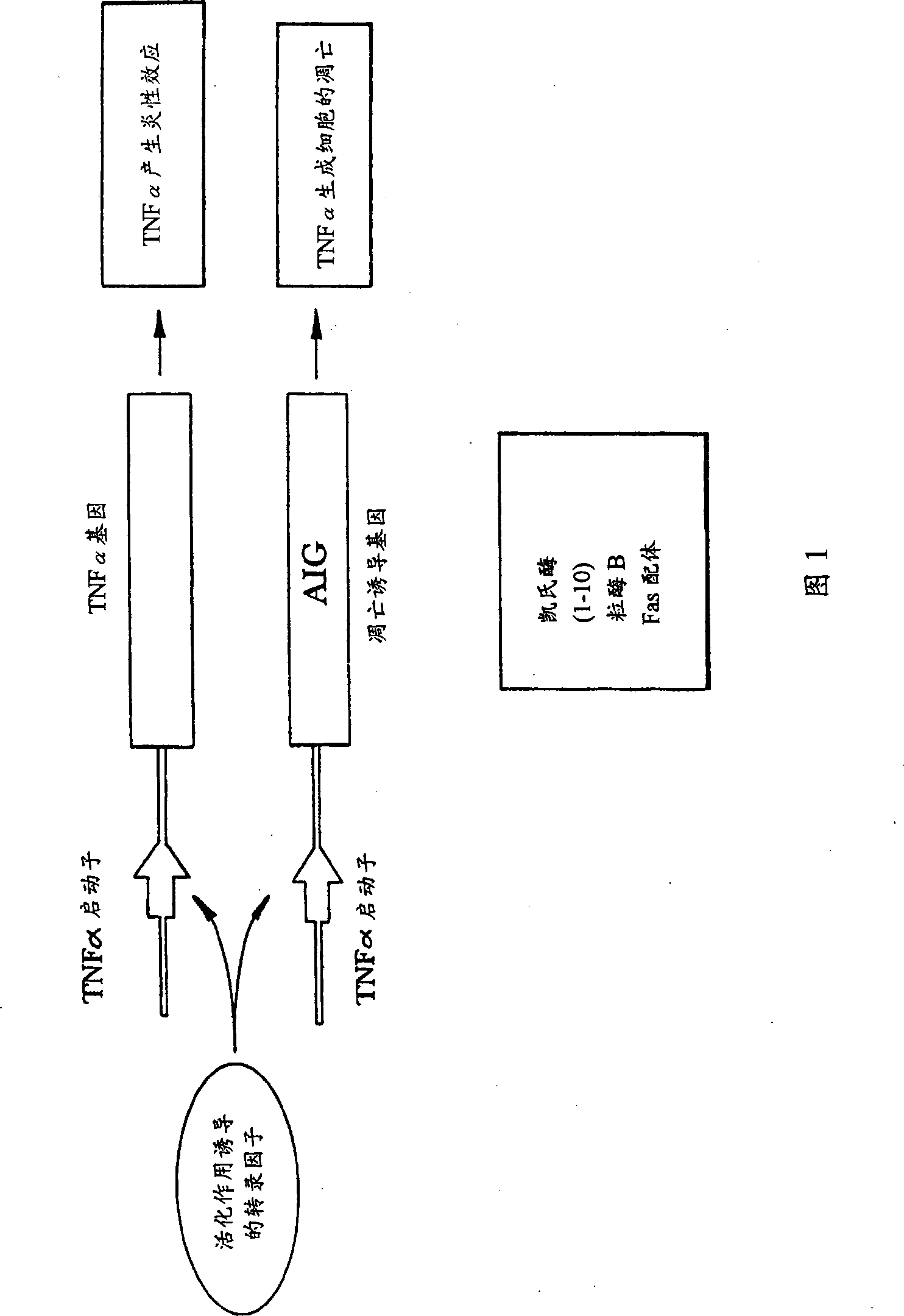
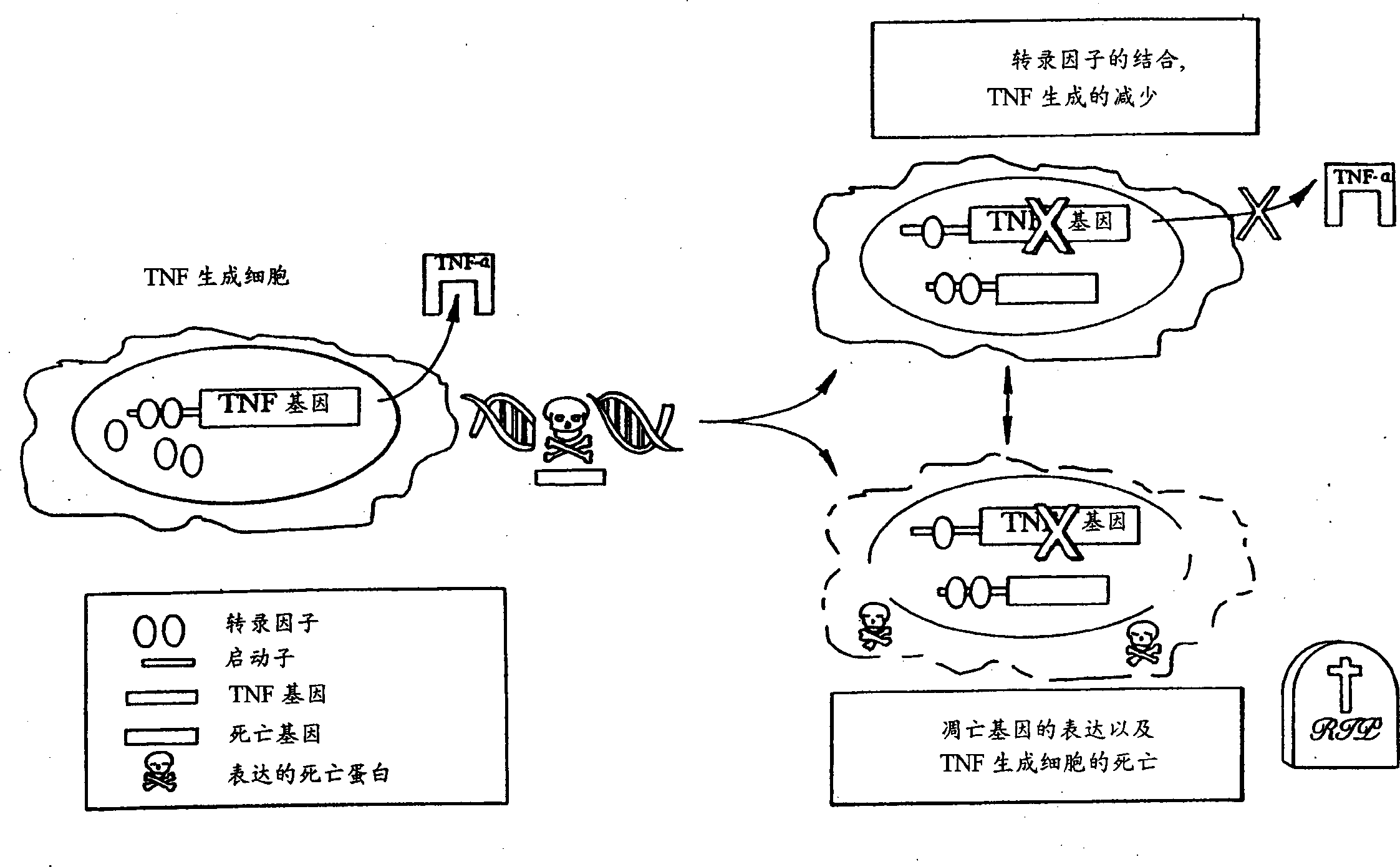
Self-regulated apoptosis of inflammatory cells by gene therapy
A technology of apoptosis and alleles, applied in the fields of molecular biology and immunology, can solve the problems of high cost, inconvenience, danger and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Generation of TNFp-granzyme B constructs
[0111] For the construction of chimeric granzyme B driven by the enhancer cis-element of the TNF promoter (single or multiple copies of the same region or different regions), identification of the region of interest that determines the optimal induction of expression of the reporter gene . Screening for TNF[alpha] promoter elements for construction of chimeric nucleic acids.
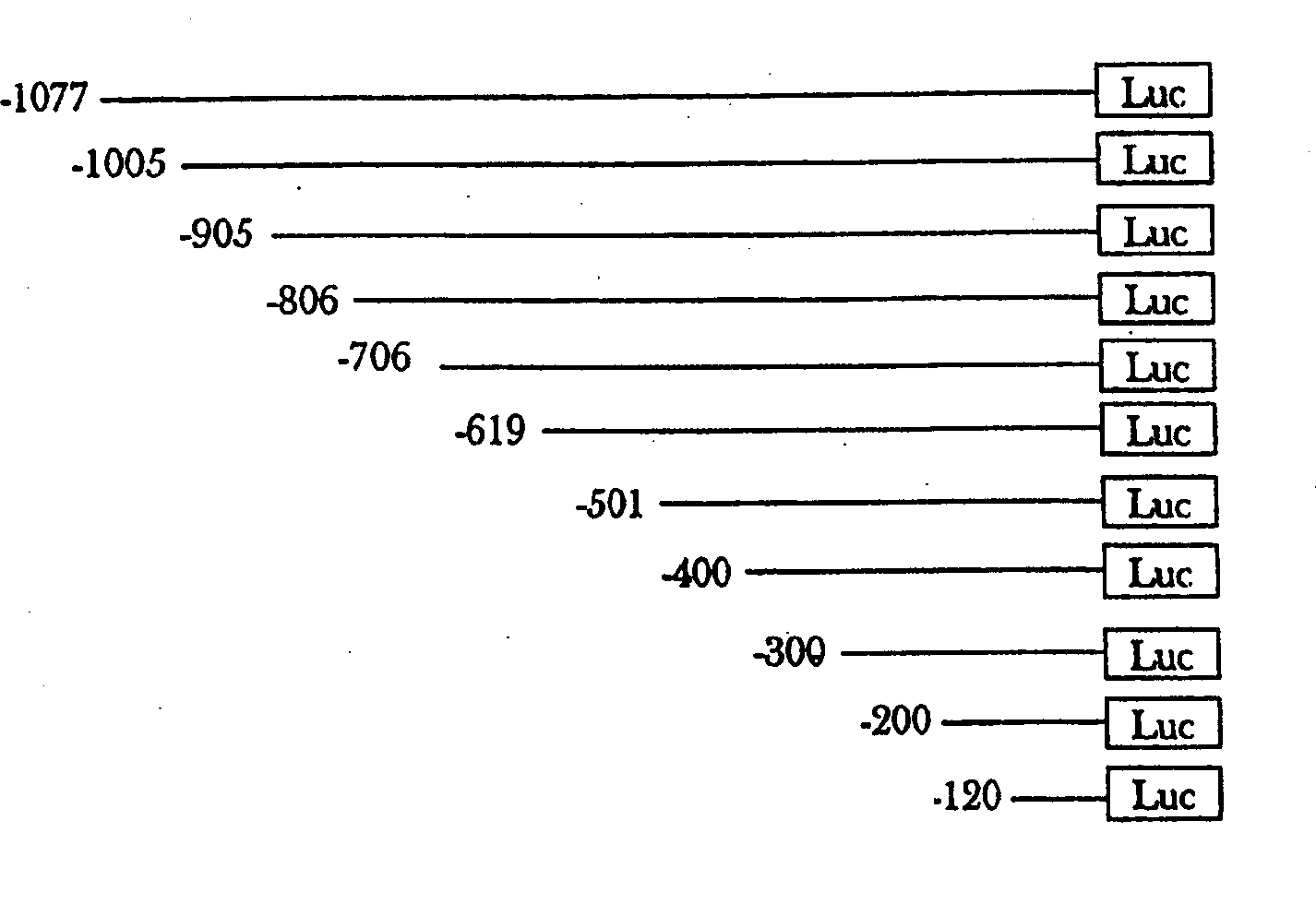
[0112] The TNFα promoter region ( image 3). Regions identified by other investigators in various other cell systems were used as references (Rhoades, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 1992, 267, 22102-22107; Leitman, et al., Mol. Cell Biol. , 1992, 12, 1352-1356; Pauli U., An important review of gene expression in eukaryotic cells, 1994, 4, 323-344). The PCR-amplified gene is then cloned upstream of a reporter gene (eg luciferase) in a commercially available promoterless vector. These constructs were tested in various cell lines such as Jurkat (T lymphoblasto...
Embodiment 2
[0128] Assay Protocol In vitro method: Luciferase assay: Luciferase activity was determined using commercially available reagents (Promega). Granzyme B gene expression:
[0129] a) Western blots of transfected cell lysates were developed using anti-granzyme B antibody.
[0130] b) Apoptosis of transfected cells: Apoptosis of transfected cells caused by granzyme B was detected by staining nuclei with propidium iodide (Krishan, A., J. Cell Biol., 66, 1994, 188-193), and determined by a commercially available cell death ELISA kit (Boehringer Mannheim). animal model
[0131] Rabbit model of IL-1β-induced arthritis (Pettipher E.R. et al, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1986, 83, 8749-8753): IL-1β was injected into knee joints of New Zealand white rabbits. Intra-articular infusion of IL-1β caused a dose-dependent infiltration of leukocytes into the joint cavity and caused loss of proteoglycans from articular cartilage.
[0132] Antigen-Induced Arthritis: Intra-articular injection of ant...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Screening for somatic variants that do not produce TNFα
[0138] Cells (THP-1, Jurkat cells) were stably transfected in vitro with TNFp-AIG chimeric nucleic acid. After several rounds of stimulation to induce apoptosis of cells expressing the TNFp-AIG gene, surviving cells were harvested. From these cells cDNA libraries were constructed for functional cloning (Legerski R and Peterson C., Nature, 1992, 359, 70-73; Jaattela M., et al., Oncogene, 1995, 10, 2297-2305).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com