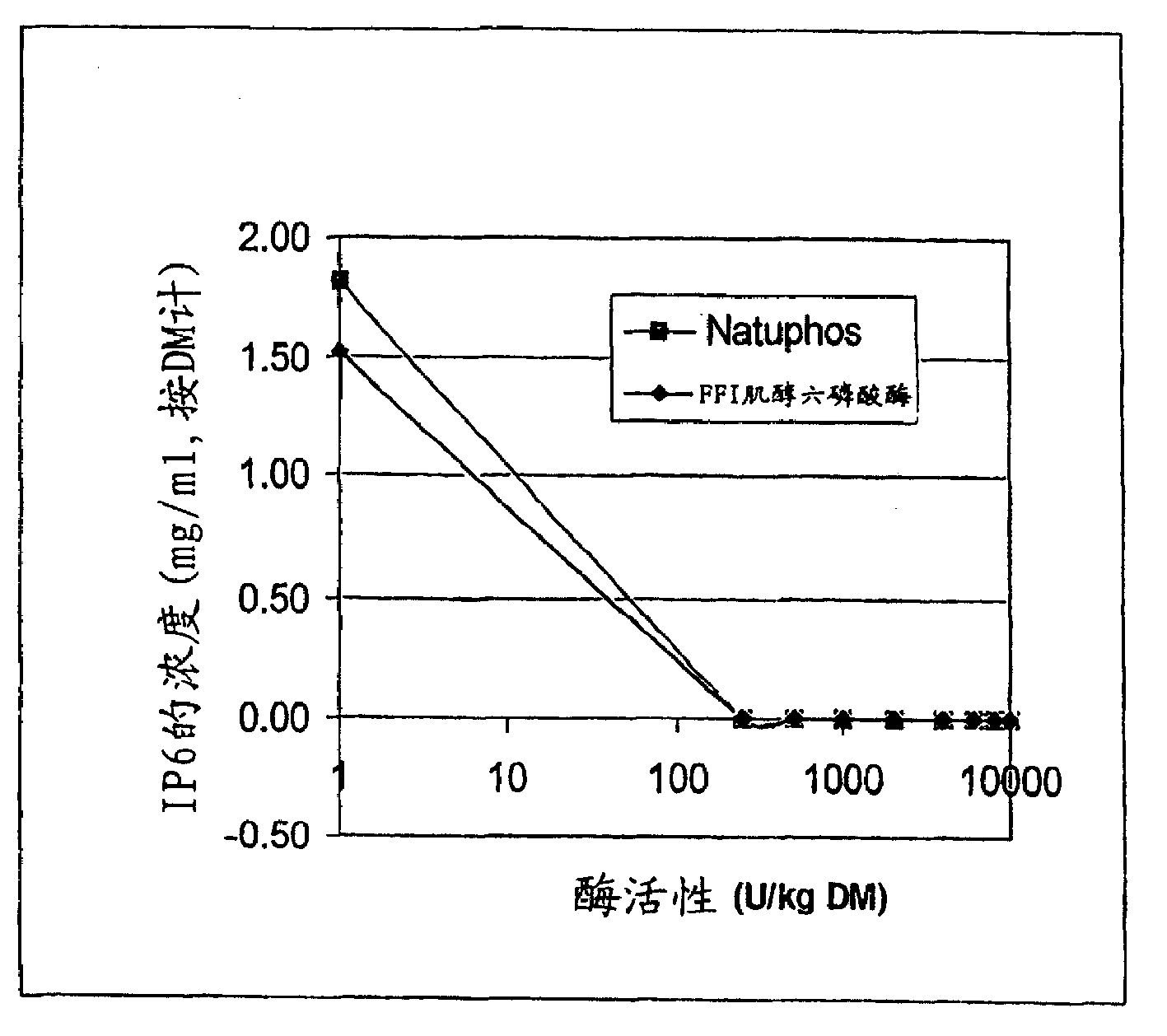
[0047] De-phytate of canola flake extract
[0048] Phytase (Natuphos® 5000, BASF) or FFI phytase (non-commercial enzyme supplied by FinnFeeds International) was diluted in water so that 250 μl aliquots were added to 0, 250, 500, 1000, Phytase equivalents of 2000, 4000, 6000, 8000 and 10000 U. One unit of phytase activity is defined as the amount of enzyme source that liberates 1 micromole of inorganic phosphorus per minute from an excess of sodium phytate at pH 5.5 at 37°C.
[0049] In a conical centrifuge tube, 20 g of unroasted desolvated canola flakes were mixed with 100 ml of 50°C, 0.75% NaCl. Press the slurry to 3000 * centrifuge for 10 minutes. The supernatant was removed and divided into 2 ml aliquots in glass test tubes and placed in a 50°C water bath. After 60 minutes had elapsed, the reaction was quenched by adding 1 ml of ice-cold 1M HCl and vortexing. Keep these samples on ice to ensure that the reaction is stopped. Samples were analyzed for soluble phosphoru...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Heat-induced protein curdling of a de-phytic acid extract of canola flakes.
[0053] Unroasted desolvated canola flakes were processed by extraction-dehydration as described in the Examples. In this case, however, the desolvated flakes were screened through a No. 10 U.S. sieve to remove large aggregates from the feedstock.
[0054] The final extract was placed in a 100L steam pot and the temperature of the extract was raised to 50°C. To this mixture was added a phytase (FFI phytase as described in Example 2) to provide 1500 FTU / kg of raw flake stock. The mixture was stirred continuously with a mechanical stirrer and incubated for 60 minutes to affect the dephytase of the extract. At the end of the phytate period, the temperature of the mixture was increased to 95°C and held at this temperature for 5 minutes. At the end of the heat treatment period, the steam to the pot was turned off and cold water was passed through the pipes. A protein-rich curd was formed on top ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com