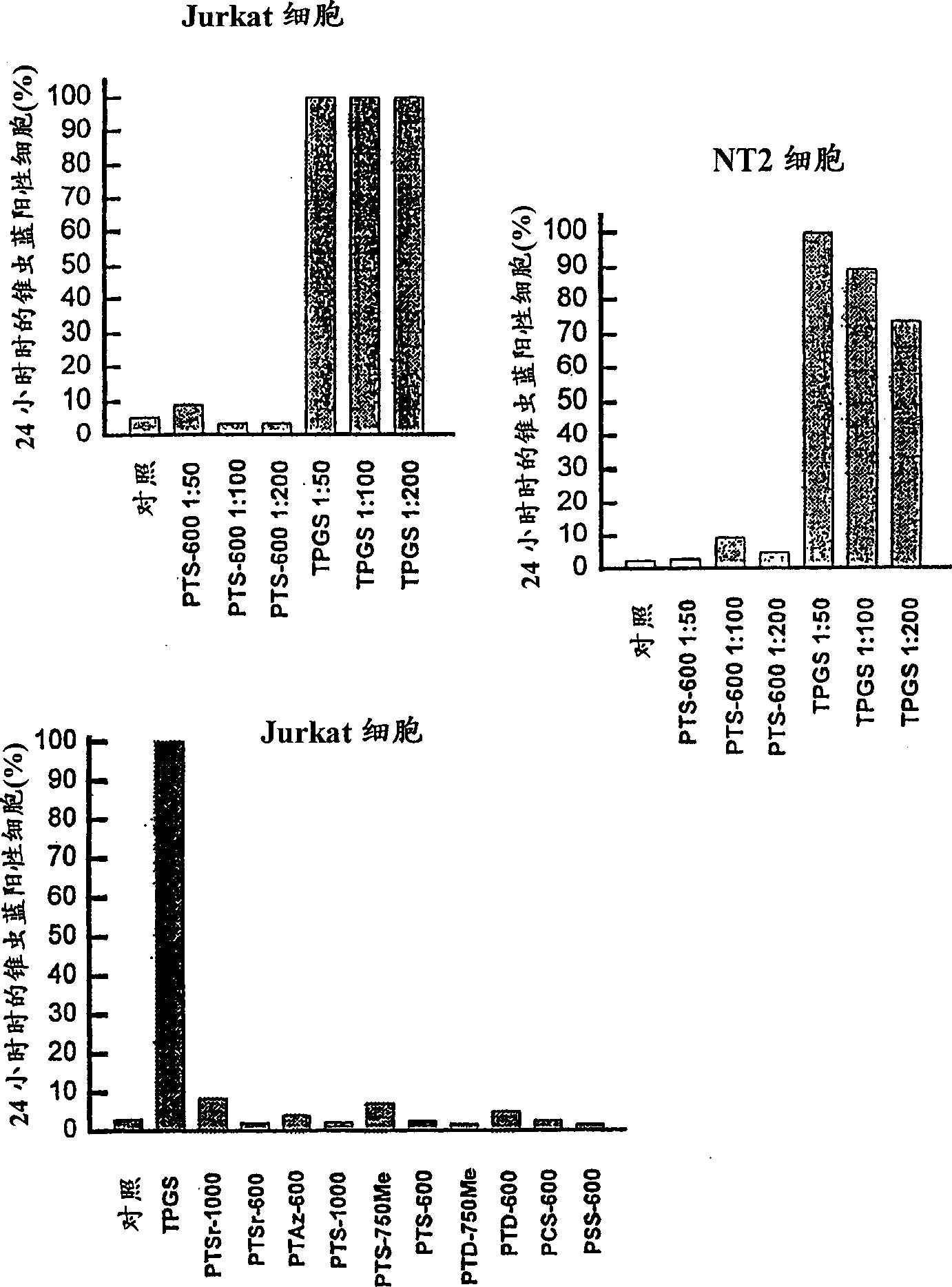
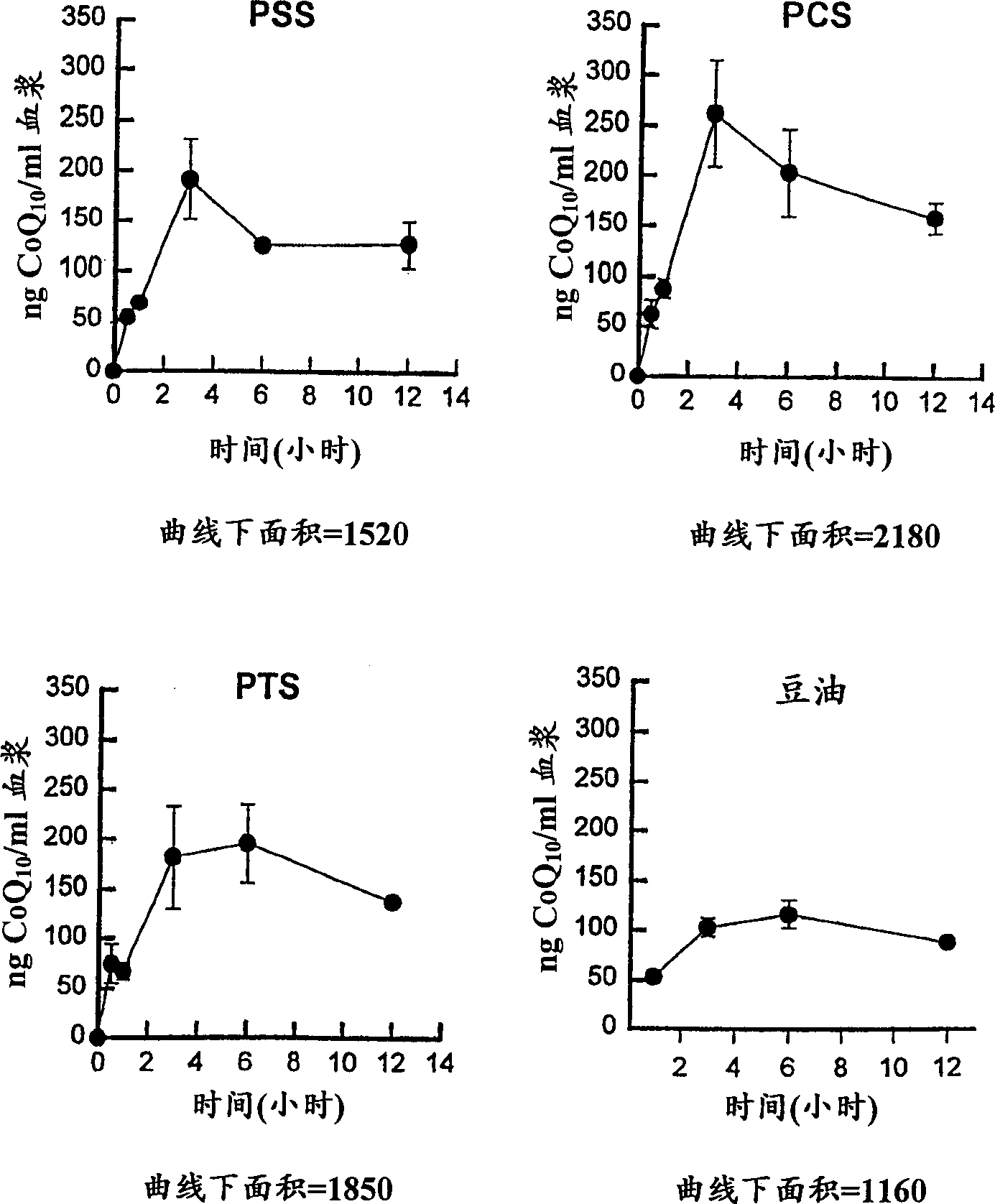
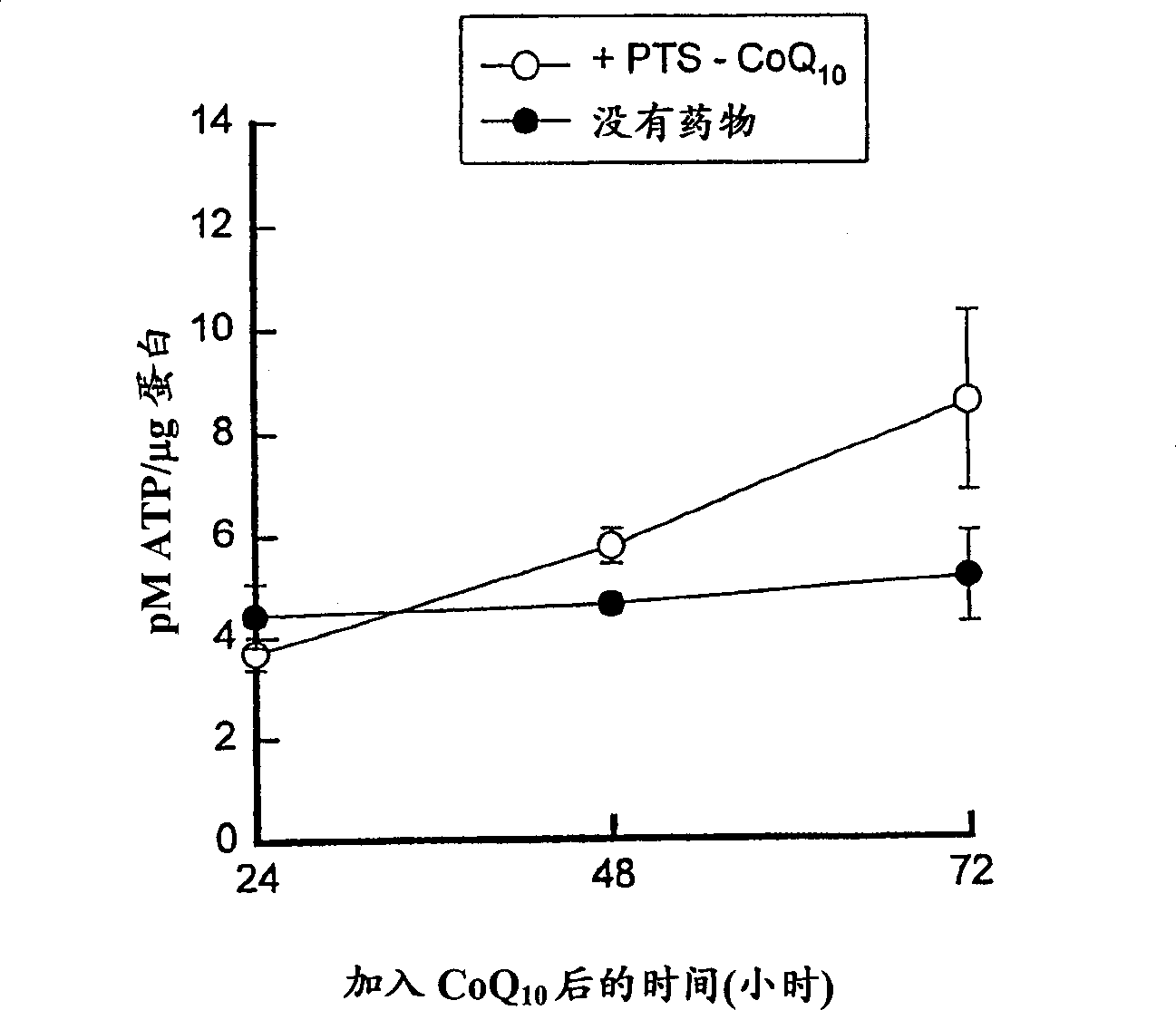
Water soluble compositions for bioactive lipophilic compounds
A technology of biological activity and composition, which is applied in the directions of drug combination, active ingredients of hydrocarbon compounds, active ingredients of hydroxyl compounds, etc., can solve the problems of simplicity and unbalanced stability of preparations in the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] The numbers following the above abbreviations (eg PCS-600) indicate the average molecular weight of the polyoxyethylene portion of the compound. A number followed by a Me abbreviation (eg, PTS-750Me) indicates a methyl terminated polyoxyethylene moiety (methoxypolyoxyethylene). Examples 1 and 2 illustrate the method of the present invention for preparing solubilizers. Embodiment 1. Preparation of polyoxyethylene-sitosterol sebacate (PSS-600)
[0084] 0.83 g of b-sitosterol (Sigma Chem. Co., #S-5753 product, approximately 60%) was dissolved in 3 ml of anhydrous toluene at 40°C, followed by the addition of 1.33 mM triethylamine (TEA). To the b-sitosterol-TEA solution was then added (dropwise, with stirring, and under anhydrous conditions) 1.33 mM sebacoyl chloride dissolved in 2 ml of anhydrous toluene. When the reaction was carried out at room temperature for 10 min, 2 mMPEG-600 (polyethylene glycol, Sigma Chem. . Stirring of the reaction was continued at room temper...
Embodiment 2
[0085] To 1.33 mM sebacoyl chloride dissolved in 2 ml of anhydrous toluene was added (dropwise under anhydrous conditions while stirring) 1 mM a-tocopherol (Sigma Chem. Co., #P-3251 product) and 1.33 mM TEA 3ml of anhydrous toluene solution. The reaction was carried out at room temperature for 10 minutes, followed by the dropwise addition of 2 mM PEG-600 (polyethylene glycol, Sigma, P-3390) and 2.66 mM TEA dissolved in 3 ml of toluene. The reaction was continued to stir at a constant rate for 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction mixture was extracted four times with 3 ml of a saturated solution of sodium chloride each time, and the toluene was evaporated under reduced pressure. The product was dissolved in 5 ml of water and co-evaporated with water under reduced pressure to further remove residual toluene. Lyophilization afforded the final waxy product (1.15 g).
Embodiment 3
[0086] Polyethylene glycol (average molecular weight 1000, Sigma Chem. Co., #P-3515 product) or Polyethylene glycol methyl ether (average molecular weight 750, Sigma Chem. Co., product #P-7018) was linked to a-tocopherol to obtain other solubilizers (Table 1). They were synthesized according to the method of Example 2, and their properties were confirmed by mass spectrometry using MALDI-TOF technology. Example 3 provides the molecular characterization of the synthetic solubilizer. Example 3. Molecular characteristics of the solubilizer obtained by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis
[0087] Solubilizer
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com