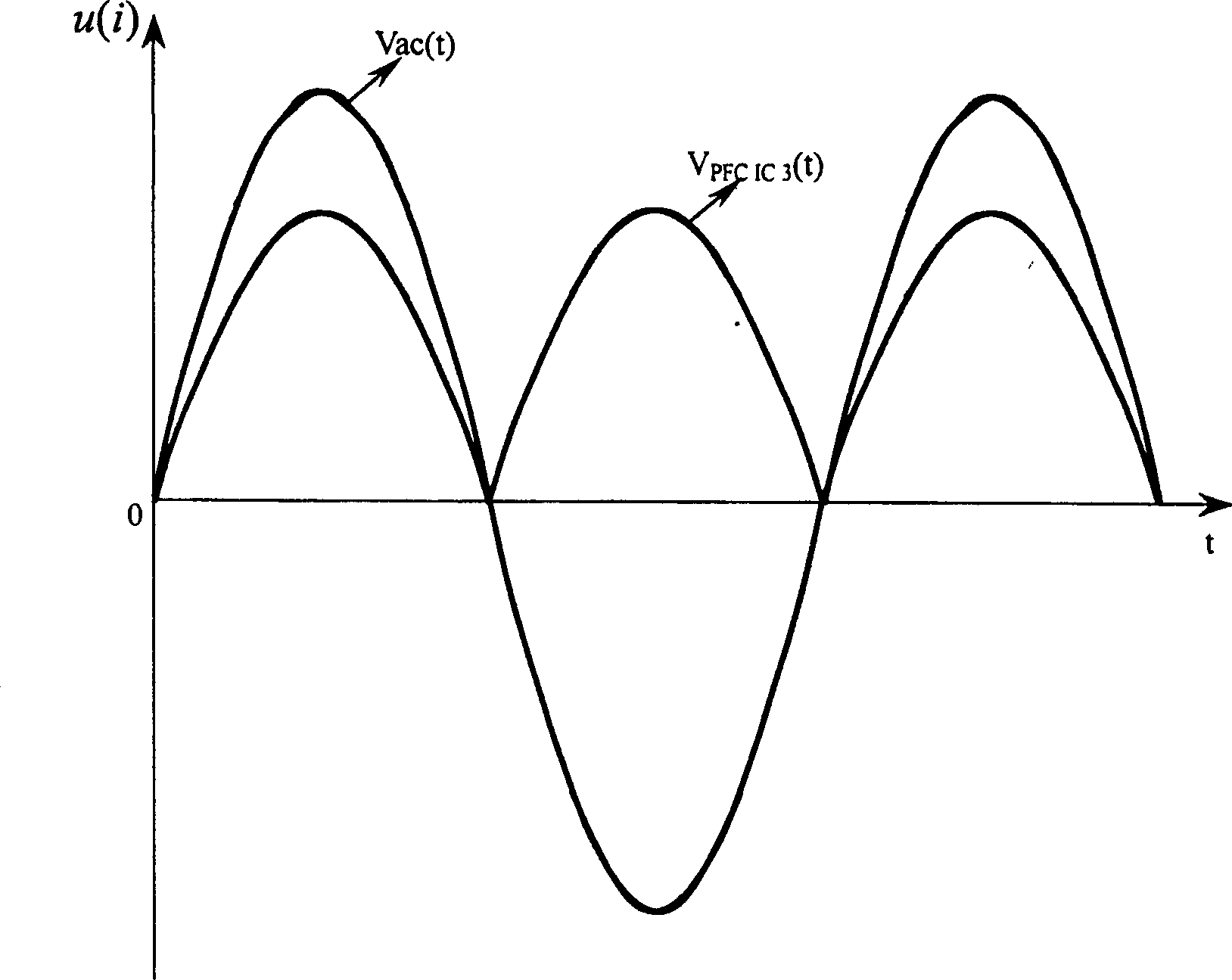
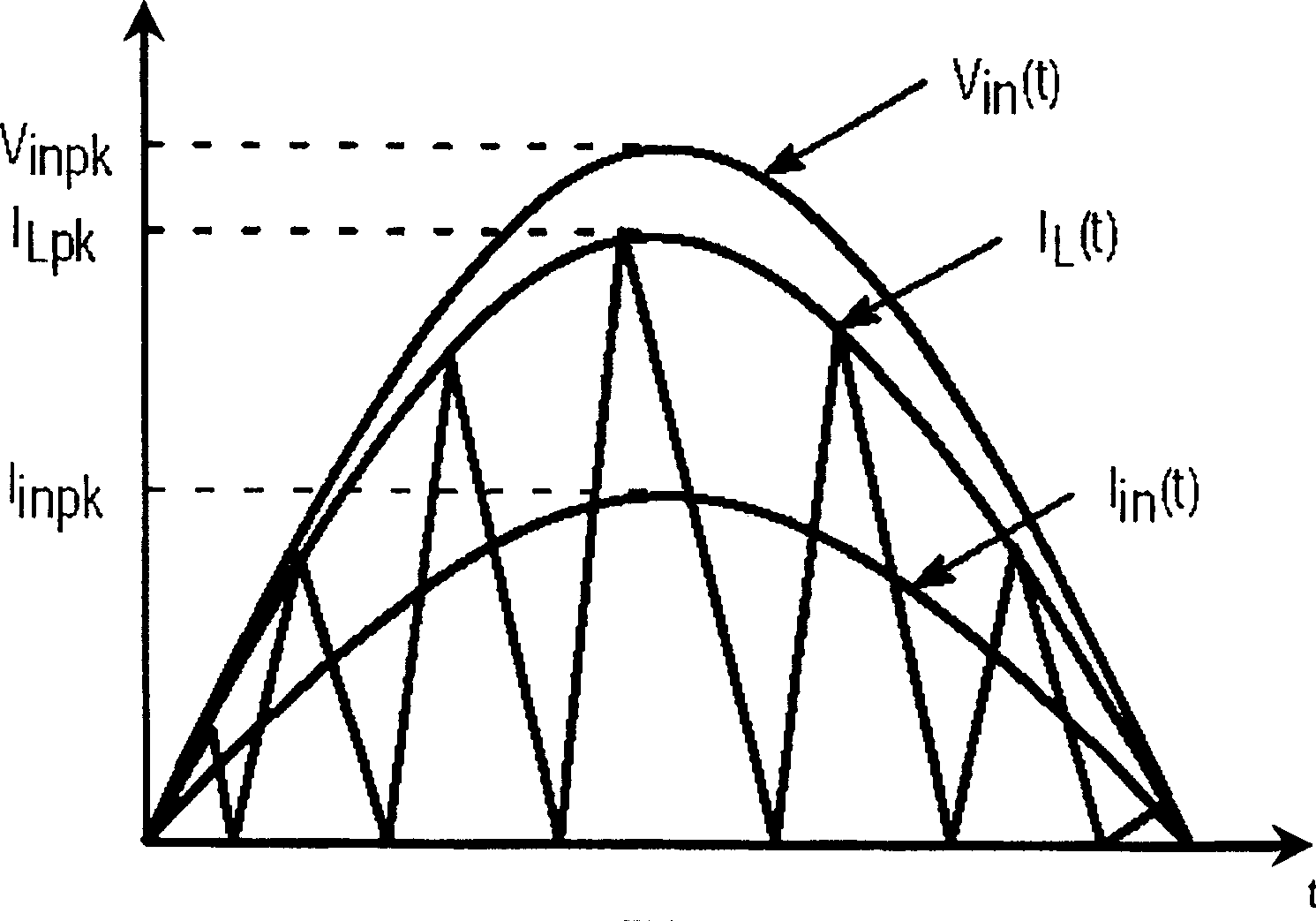
Power factor correction circuit within broad voltage range
A power factor correction and wide voltage technology, which is applied in the field of power factor correction circuits, can solve the problems of input current zero-crossing distortion increase and input current distortion, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating zero-crossing distortion, ensuring accurate detection, and realizing real-time tracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
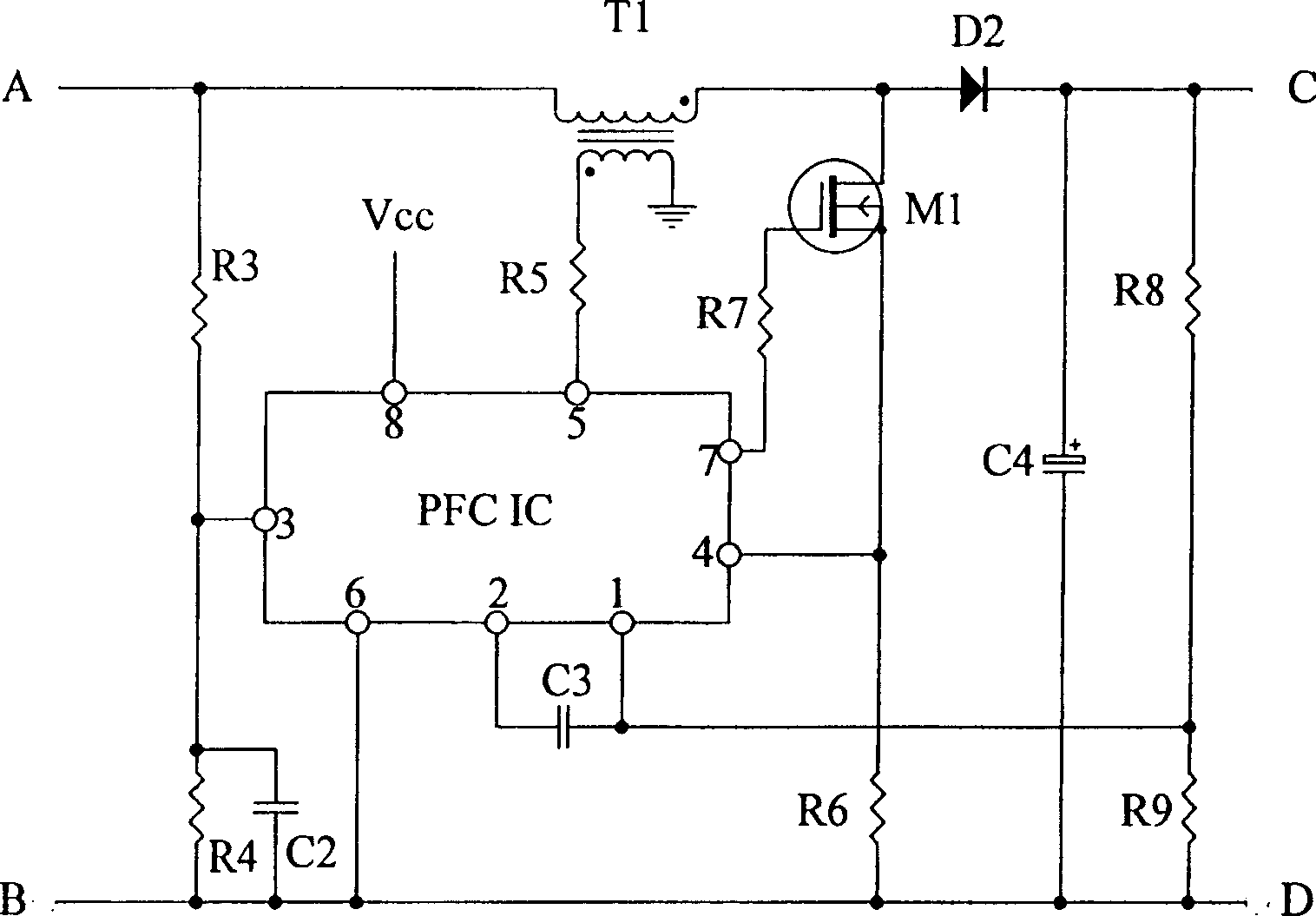
[0065] Embodiment 1: see Figure 7a , the transistor in the nonlinear compensation circuit is a crystal diode D1. The first voltage-dividing resistor R1 and the second voltage-dividing resistor R2 are connected in series to the output terminals of the rectifier circuit, that is, the input terminals A and B of the circuit, that is, one end of the first voltage-dividing resistor R1 is connected to the circuit input terminal A and connected to the third voltage-dividing resistor The piezoresistor R3 is connected to the common end of the primary coil of the boost inductor T1, the other end of the first voltage dividing resistor R1 is connected to the second voltage dividing resistor R2 and one end of the filter capacitor C1, and the other end of the second voltage dividing resistor R2 The other end of the filter capacitor C1 is connected to the circuit input terminal B; the cathode of the regulator tube ZD1 is connected to the common point of the first voltage dividing resistor R1...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: see Figure 7b , the transistor in the nonlinear compensation circuit is a transistor TR1. The first voltage-dividing resistor R1 and the second voltage-dividing resistor R2 are connected in series to the output terminals of the rectifier circuit, that is, the input terminals A and B of the circuit, that is, one end of the first voltage-dividing resistor R1 is connected to the circuit input terminal A and connected to the third voltage-dividing resistor The piezoresistor R3 is connected to the common end of the primary coil of the boost inductor T1, the other end of the first voltage dividing resistor R1 is connected to the second voltage dividing resistor R2 and one end of the filter capacitor C1, and the other end of the second voltage dividing resistor R2 It is connected to the other end of the filter capacitor C1 and then connected to the circuit input terminal B; the cathode of the regulator tube ZD1 is connected to the common point of the first voltage ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com