Method of fabricating semiconductor device
A manufacturing method, semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor lasers, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as uneven composition, increased optical loss, and polluted surfaces, so as to achieve yield and quality improvement and avoid compositional inhomogeneity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
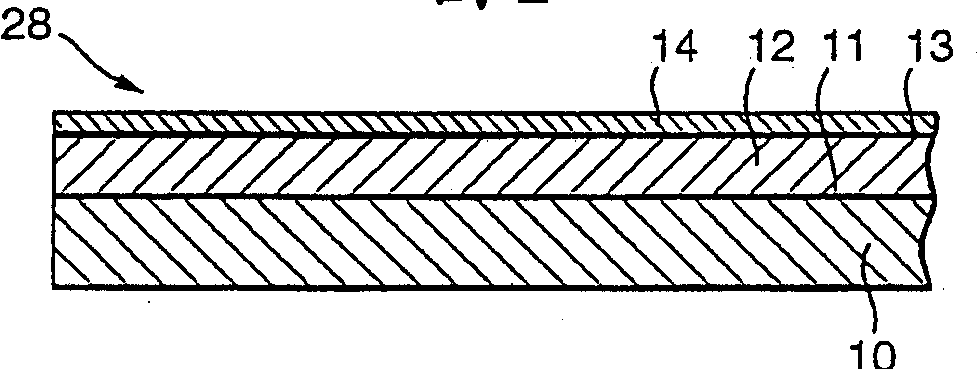
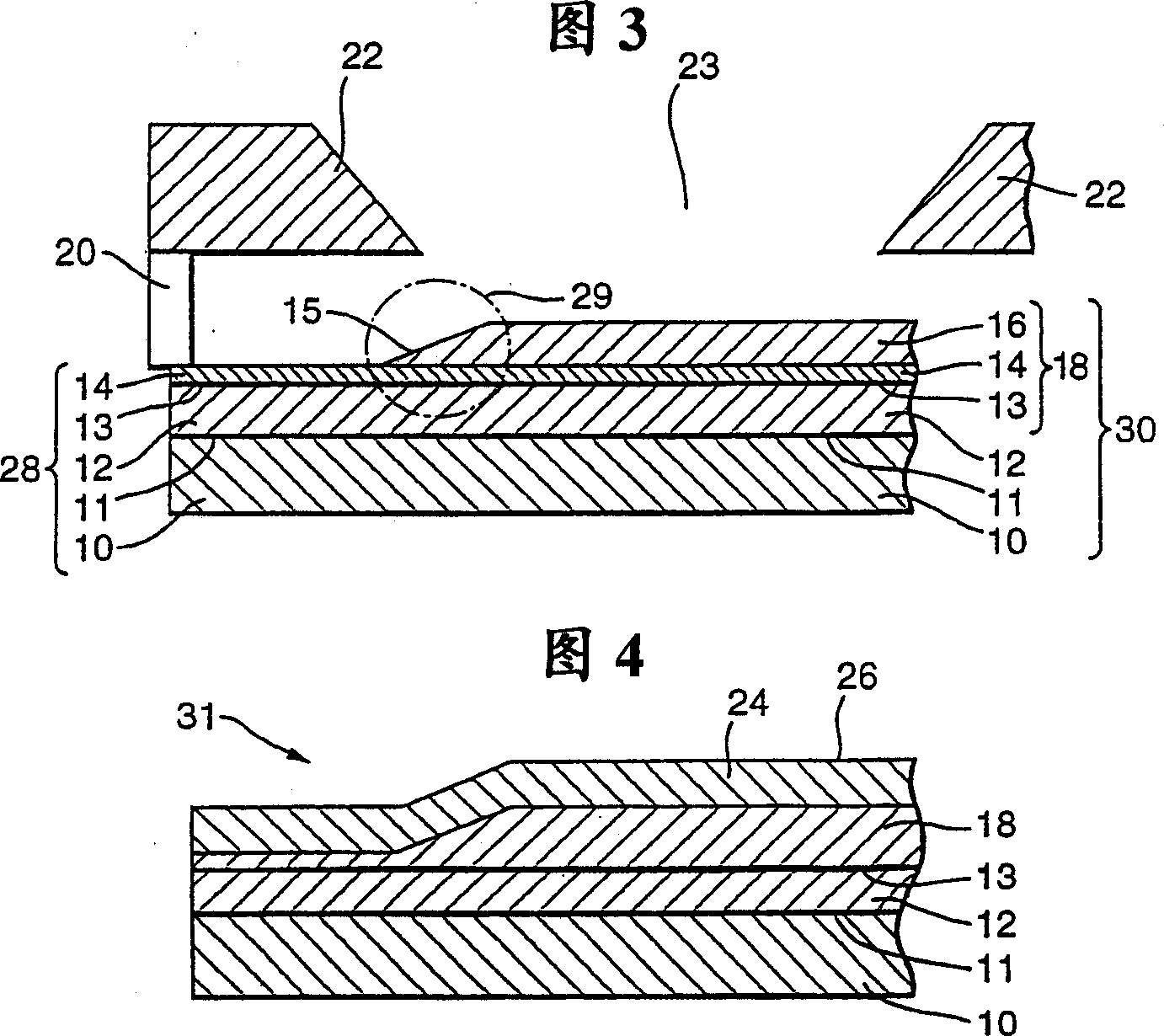
[0030] refer to figure 1 , a portion of a vertical cross-section of a gallium arsenide (GaAs) based wafer 10 is shown in the figure. Substrate 10 has been prepared for epitaxial growth according to standard procedures well known to those skilled in the art of semiconductor device fabrication. The substrate 10 is mounted on a molybdenum holder (not shown). The mounted substrate 10 is placed in a chemical beam epitaxy (CBE) apparatus, and then stored under ultra-high vacuum (UHV). Then put the substrate 10 into the growth chamber of the CBE device under ultra-high vacuum, and heat it to about 650 degrees Celsius under the ultra-high pressure of arsenide to remove the oxide deposition on the surface, while maintaining a stable surface and avoiding It gets rough. The temperature of substrate 10 is then set to a growth temperature in the range of 400 to 700 degrees Celsius, typically 540 degrees Celsius, to reduce unintentional accumulation of impurities during CBE growth using ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com