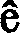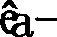Method and kit for detection of schistosomiasis through polymerase chain reaction
A technology of schistosomiasis and reagent kit, applied in the field of diagnosing schistosomiasis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] The present invention is described in detail by referring to the following examples. It must be understood that the present invention is not limited to these embodiments, but also includes changes and modifications within the functional scope of the invention. Example 1 Rupture Schistosoma monsonii eggs
[0048] Eggs were extracted from the liver of mice previously infected with 100 cercariae of Schistosoma monsonii and stored in 0.9% saline solution at -20°C until use (Pellegrino and Siqueira, 1956, Rev. Bras. Malar. 8:589) . To disrupt eggs, 10 μl of saline solution containing 100,000 eggs / ml was mixed with 90 μl of distilled water and the final solution was shaken for 5 minutes in a mechanical mixer. This mixture containing ruptured eggs was used directly for DNA extraction. Example 2 By the modified Steiner method (J.J.Steiner, C.J.Polkemba, R.G.Fjellstrom, and L.F.Elliott, 1995, a rapid single-tube genomic DNA extraction method for PCR and RAPD analysis, Nucleic...
Embodiment 4
[0051]Figure 2 shows the electrophoretic pattern obtained from the amplification of Schistosoma monsonii DNA and the maximum sensitivity achievable for the detection of this DNA. Lane M is the molecular weight standard; lanes 1-5 are 20, 10, 5, 1, and 0.5fg DNA in sequence. The PCR reaction was able to detect as little as 1 fg of Schistosoma monsonii DNA. Figure 3 shows the electrophoretic patterns obtained after amplifying DNA from five other Schistosoma species using the same primers under the same PCR conditions as used for Schistosoma monsonii. Lane M: molecular weight standard; Lane 1: Schistosoma monsonii; Lane 2: Schistosoma haematobium; Lane 3: Schistosoma japonicum (strain from the Philippines); Lane 4: Schistosoma japonicum (strain from Japan); Lane 5: Schistosoma sheep (S .matthei); Lane 6: Schistosoma bovis (S.bovis); Lane 7: S. leipperi; Lane 8: negative control. The PCR reaction was able to amplify DNA from all species of schistosomes examined. Figure 4 shows ...
Embodiment 5
[0054] Figure 6 shows the results of previous Kato-Katz assays for the amplification of S. monsonii DNA in feces of patients with various concentrations of the parasite. Lane M: molecular weight standard; Lane 1: positive control; Lane 2-9: human feces samples containing 0.96, 0.168, 432, 600, 96.912, and 72 eggs per gram in sequence. PCR results were consistent with those obtained by parasitological examination in all samples. Example 5 Detection of Schistosoma monsonii in patient serum
[0055] For 4 serum samples, 100 μl of each sample was used to purify DNA using a Glass-max(R) DNA separation spin column system (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Then 2 µl of this DNA was used for PCR amplification under the same conditions as above. The human sera used were previously tested by the Kato-Katz method, 2 samples were positive and 2 samples were negative.
[0056] Figure 7 shows the amplification results. Lane M: molecular weight standard; La...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com