Treating prostate cancer with anti-ErbB2 antibodies
A prostate cancer and antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibody medical components, antibodies, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve problems such as unreported mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
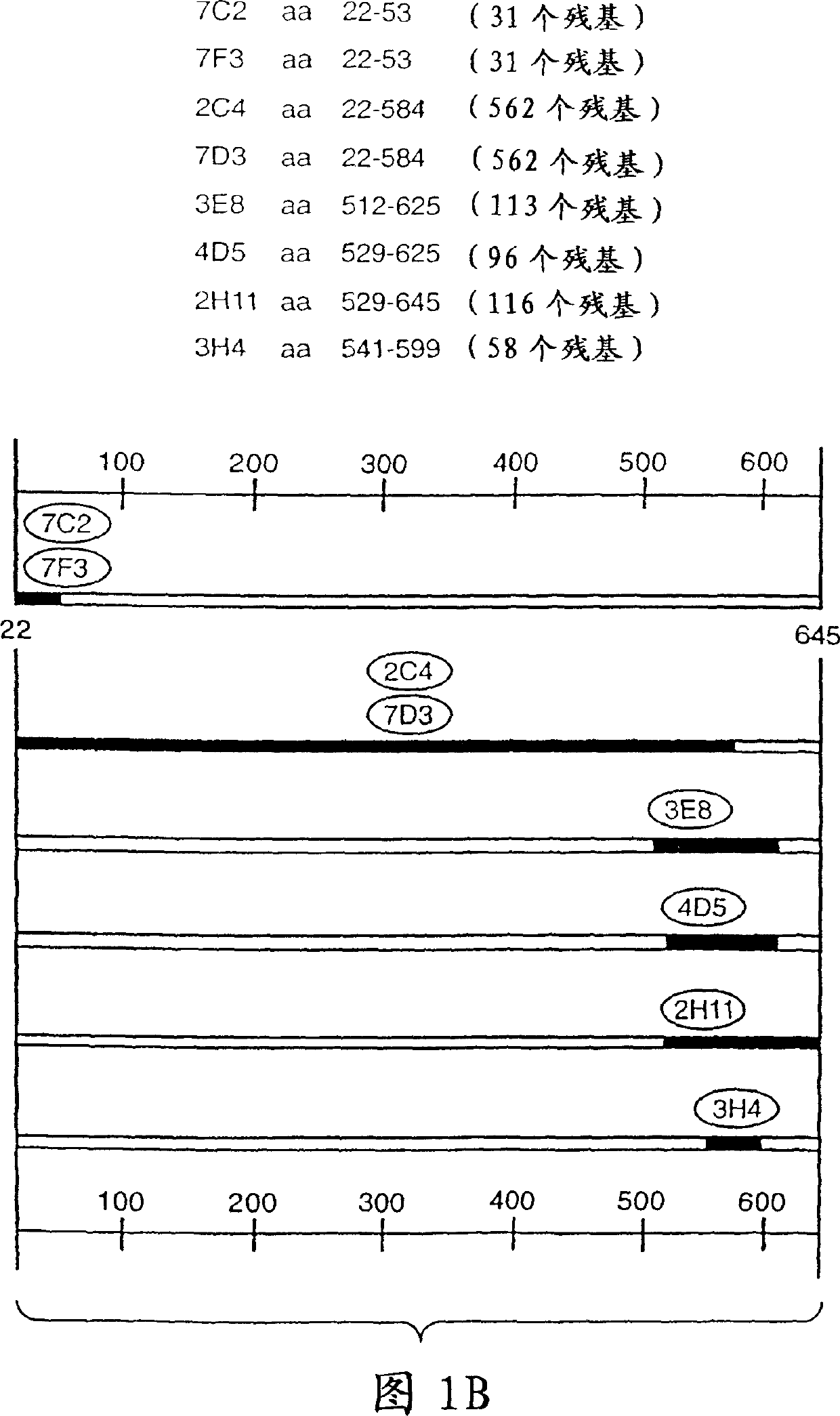
[0245] Production and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibody 2C4
[0246] Murine monoclonal antibodies 2C4, 7F3 and 4D5 that specifically bind to the ErbB2 extracellular domain were produced as described by Fendly et al., Cancer Research 50: 1550-1558 (1990). Briefly, DNA produced as described by Hudziak et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 84:7158-7163 (1987) was collected in phosphate buffered saline containing 25 mM EDTA. NIH 3T3 / HER2-3 400 cells (expressing approximately 1 x 10 ErbB2 molecules / cell) and used to immunize BALB / c mice. At 0, 2, 5, and 7 weeks, mice were injected intraperitoneally with 10 dissolved in 0.5 ml PBS. 7 cells. Mice bearing immunoprecipitated 32P-labeled ErbB2 antiserum were injected intraperitoneally with wheat germ agglutinin-agarose (WGA) purified ErbB2 membrane extracts at 9 and 13 weeks. This step was followed by iv injection of 0.1 ml of the ErbB2 preparation and fusion of splenocytes with the mouse myeloma line X63-Ag8.653. ...
Embodiment 2
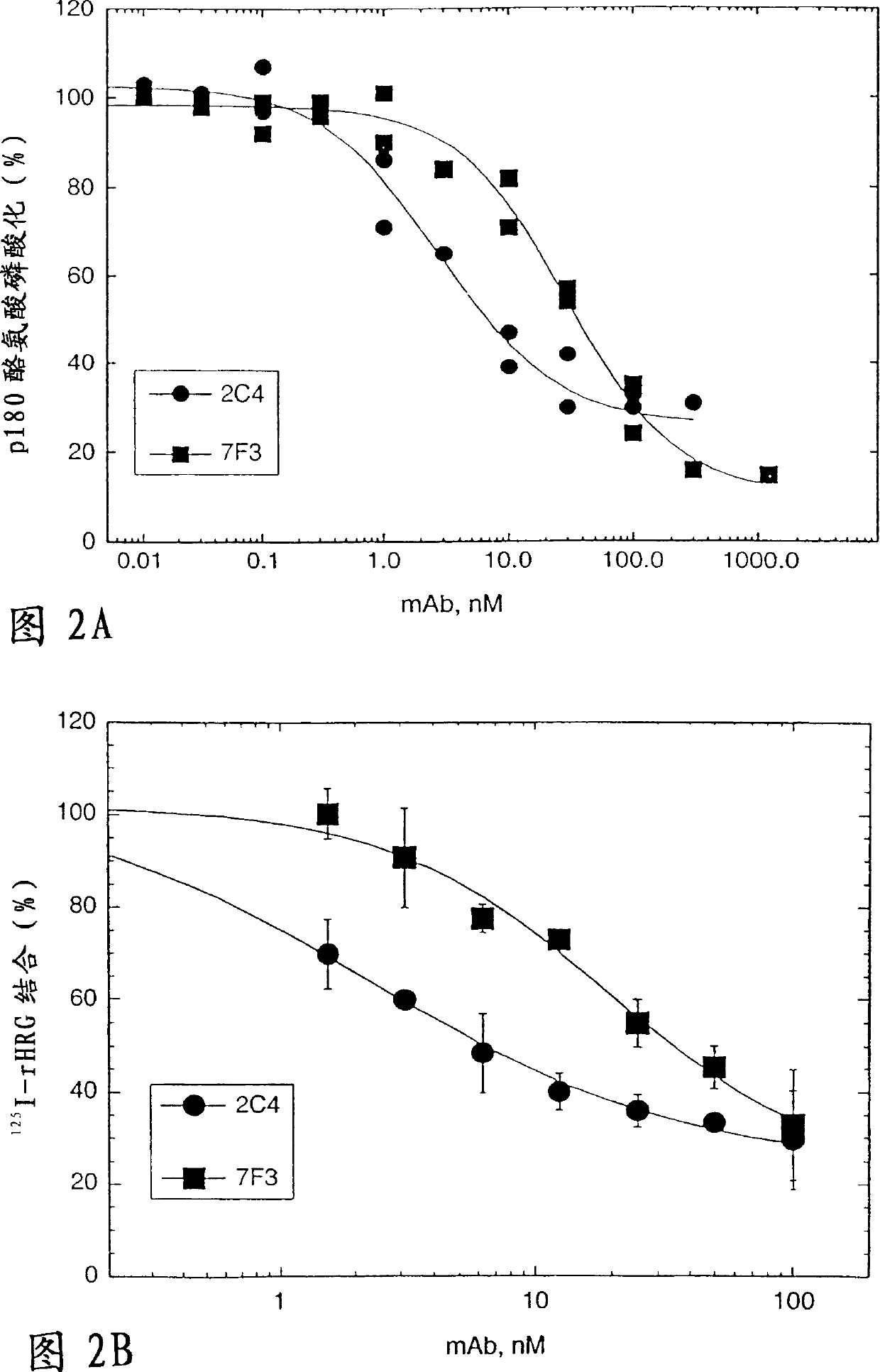
[0256] Blocking of HRG-dependent binding of ErbB2 to ErbB3 by monoclonal antibody 2C4
[0257] The ability of ErbB3 to bind ErbB2 was tested using a co-immunoprecipitation assay. will be 1.0×10 6 MCF7 or SK-BR-3 cells were seeded in 6-well tissue culture plates in 50:50 DMEM / Ham's F12 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 10 mM HEPES (growth medium) at pH 7.2 and allowed to adhere overnight. Cells were starved for 2 hours in serum-free growth medium before starting experiments.
[0258] Cells were washed briefly with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and then diluted with 100 nM into 0.2% w / v bovine serum albumin (BSA), RPMI medium for the indicated antibodies, with 10 mM HEPES (binding buffer) at pH 7.2 or Incubate with binding buffer alone (control). After 1 hour at room temperature, HRG was added to half of the wells (+) to a final concentration of 5 nM. A similar volume of binding buffer was added to the other well (-). The incubation was continued for a...
Embodiment 3
[0264] Humanized 2C4 Antibody and Affinity Matured 2C4 Antibody Variants
[0265] The variable domains of the murine monoclonal antibody 2C4 were first cloned into a vector that yielded mouse / human chimeric Fab fragments. Total RNA was isolated from hybridoma cells using the Stratagene RNA extraction kit following the manufacturer's protocol. The variable domains were amplified by RT PCR as described above, gel-purified and inserted into pUC119-based plasmid derivatives containing human kappa constant domains and human C H 1 domain (Carter et al. PNAS (USA) 89:4285 (1992); and US Pat. No. 5,821,337). The resulting plasmid was transformed into E. coli strain 16C9 for expression of the Fab fragment. Growth of cultures, induction of protein expression, and purification of Fab fragments were as described above (Werther et al. J. Immunol. 157:4986-4995 (1996); Presta et al. Cancer Research 57: 4593-4599 (1997)). Comparison of the inhibition of purified chimeric 2C4 Fab fra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com