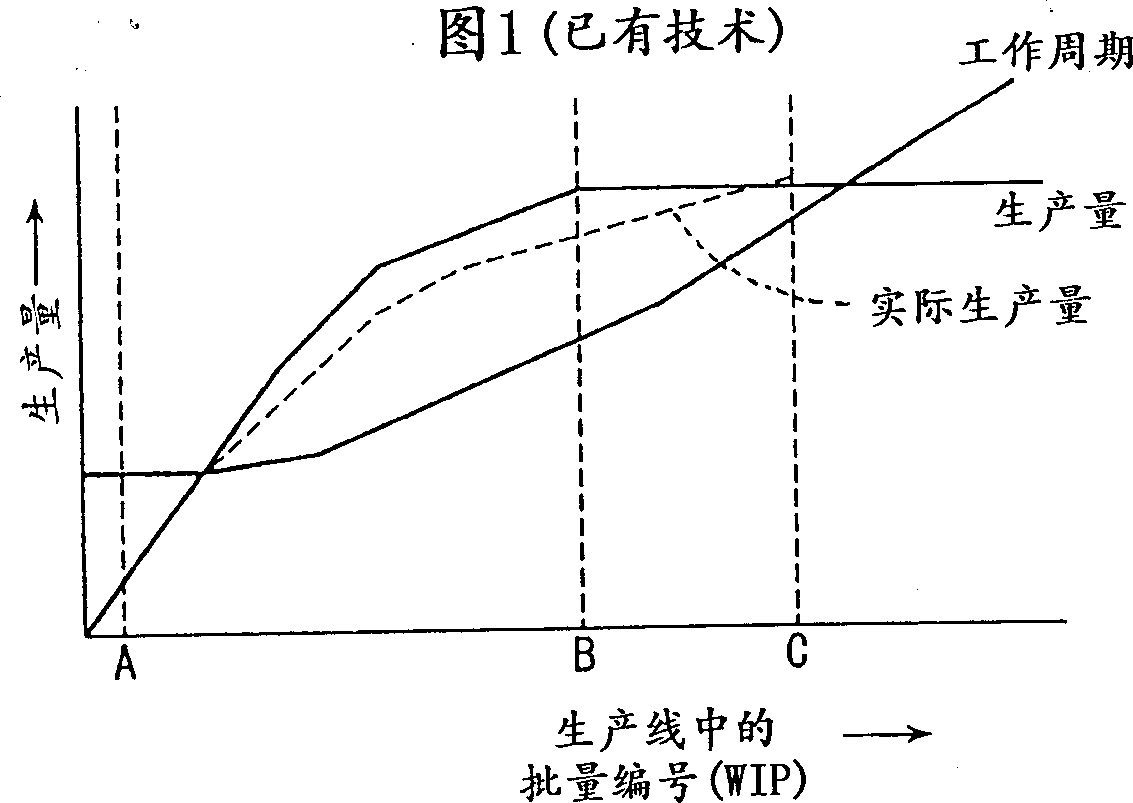
Semiconductor article production and producing apparatus, and electronic transaction system and method
An electronic transaction and production system technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, buying and selling/lease transactions, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in batch progress, difficulty in selecting the most appropriate one, and difficulty in simulation, and shorten the construction period. , the effect of increasing production and improving productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
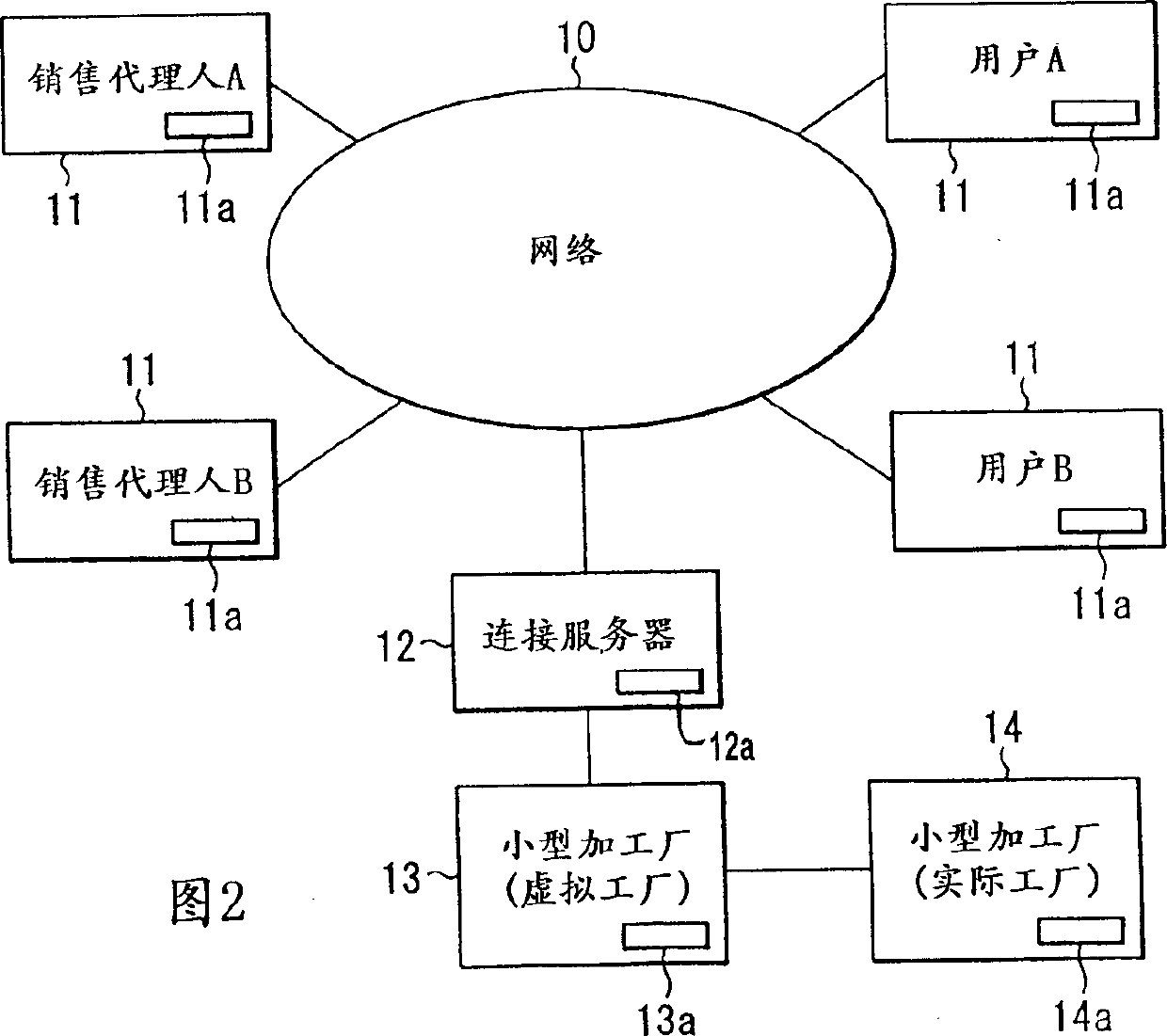
[0066] FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of the electronic transaction system for semiconductor products according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0067] The network 10 is, for example, a computer network represented by the Internet, and the present system completes electronic transactions through the network 10 .
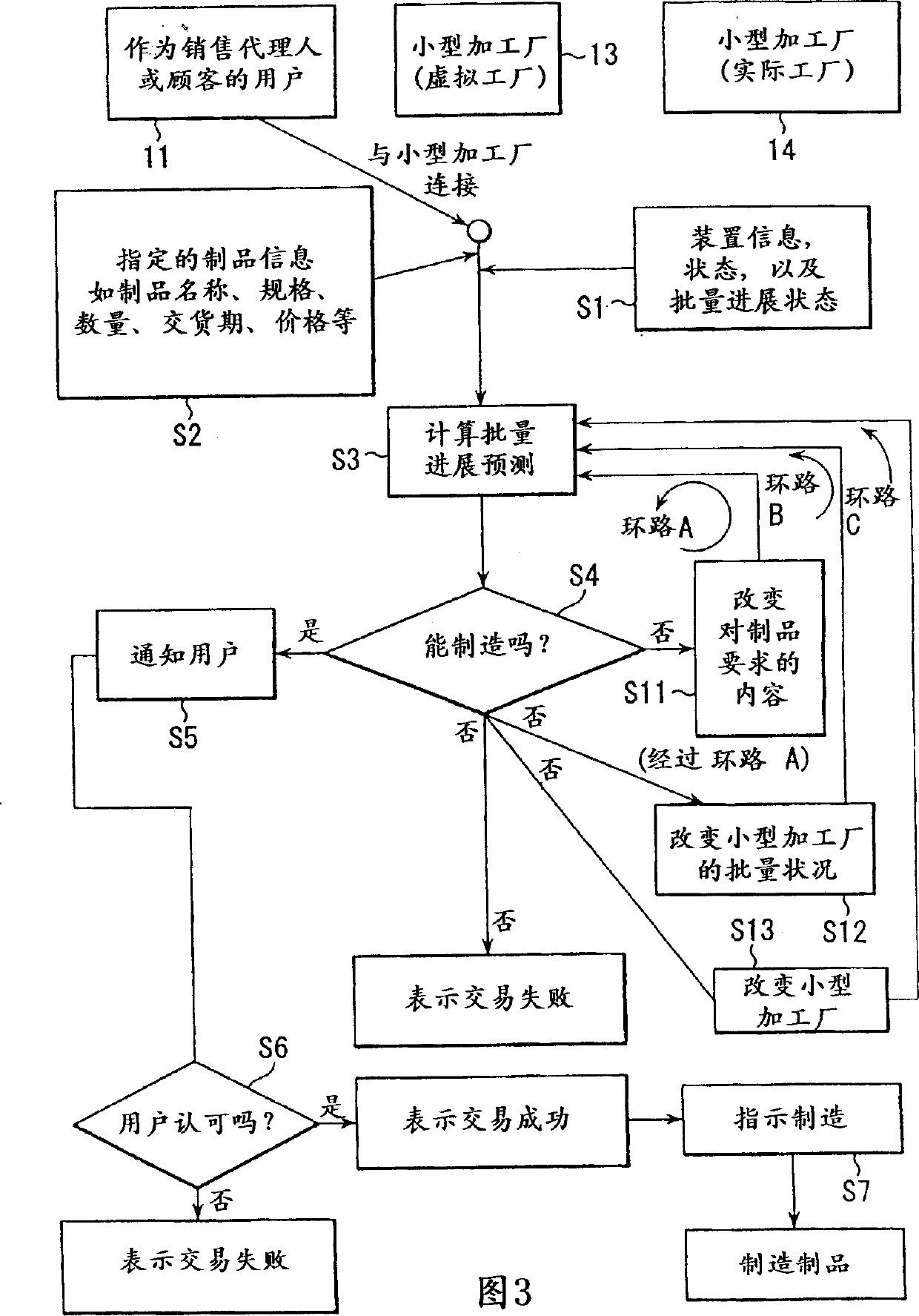
[0068] A plurality of customer terminals 11 and a connection server 12 are connected to the network 10 . The customer terminal 11 is a terminal operated by a user who is a customer and an employee, and a personal computer or a mobile phone that can be connected to the Internet can be used. A virtual factory (virtual production line) 13 called a small processing factory is connected to the connection server 12 . The connection server 12 exchanges various data between the customer terminal 11 and the virtual factory 13 . The virtual factory 13 is connected to the actual factory 14, which is a small-scale processing fact...
no. 2 Embodiment
[0098] Fig. 11 is a block diagram showing an example of a semiconductor production system according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0099] In the actual factory 14 (actual production line) that actually manufactures semiconductor products (and prototypes), there are manufacturing equipment groups, and products flow on each actual production line in the actual factory 14 . The batch progress status of each product is managed by the computer in the actual factory 14 . For example, by performing appropriate processing on the computer screen, it is possible to know which device a certain lot is in, whether it is in processing or waiting, or is being transported. In this computer, in addition to batch progress data, information on the state of the device (in operation or idling, in maintenance, in failure, maintenance schedule, etc.) is also stored.
[0100] Various information in the actual factory 14 is manually or automatically transferred to the virtual fact...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0130] This embodiment is a modified example of the second embodiment.
[0131] The second embodiment describes the case of seeking the optimum processing for the purpose of manufacturing high-priority lots in a short period of time and for the purpose of preferentially processing lots that are not affected or less affected by maintenance. This embodiment is an embodiment of seeking the best processing in order to achieve the purpose of processing that the electric power does not exceed the set value.
[0132] FIG. 18 shows the configuration of a virtual factory 13 capable of stabilizing electric power (or materials). The difference between Fig. 18 and Fig. 12 is that the power and material information data of the device and the condition data of power and material are additional input data. Fig. 19 and Fig. 20 show the vertical section of power and material of each device and the condition data of power and material. In this embodiment, the restriction on electric power is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com