Liquid crystal display device and driving method and circuitry thereof
A technology of liquid crystal display and driving method, which is applied to static indicators, instruments, circuits, etc., and can solve problems such as abnormality, which must be rebooted before restarting, and instant booting cannot be achieved.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
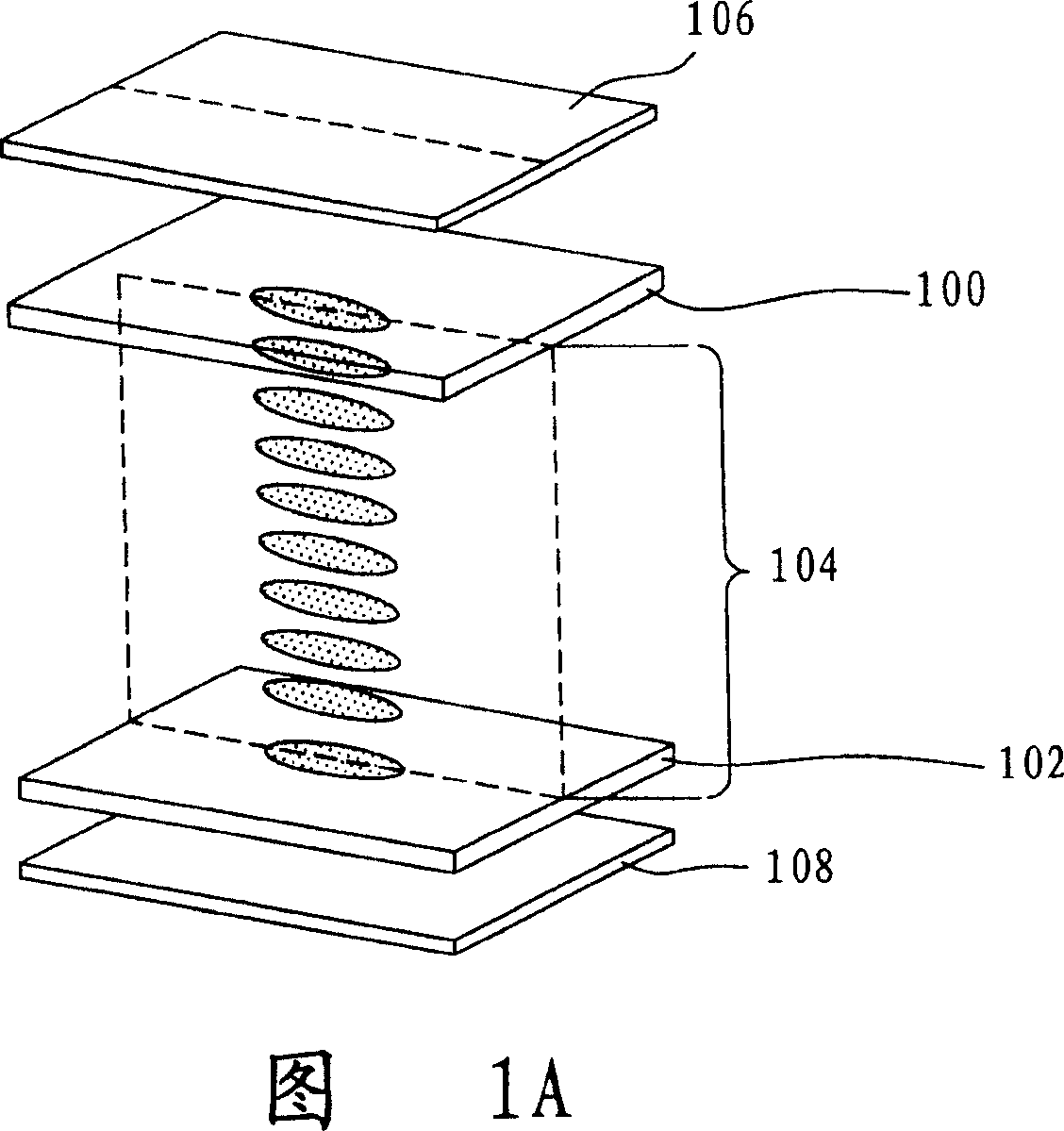
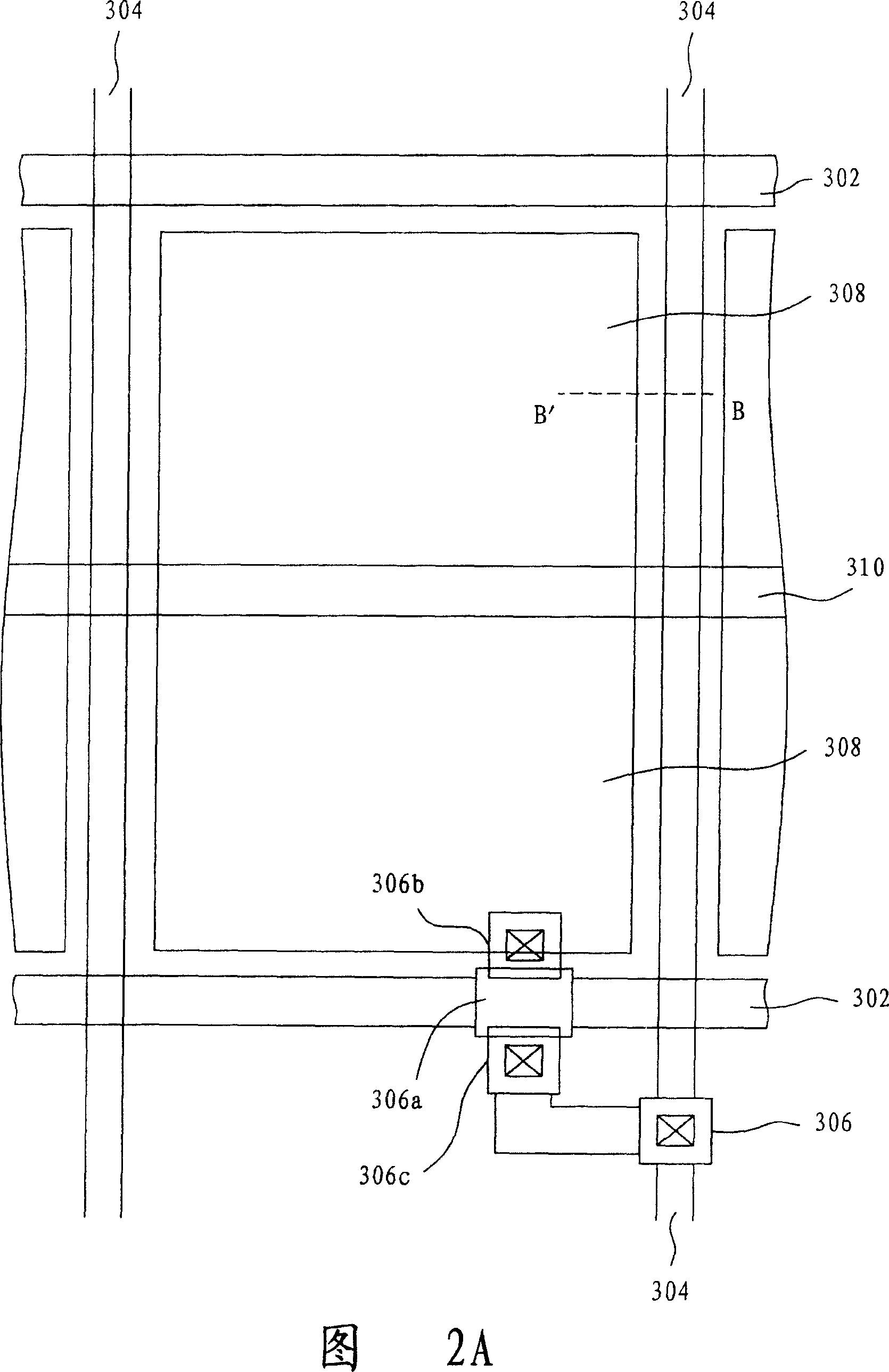
[0071] 3A is a top view of the pixel region of the first embodiment of the present invention, wherein the silicon island (silicon island) 506a of the switching transistor 506 is connected to the scanning line 502. When the switching transistor 506 is selected by the scanning signal, the scanning The signal will turn on the switching transistor 506, so the image signal on the image data line 504 will be transmitted and connected through the switching transistor 506, and the drain 506b of the switching transistor 506 is connected to the pixel electrode 508, and the other source 506c is connected to the image The data line 504 and a common electrode line 510 serve as the common electrode of the pixel electrode 508 . In the present invention, a metal electrode 512 is additionally arranged around the pixel electrode area, and the metal electrode 512 is controlled by the common electrode line 510 .
[0072] Generally speaking, for the pixel structure shown in FIG. 3A , for a selected...
Embodiment 2
[0078] 4A is a top view of the pixel region of the second embodiment of the present invention, wherein the silicon island (silicon island) 706a of the switching transistor 706 is connected to the scanning line 702. When the switching transistor 706 is selected by the scanning signal, the scanning The signal will turn on the switching transistor 706, so the image signal on the image data line 704 will be transmitted and connected through the switching transistor 706, and the drain 706b of the switching transistor 706 is connected to the pixel electrode 708, and the other source 706c is connected to the image The data line 704 and a common electrode line 710 are used as the common electrode of the pixel electrode 708. In the second embodiment of the present invention, a metal electrode 712 is arranged around the pixel electrode, and the metal electrode 712 is formed by the common electrode Controlled by line 710.
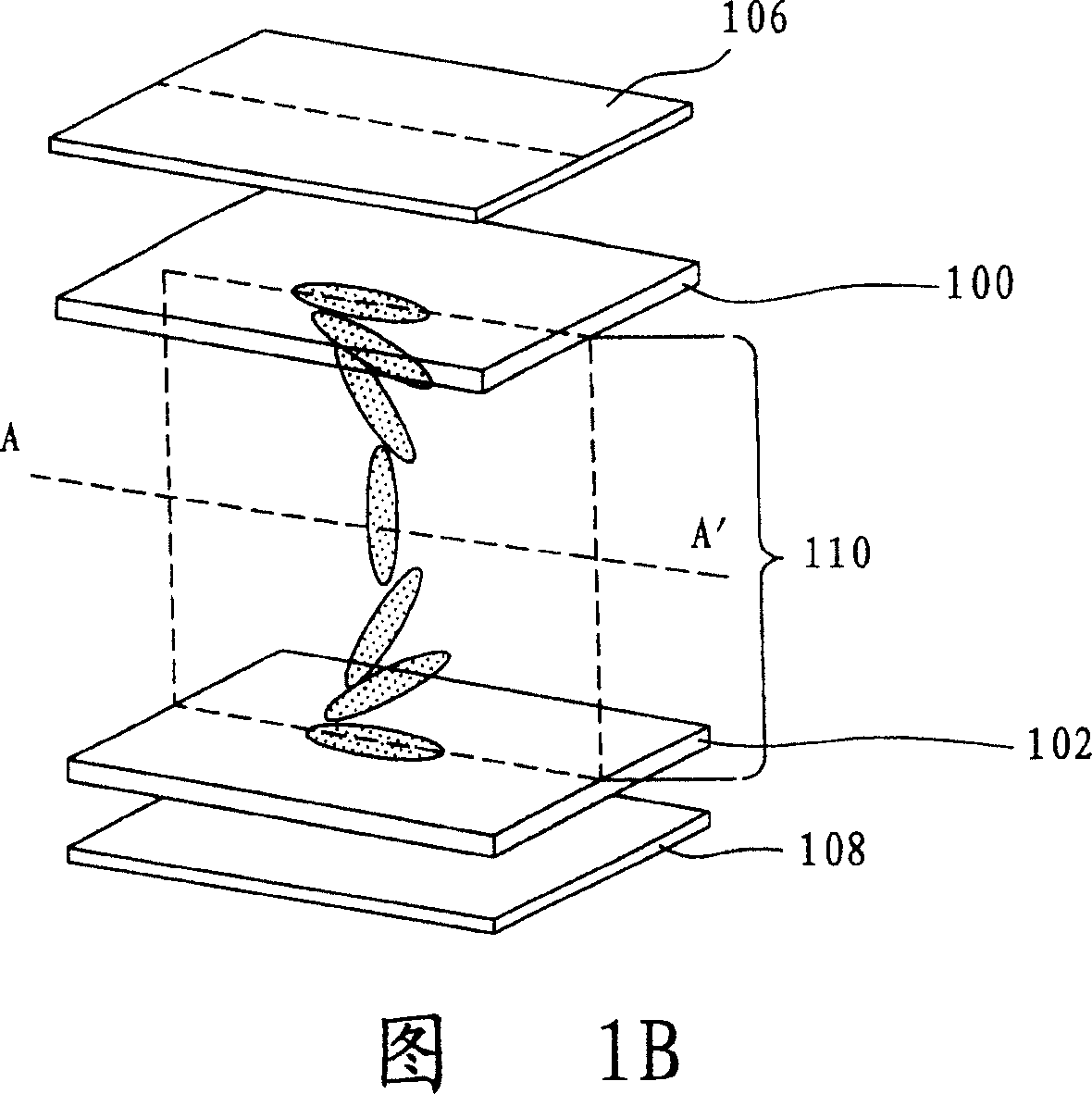
[0079] Please refer to FIG. 4B , which is a side view of the pix...
Embodiment 3
[0084] 5A is a top view of the pixel region according to the third embodiment of the present invention, wherein the silicon island (silicon island) 806a of the switching transistor 806 is connected to the scan line 802, and the drain 806b of the switching transistor 806 is connected to the pixel electrode 808. Another source electrode 806c is connected to the image data line 804, and a common electrode line 810 is used as the common electrode of the pixel electrode 808. In the third embodiment of the present invention, the metal electrode 812 and the common electrode 810 are in an "H" shape, And the metal electrode 812 is controlled by the common electrode line 810 .
[0085] Please refer to FIG. 5B , which is a side view of the pixel electrode according to the third embodiment of the present invention, which is a schematic cross-sectional view of the structure along line AA' in FIG. 5A . A lower substrate 814 and an upper substrate 816 formed of a transparent insulating mater...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com