Method for controlling bias current for magnetoresistive head, fixed magnetic recording device, and magnetic disc therefor
A magnetoresistive magnetic head, bias current technology, applied in the direction of information recording, magnetic recording, magnetic recording head, etc. on the magnetic disk, can solve the problems of limiting the amount of bias current, signal distortion, change of the resistance value of the magnetic head, etc., to improve production amount of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
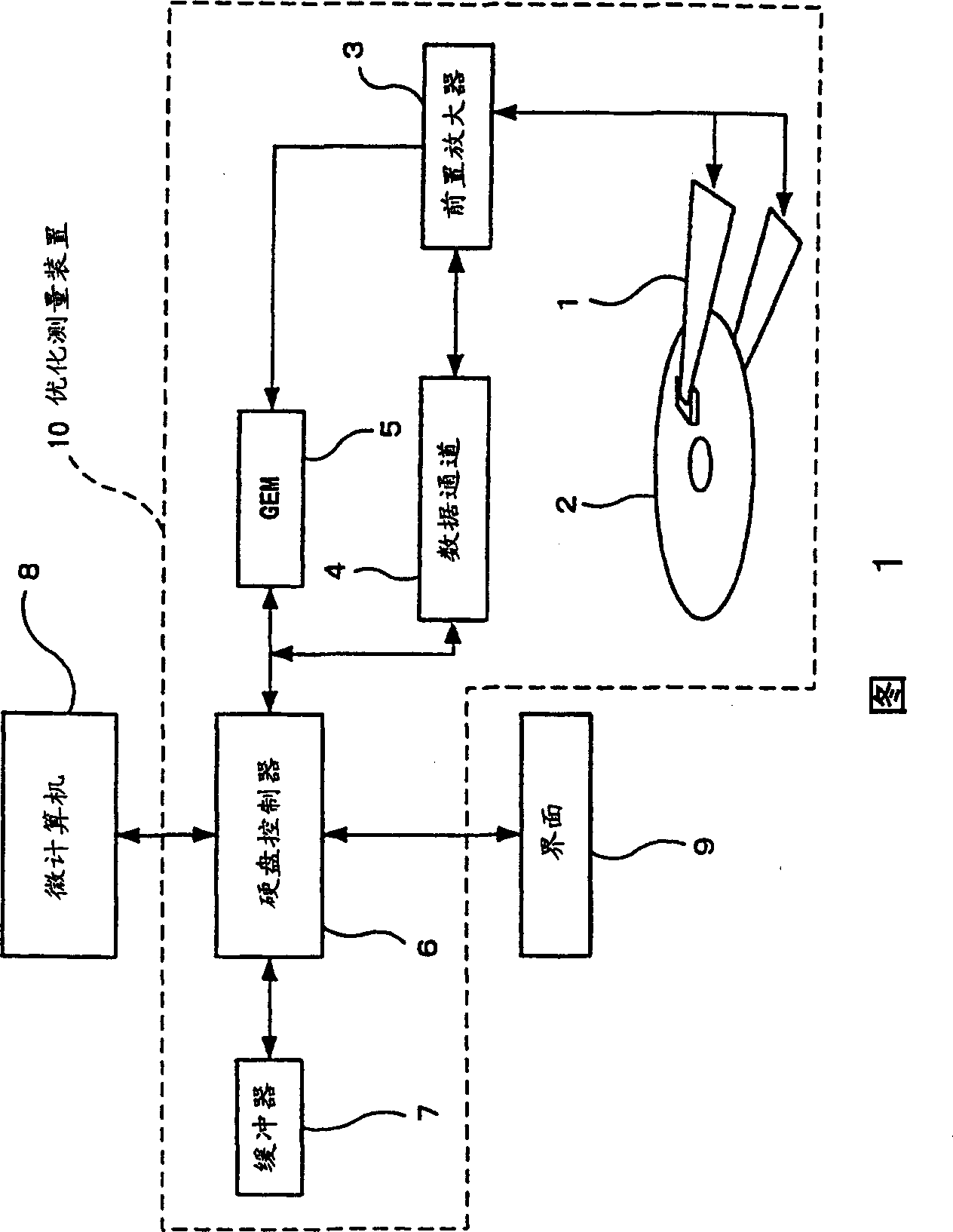
[0075] As shown in FIG. 1, according to a first embodiment of the present invention, a fixed magnetic recording apparatus has an optimization measurement device 10 (for whenever an MR head accesses a magnetic disk 2, various measurements are performed to optimize the MR in the head structure part 1. [magnetoresistance] magnetic head bias current value) and the microcomputer 8 as processing device (for controlling optimization measuring device 10 and outputting two instructions. One instruction is: the bias current value of MR magnetic head is updated as the most measured above-mentioned The optimal bias current value is used for storage; another instruction is: to provide the MR head with the above updated and stored optimal bias current).
[0076]The optimized measurement device 10 is composed of a magnetic disk 2 , a preamplifier 3 , a data channel 4 , a hard disk controller 6 and a buffer 7 .
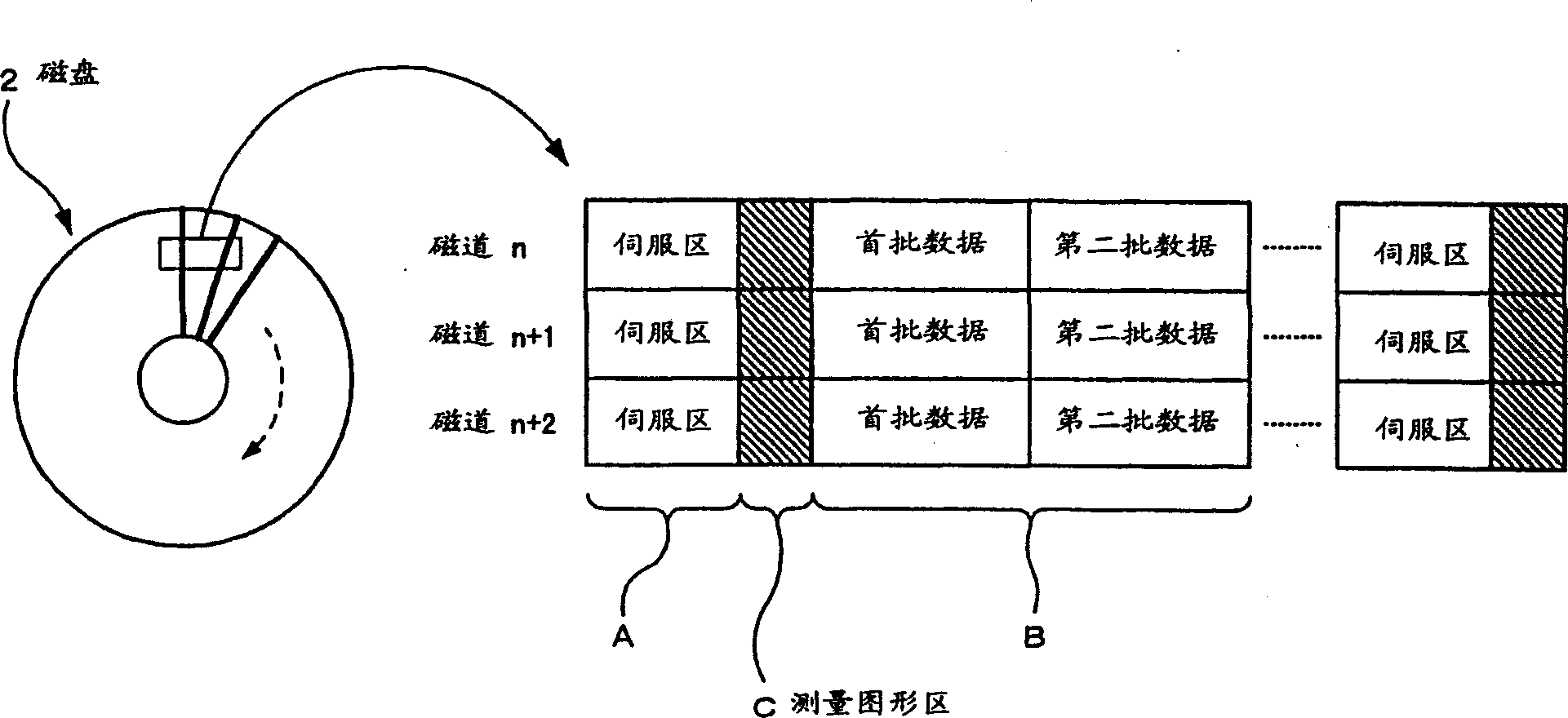
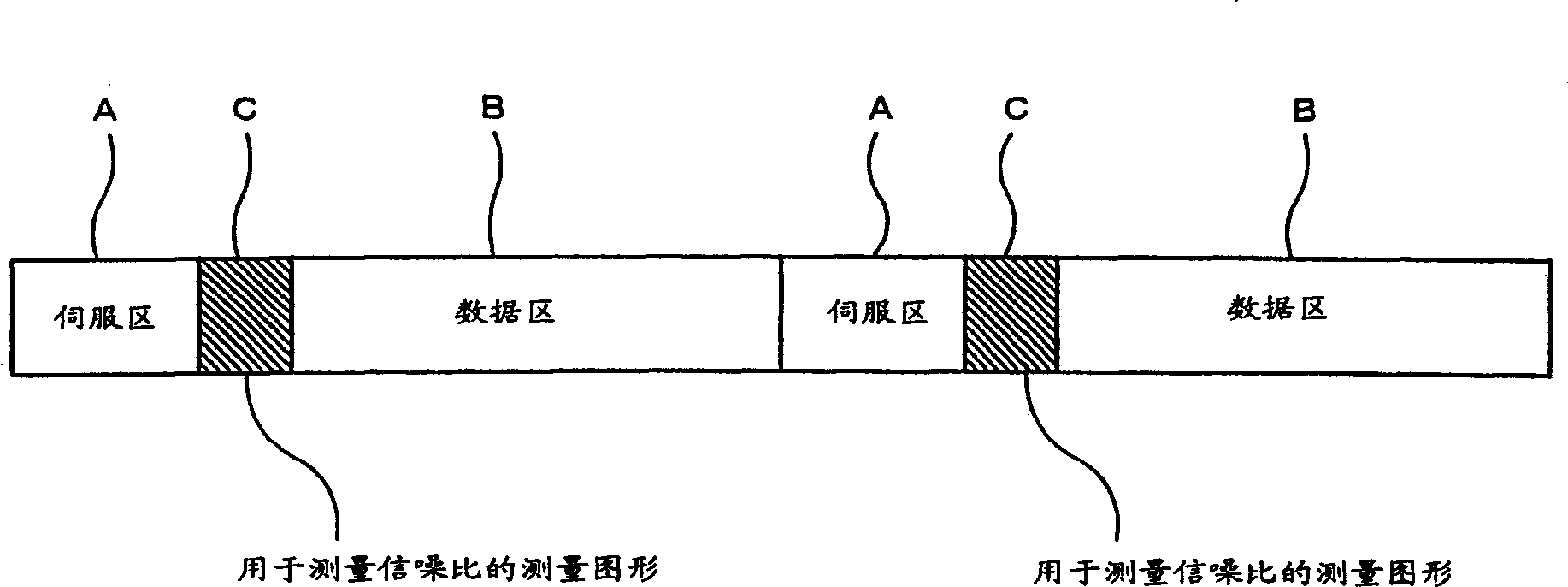
[0077] like figure 2 As shown, the magnetic disk 2 generally has a plurality o...
no. 2 example
[0091] As shown in Figure 7, according to the second embodiment of the present invention, the fixed magnetic recording device has an optimized measuring device 11 (instead of the optimized measuring device 10 in the above-mentioned first embodiment), which is used as an MR (magnetoresistive ) Various measurements are made to optimize the value of the bias current when the head enters the standby state. The magnetic disk 12 does not have the measurement pattern area C and the measurement pattern in the first embodiment described above.
[0092] The optimization measurement device 11 is composed of a plurality of (eg 2) preamplifiers 3 a and 3 b , a data channel 4 , a GEM 13 , a hard disk controller 14 and a buffer 15 .
[0093] The head structure section 1a, 1b with the corresponding MR head is structured to be connected to a preamplifier 3a or 3b. The output from the preamplifiers 3a, 3b is provided to the data channel 4 . One of the MR heads that has been accessed is connec...
no. 3 example
[0111] As shown in Figure 9, according to the third embodiment of the present invention, the fixed magnetic recording apparatus adds a buffer 16, stores the temperature characteristic of the head resistance value of the MR magnetic head, instead of the buffer 15 in the above-mentioned second embodiment; Instead of the microcomputer 8 in the second embodiment, there is a microcomputer 17 (with an additional arithmetic function of calculating the temperature from a measured head resistance value).
[0112] The buffer 16 has a temperature characteristic of the head resistance value of each MR head stored therein.
[0113] The head resistance value of an MR head depends on the design of a corresponding MR element. However, the dependence of the head resistance value on temperature is predictable because it varies almost linearly with temperature, and the head resistance value of multiple (for example, 6) MR heads varies with their temperature as shown in Figure 10 shown. The te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com