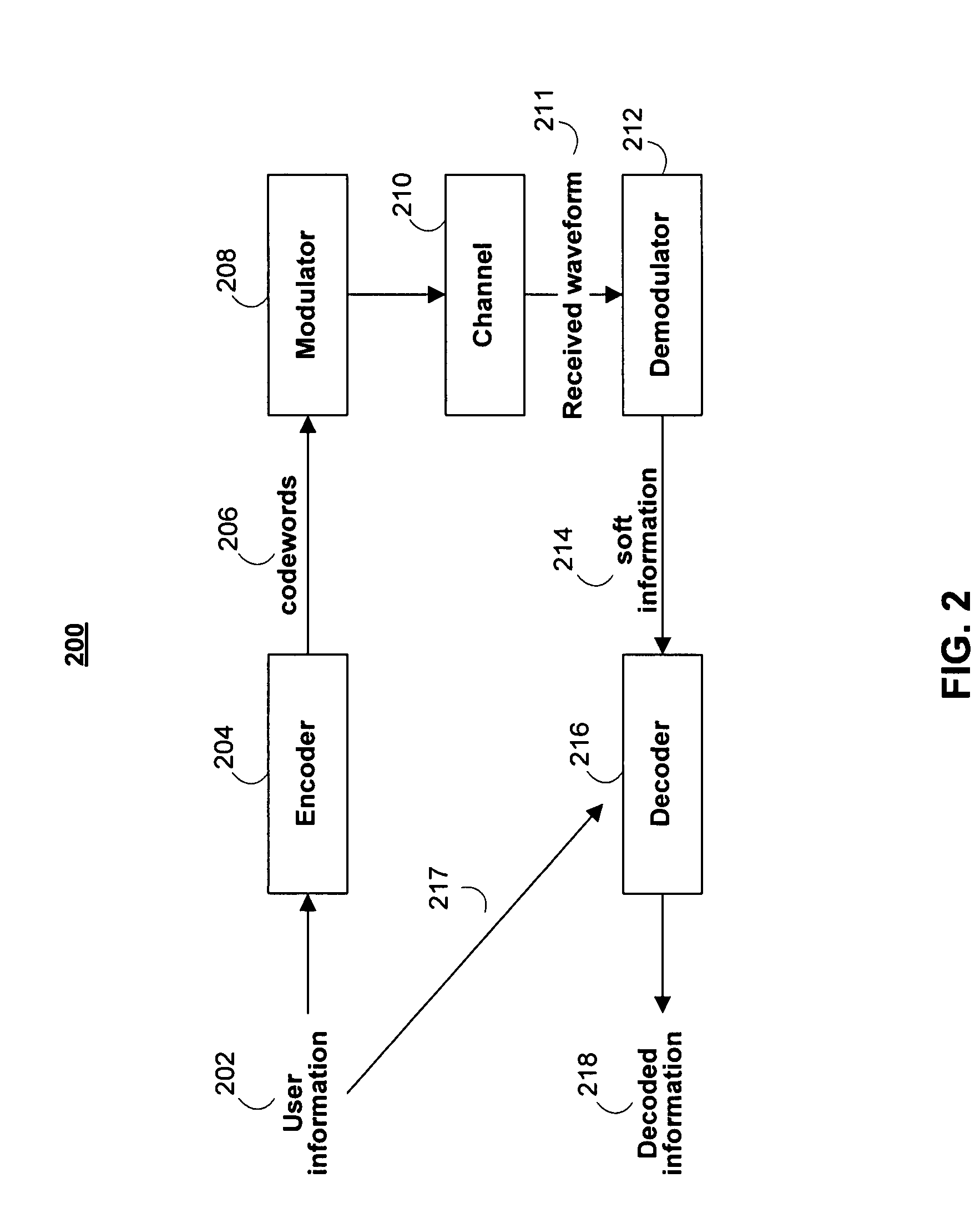
Patents
Literature
73results about "Magnetic discs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
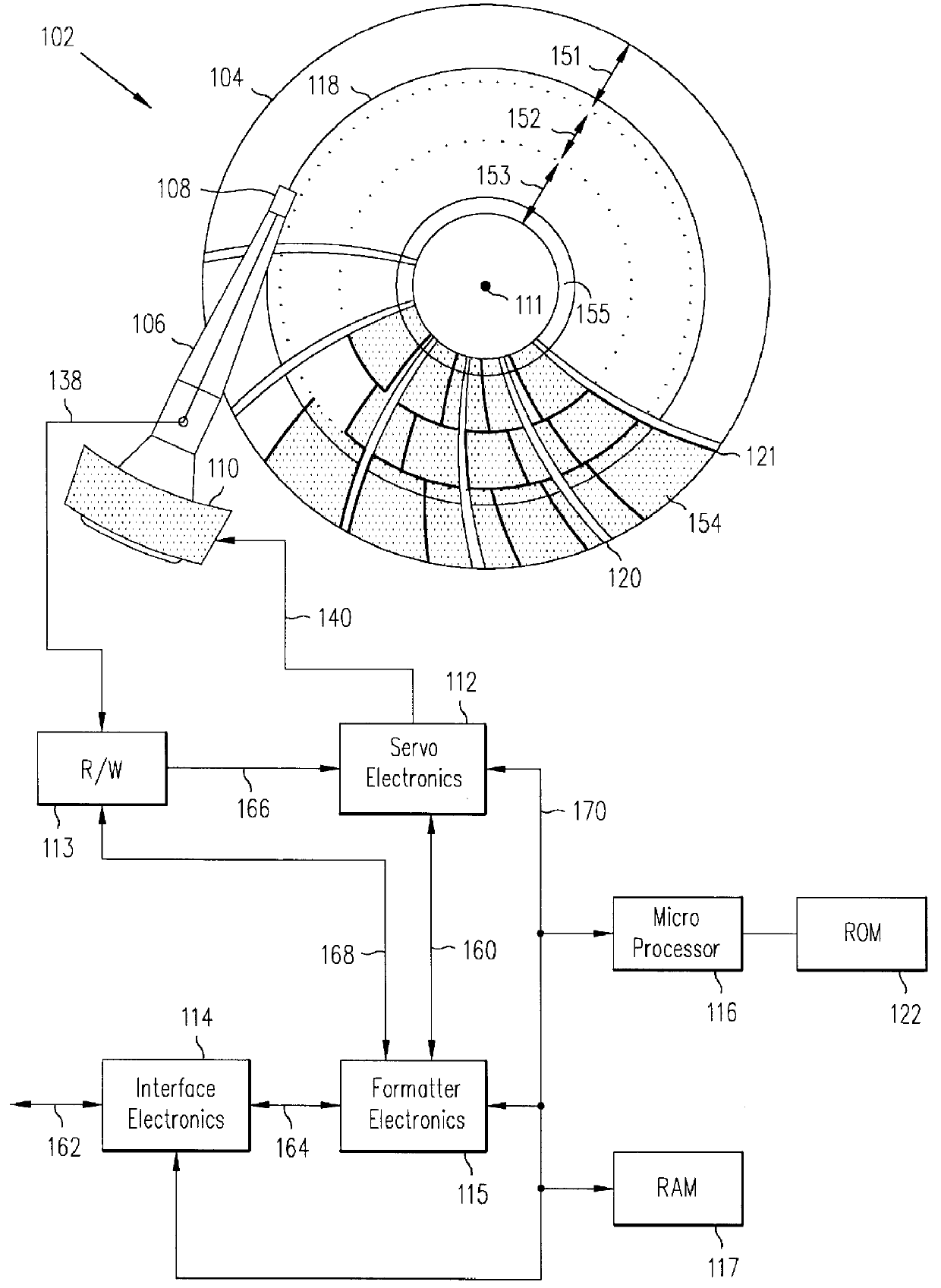
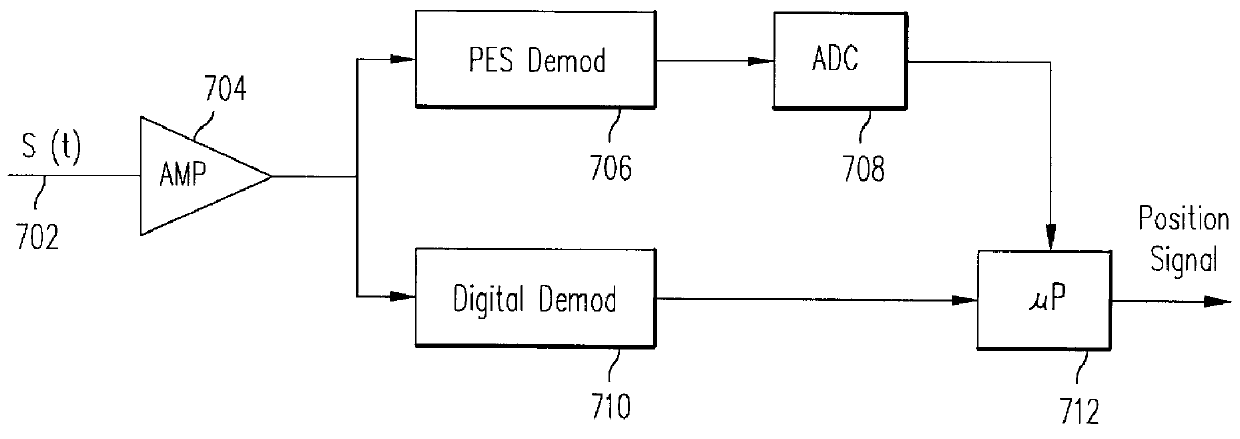
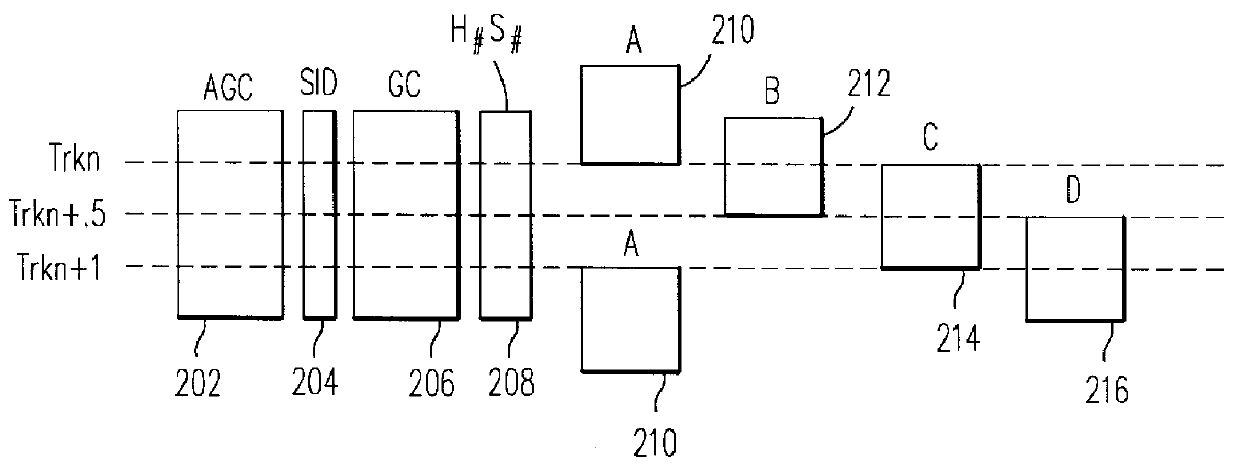
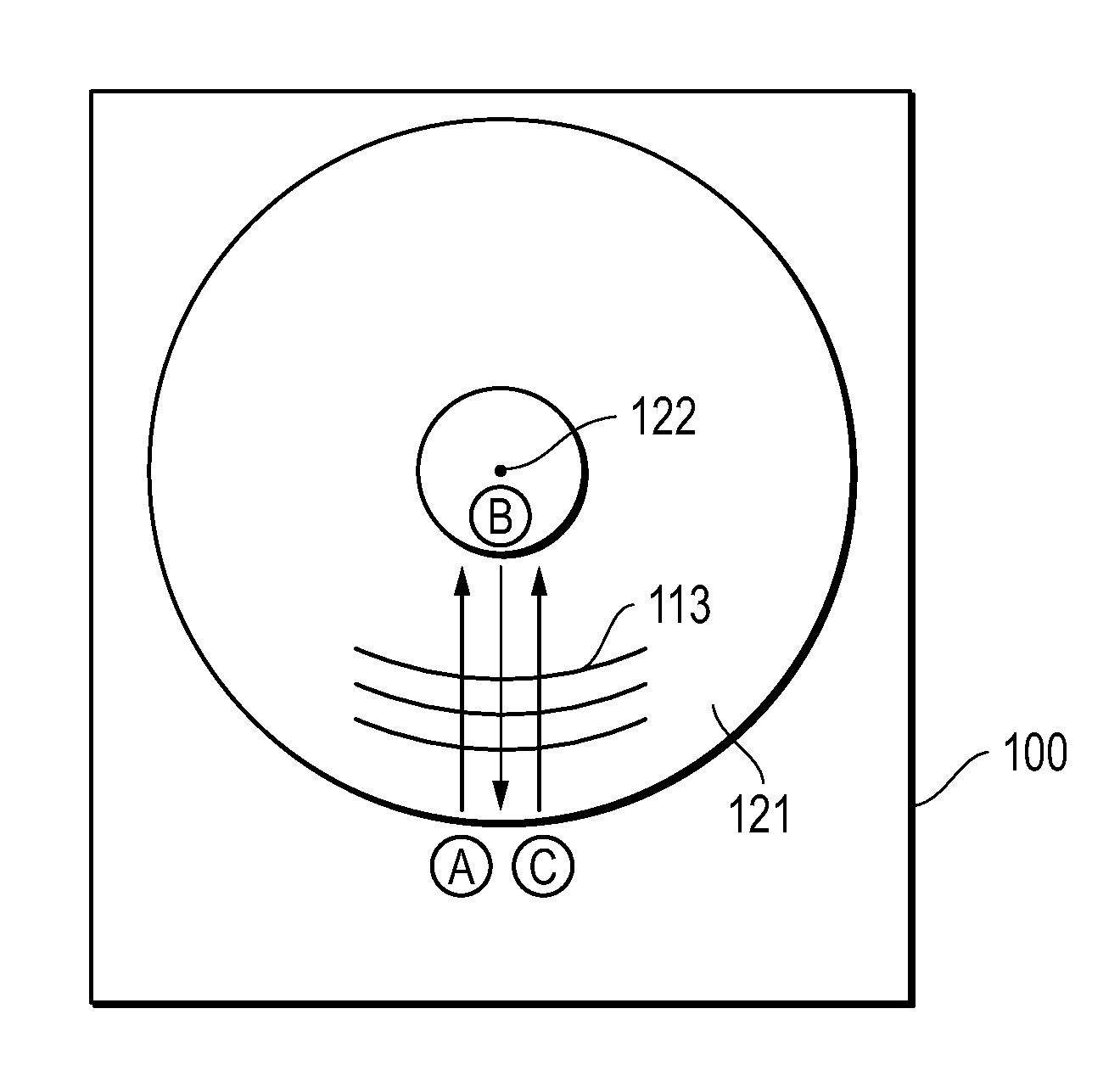
Method and apparatus for encoding digital servo information in a servo burst
InactiveUS6049438AHigh quality PESAccurate integration detectionTrack finding/aligningMagnetic discsPeak valueBurst frequency
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
System, method and apparatus for data track usage sequence to reduce adjacent track interference effect
ActiveUS20140160589A1Reduce impactMagnetic discsRecord information storageHard disc driveComputer science
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Information recording device and information recording method
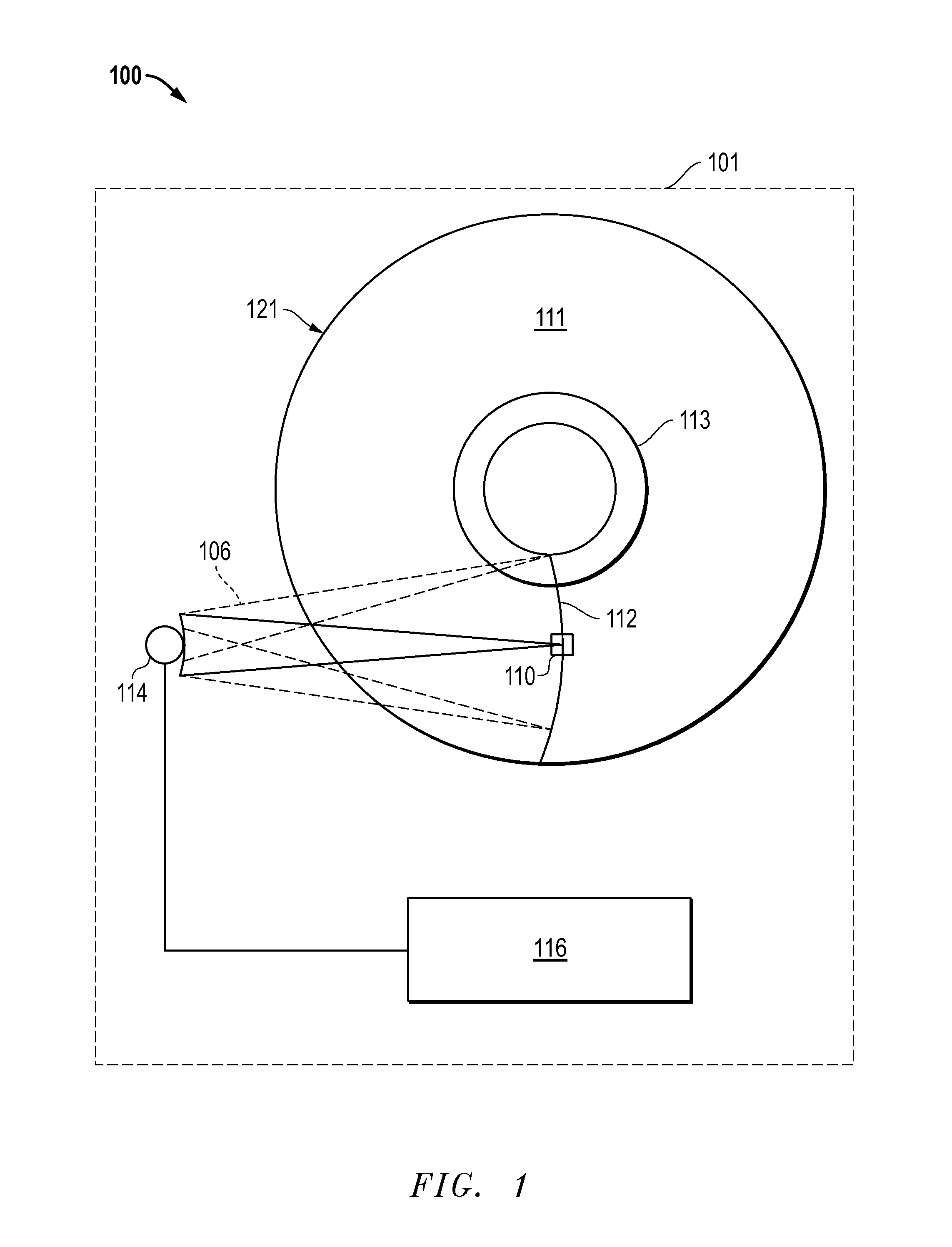
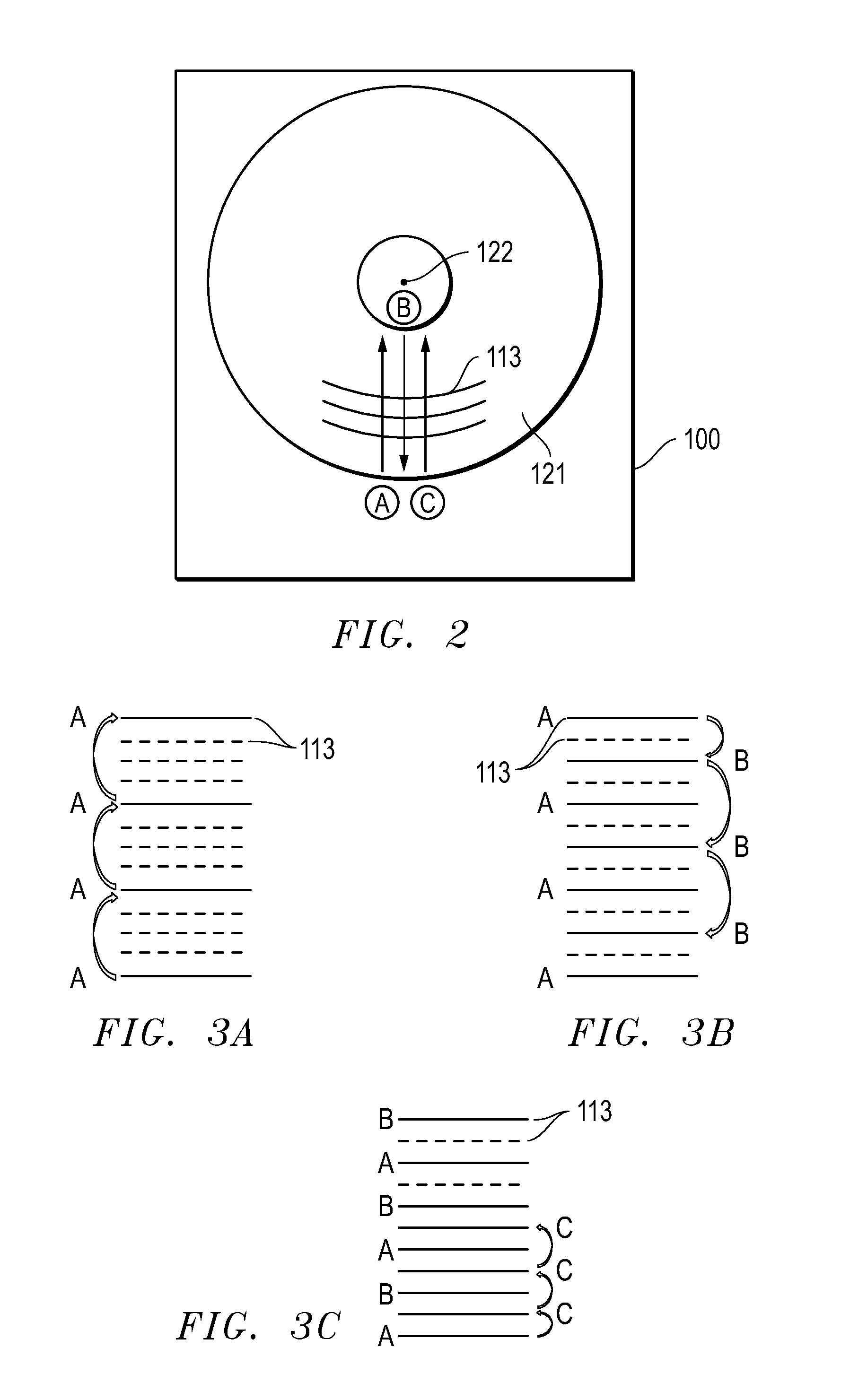
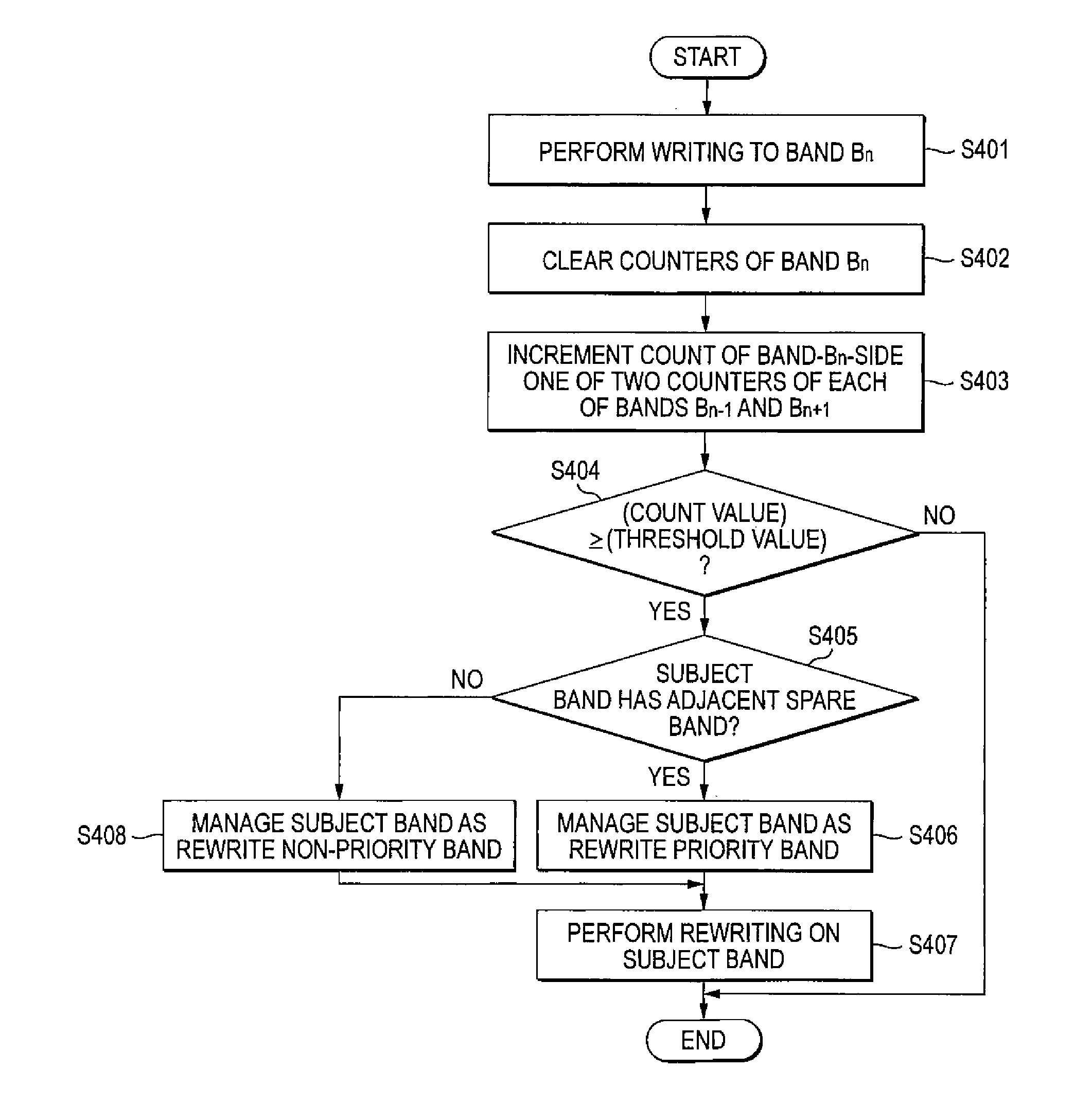
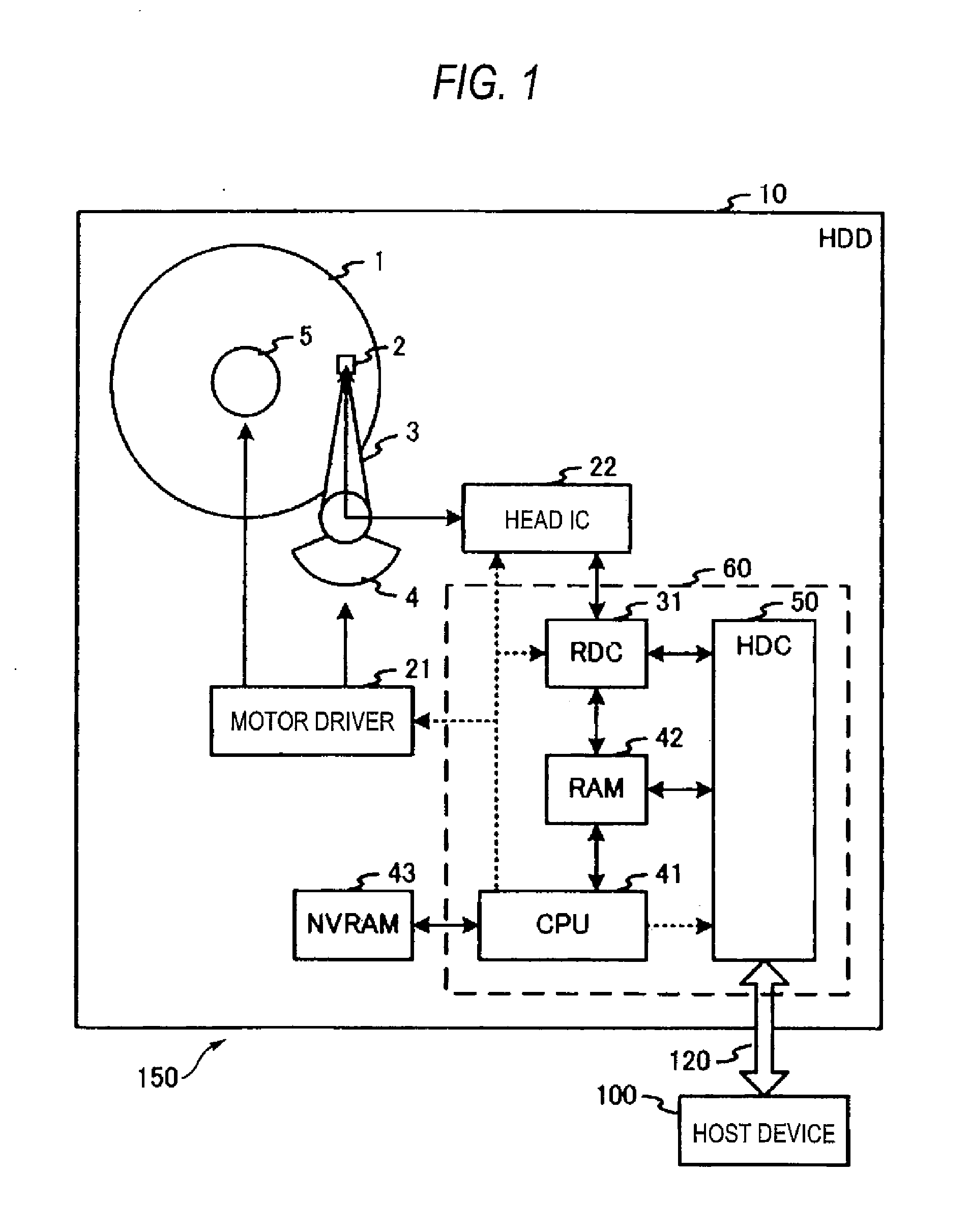
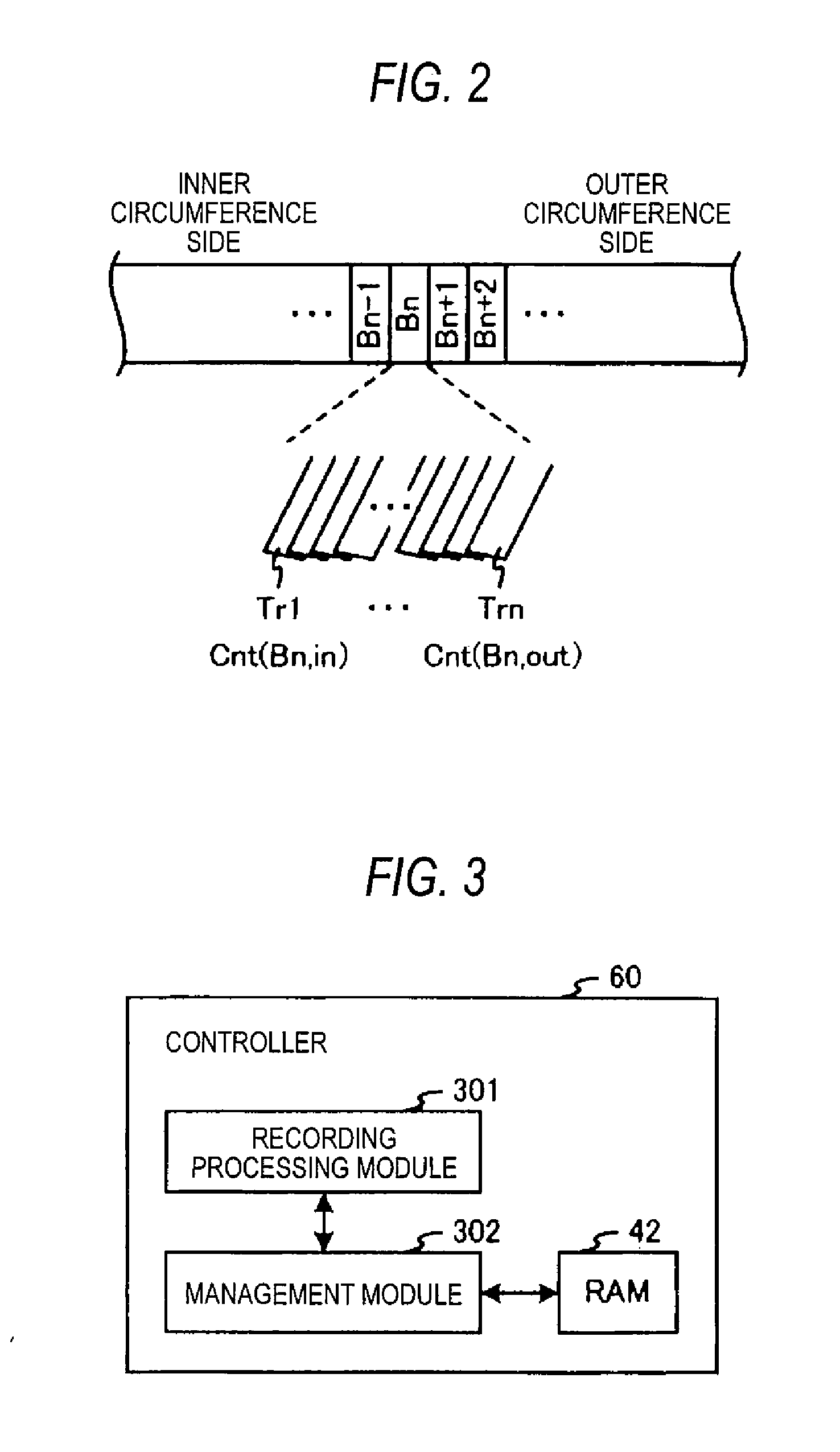
According to one embodiment, an information recording device includes: a recording controller configured to control recording of information on a magnetic recording medium having tracks by a recording method; a managing module configured to manage two or more counters corresponding to each of plural track groups that are adjacent to each other; an updating module configured to update a count of one of the two or more counters corresponding to a second track group that is adjacent to a first track group of the plural track groups when information has been recorded on the first track group; a determining module configured to determine an attribute of the second track group based on the updated count of the one counter; and a rewriting module configured to rewrite information recorded in the second track group based on the determined attribute.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
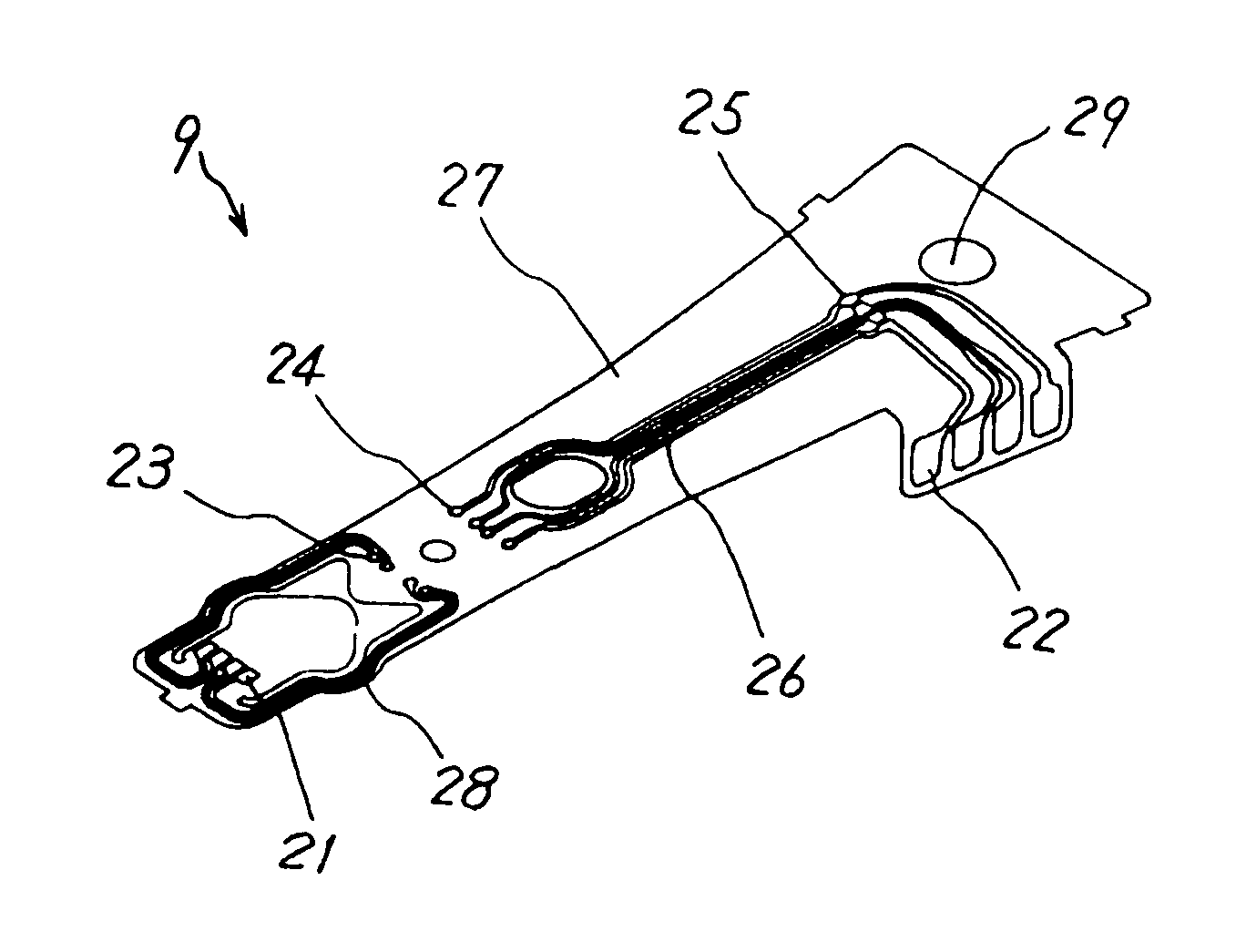
Head support mechanism, information recording/reproducing apparatus, and method of manufacturing head support mechanism
InactiveUS6943990B1Avoid low process precisionElectrical connection between head and armMagnetic discsBiomedical engineering
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
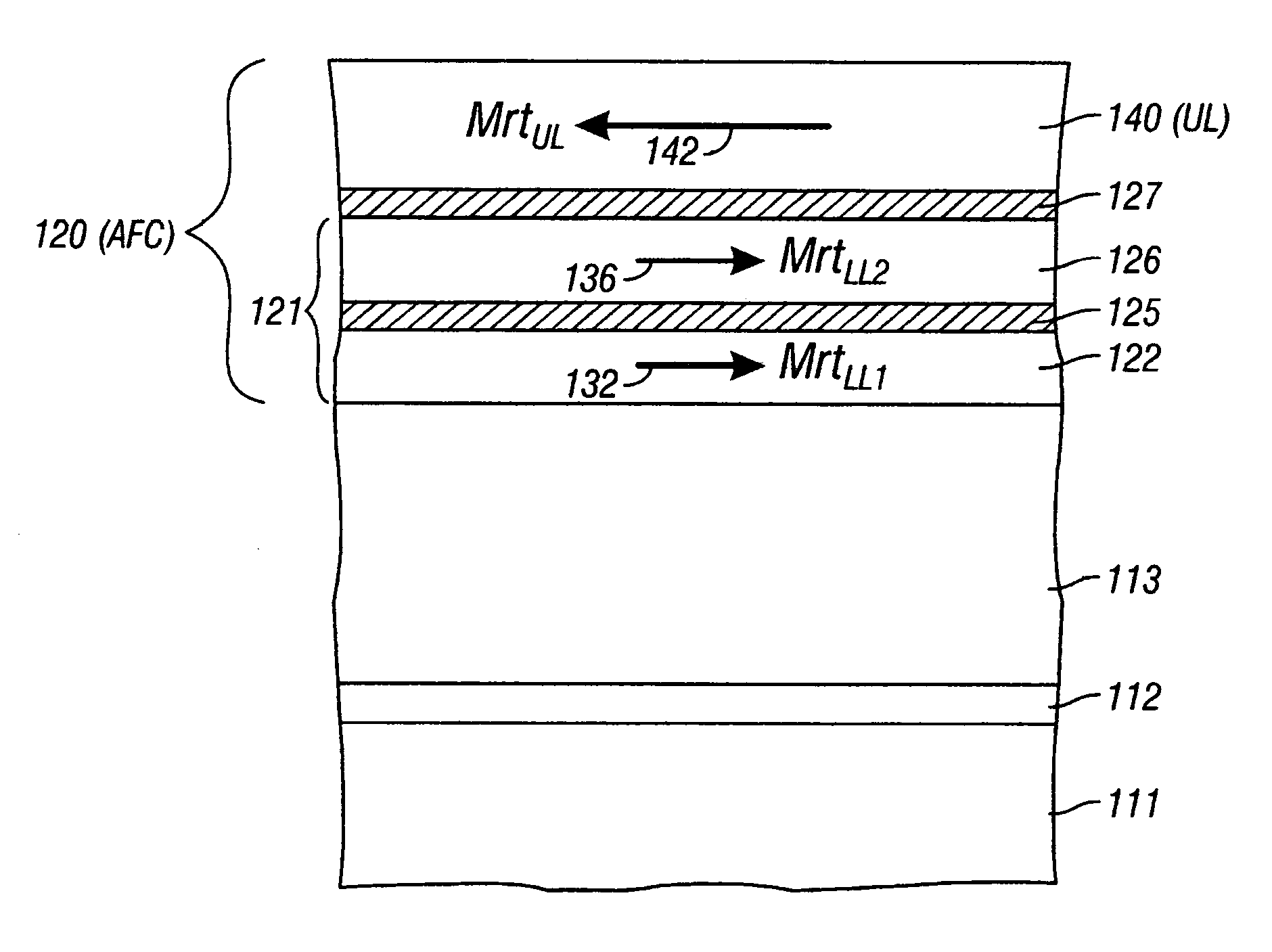
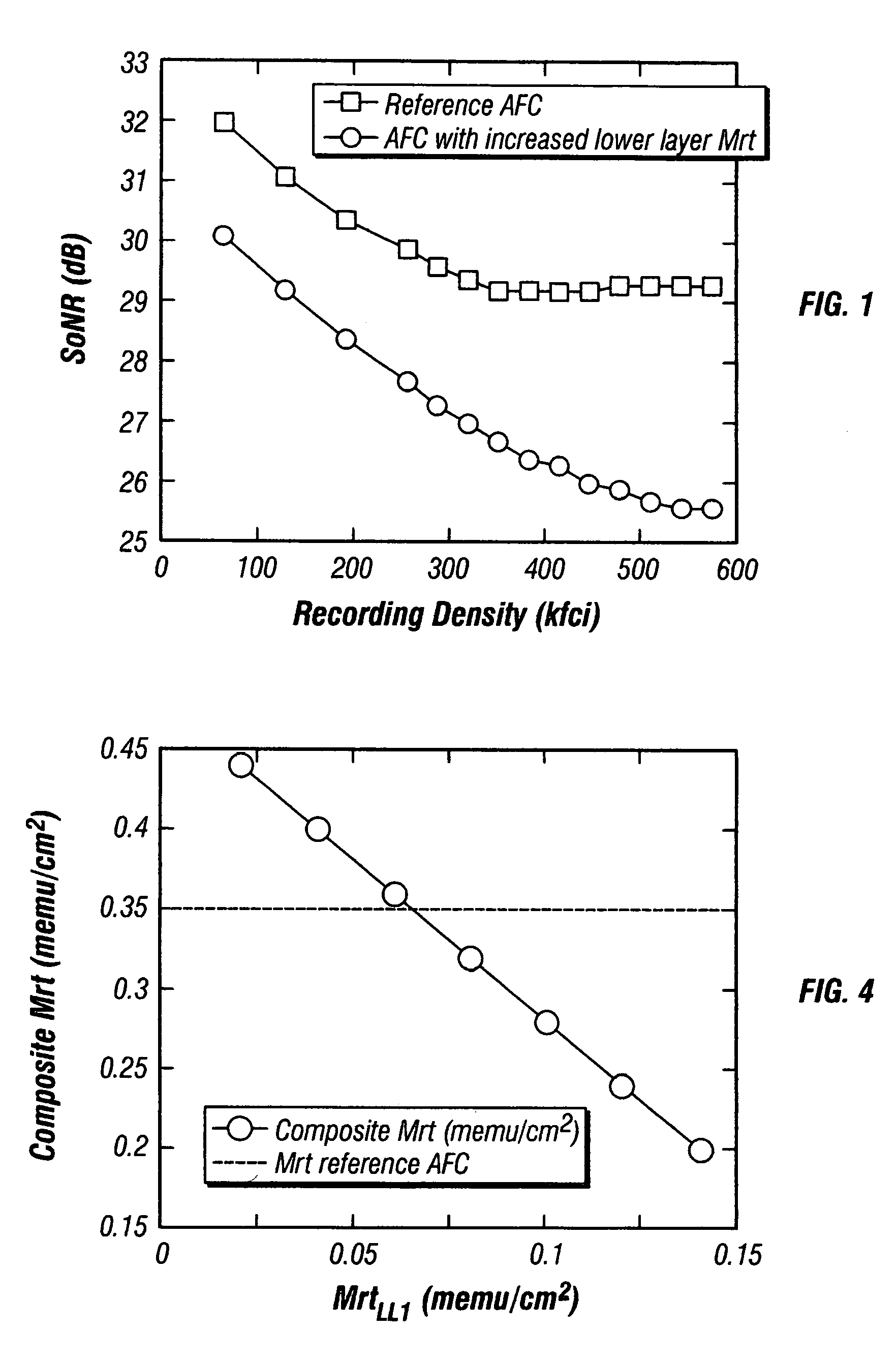
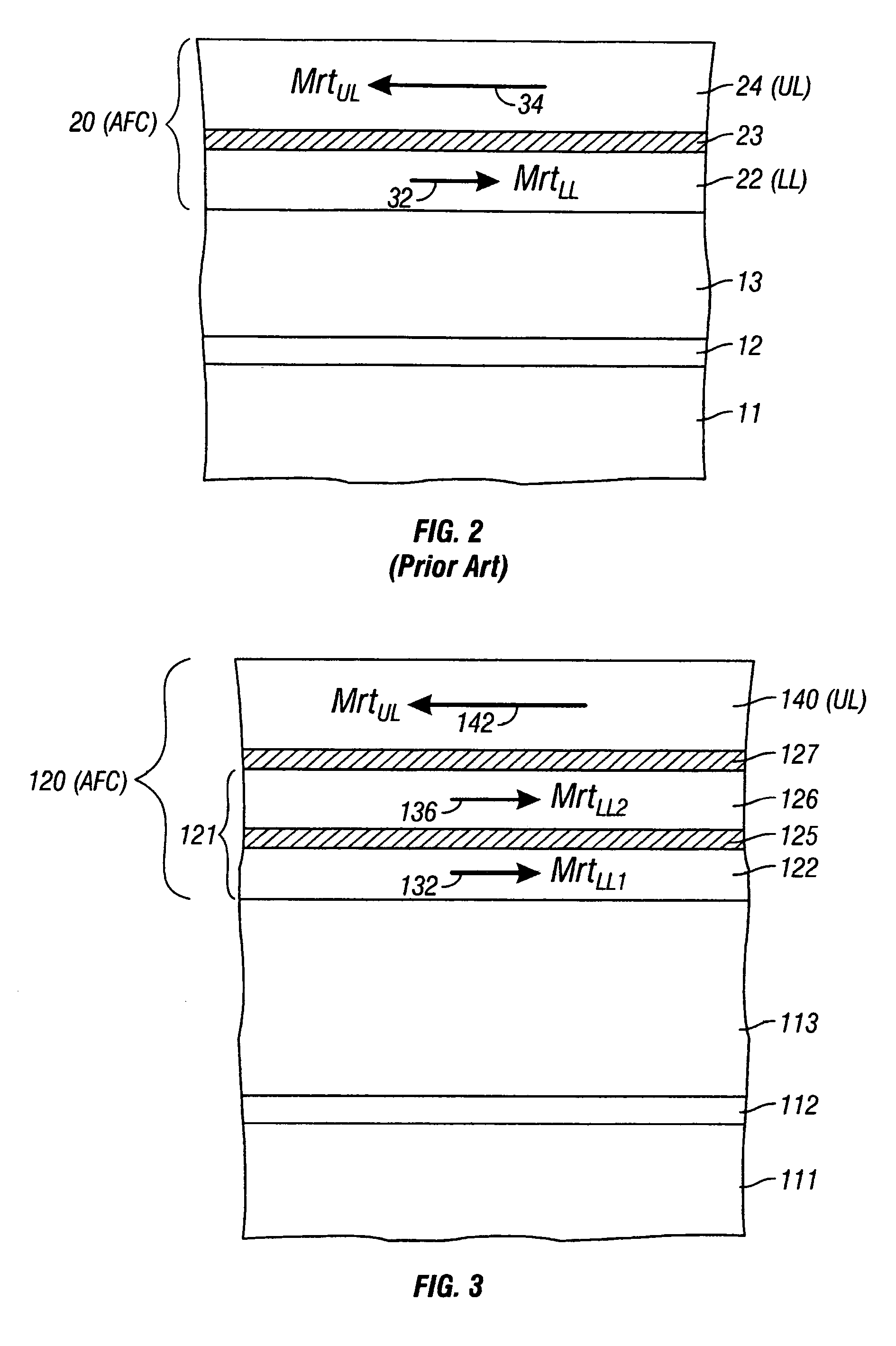
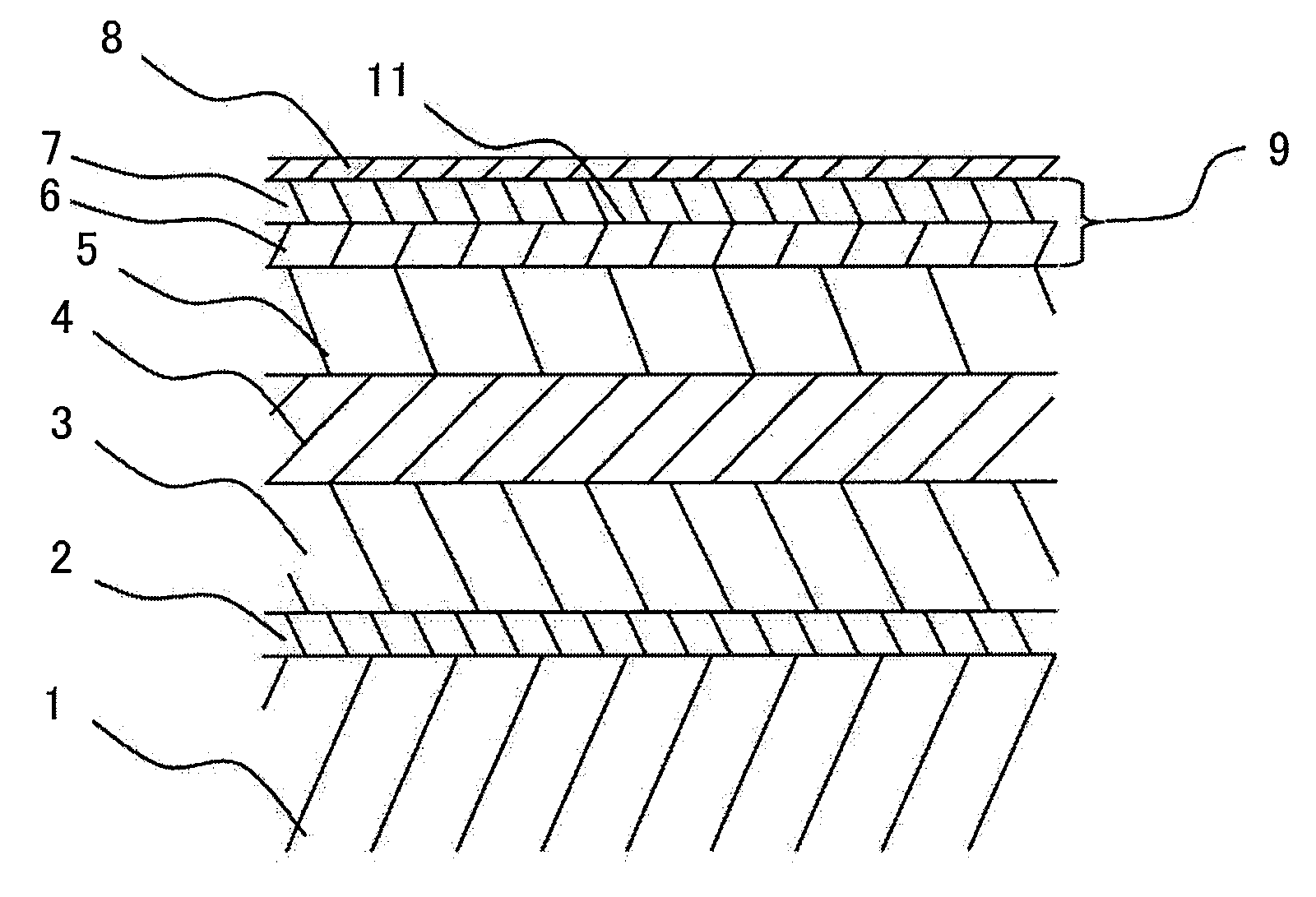
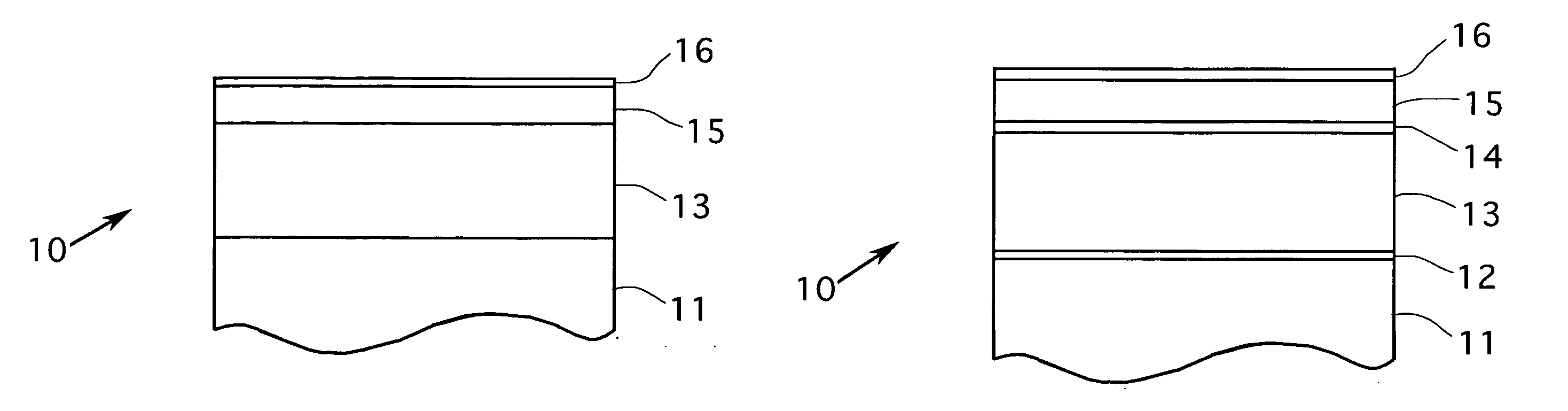
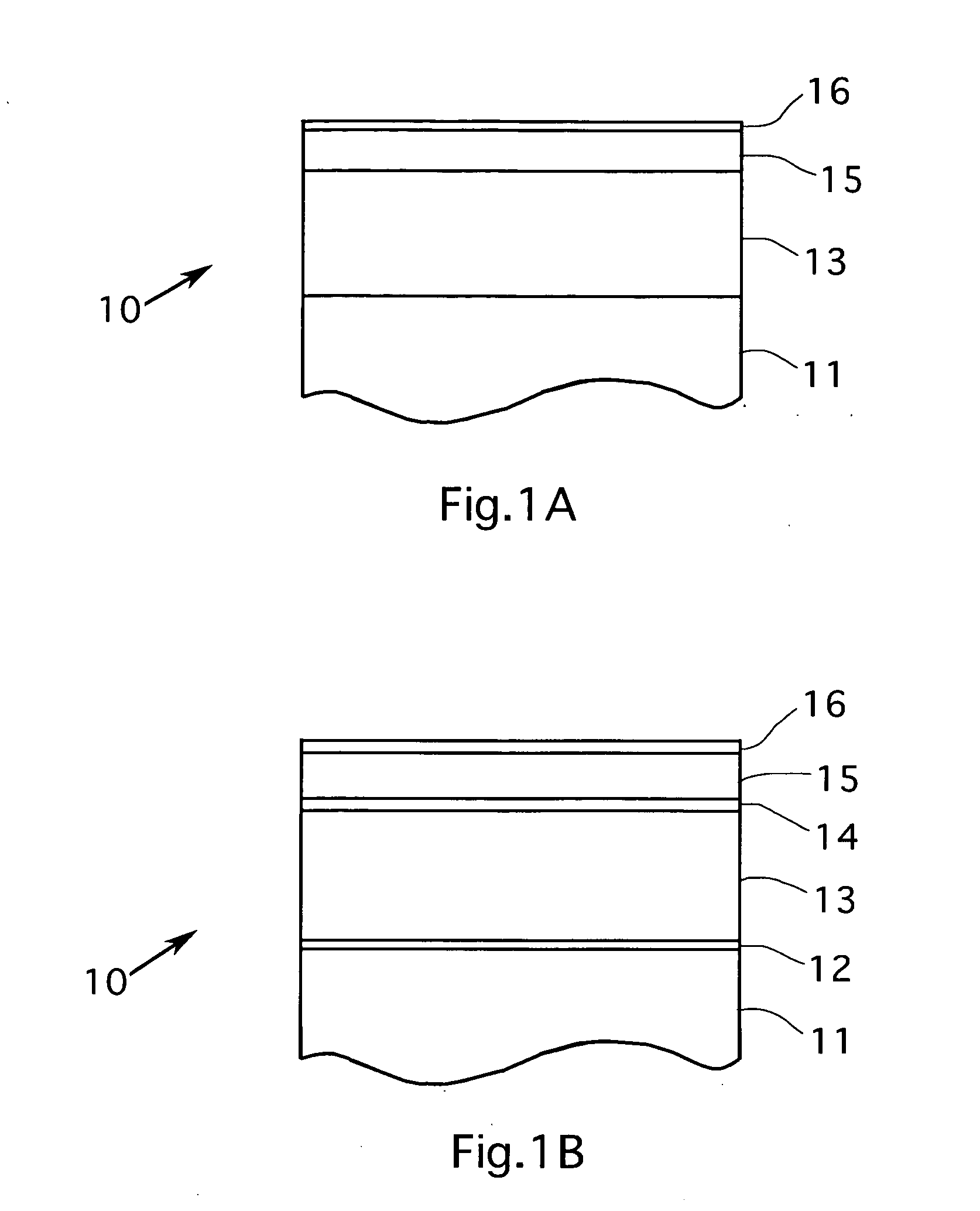
Magnetic recording disk with antiferromagnetically-coupled magnetic layer having multiple ferromagnetically-coupled lower layers
InactiveUS7081309B2Protective coatings for layersRecord information storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetization
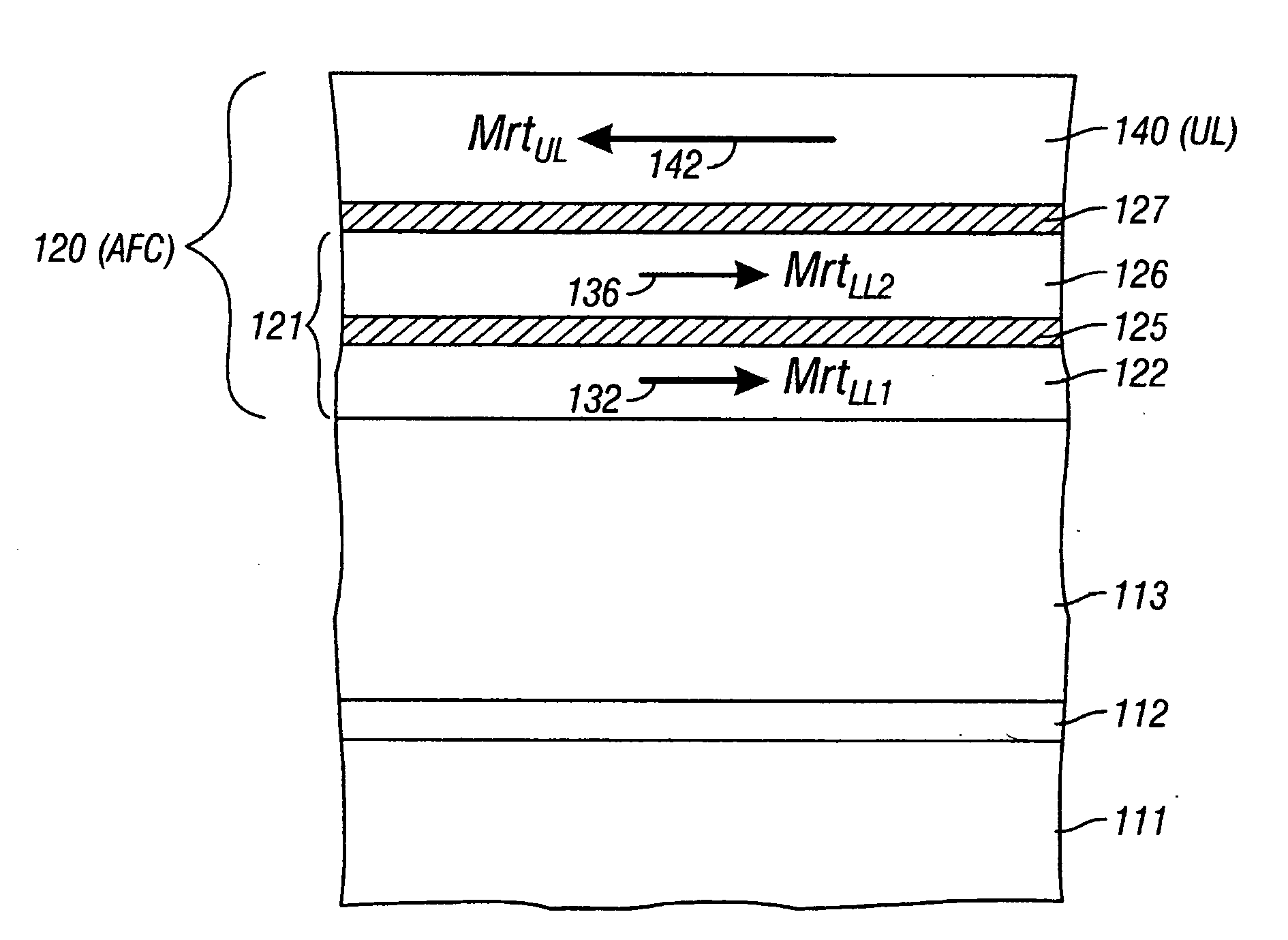
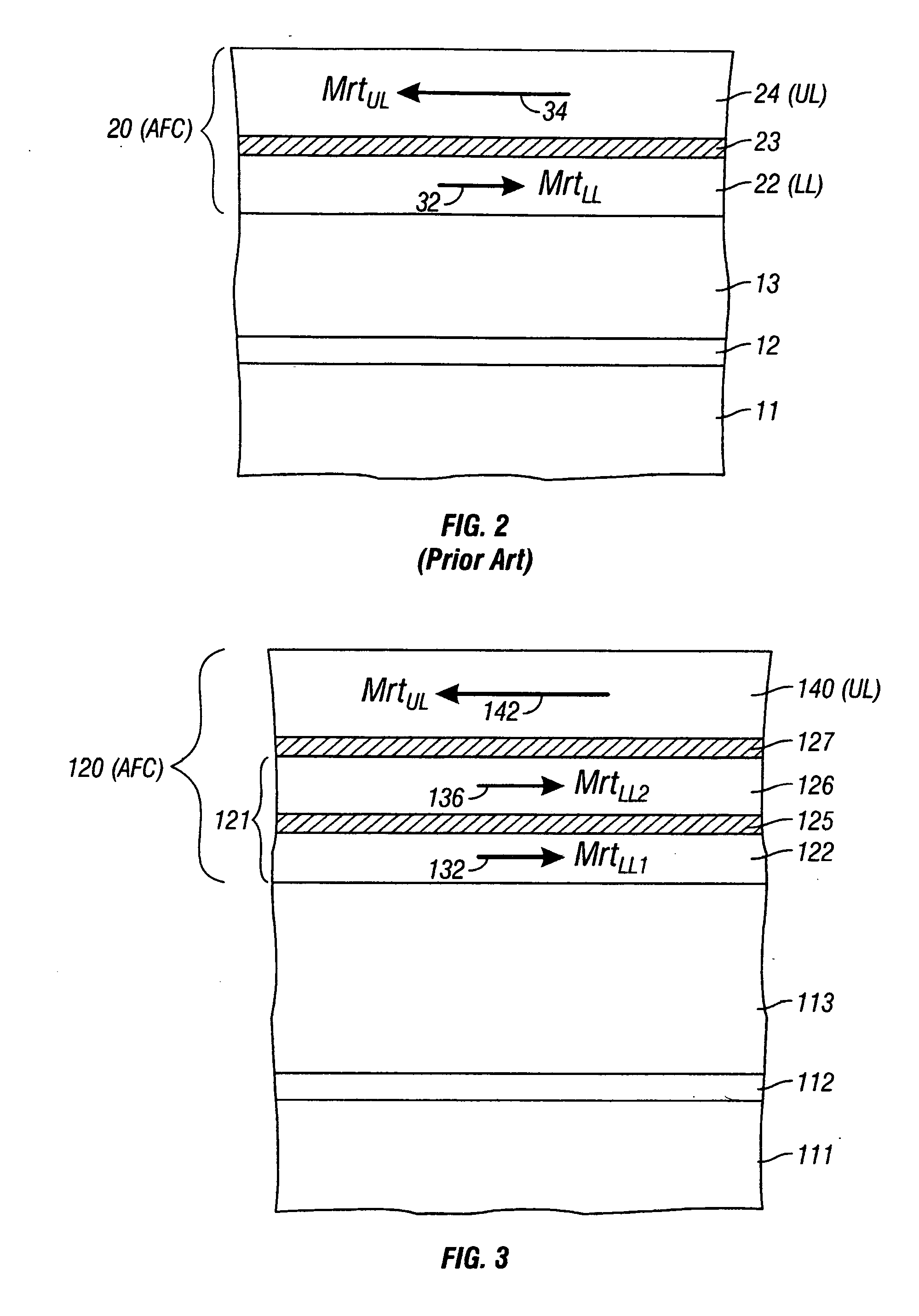
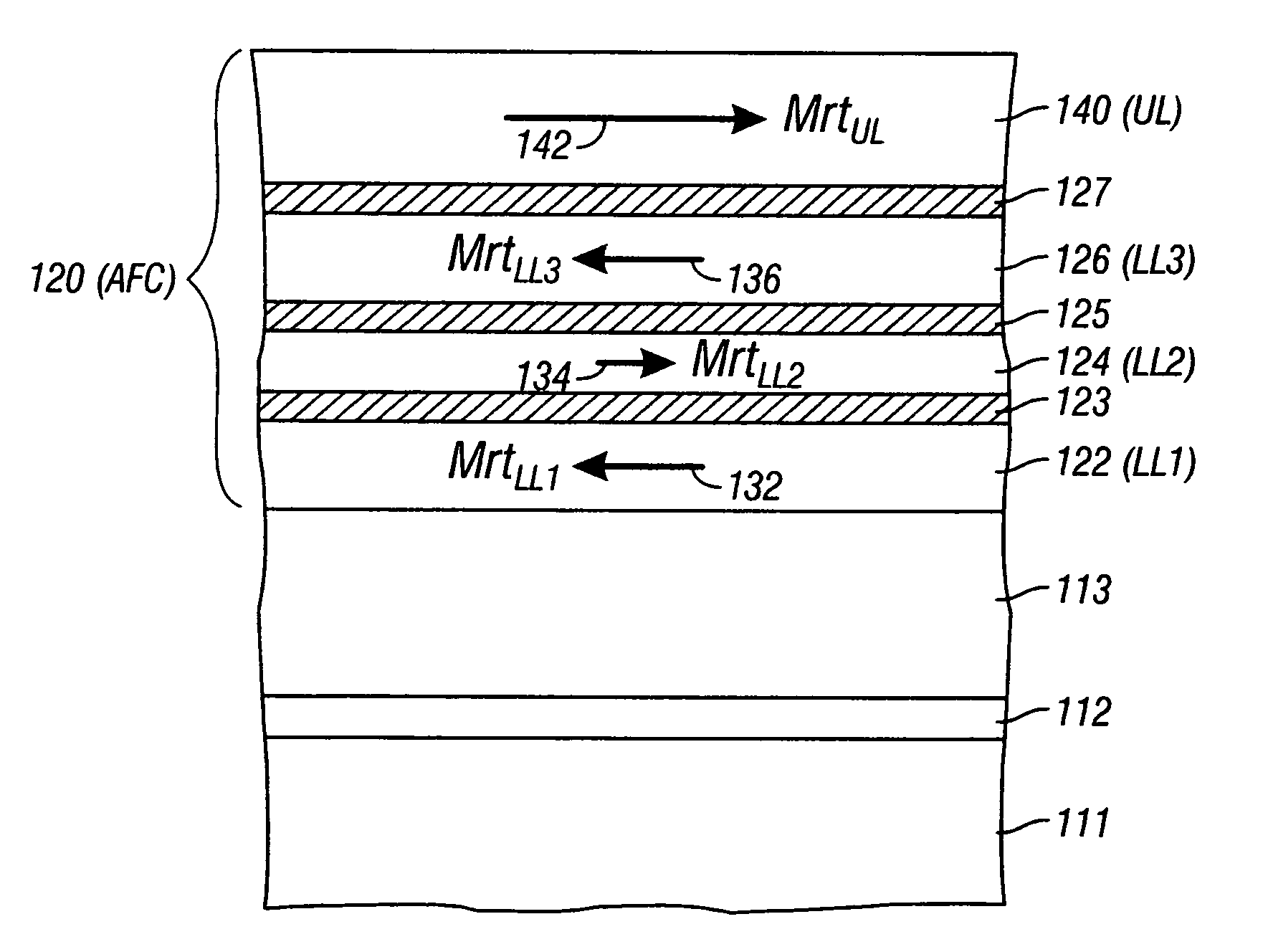
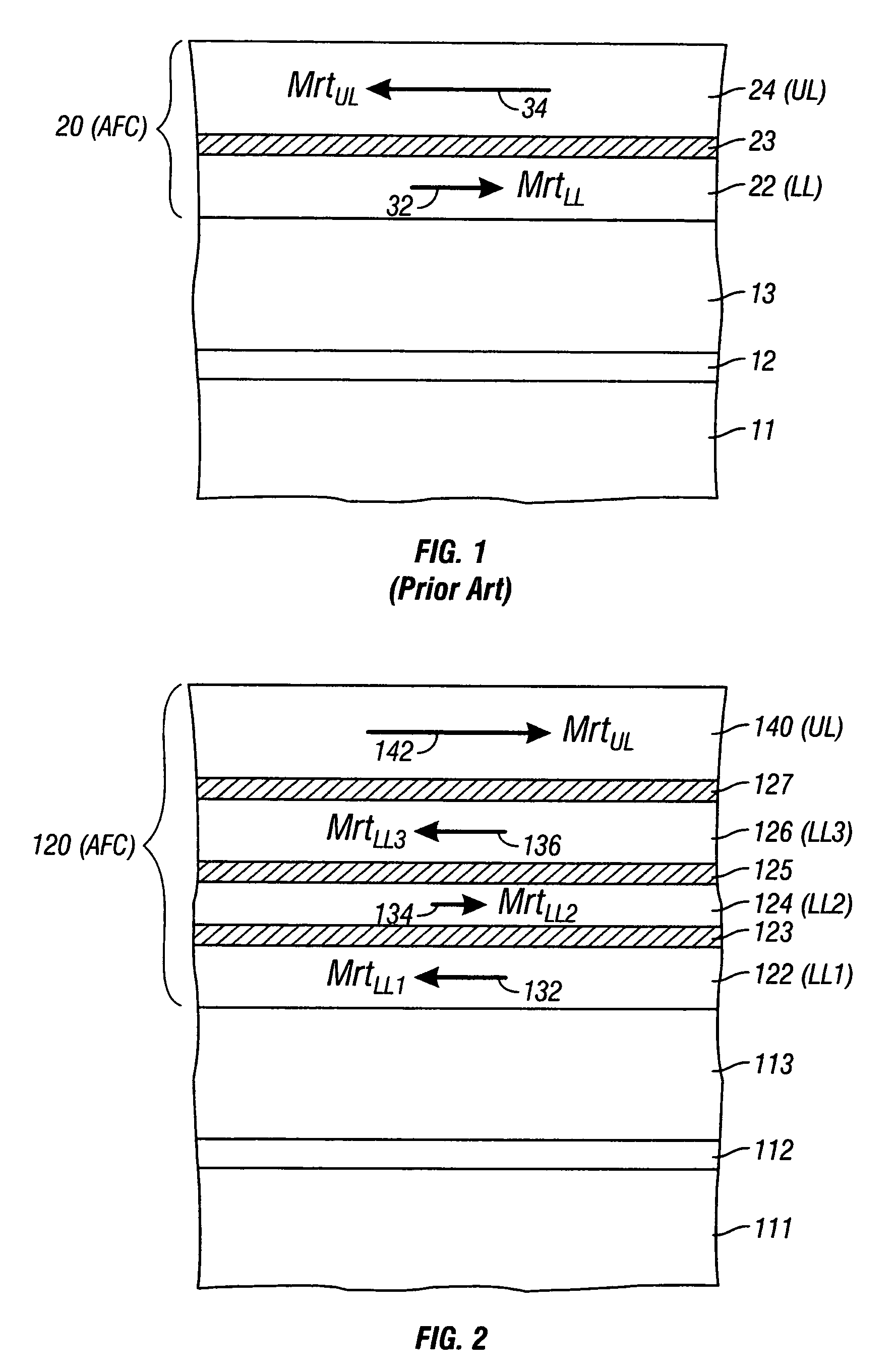
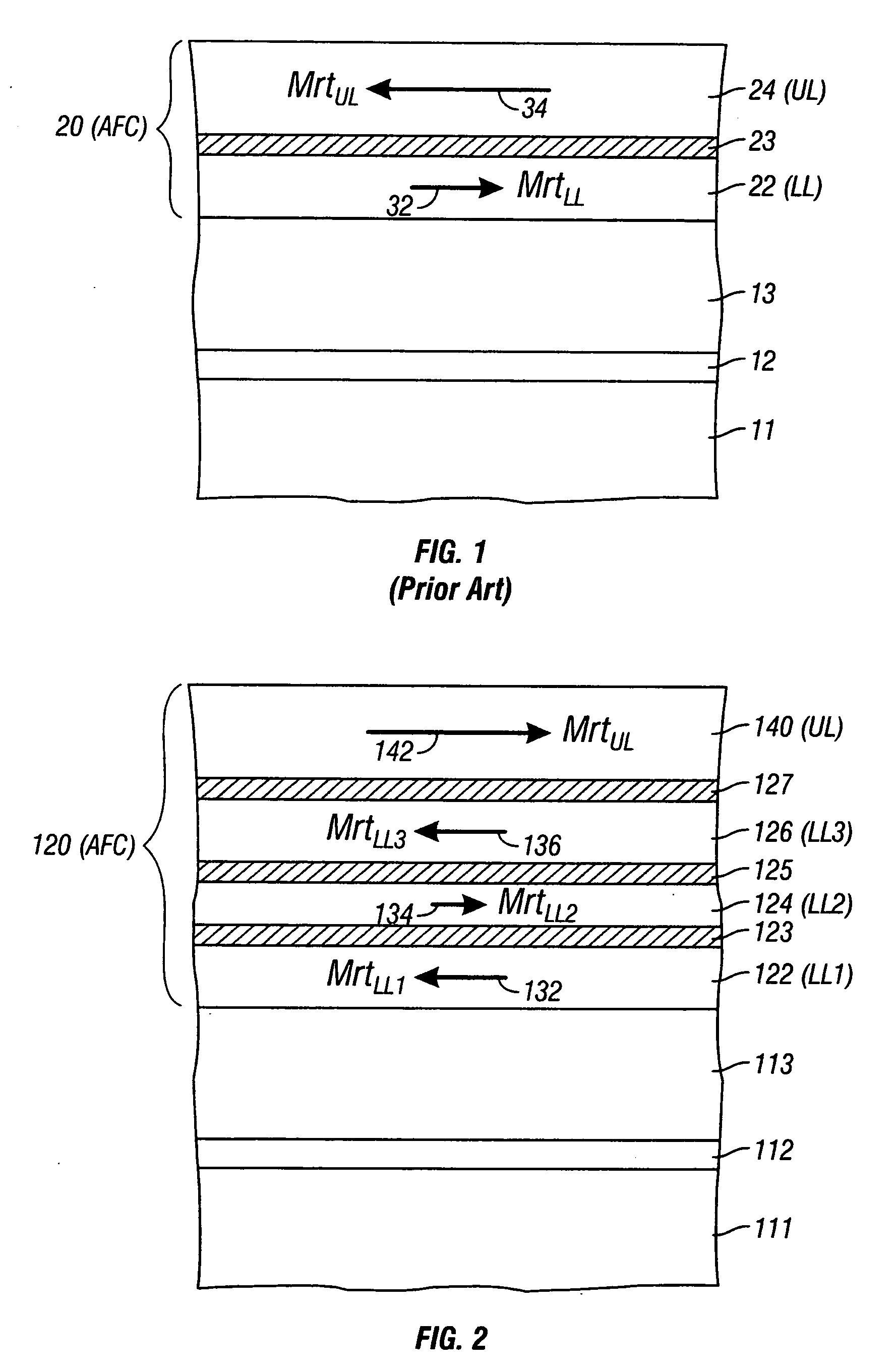
A magnetic recording disk has an antiferromagnetically-coupled (AFC) structure that has an upper ferromagnetic layer (UL), and a lower ferromagnetic layer structure formed of two ferromagnetically-coupled lower layers (LL1, LL2). The UL is antiferromagnetically-coupled to the lower layer structure across an antiferromagnetically-coupling layer. LL1 and LL2 are ferromagnetically coupled across a ferromagnetic coupling layer so the magnetizations of LL1 and LL2 remain parallel in each remanent magnetic state, but are antiparallel to the magnetization of the UL in each remanent magnetic state. The UL has an Mrt greater than the sum of the Mrt values of LL1 and LL2.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Electronic equipment and operation control method for electronic equipment
An electronic unit that is permitted to undergo operation control on the basis of a timer reservation set by a user includes a setting section for setting a time designated by the user, an operation control section for controlling the operation of the electronic unit in accordance with time set by the setting section, a display section for displaying an operation portion for operating the electronic unit, a display control section such that when the electronic unit is operative in accordance with the operation control section, it controls the display section so that a specific display is carried out on the display section, and a designation detecting section for detecting a designation of the user with respect to the specific display, whereby when a designation of the user is detected by the designation detecting section, the operation control section conducts a control to neglect the time set by the setting section and to continue the operation of the electronic unit when the designation of the user is detected.
Owner:SONY CORP
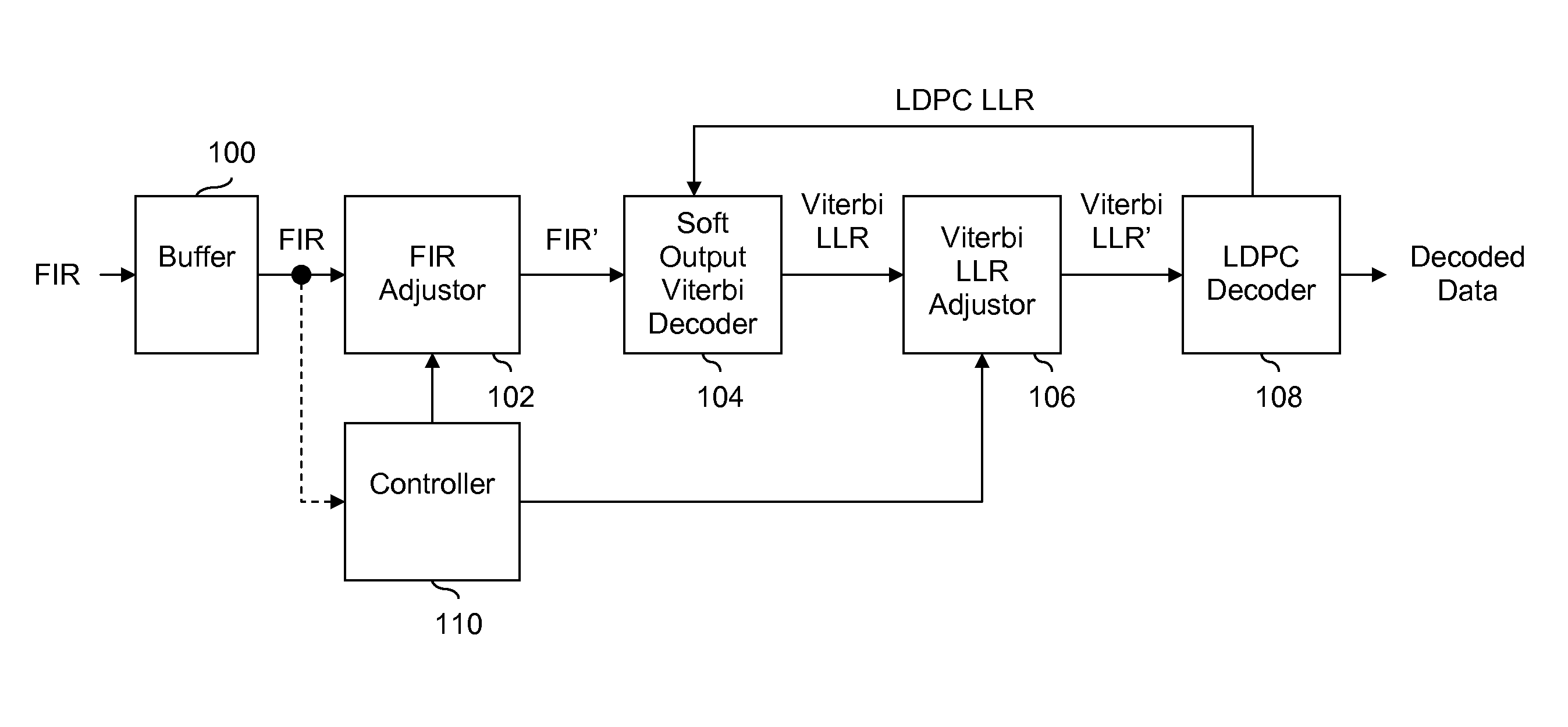
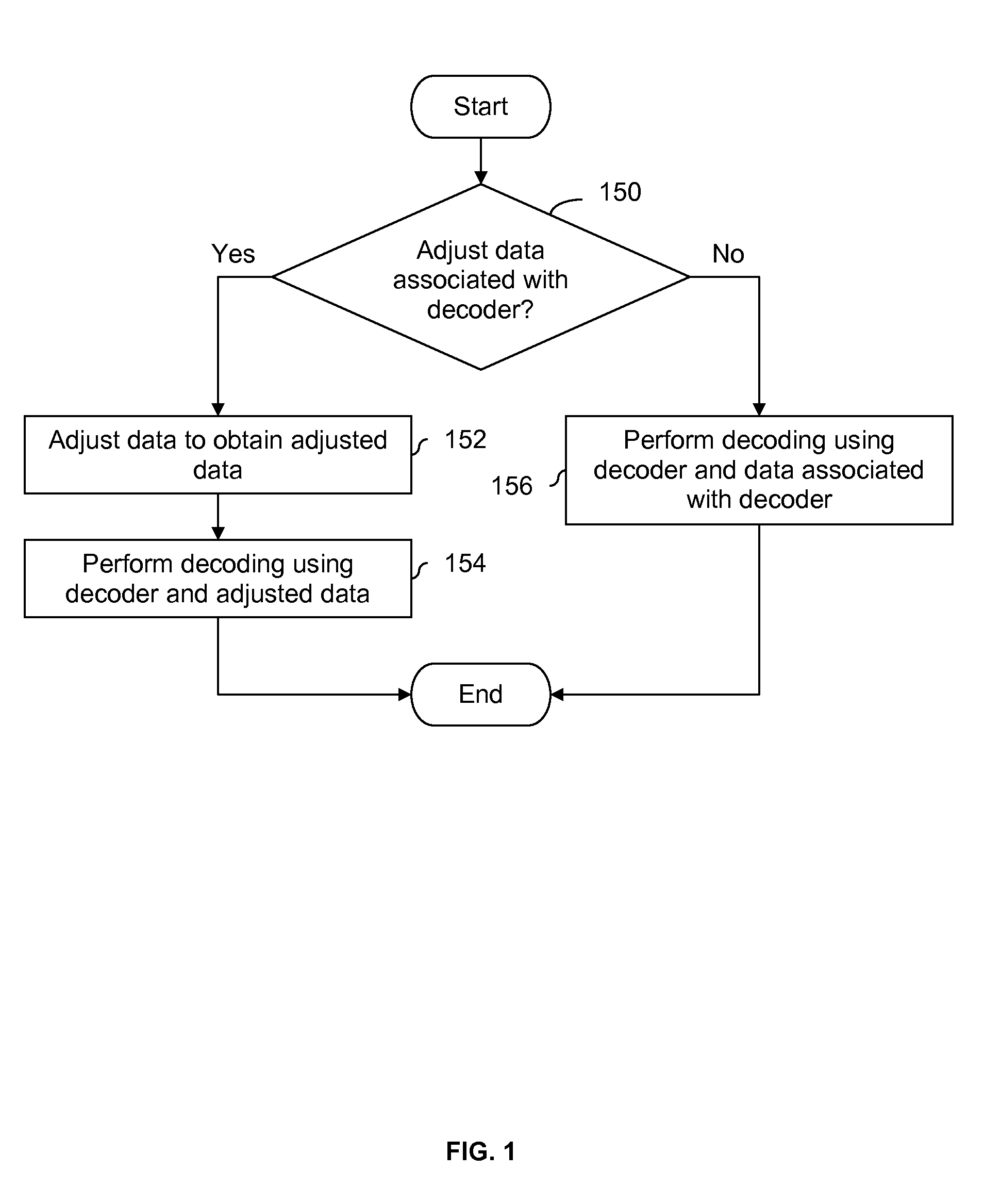
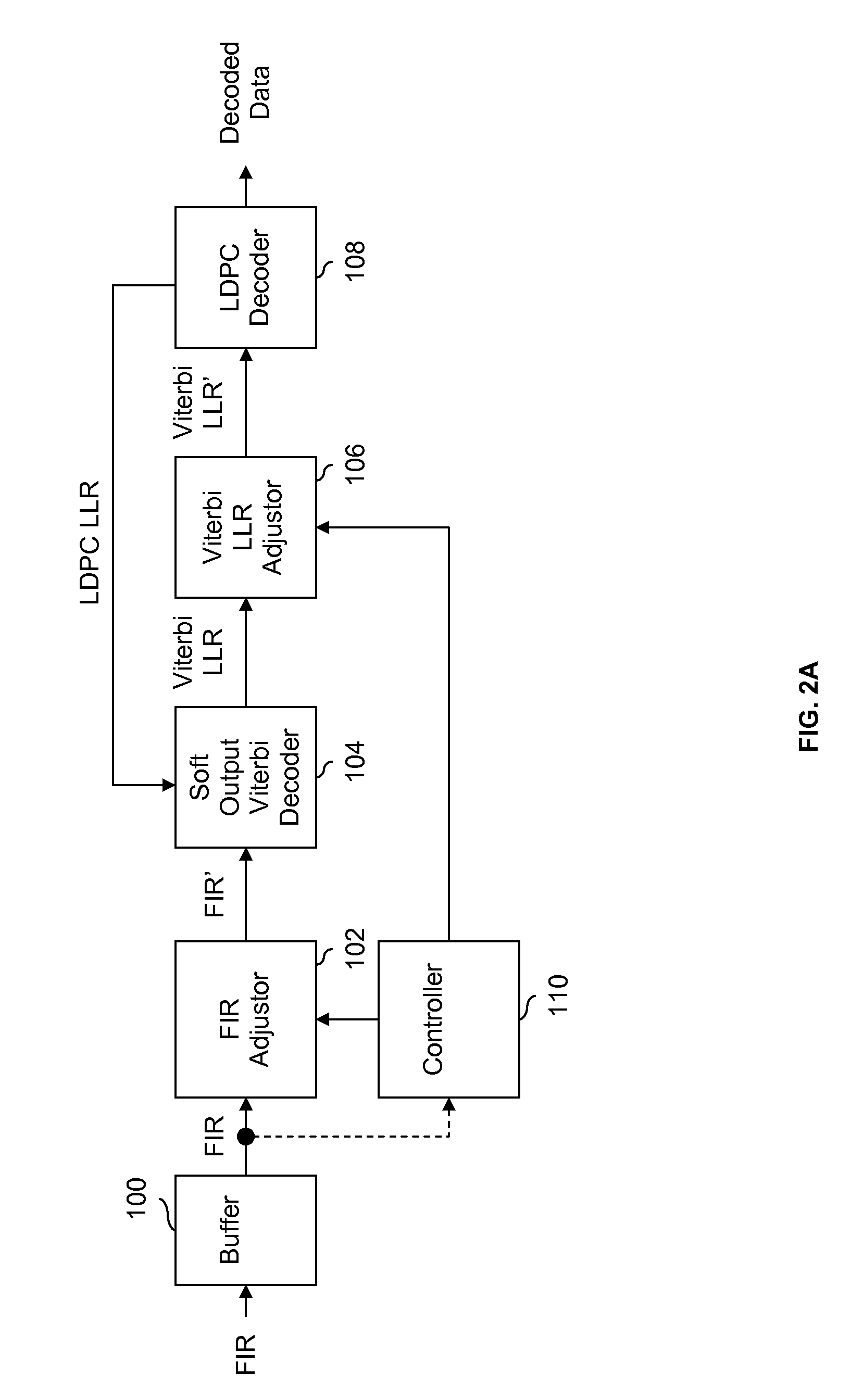
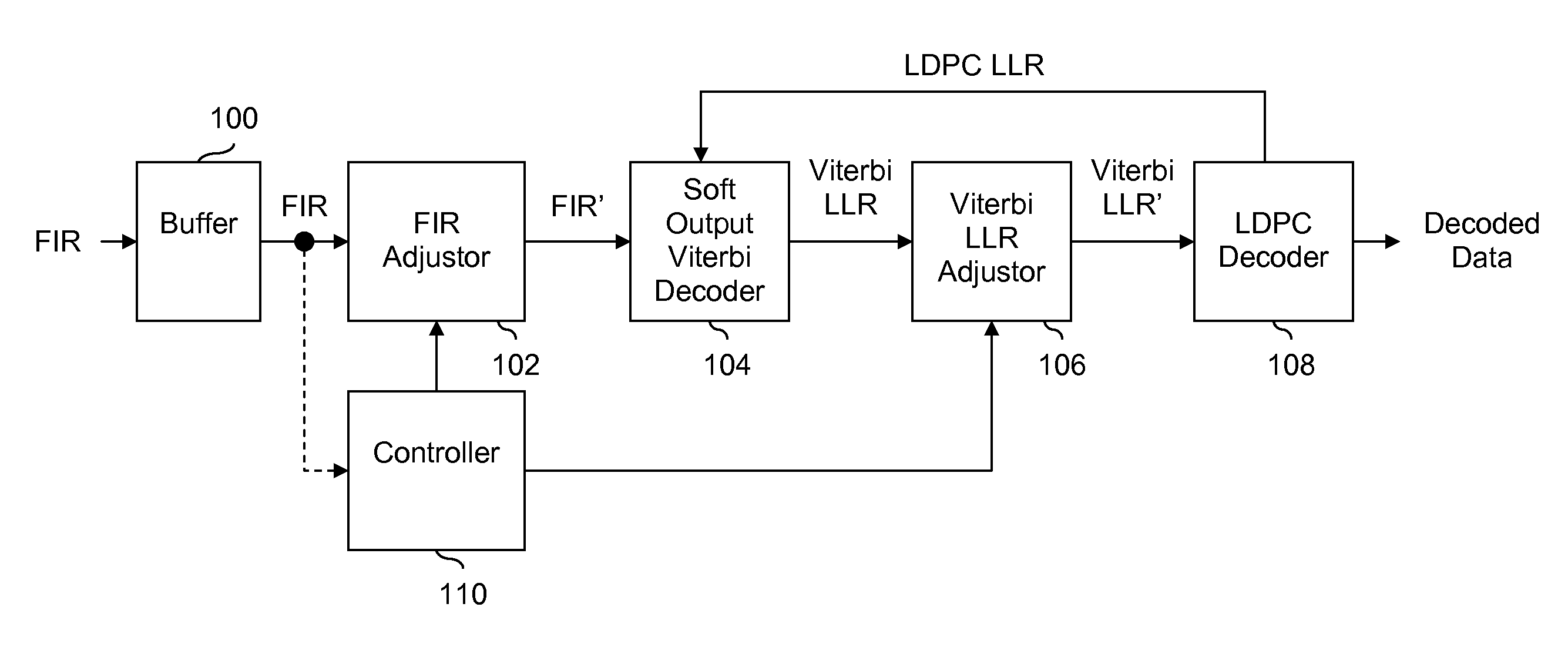
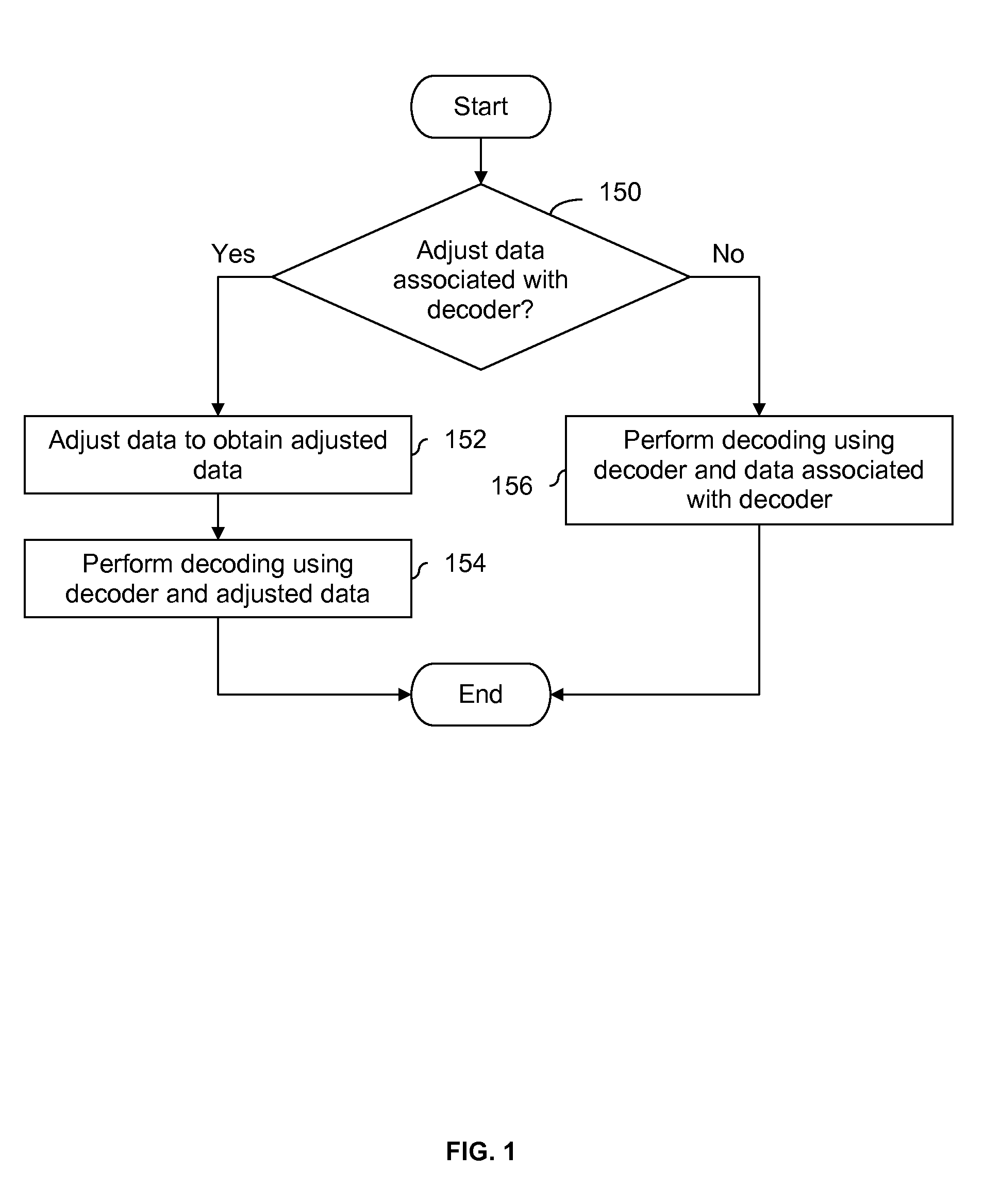
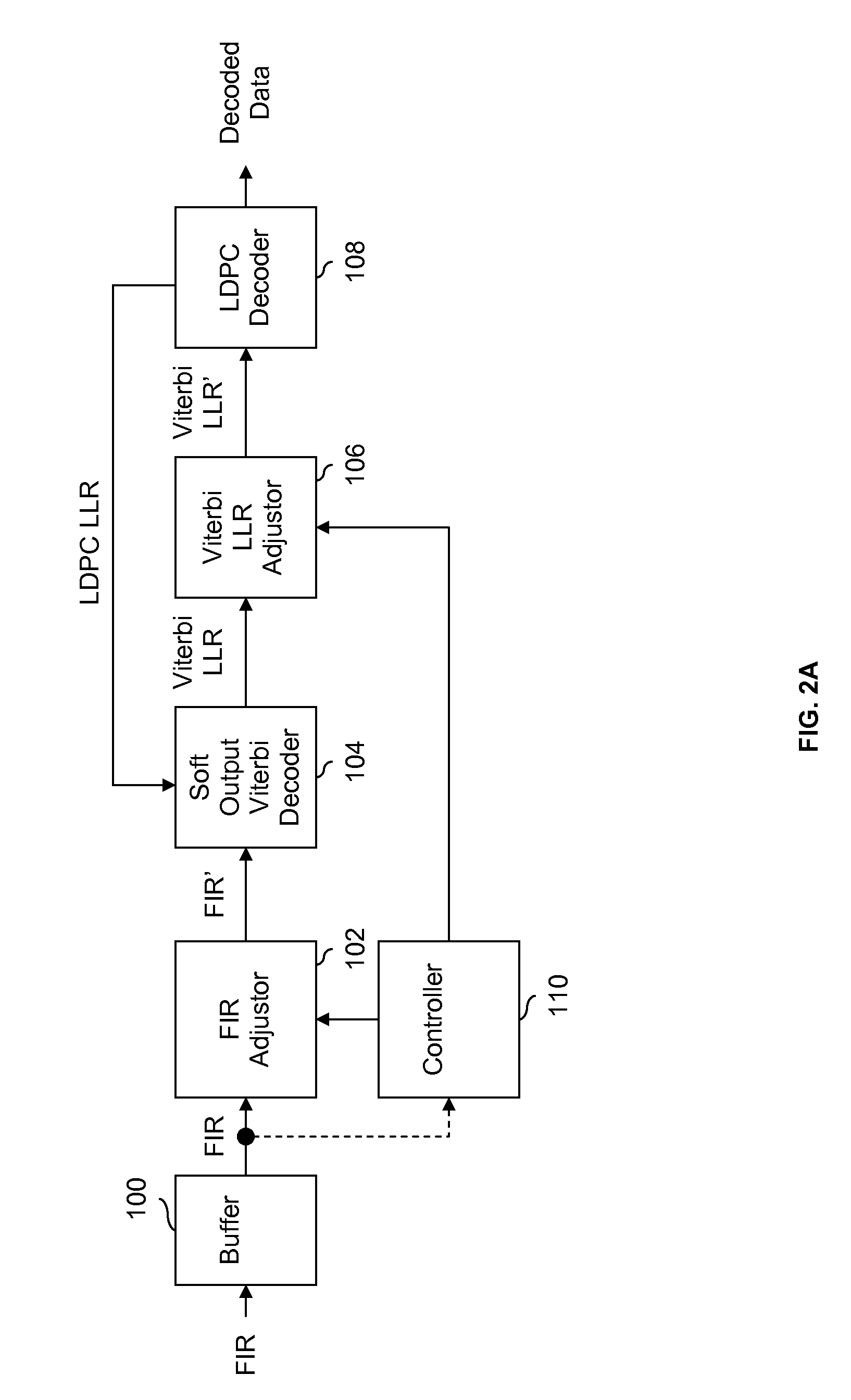
LDPC decoding with on the fly error recovery
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
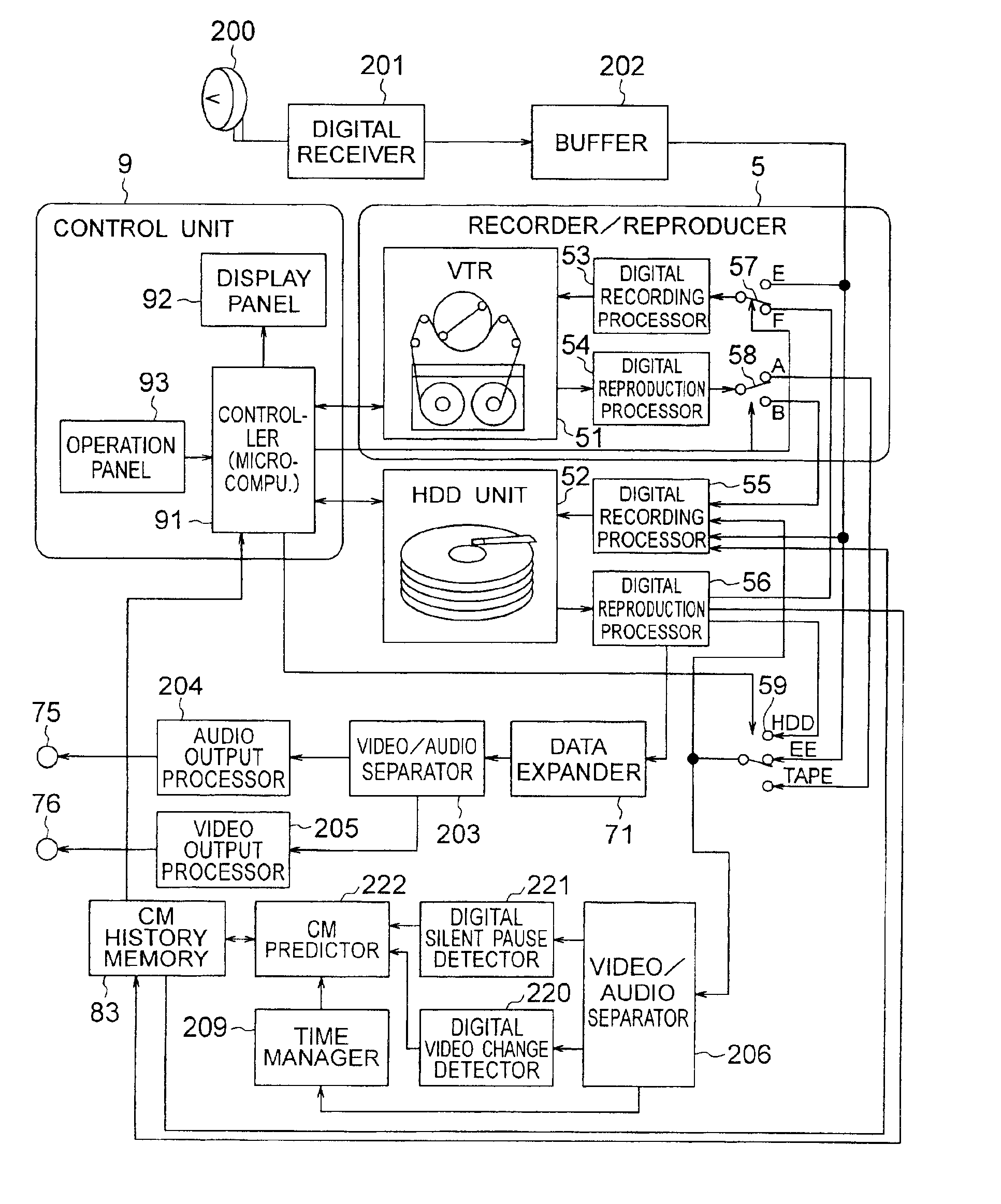
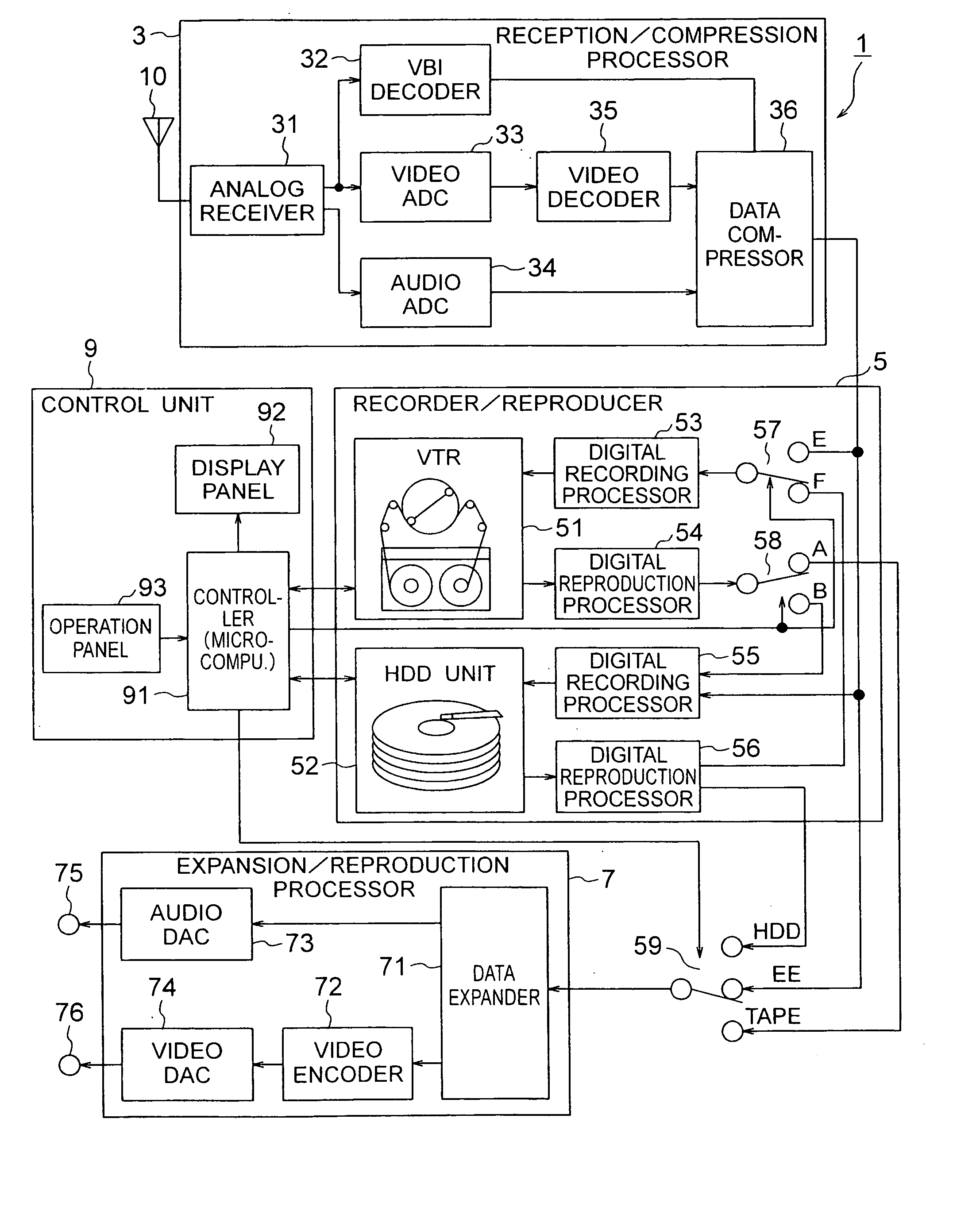
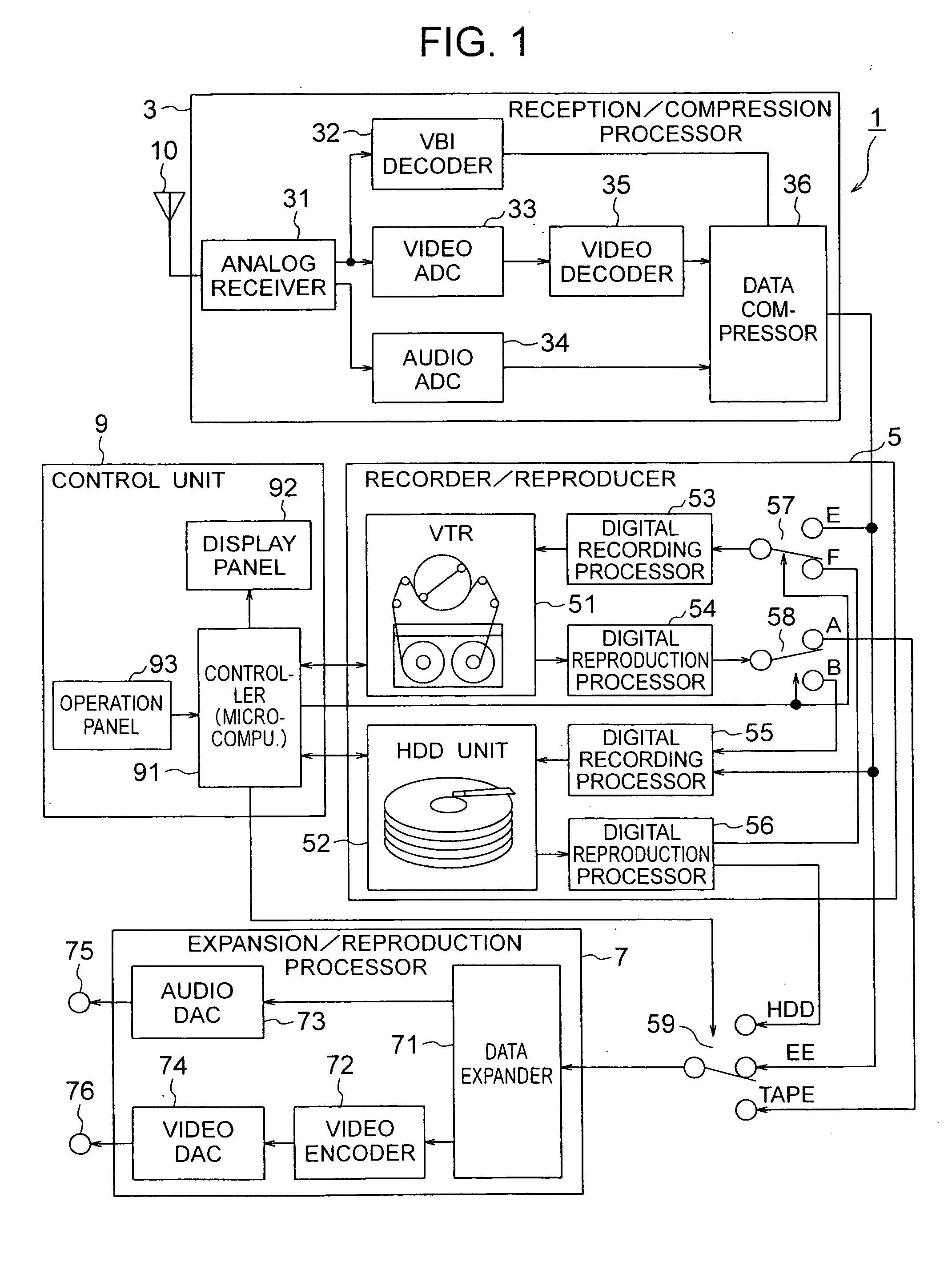
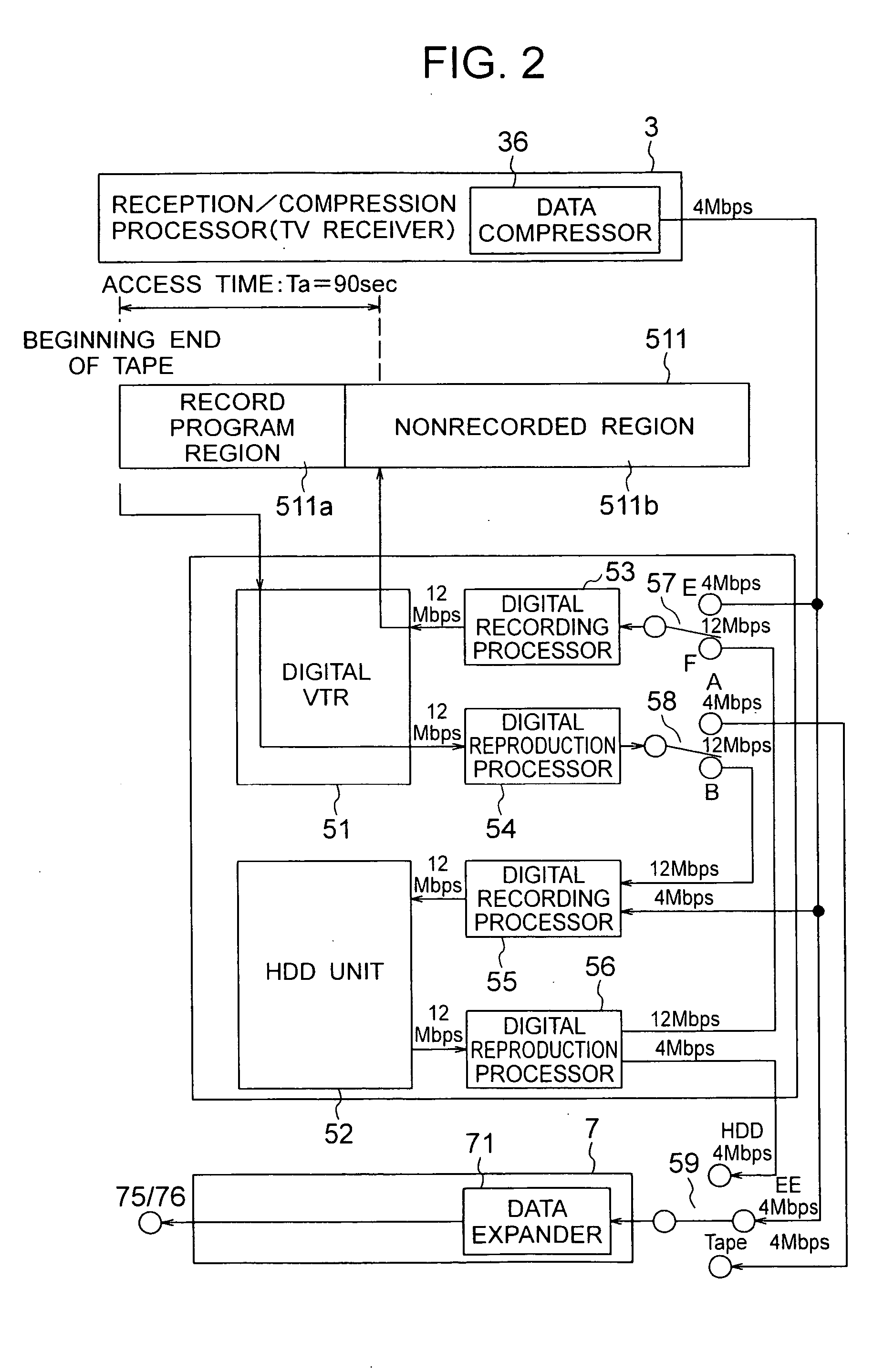
Recorder/reproducer
InactiveUS6987924B1Improve usabilityEfficient preparationTelevision system detailsMagnetic discsComputer scienceSignal processing
A recorder / reproducer for recording and reproducing signals such as video and audio signals has first and second recording media. When an input signal is recorded on the first recording medium, it is once recorded on the second recording medium, and a certain time later it is transferred to the first recording medium, thus recorded thereon. During this certain time, other signal processings are made, such as recording / reproduction of other signals and discrimination of commercials from the program itself. In addition, when a signal is reproduced from the first recording medium, the signal is once recorded on the second recording medium, and a certain time later reproduced and supplied, and thus similarly other processings can be made during this certain time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low-density parity check codes for holographic storage
InactiveUS20120233524A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHolographic discsError preventionHolographic storageParity-check matrix
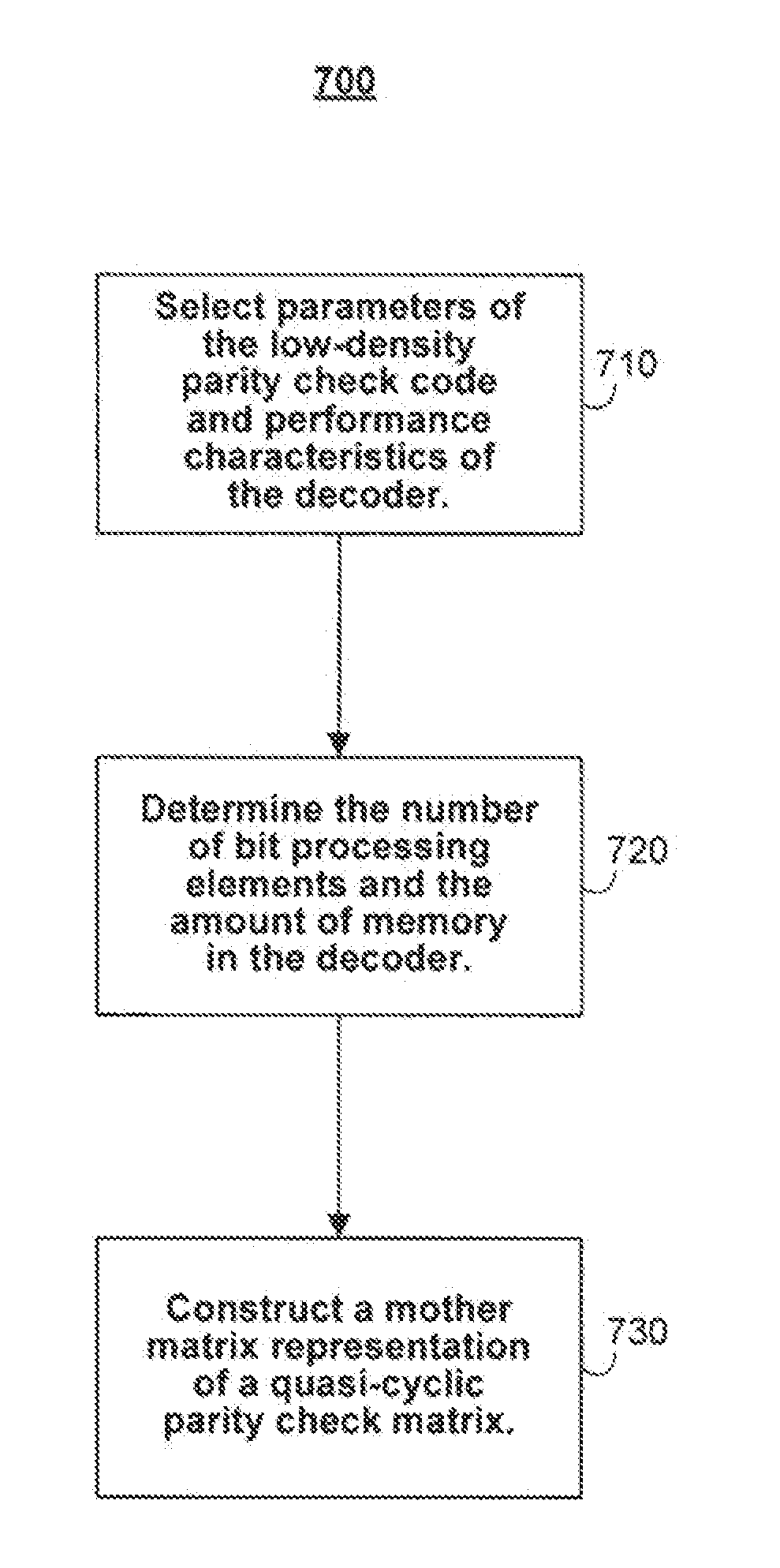
Systems and methods for constructing low-density parity check codes for holographic storage are provided. The methods include selecting parameters of a low-density parity check code, determining the number of bit processing elements and the amount of memory in an accompanying decoder, and constructing a mother matrix representation of a quasi-cyclic parity check matrix. The low-density parity check codes are optimized for performance, memory considerations, and throughput.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
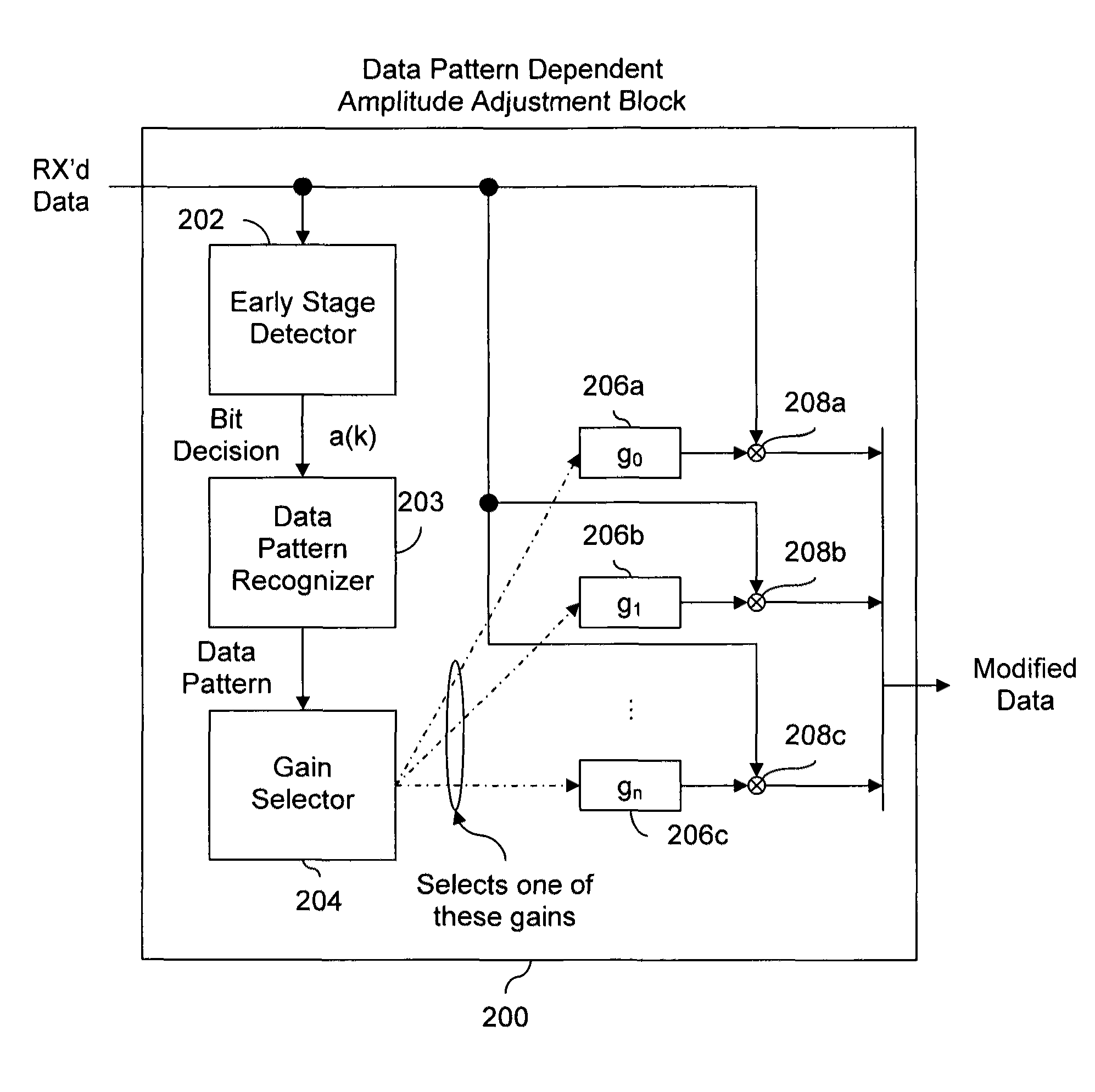
Data pattern dependent amplitude adjustment
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
Low-density parity check codes for holographic storage
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
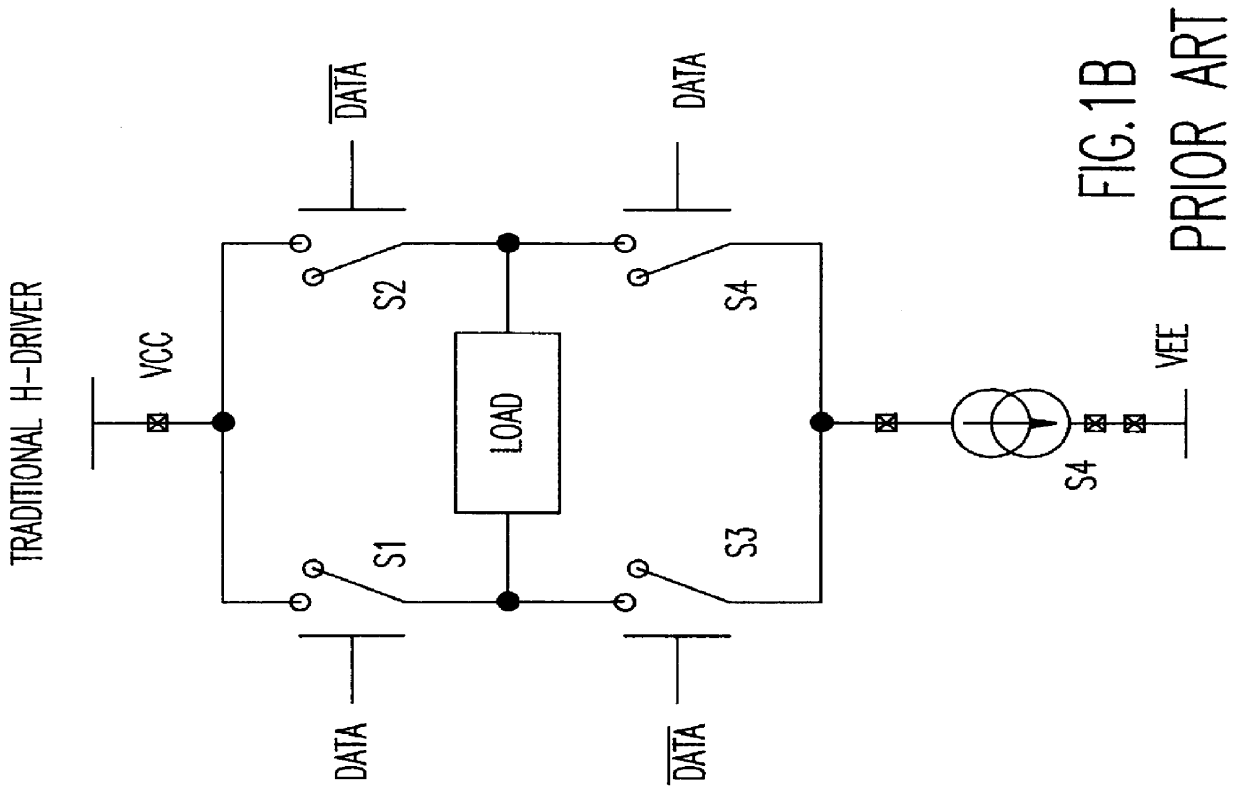
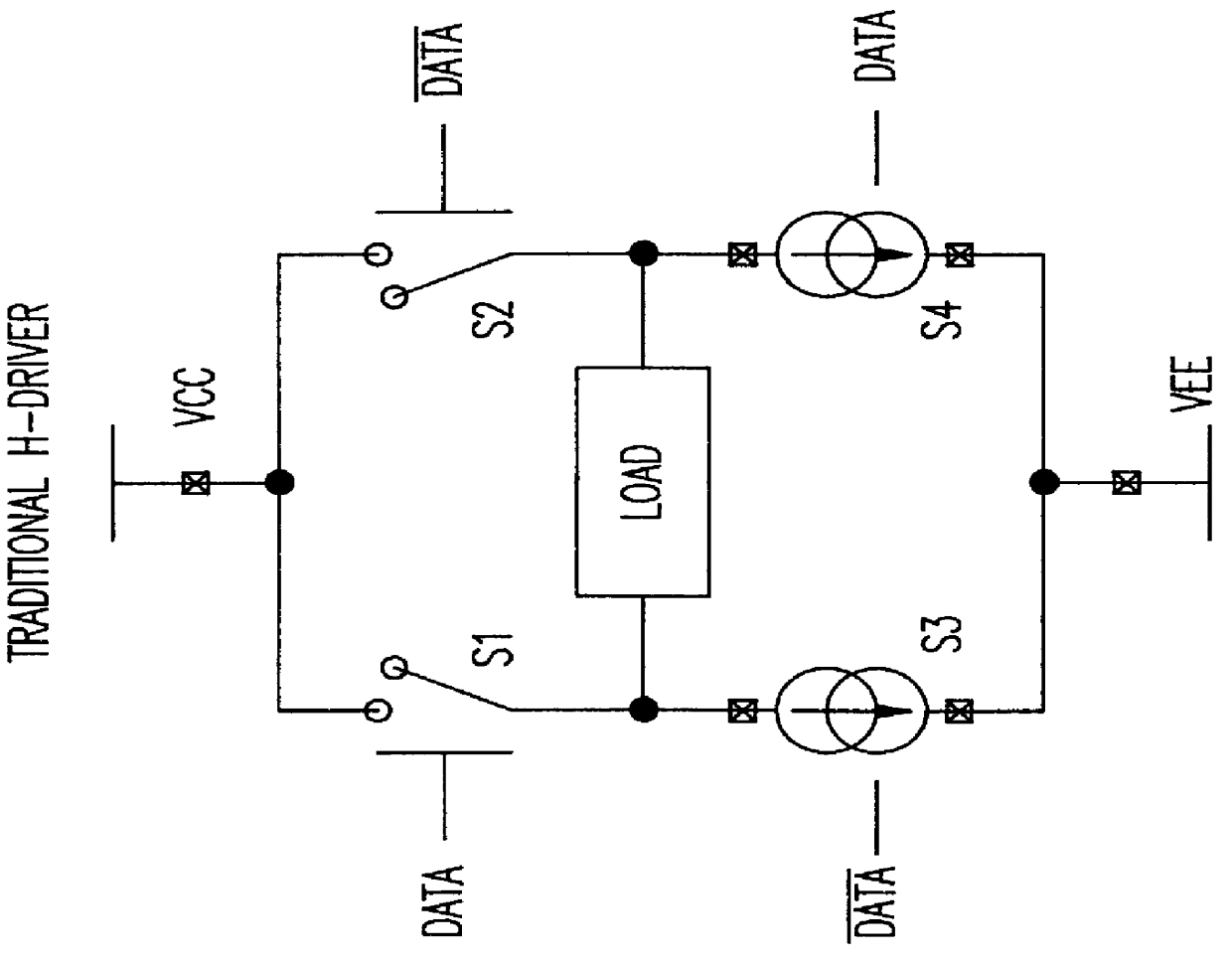
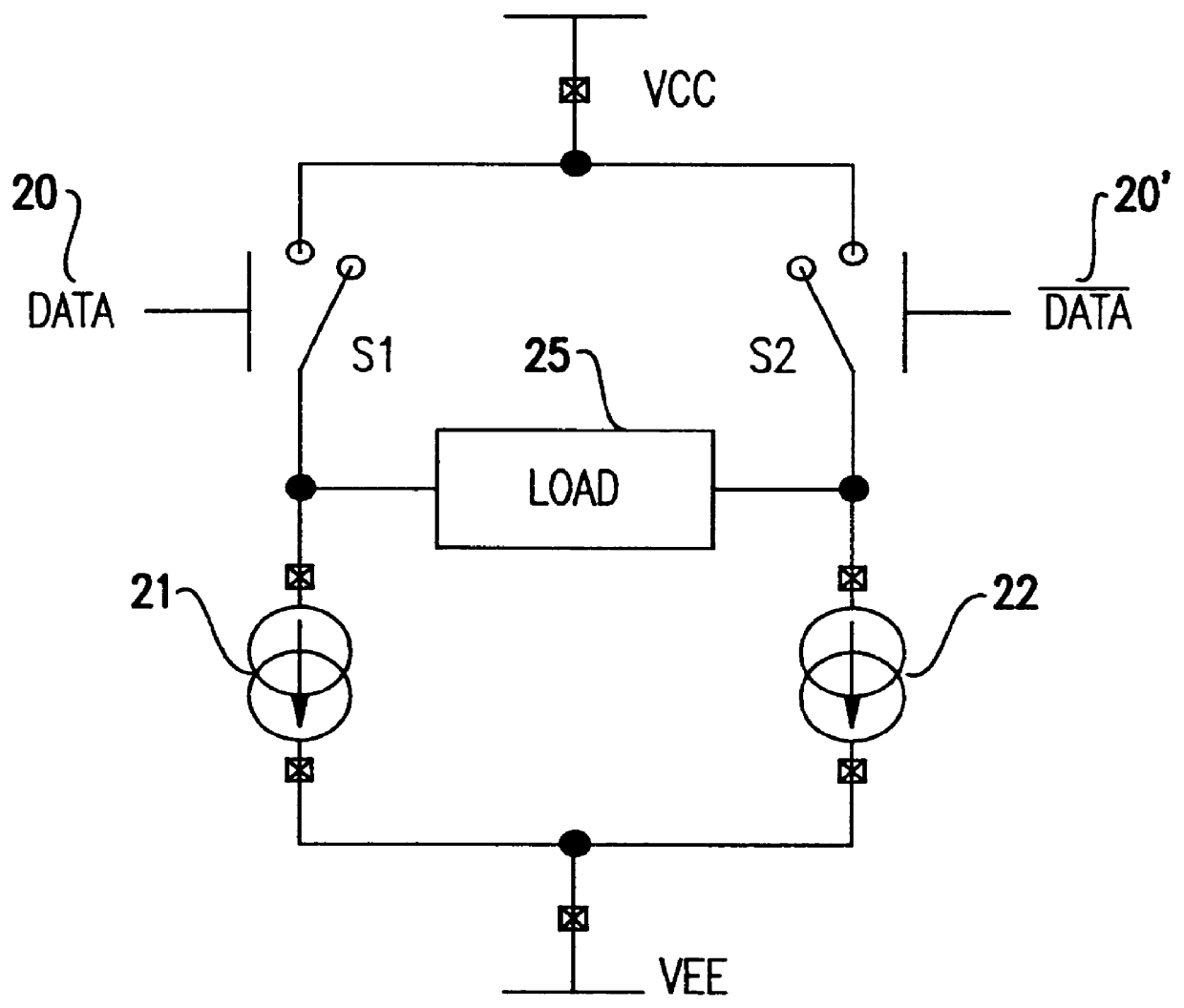
High speed write driver for magnetic inductive write head using a half-switched H-driver
Owner:IBM CORP
Testing method for a head IC
InactiveUS7051423B2Increase productionLow costElectrical transducersCarrier constructional parts dispositionElectricityEmbedded system
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
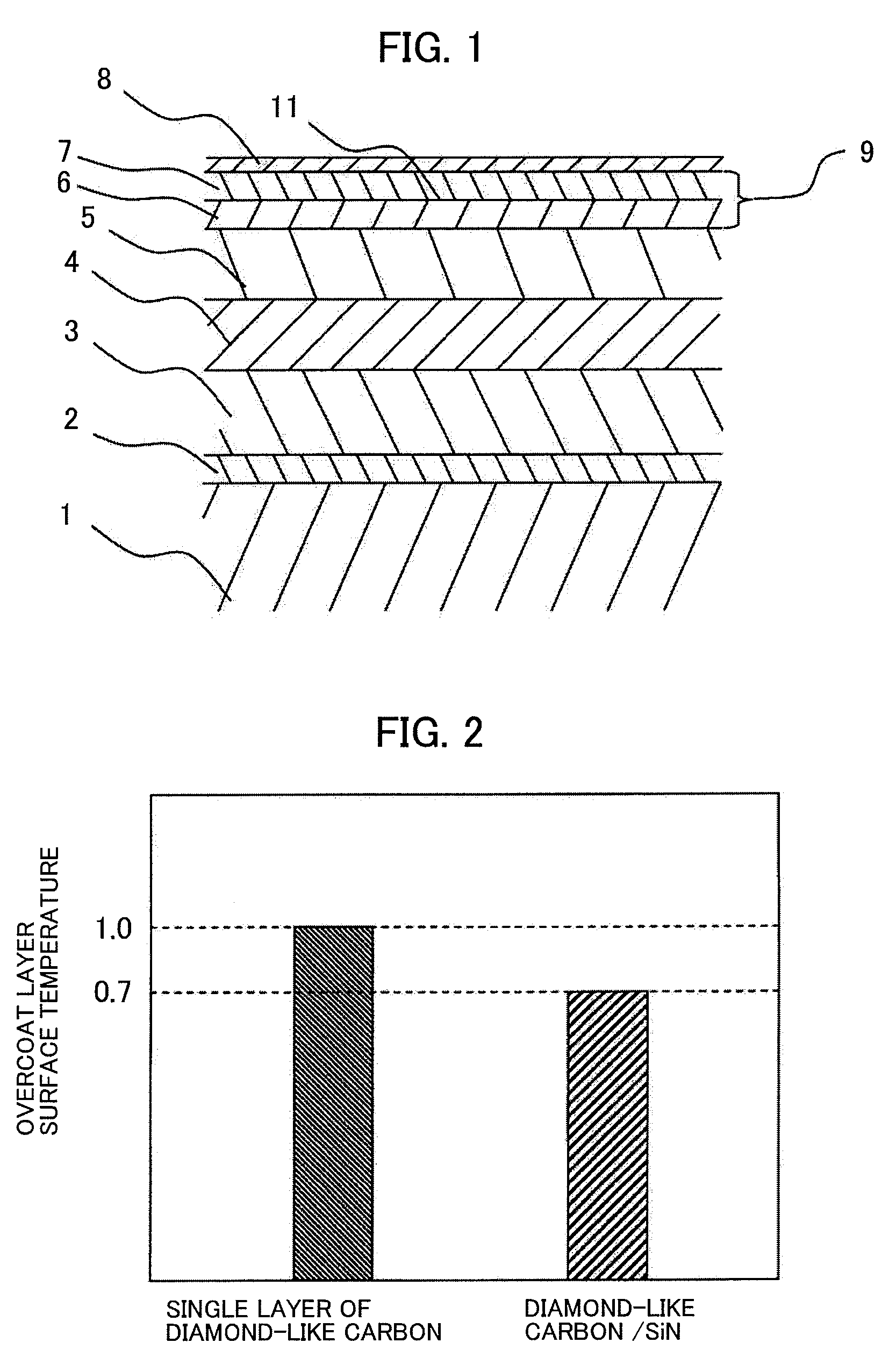
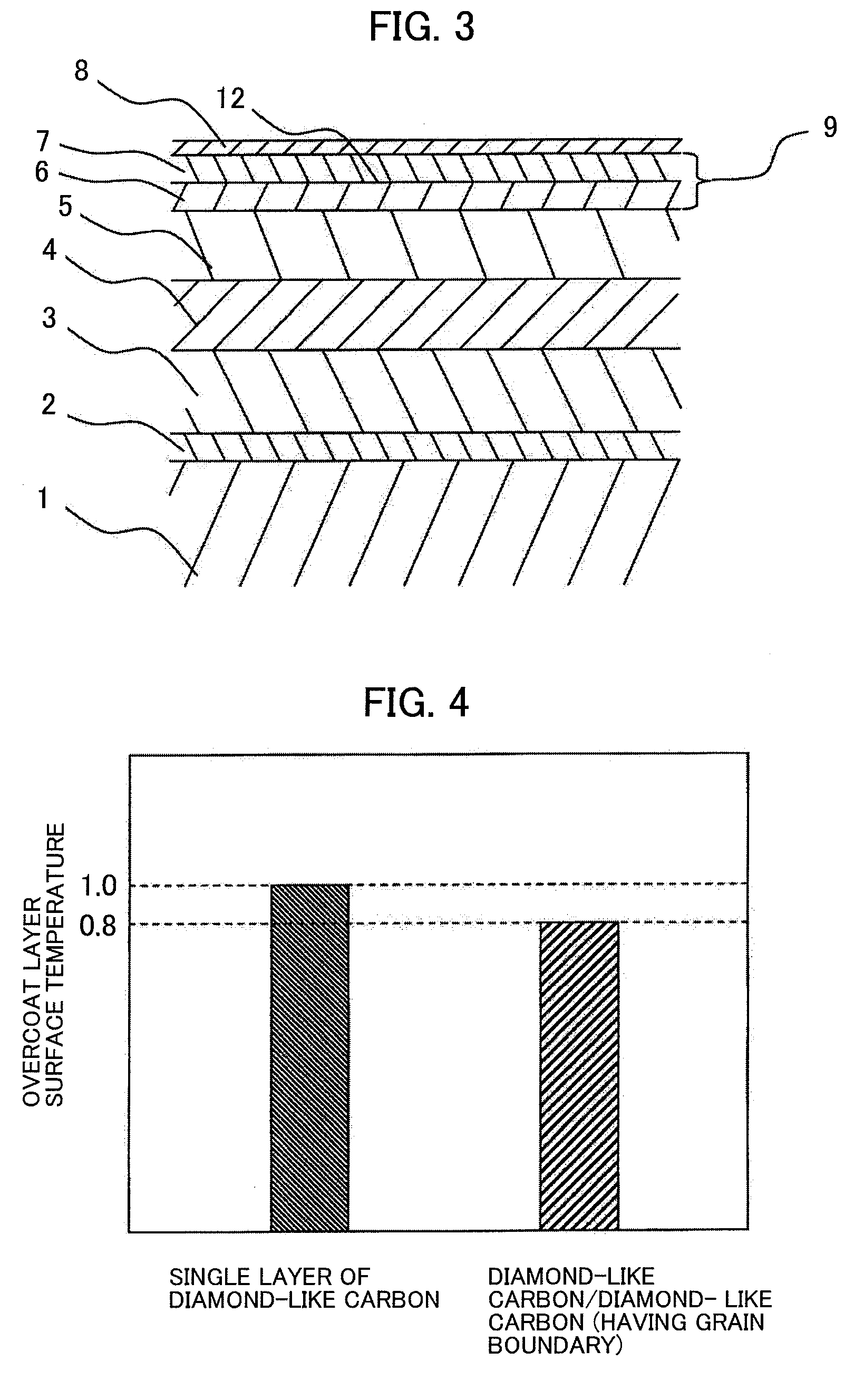
Magnetic disk for thermally assisted magnetic recording and magnetic disk applying the same therein
InactiveUS20090316289A1Improve heating efficiencyProtective coatings for layersMagnetic discsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A magnetic disk, comprises, a magnetic disk, a disk driving portion for driving the magnetic disk, a slider, mounting thereon a recording element and a reproducing element, for generating a recording magnetic field, and a heating element for use in generation a near field light, and a driver portion for positioning the slide above a desired track of the magnetic disk, wherein the magnetic disk has a recording layer, an overcoat layer formed on the recording layer, a lubricant provided on the overcoat layer, wherein the overcoat layer has a first overcoat film and a second overcoat film, which is formed on the first overcoat film, or has structure of laminating a plural number of overcoat films, and within an inside thereof are provided a plural number of interfaces between different materials and / or grain boundary surfaces.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
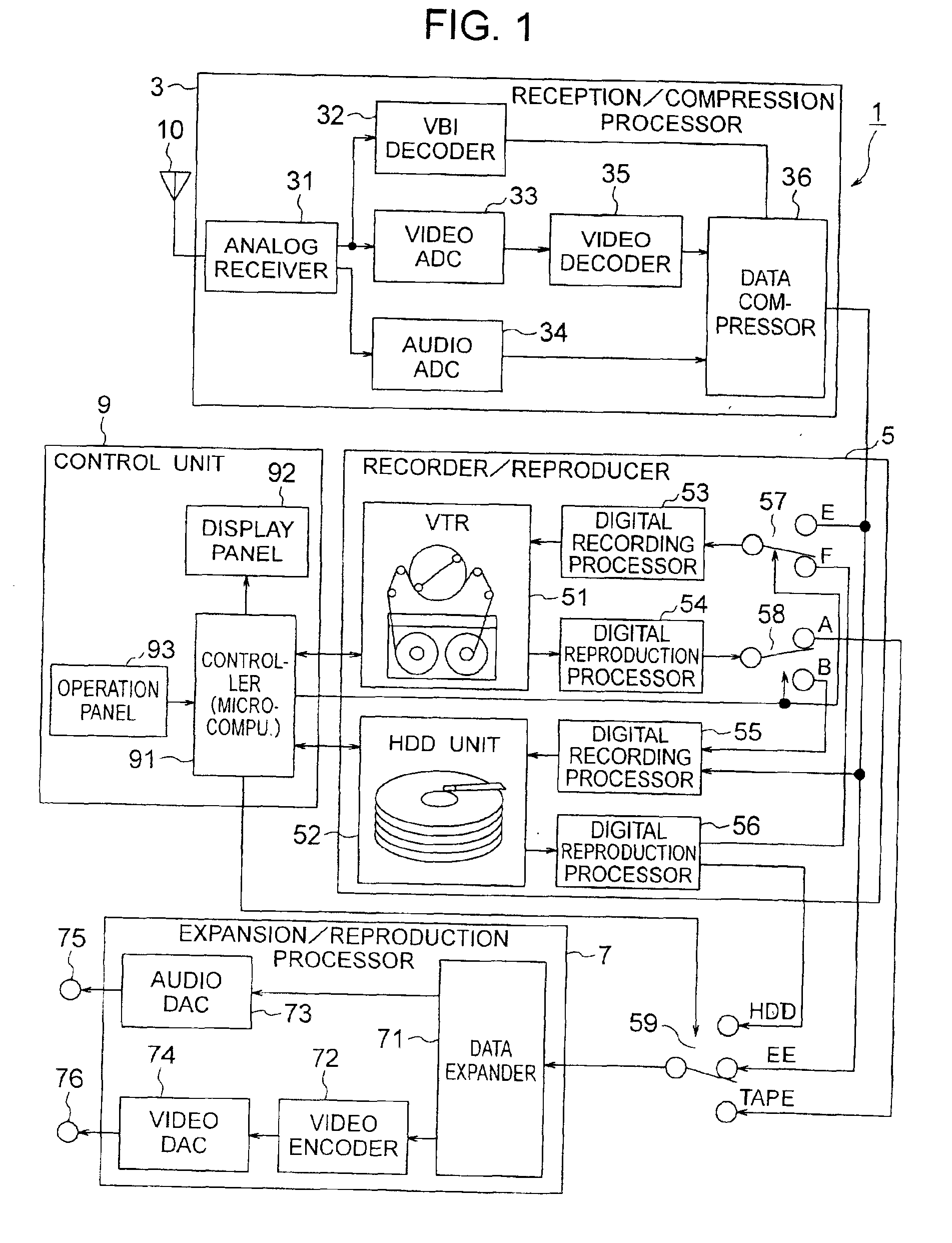
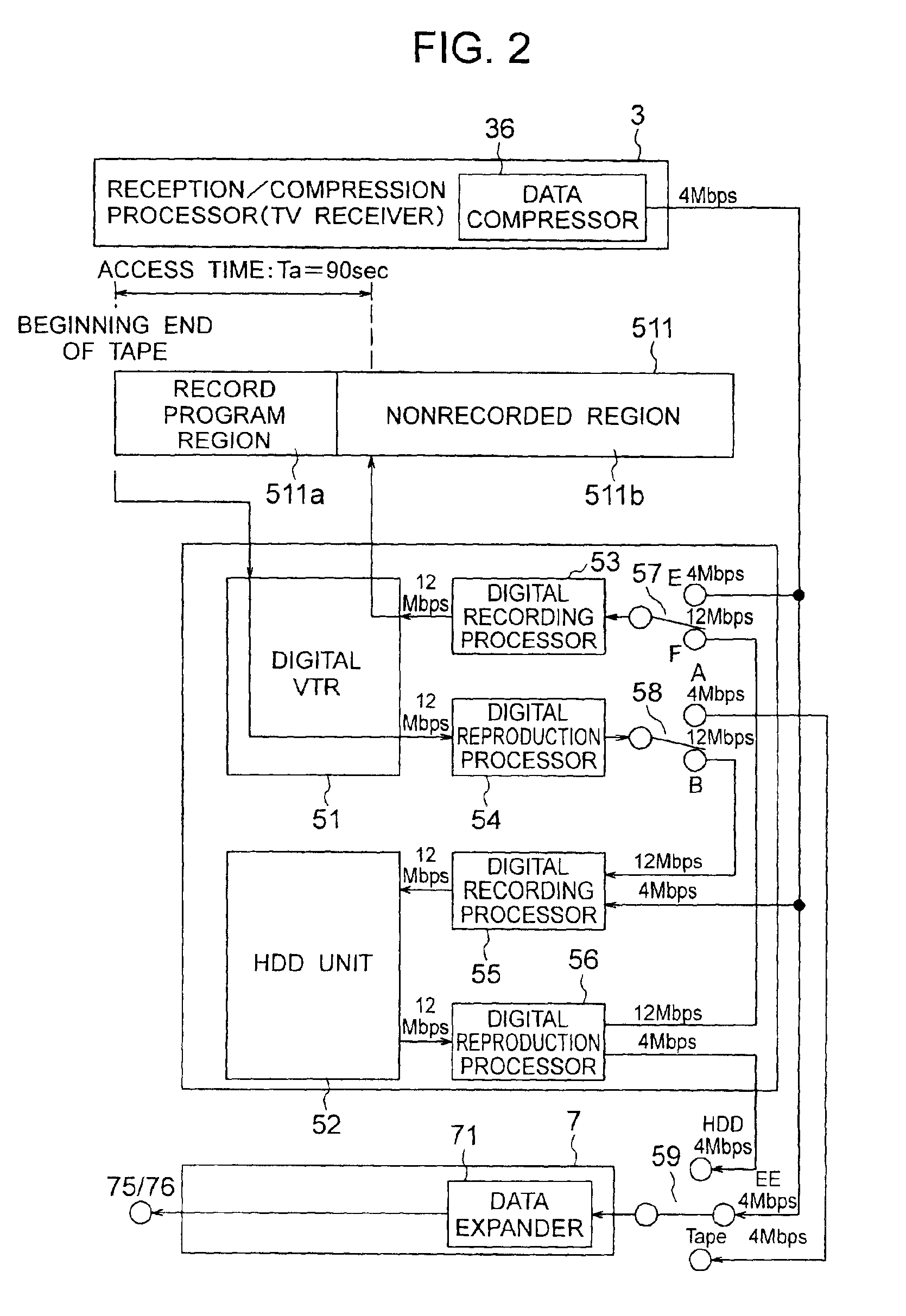
Recorder/reproducer
InactiveUS20050201721A1Efficient preparationEfficient data processingTelevision system detailsMagnetic discsComputer hardware
A recorder / reproducer for recording and reproducing signals includes a receiver which receives signals, a first recorder which records the signals received by the receiver on a first recording medium, and a first reproducer which reproduces the signals recorded on the first recording medium. A second recorder is provided which records the signals reproduced by the first reproducer on a second recording medium, a detector is provided which detects a commercial message portion from the signals recorded on the second recording medium, and a second reproducer is provided which reproduces the signals recorded on the second recording medium while excluding the commercial message portion detected by the detector.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
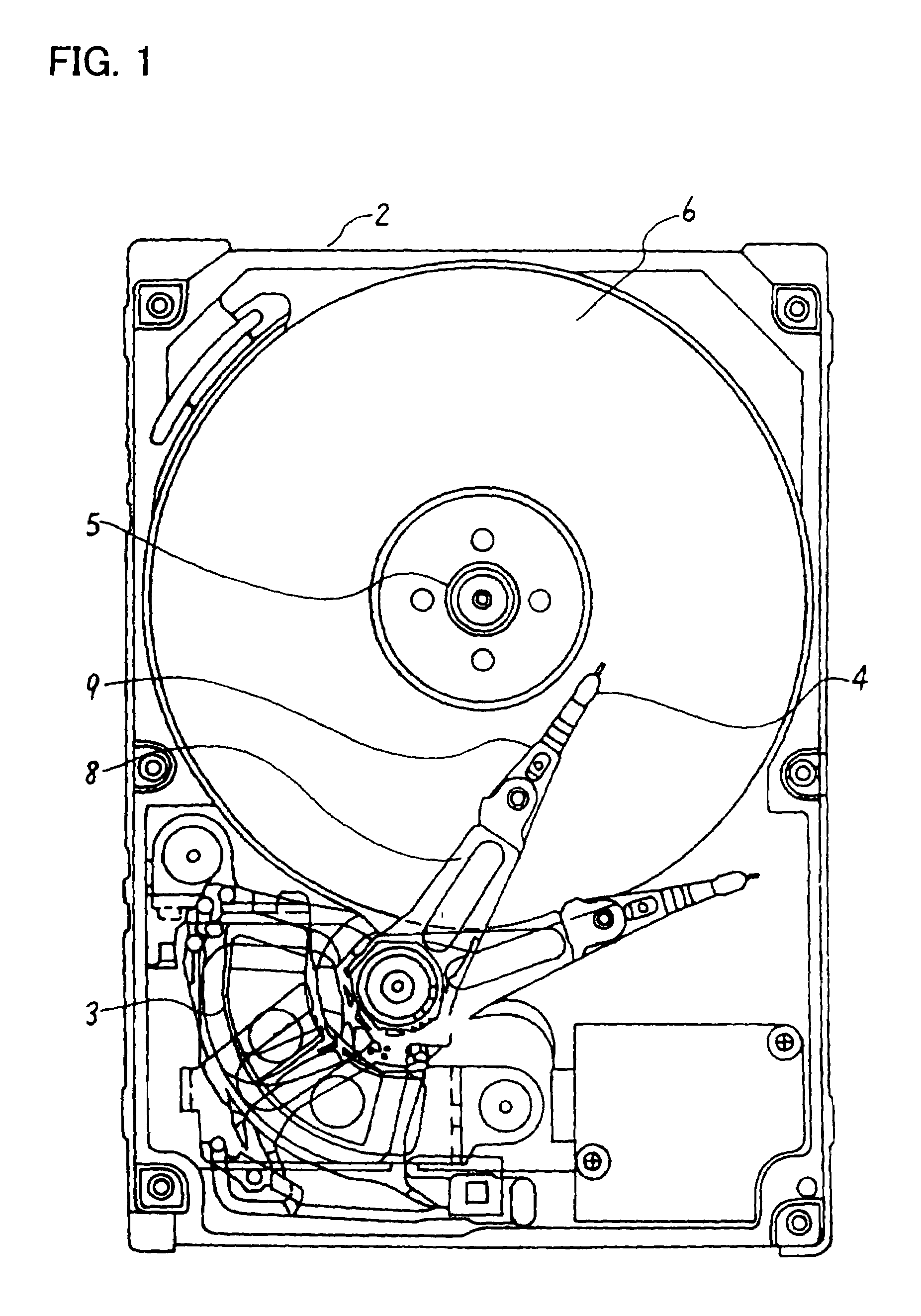
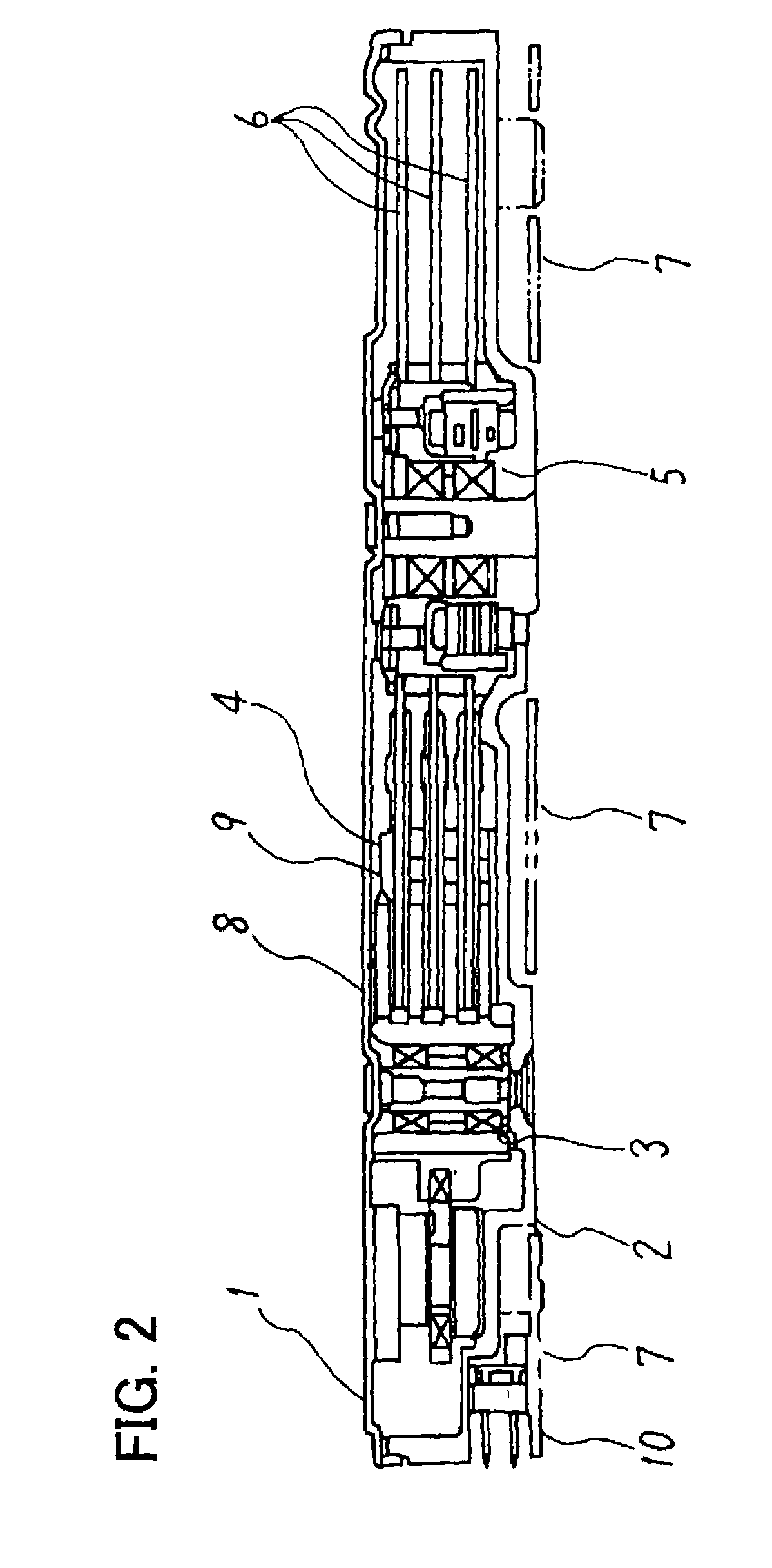
Disk device
InactiveUS6765752B2Efficient arrangementGenerate sufficient torqueCarrier constructional parts dispositionDriving/moving recording headsHard disc driveElectrical and Electronics engineering
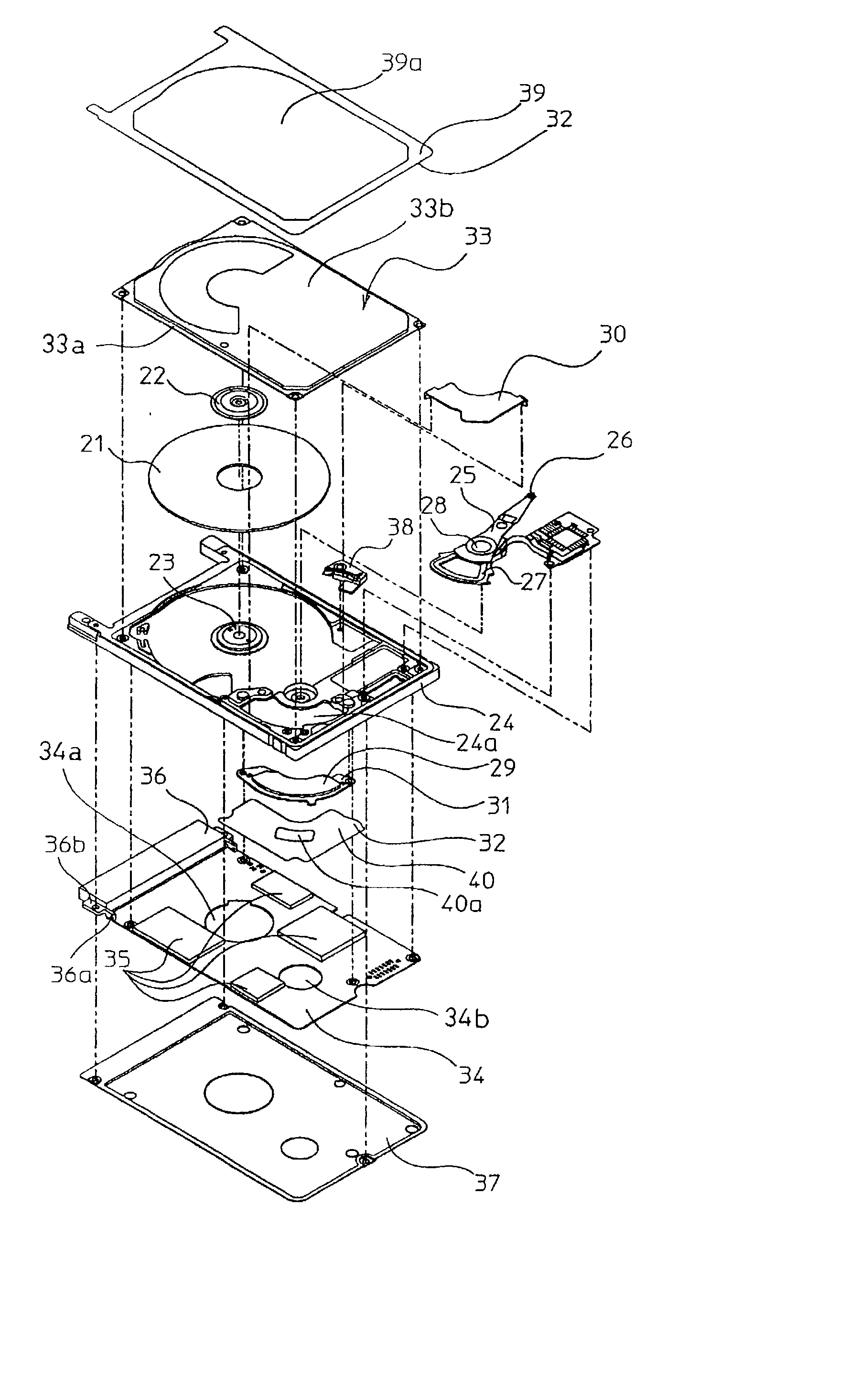
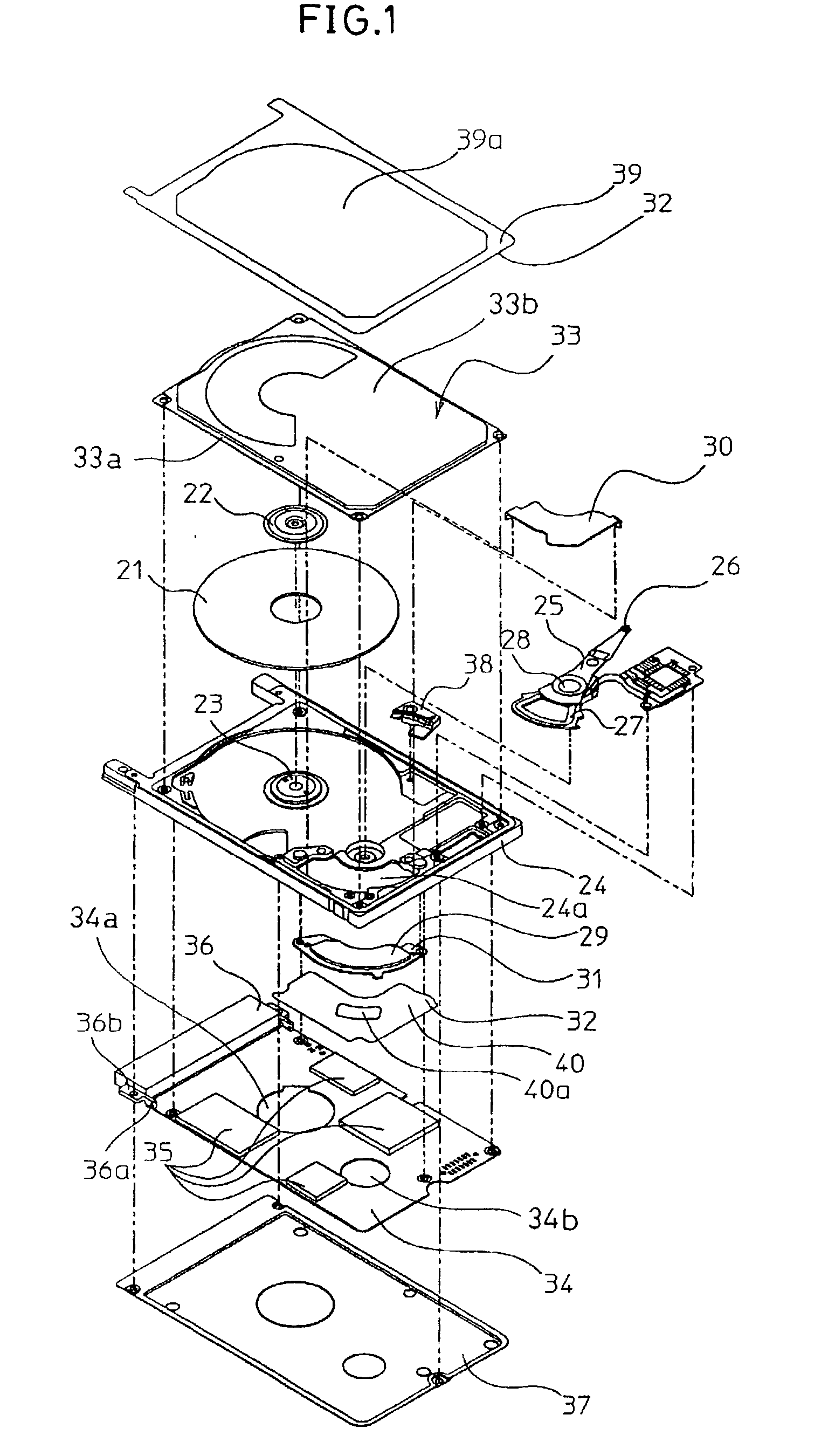
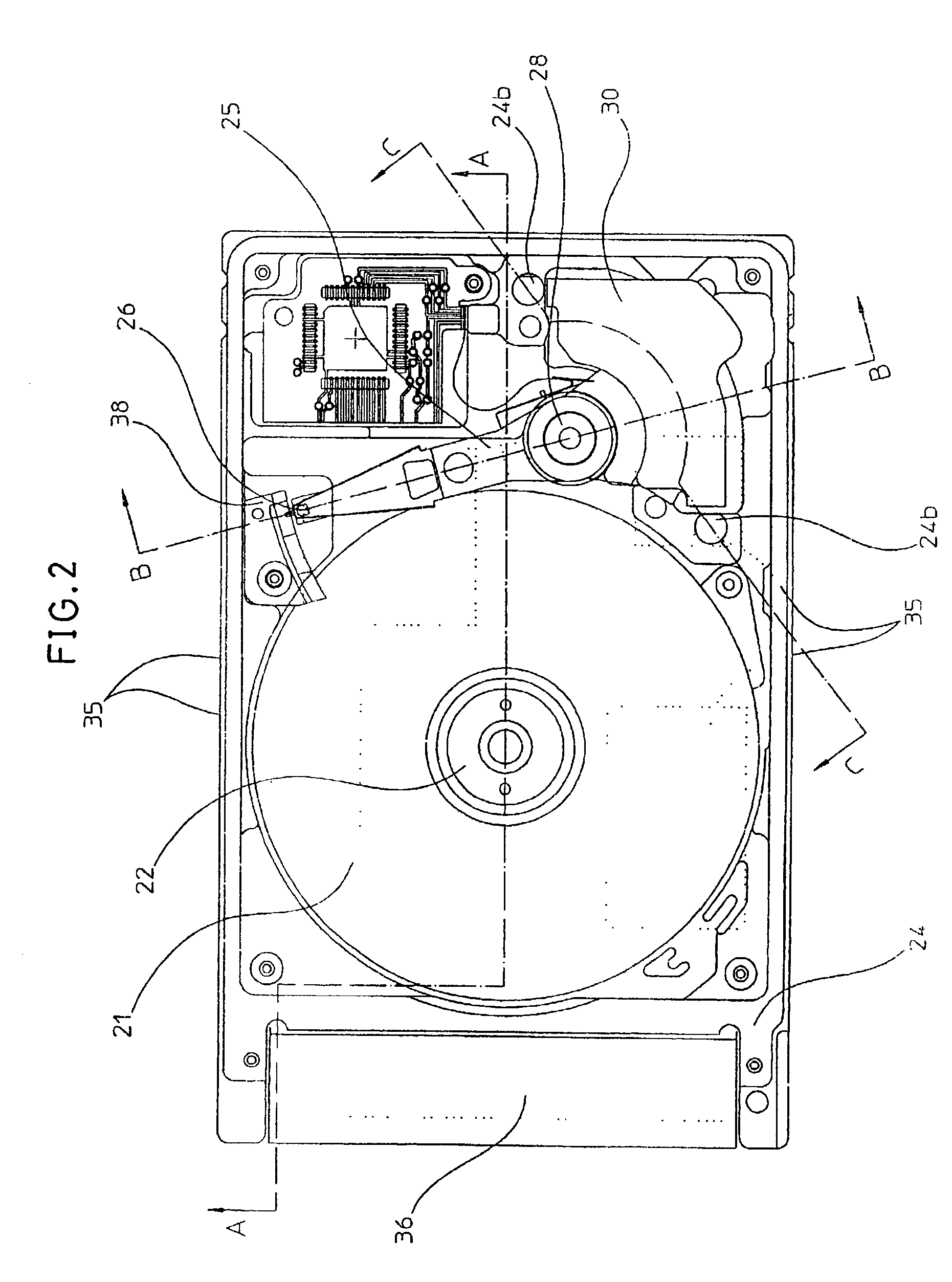
A disk device such as a magnetic hard disk drive. A disk is arranged inside a frame body. A cover is placed on the frame body, a gap is formed between a rim of the cover and the frame, and this gap is shielded by a sheet having an adhesive portion.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Magnetic recording disk with antiferromagnetically-coupled magnetic layer having multiple ferromagnetically-coupled lower layers
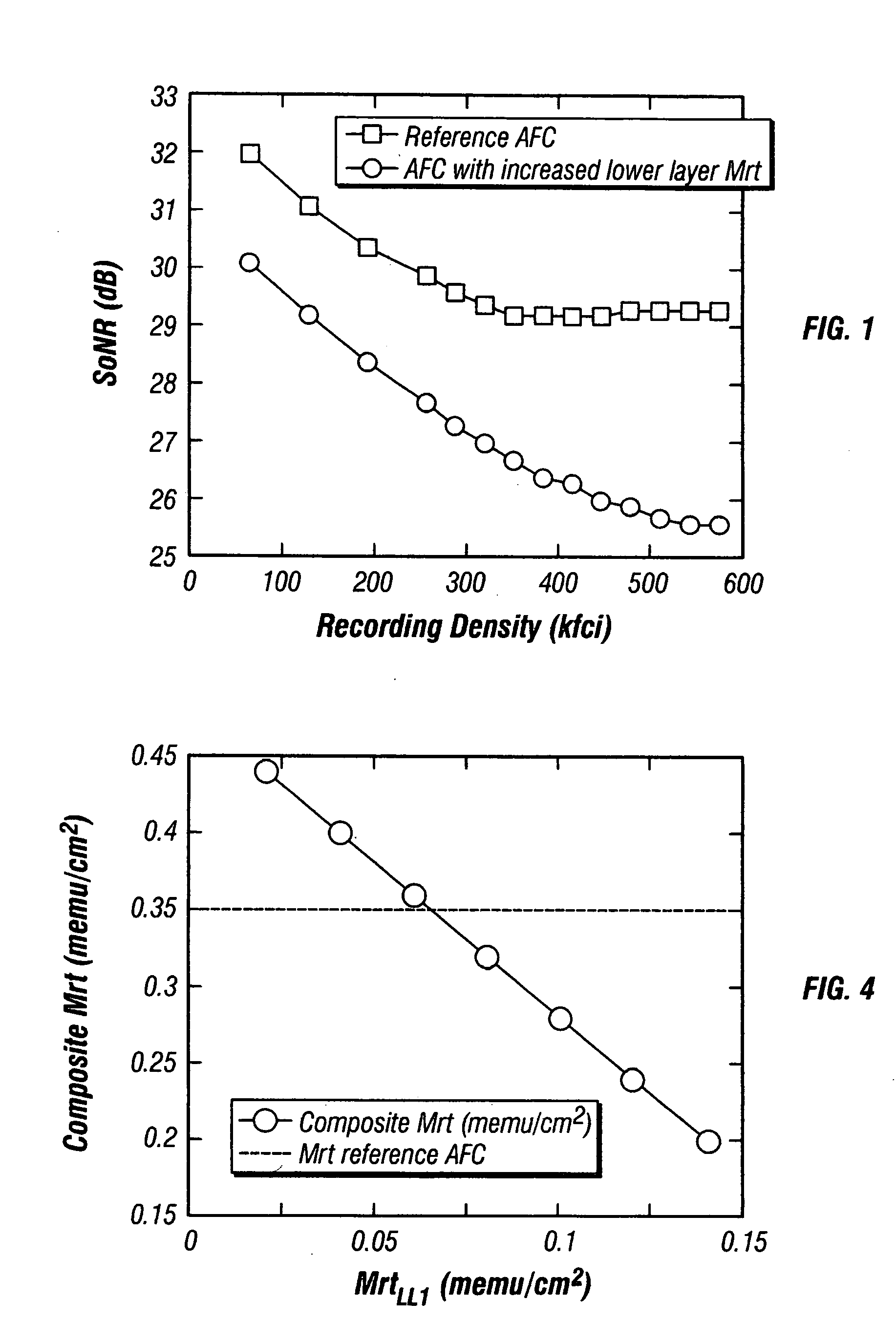
InactiveUS20050214586A1Composite MrtPrevent degradationProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetization
A magnetic recording disk has an antiferromagnetically-coupled (AFC) structure that has an upper ferromagnetic layer (UL), and a lower ferromagnetic layer structure formed of two ferromagnetically-coupled lower layers (LL1, LL2). The UL is antiferromagnetically-coupled to the lower layer structure across an antiferromagnetically-coupling layer. LL1 and LL2 are ferromagnetically coupled across a ferromagnetic coupling layer so the magnetizations of LL1 and LL2 remain parallel in each remanent magnetic state, but are antiparallel to the magnetization of the UL in each remanent magnetic state. The UL has an Mrt greater than the sum of the Mrt values of LL1 and LL2.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Disk
ActiveUS20150024161A1Evenly supportedExtend delivery timeFlat record carrier combinationsMagnetic discsBiomedical engineering
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
System, method and apparatus for data track usage sequence to reduce adjacent track interference effect
ActiveUS8879180B2Reduce impactMagnetic discsFilamentary/web record carriersHard disc driveComputer science
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording disk with antiferromagnetically-coupled magnetic layer having multiple lower layers
InactiveUS7125616B2Heads using thin filmsRecord information storageRemanenceAntiferromagnetic coupling
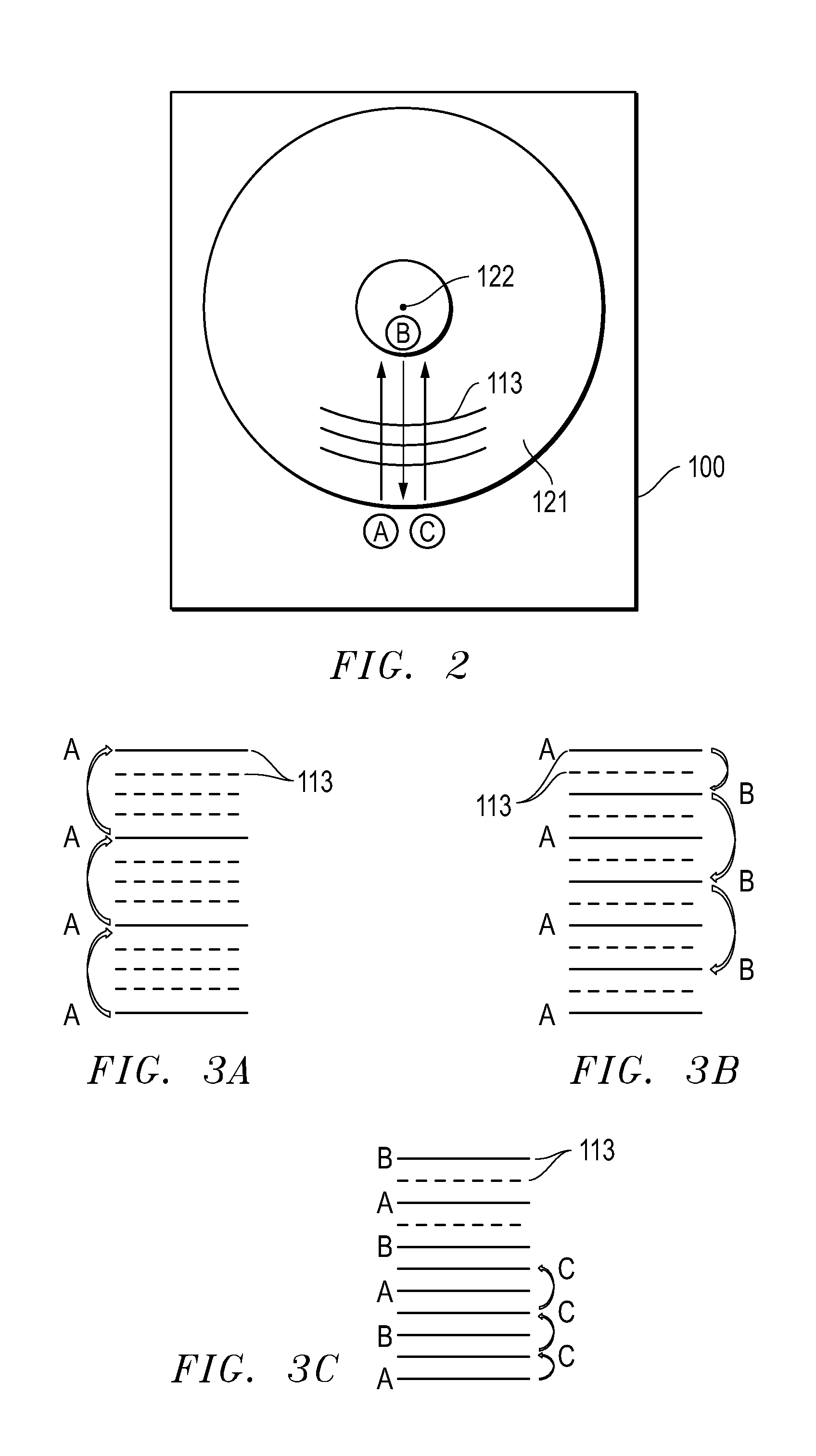
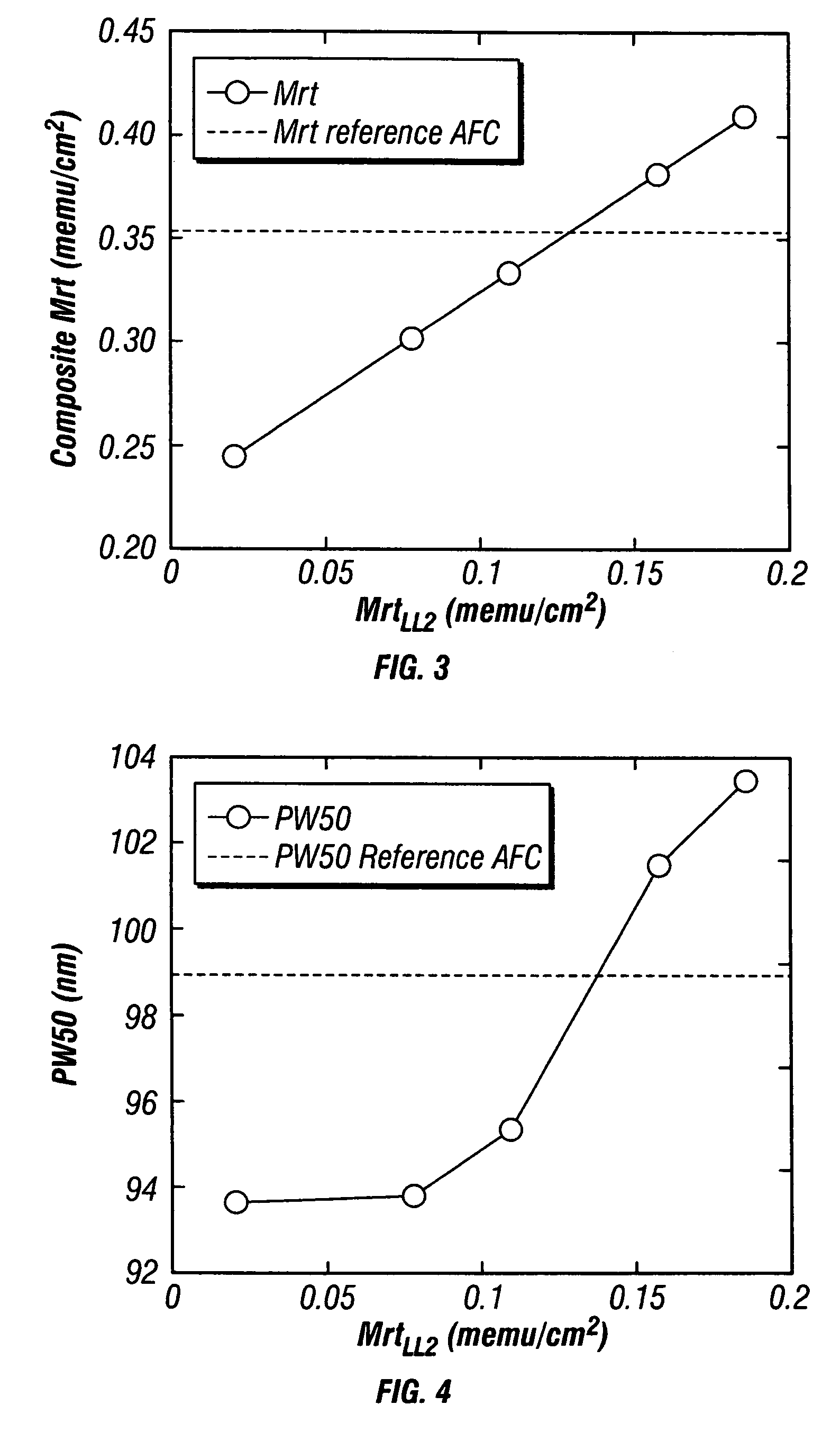
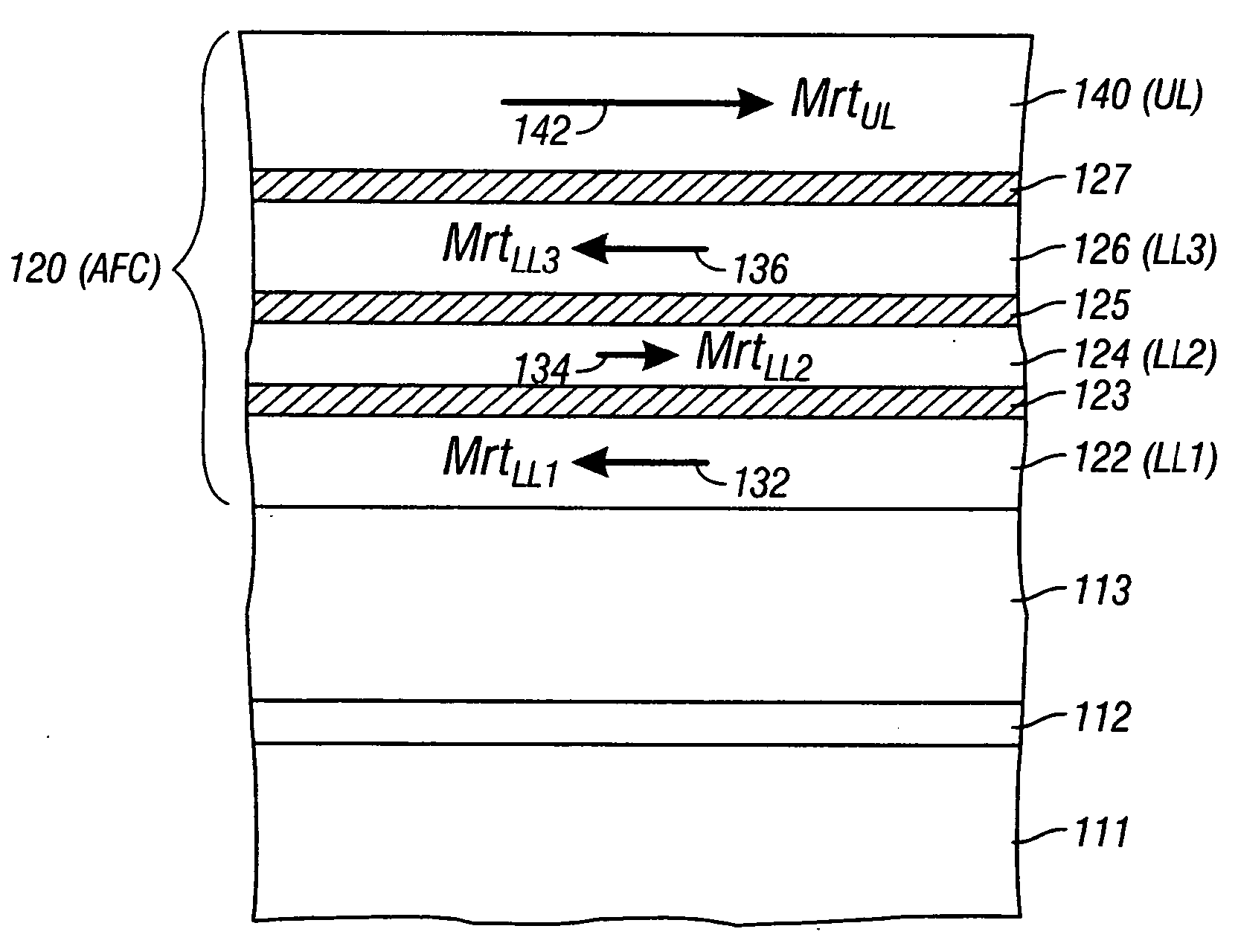
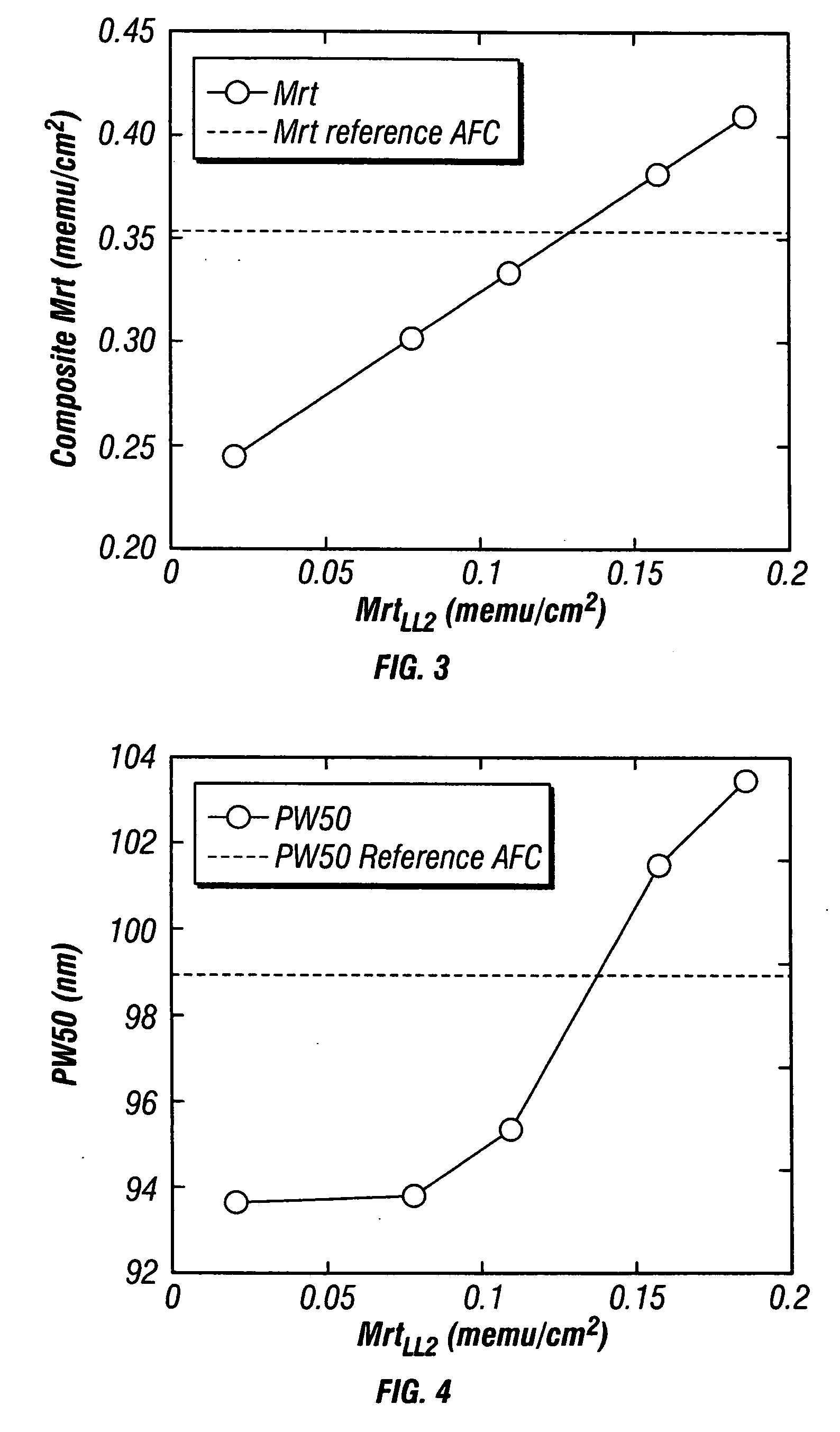
A magnetic recording disk has an antiferromagnetically-coupled (AFC) structure that has three lower ferromagnetic layers (LL1, LL2, LL3) and an upper ferromagnetic layer (UL), all four ferromagnetic layers being antiferromagnetically-coupled together across corresponding antiferromagnetically-coupling layers. The UL has a magnetization-remanence-thickness product (Mrt) greater than the Mrt each of the three lower layers LL1, LL2, LL3, and greater than the sum of the Mrt values of LL1 and LL3. The middle lower layer LL2 has an Mrt less than the Mrt of each of the other lower layers LL1 and LL3, and as a result the composite Mrt of the AFC structure is less than the composite Mrt of a conventional AFC structure having only a single lower layer. The AFC structure achieves this composite Mrt reduction without increasing the Mrt of any of the three lower layers above the maximum Mrt of the single lower layer in the conventional AFC structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording disk with antiferromagnetically-coupled magnetic layer having multiple lower layers
InactiveUS20050190498A1Prevent degradationHeads using thin filmsRecord information storageRemanenceAntiferromagnetic coupling
A magnetic recording disk has an antiferromagnetically-coupled (AFC) structure that has three lower ferromagnetic layers (LL1, LL2, LL3) and an upper ferromagnetic layer (UL), all four ferromagnetic layers being antiferromagnetically-coupled together across corresponding antiferromagnetically-coupling layers. The UL has a magnetization-remanence-thickness product (Mrt) greater than the Mrt each of the three lower layers LL1, LL2, LL3, and greater than the sum of the Mrt values of LL1 and LL3. The middle lower layer LL2 has an Mrt less than the Mrt of each of the other lower layers LL1 and LL3, and as a result the composite Mrt of the AFC structure is less than the composite Mrt of a conventional AFC structure having only a single lower layer. The AFC structure achieves this composite Mrt reduction without increasing the Mrt of any of the three lower layers above the maximum Mrt of the single lower layer in the conventional AFC structure.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
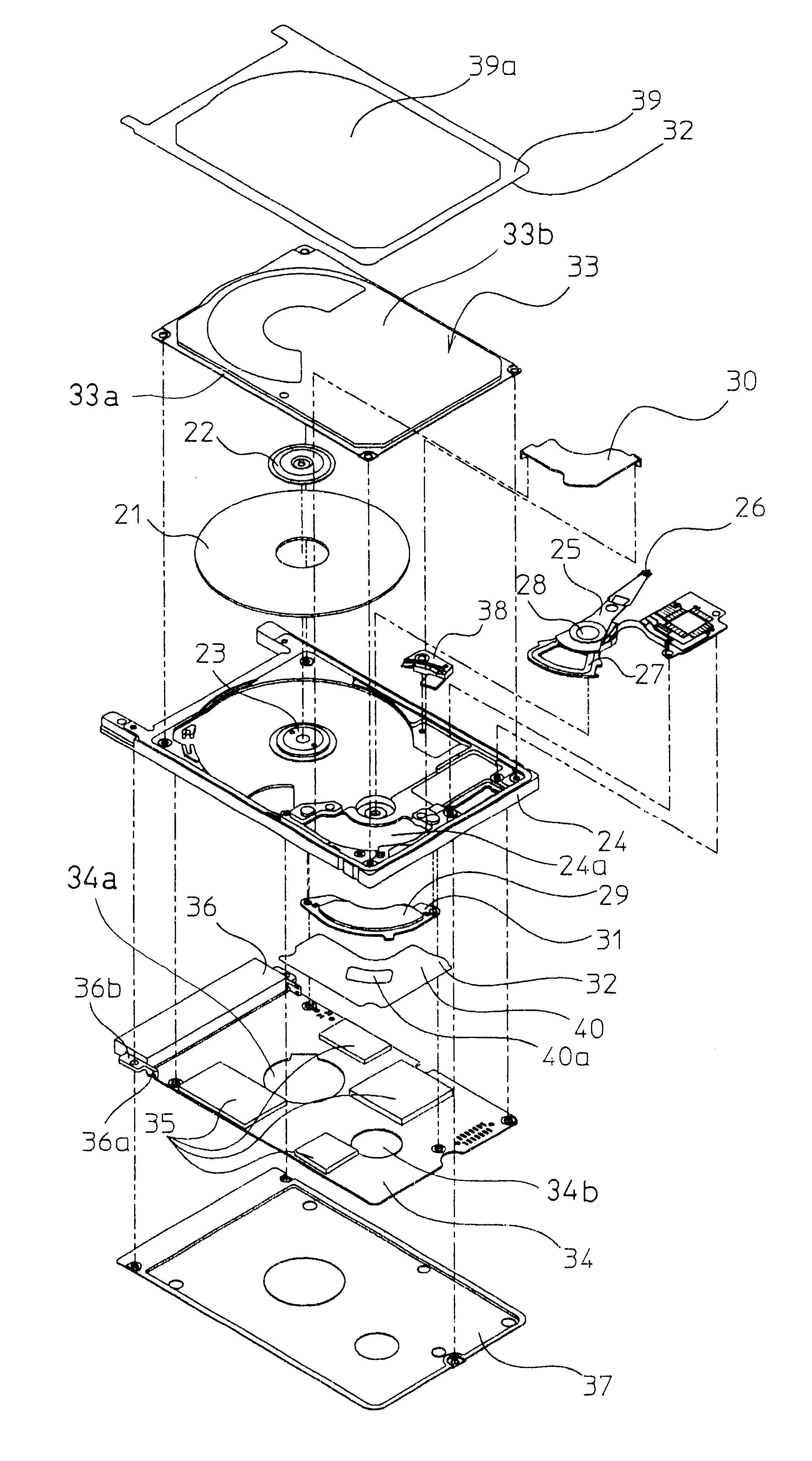
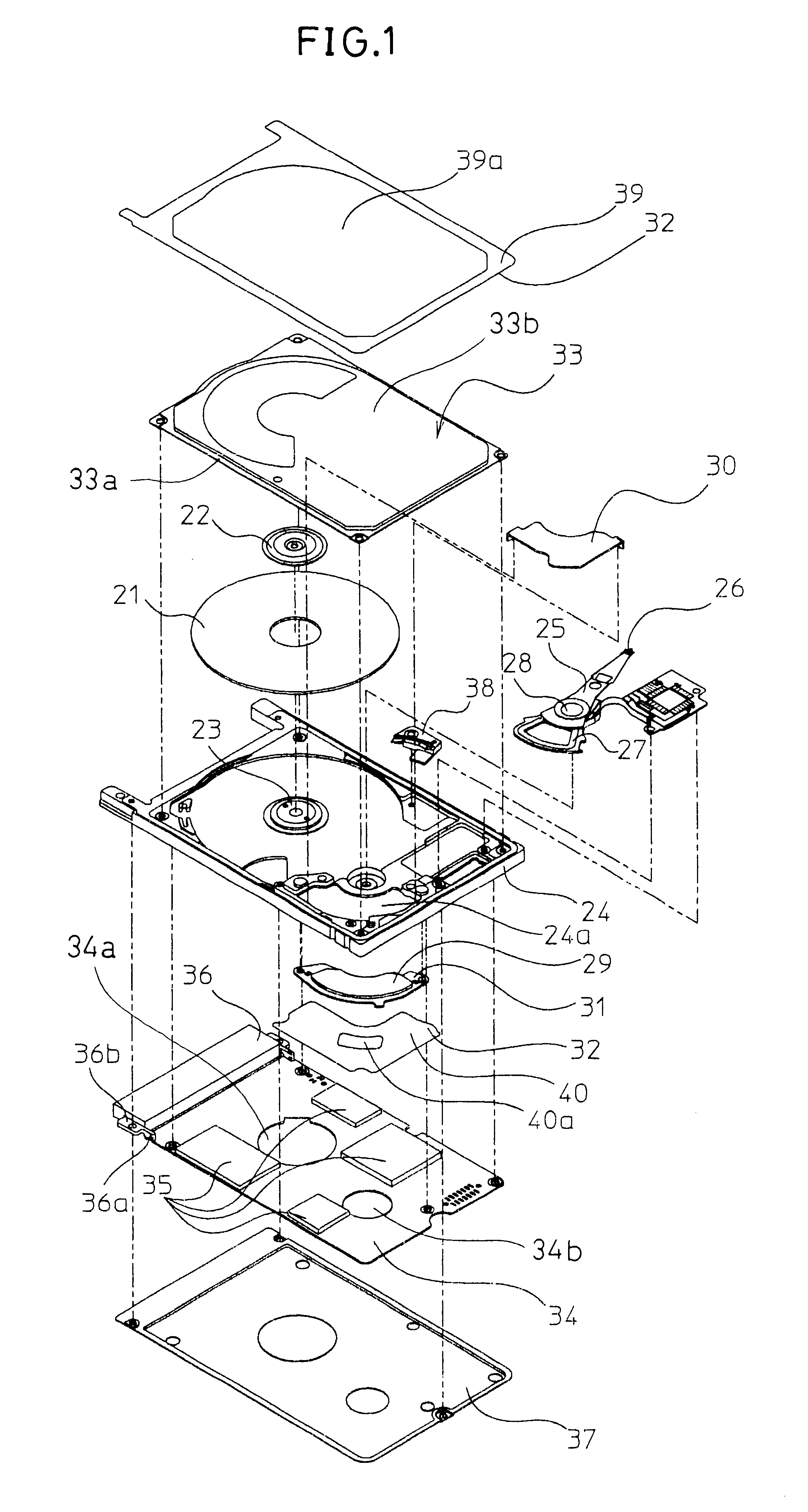
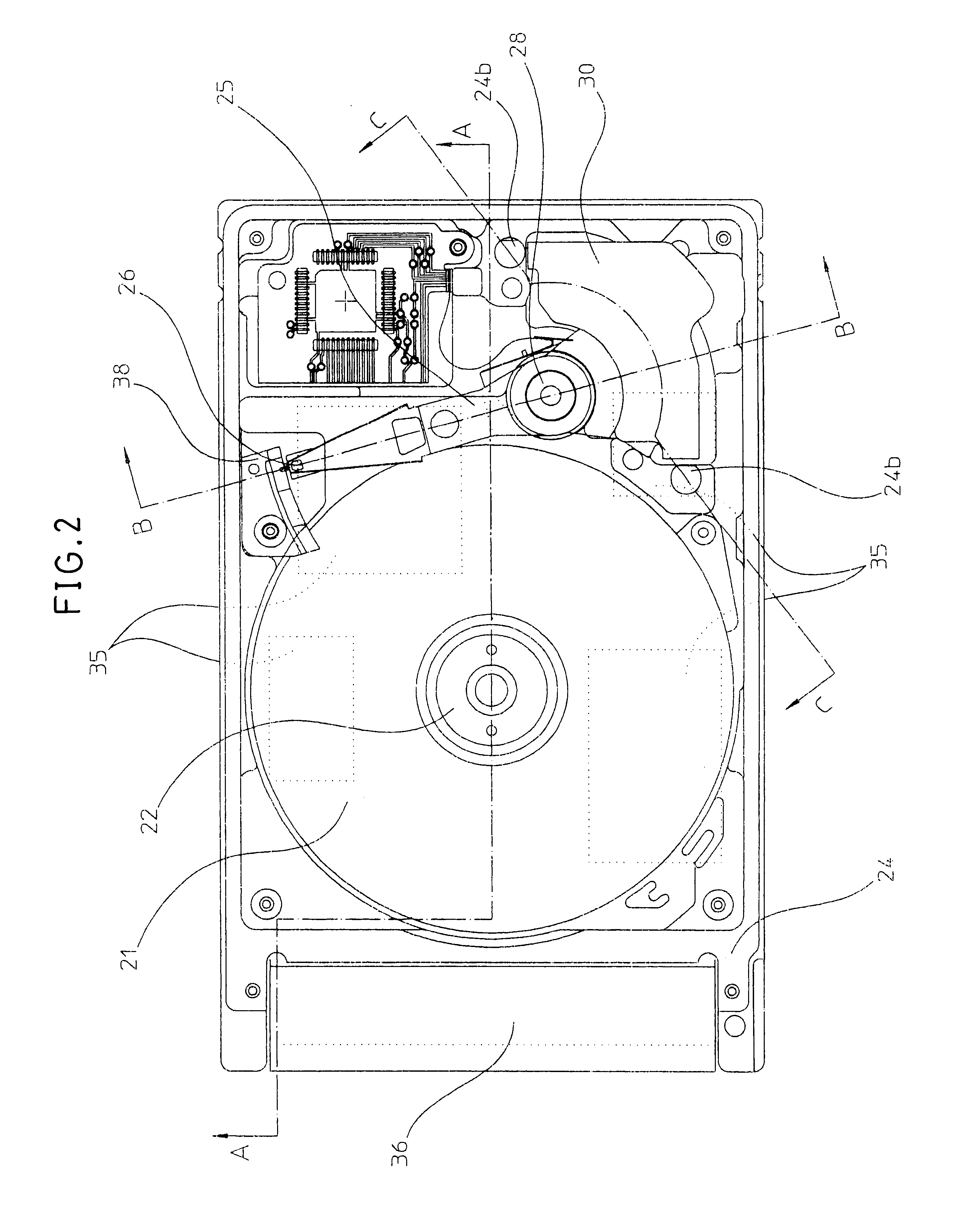
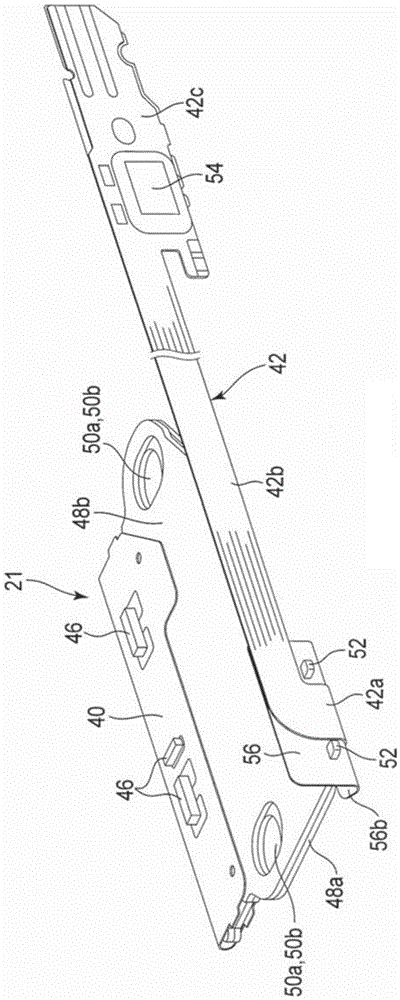
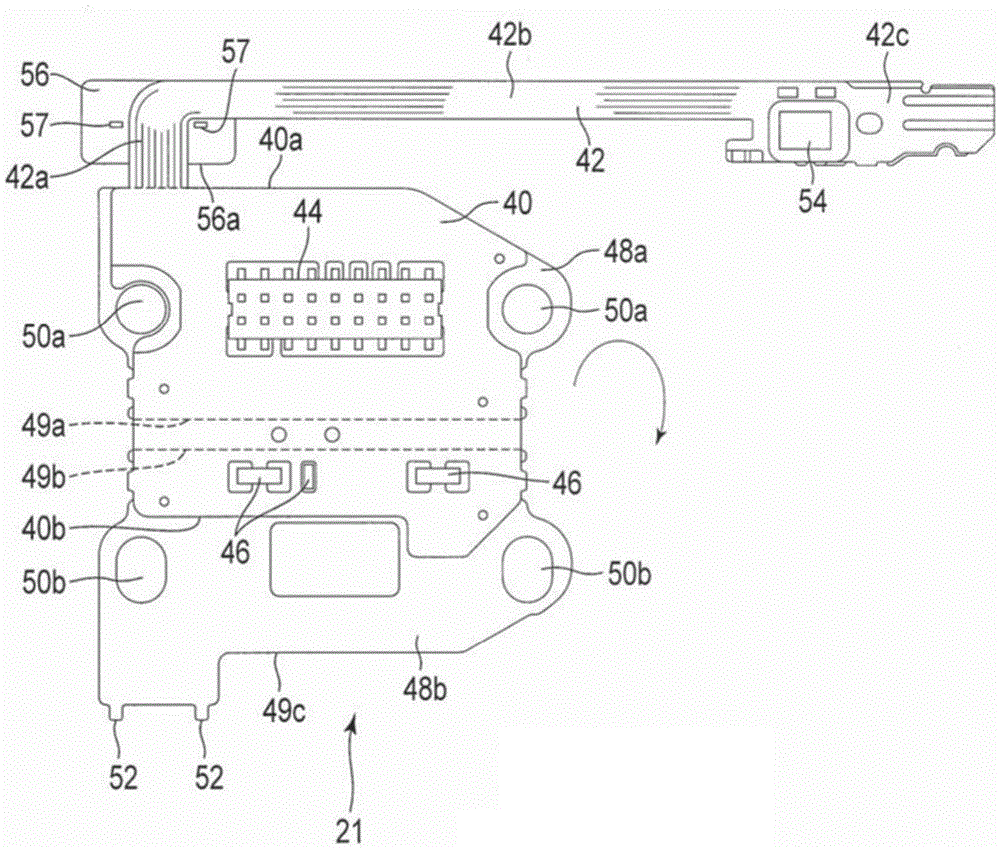
Flexible printed circuit assembly and disk drive including same
A flexible printed circuit assembly includes a flexible printed circuit board including a base portion and a relay portion extending from a first edge of the base portion and capable of being bent relative to the base portion, a first reinforcing member disposed at the relay portion, and a second reinforcing member attached to a first region of the base portion that includes a second edge opposite to the first edge and having an engaging portion. The first region of the base portion is capable of being folded back towards a second region of the base portion that includes the first edge, and the engaging portion of the second reinforcing member is capable of being engaged with the first reinforcing member.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of producing perpendicular magnetic recording disk
InactiveUS20060027527A1Flat surfaceDecorative surface effectsBelt grinding machinesMetallurgyRecording layer
A perpendicular magnetic recording disk is produced by polishing to make smoother both surfaces of a substrate and sequentially forming a soft magnetic layer, a perpendicular recording layer and a protective layer on each of the polished surfaces of the substrate. The surfaces of the soft magnetic layers are polished by a fixed particle polishing method to be made smoother, and the perpendicular recording layers is formed on the smoothed surfaces of the soft magnetic layers either directly or with an intermediate layer in between.
Owner:NIHON MICRO COATING
Method for controlling bias current for magnetoresistive head, fixed magnetic recording device, and magnetic disc therefor
InactiveCN1294733APrevent variabilityPrevent degradationMagnetic discsRecord information storageMicrocomputerEngineering
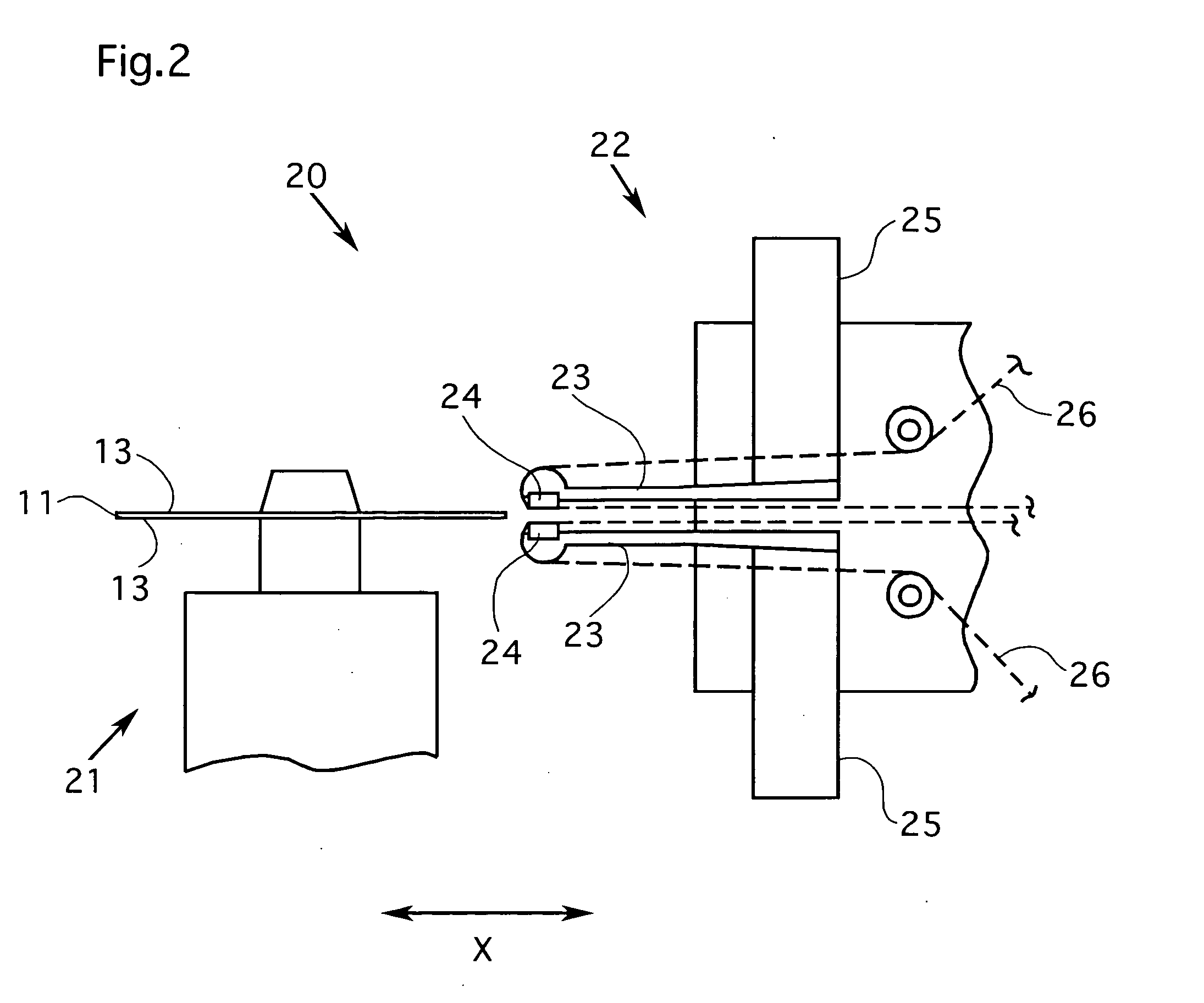
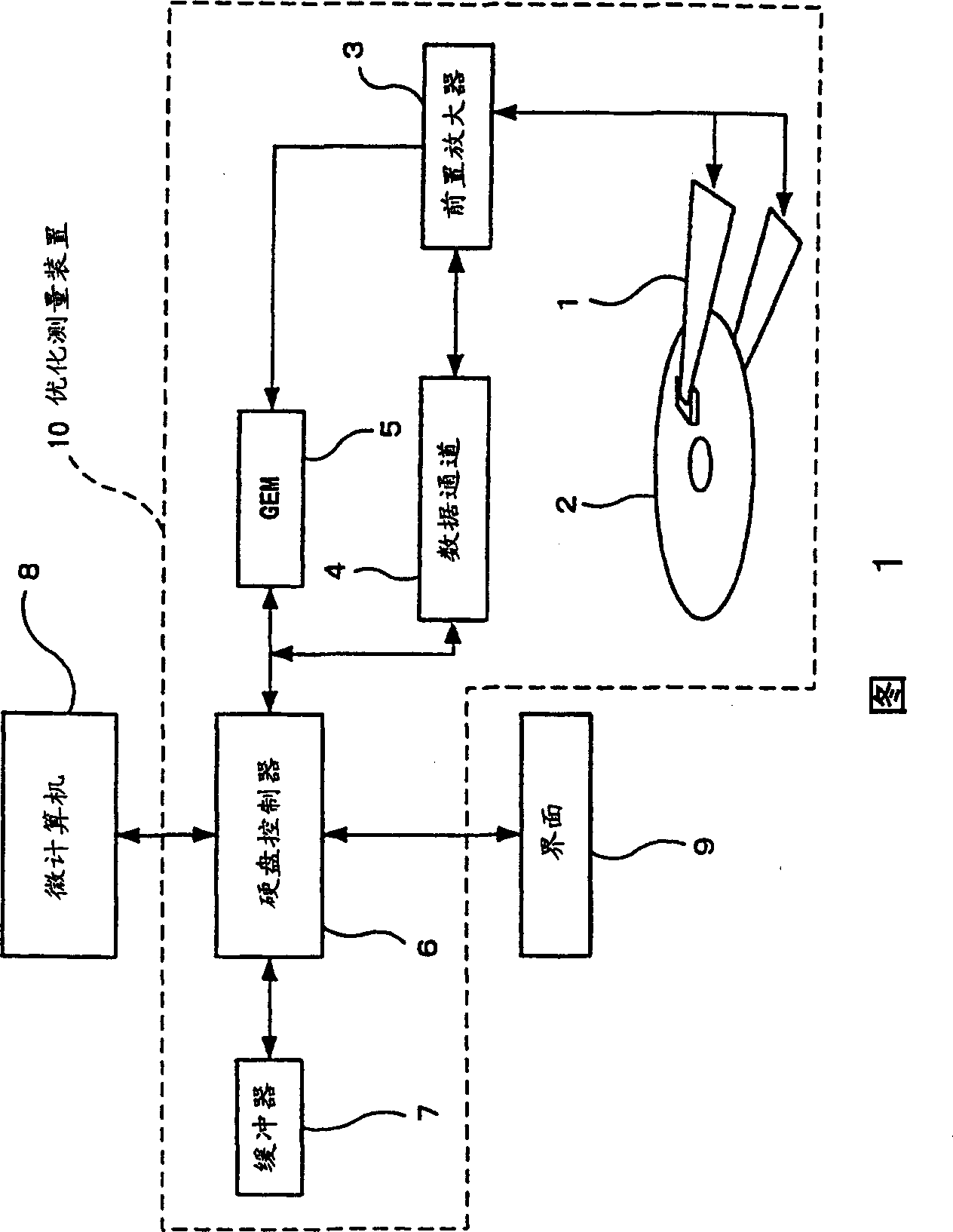
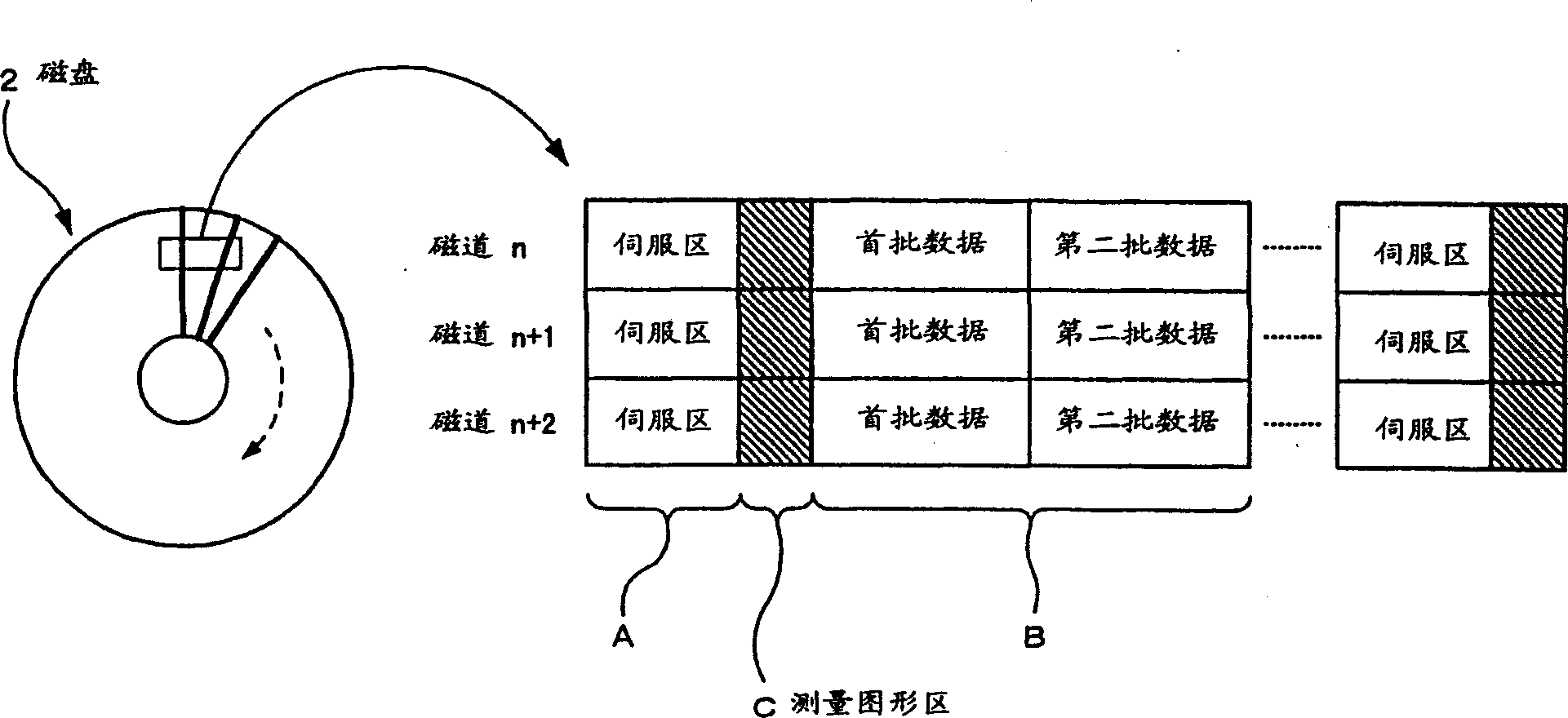
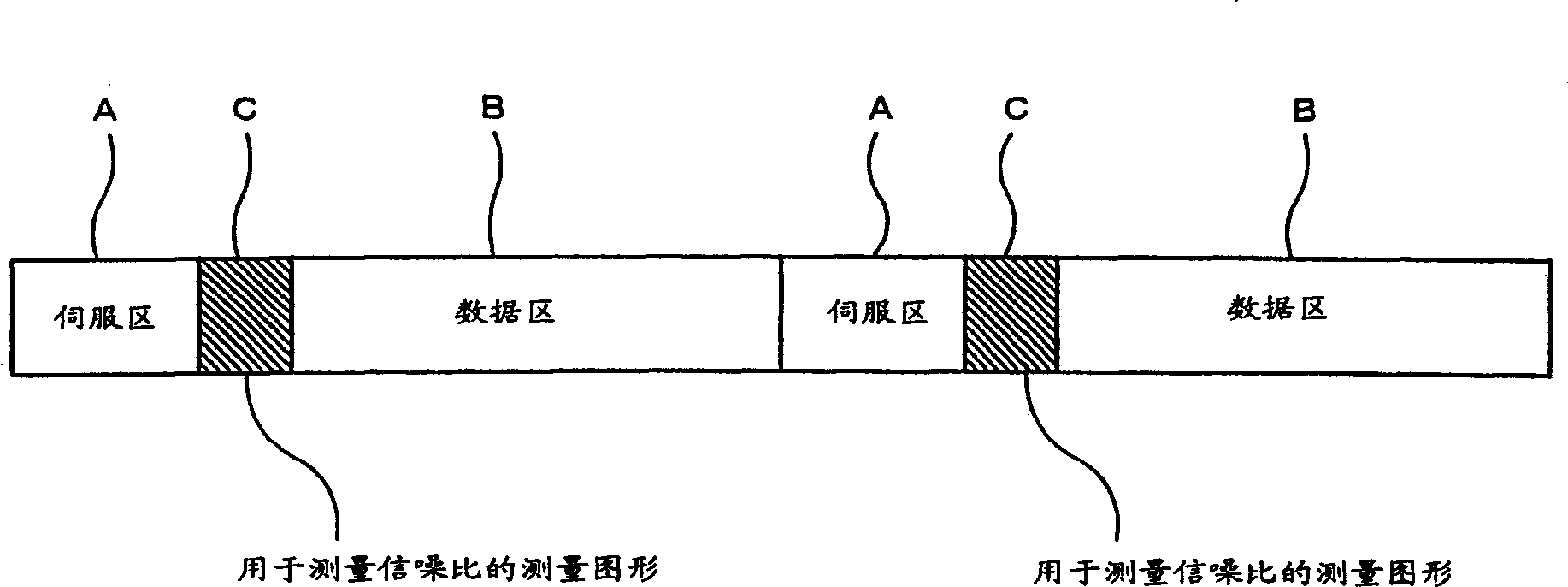
It is an object of the present invention to enable a bias current for an MR head to be optimized as appropriate during an operation of a fixed magnetic recording device in order to restrain a possible asymmetrical distortion originating in a saturation in the reproduced signal from the MR head, thereby reducing the error rate during data read-outs. A fixed magnetic recording device according to the present invention comprises optimizing measurement means (10) for conducting measurements for optimizing a bias current value for the MR head in a head structure section (1) each time the MR head accesses a magnetic disc (2), and a microcomputer (8) for controlling optimizing measurement means (10) and outputting an instruction for updating of a bias current value for the MR head to the measured optimum bias current value for storage and an instruction for the supply of the updated and stored optimum bias current to the MR head.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Disk device
InactiveUS20030011926A1Efficient arrangementLow priceCarrier constructional parts dispositionDriving/moving recording headsHard disc driveEngineering
A disk device such as a magnetic hard disk drive. A disk is arranged inside a frame body. A cover is placed on the frame body, a gap is formed between a rim of the cover and the frame, and this gap is shielded by a sheet having an adhesive portion.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
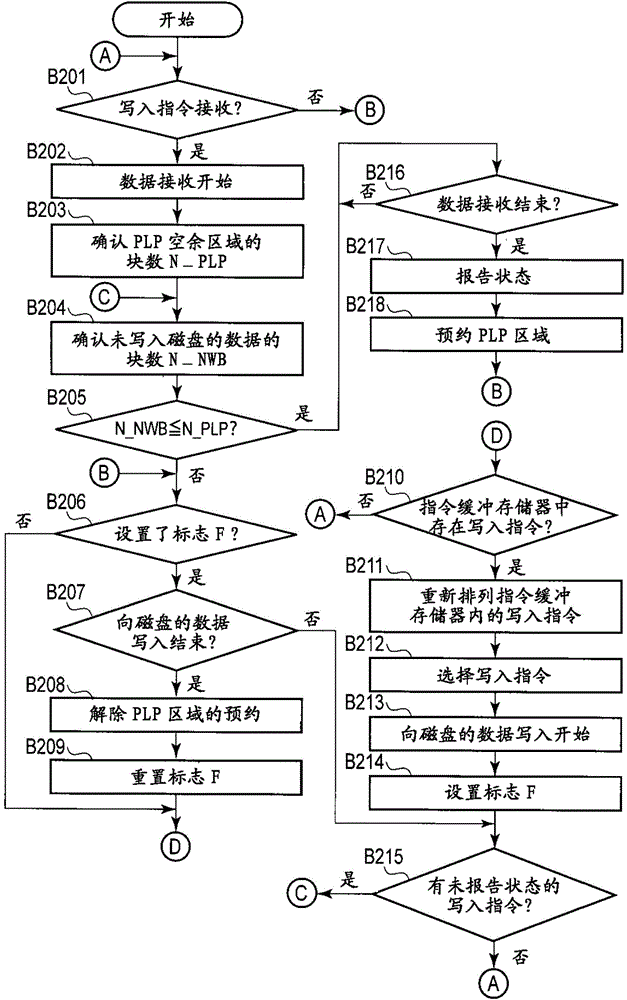
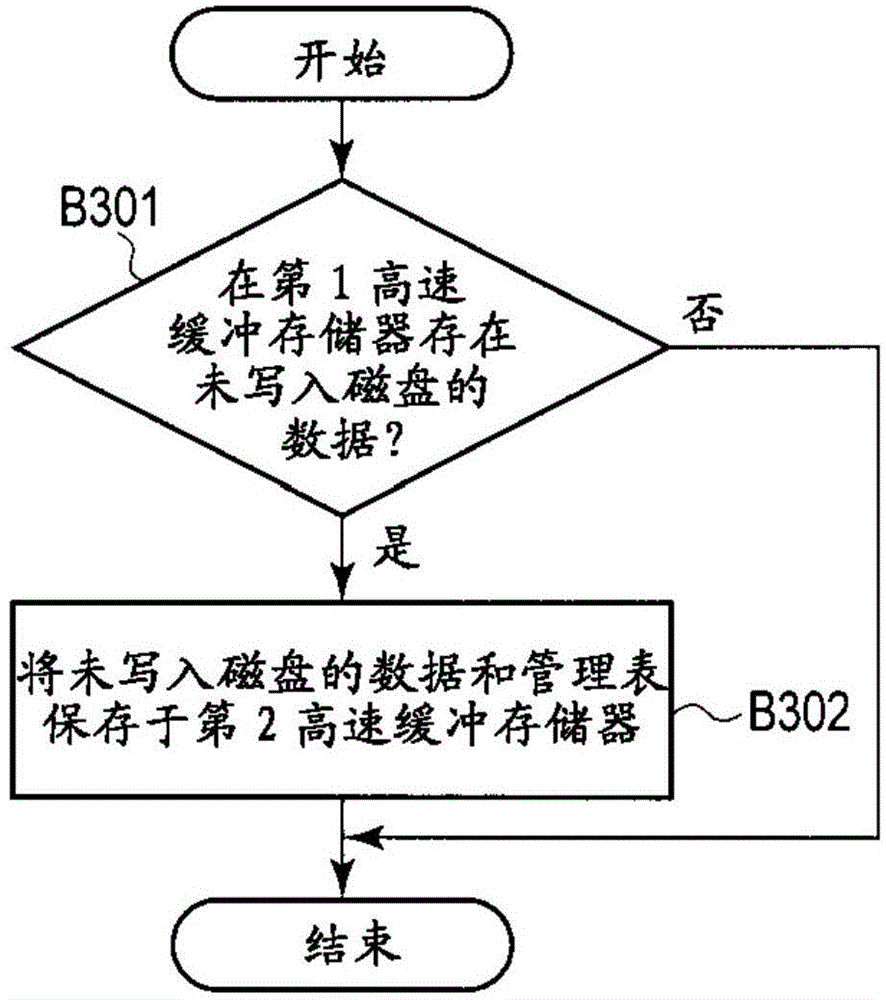
Magnetic disk device and method for executing write command
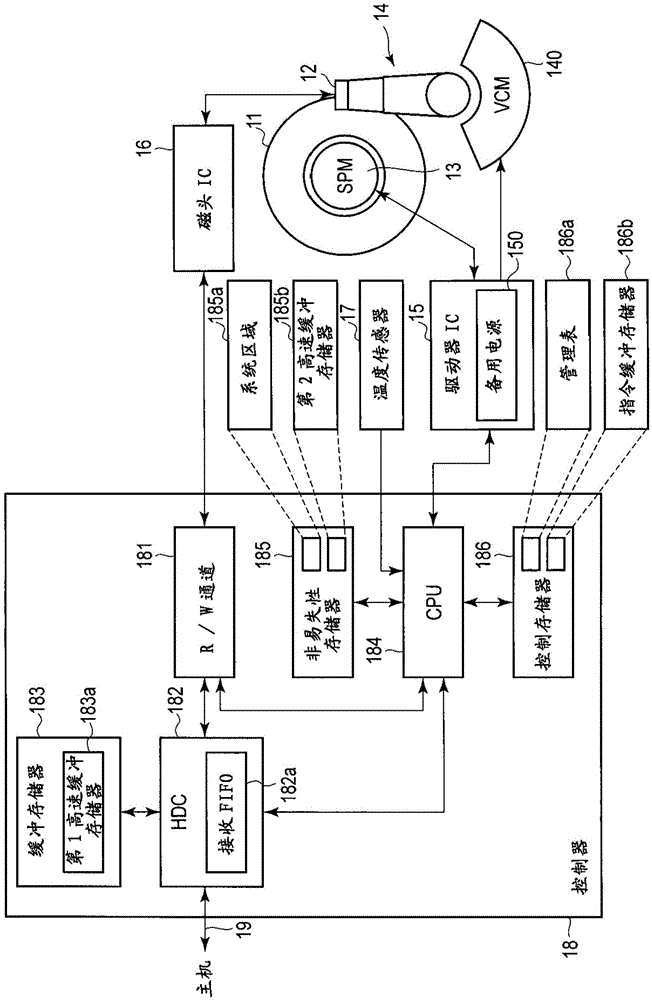
ActiveCN105304095AReduce capacityWhether the capacity is the first capacity reductionMagnetic discsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperating systemElectric power
According to one embodiment, a controller of a magnetic disk device starts to receive first data specified in a first write command from a host, and starts to write the first data to a disk in accordance with the first write command. The controller reports a status for execution of the first write command to the host depending on whether or not a second capacity of data not yet written to the disk is less than or equal to a first capacity of a first free space in a nonvolatile cache. The first free space is available to save data during a first period when a backup power supply enables power to be supplied. The second capacity decreases as writing of the first data to the disk progresses.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
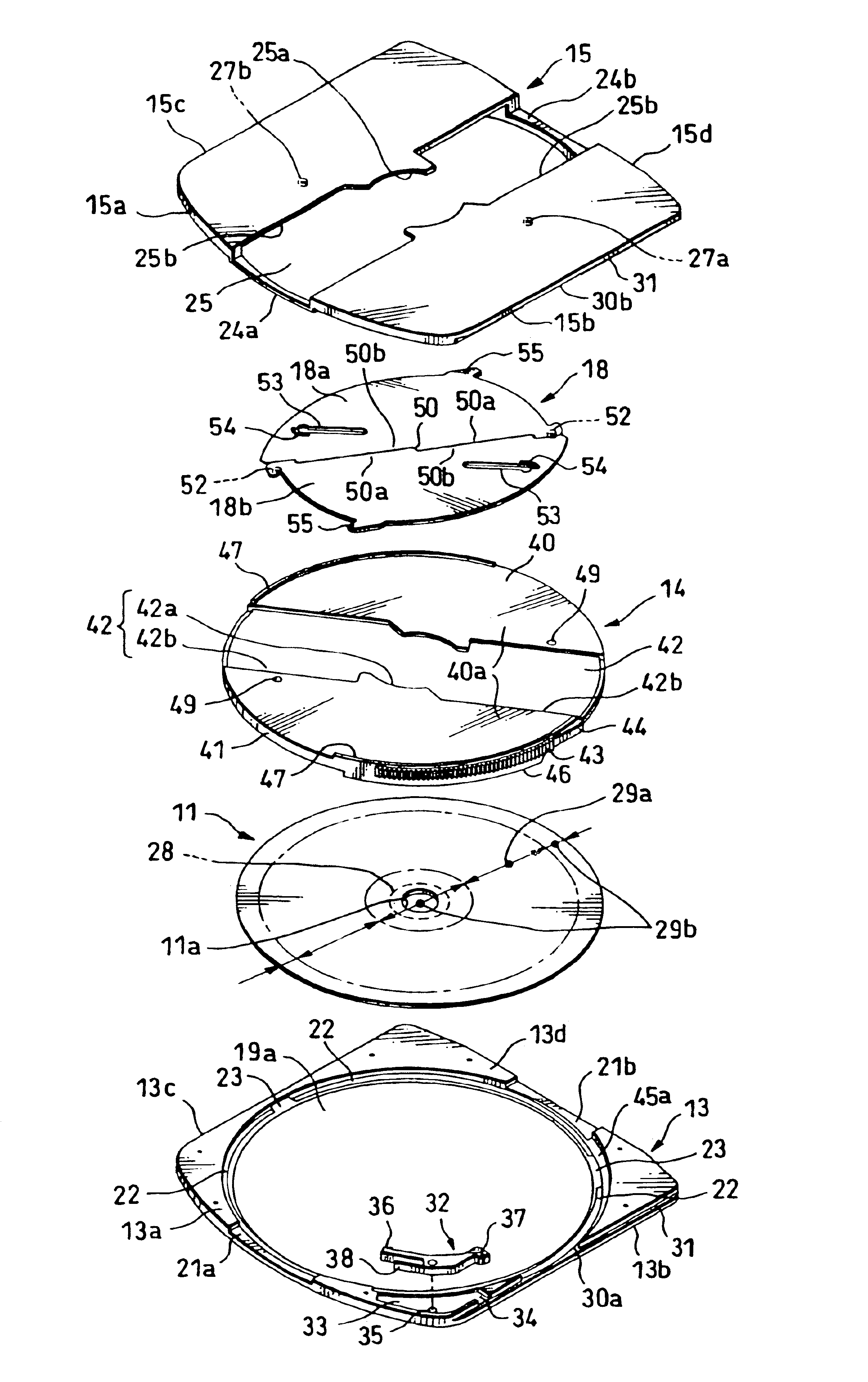
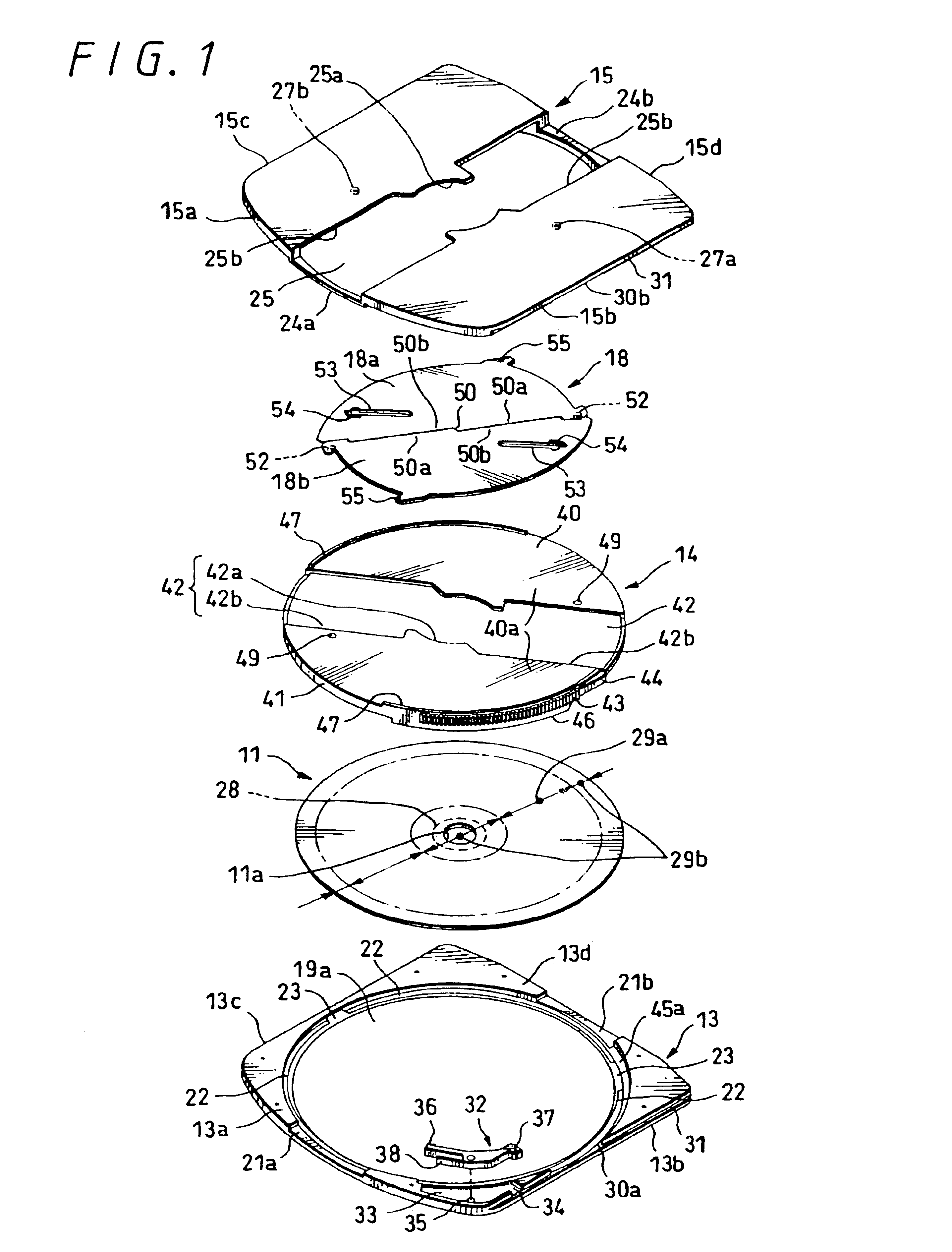
Disk cartridge
InactiveUS6900965B2Smoothly and reliably be openedSmoothly and reliably be and closedCarrier constructional parts dispositionMagnetic discsEngineeringAir tightness
A disk cartridge in which a pair of shutter members can be opened and closed smoothly and reliably, and a dust-proof property and an airtightness of a large opening portion can be increased by reducing a space between a pair of shutter members and a cartridge housing as much as possible. The disk cartridge comprises a cartridge housing in which a disk compartment is formed-between an upper shell and a middle shell by overlapping the upper shell, the middle shell and the lower shell and the middle shell is supported by the upper shell and the lower shell so as to become freely rotatable, an optical disk rotatably stored within the disk compartment and a pair of shutter members attached to the middle shell in such a manner that they can be moved in the plane direction on the same plane. A shutter opening and closing mechanism for opening and closing opening portions by moving the pair of shutter members based rotation of the middle shell.
Owner:SONY CORP
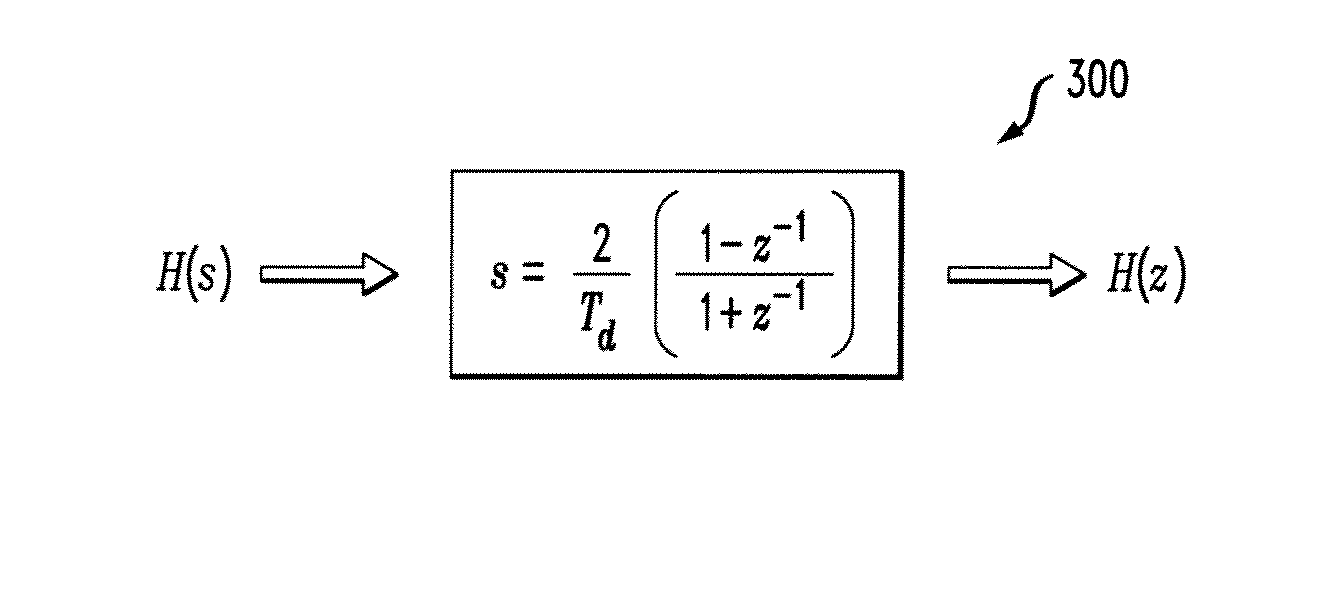
Determining Coefficients For Digital Low Pass Filter Given Cutoff And Boost Values For Corresponding Analog Version
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining coefficients for a digital low pass filter, given cutoff and boost values for a corresponding analog version of the digital low pass filter. Coefficients are determined for a digital low pass filter by obtaining cutoff and boost values for a corresponding analog version of the digital low pass filter; and determining the coefficients for the digital low pass filter based on the obtained cutoff and boost values. The coefficients can be determined, for example, by generating a transfer function, H(s), for the corresponding analog version using the obtained cutoff and boost values: transforming the transfer function, H(s), to a frequency domain characterization, H(z), using one or more bilinear transforms to obtain a plurality of coefficients for an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter; generating the IIR filter using the plurality of coefficients for the IIR filter; and applying an impulse to the IIR filter to obtain the one or more coefficients for the digital low pass filter. In another variation, the coefficients are pre-computed and obtained from a look-up table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
LDPC decoding with on the fly error recovery
Owner:SK HYNIX MEMORY SOLUTIONS
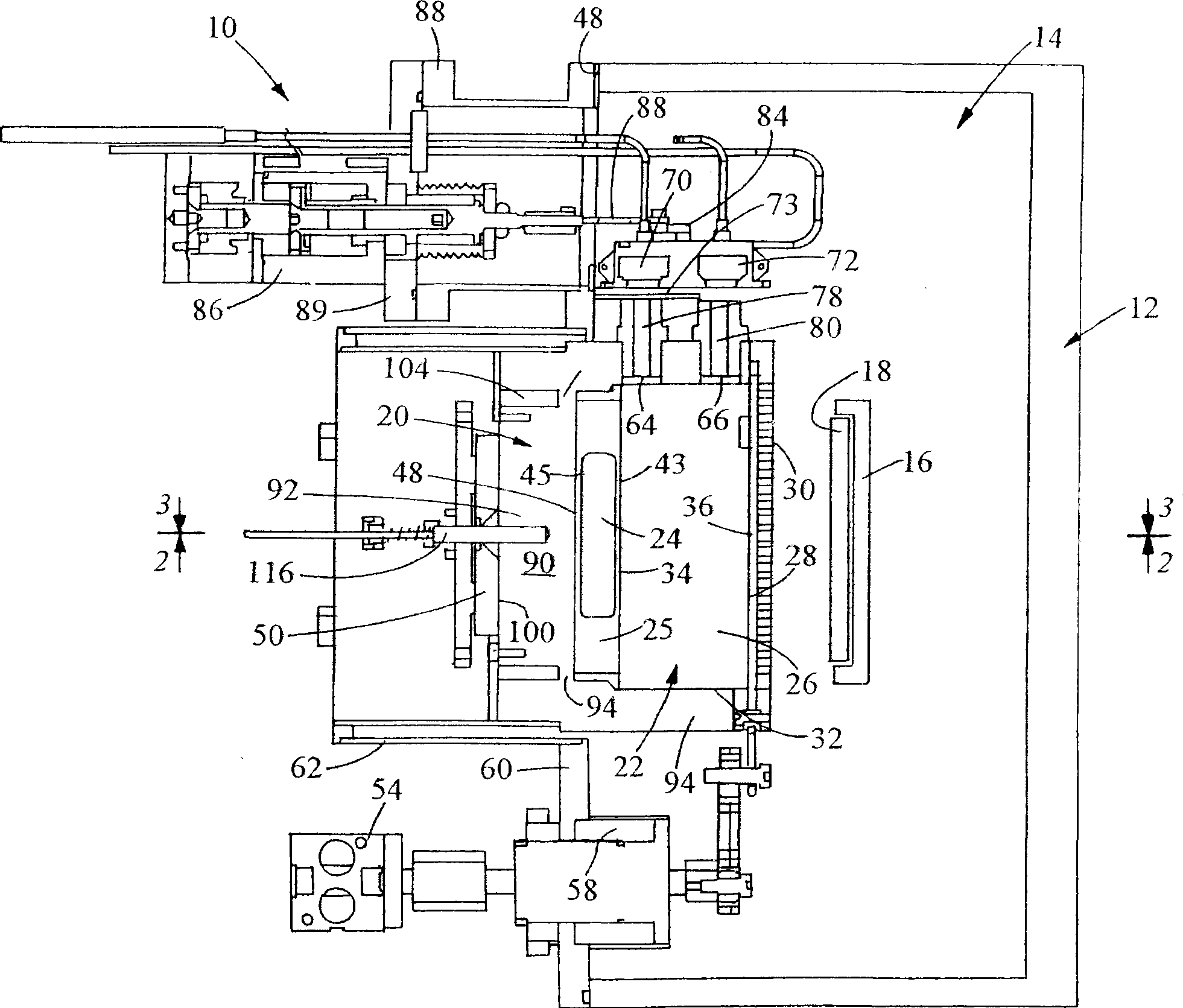
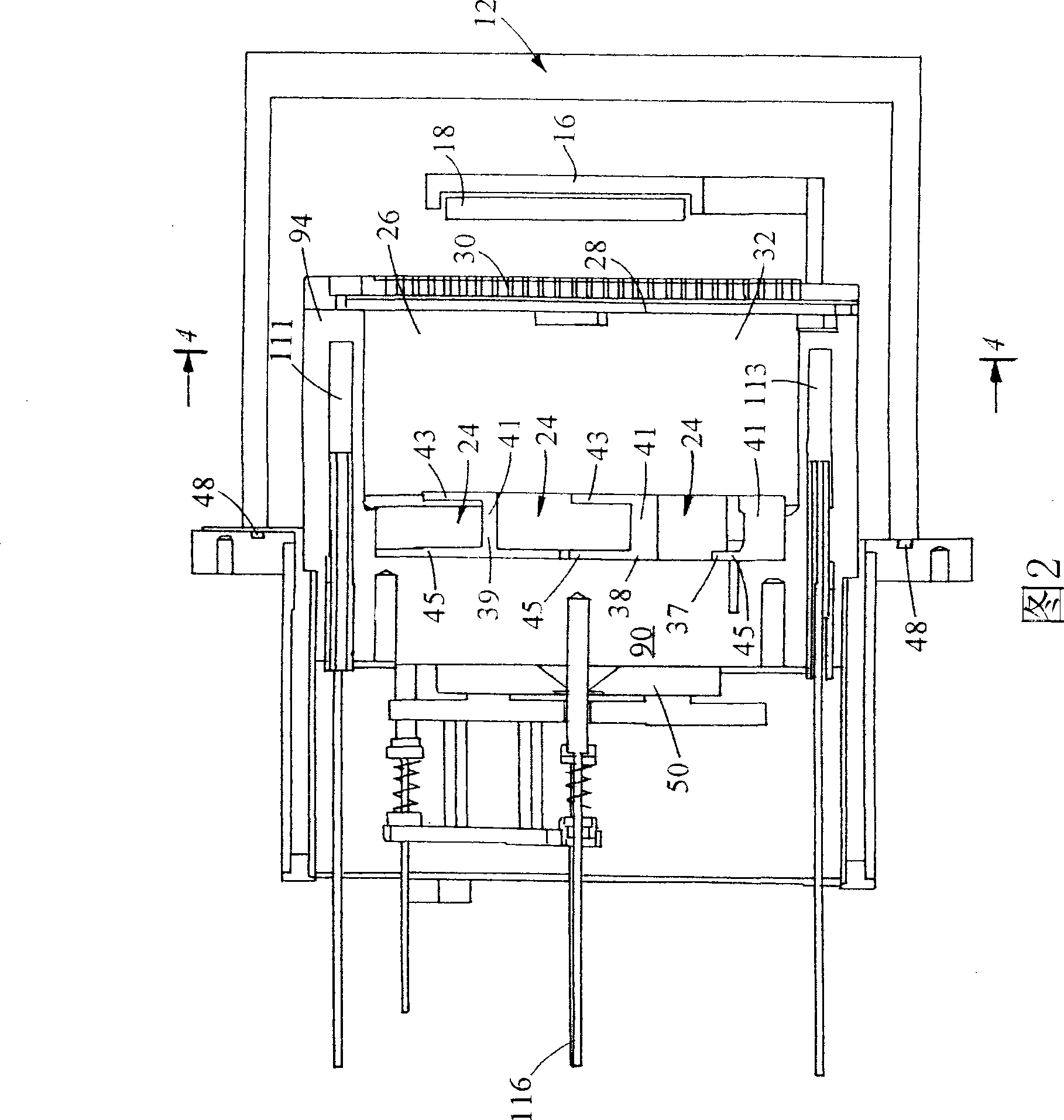
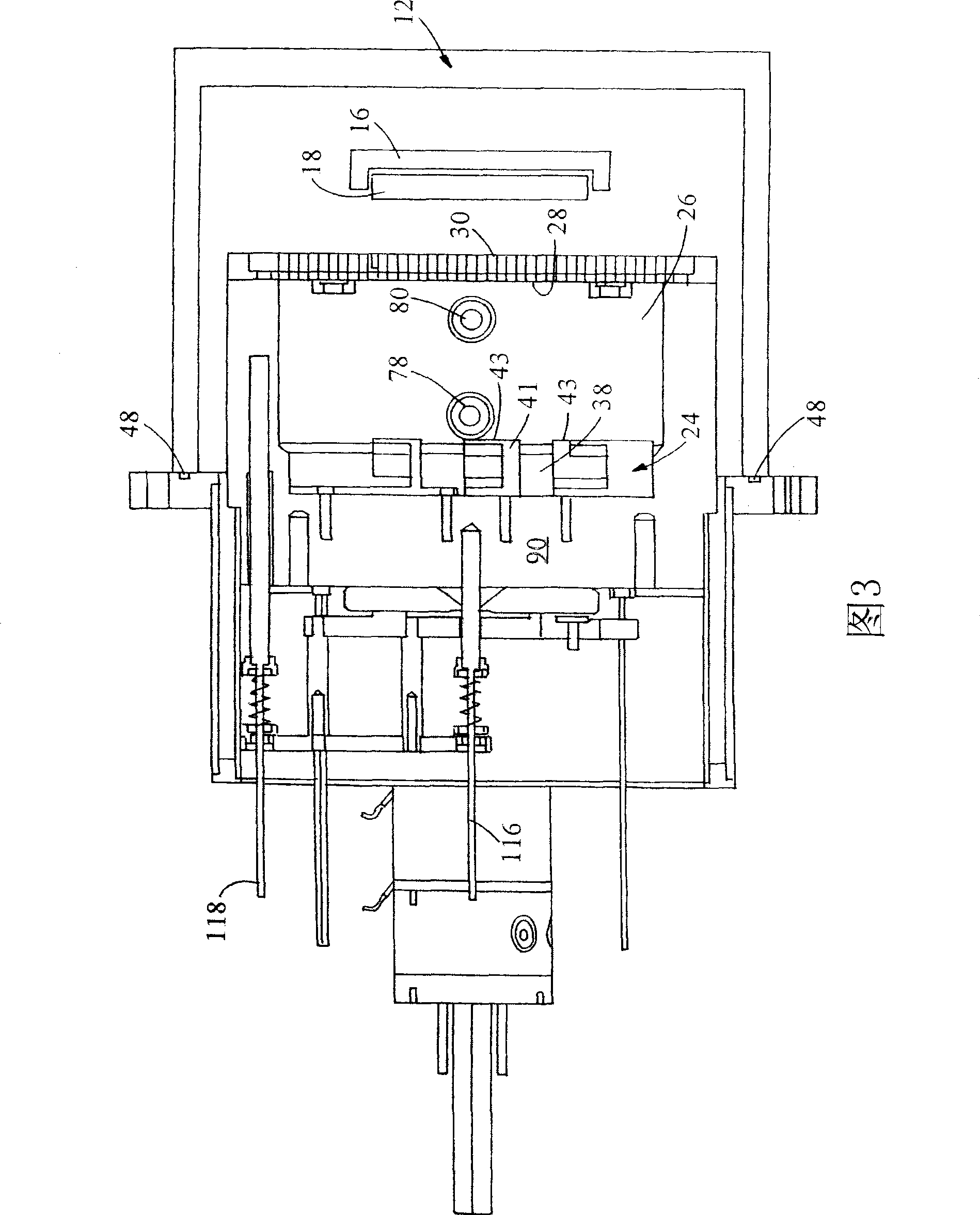
Method of and apparatus for monitoring flow of lubricant vapor forming lubricant coatings of magnetic disks
Lubricant coatings are applied as lubricant vapor to magnetic disks 18 in a lubricant vapor flow path between the disks and a reservoir 24 for liquid lubricant that is heated to the vapor. The flow path includes a vapor chamber between the reservoir and an apertured diffuser 30. Plural piezoelectric crystals selectively, at different times, monitor the flow rate of lubricant vapor flowing in the vapor chamber, a result achieved by selectively positioning a shutter 28 that is selectively opened and closed between the vapor flowing in the vapor chamber and the crystals. Temperature variations of the crystals are compensated by a feedback arrangement for maintaining the crystal temperature constant.
Owner:INTERVIDEO
Popular searches
Using detectable carrier information Alignment for track following on disks Digital signal formatting Digital recording Signal processing using self-clocking codes Signal processing using non self-clocking codes Track changing/selection Carrier monitoring Recording signal processing Recording on magnetic disks
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com