Novel diphenylethylene compound
A compound and composition technology, applied in the field of diphenylethylene compounds, can solve problems such as insulin receptor desensitization, unclear genetic factors, and defects in polysaccharide metabolism and decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Synthesis of E-3-(3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-acrylic acid
[0060] To a mixture of 3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (30 mmol) and p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (30 mmol) was added 5 mL of acetic anhydride and 2.5 mL of triethylamine (TEA). After stirring at 130-140 °C for 24 h, the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature and quenched with 25 mL of concentrated HCl and washed with CH 2 Cl 2 extraction. The organic extract was further extracted with 1N NaOH, and the NaOH extract was subsequently washed with CH 2 Cl 2 Washed, and the aqueous layer was acidified with conc. HCl and washed with water to give crude product. The crude product was recrystallized from ethanol / water to give acid Ia.
[0061] Four batches of Ia (E-isomer) 40 μl samples prepared above were separated by HPLC on an Intersil ODS-3 (GL Sciences) column, 250×4.6 mm, and 62 vol% eluent A and 38 vol % eluent B eluted. Eluent A is 0.1% formic acid in water; B is 0.1% formic acid in ACN....
Embodiment 2
[0075] Synthesis of 3-(3,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-acrylic acid
[0076] To a mixture of 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (9.97 g, 60 mmol) and p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (10.0 g, 65 mmol) was added acetic anhydride (12 mL) and triethylamine (8.0 mL, 58 mmol) under argon atmosphere . The mixture was stirred at 140°C for 18 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to 5 °C and dichloromethane (100 mL) was added. Concentrated HCl (20ml) was added to this yellow suspension and the suspension was stirred for 20 minutes. The solid that separated was filtered, dissolved in aqueous sodium hydroxide (2M, 225 mL) and reprecipitated with concentrated HCl (40 mL). The yellow solid was filtered and washed with water (2 x 30 mL), and the above wet solid was recrystallized from a water-ethanol mixture. 1 H NMR (DMSO-d 6 ): δ12.38 (br, 1H), 9.47 (br, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 6.96 (d, J=8.4Hz, 2H), 6.81-6.77 (overlap, 4H), 6.54 (br, 1H), 3.40(s, 3H) and 3.37(s, 3H).
[0077] Synthesis o...
Embodiment 3
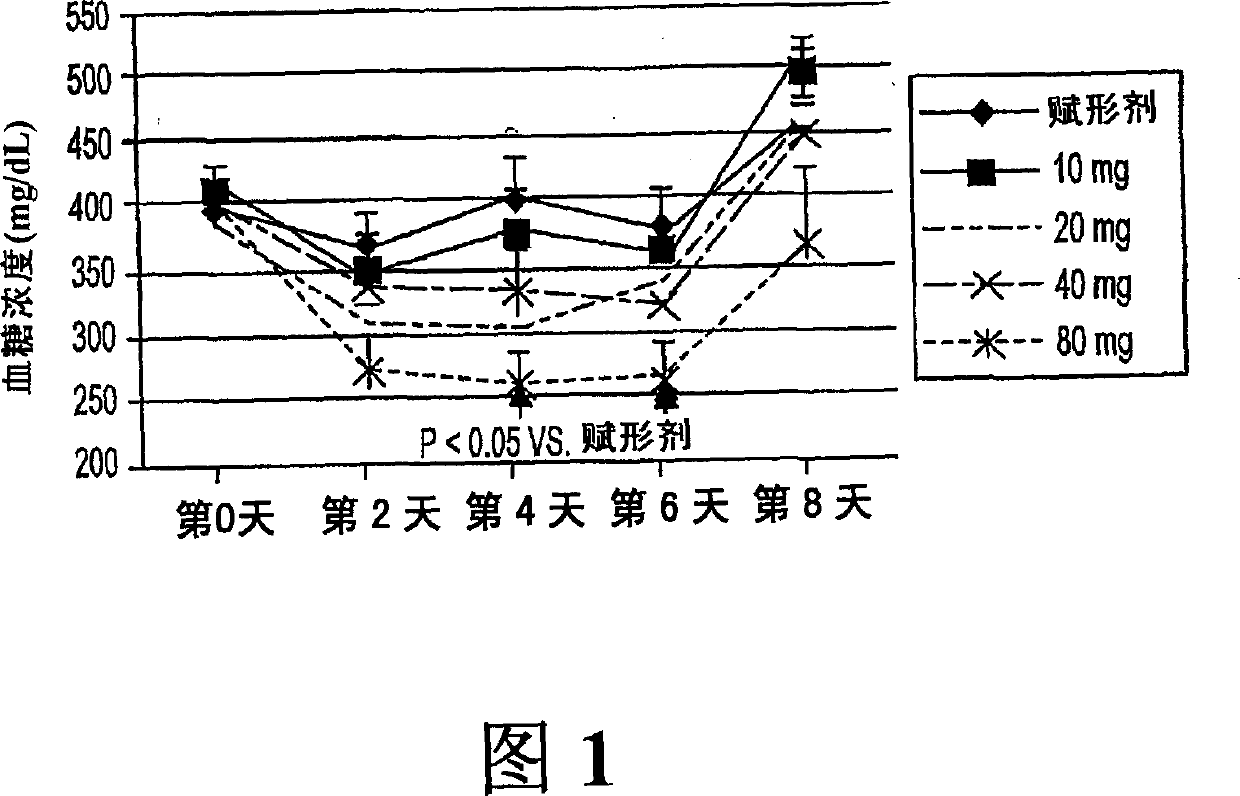
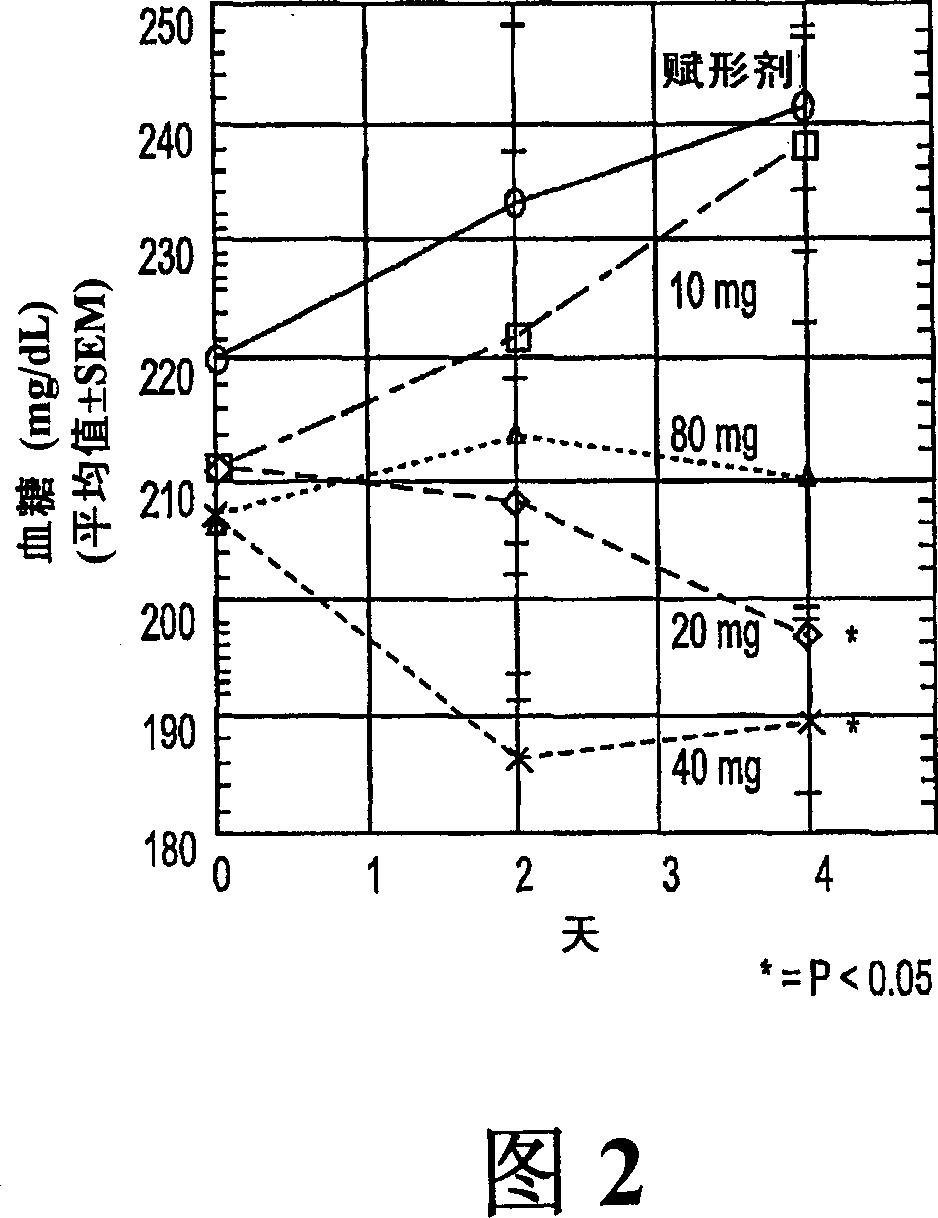
[0084] 60 mg streptozotocin by IV injection induced diabetes in Sprague-Dawley (SD) male rats (average body weight, 180 g). After 5 days, the average glucose concentration was about 350-400 mg / dL. Rats were then divided into 5 groups (n=7) and administered orally with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (vehicle) or Compound Ia (10, 20, 40 or 80 mg / kg body weight) daily for 8 days. Treatment of Ia at doses of 20, 40 or 80 mg / kg reduced blood glucose concentrations in these rats from day 2 to day 6 (compared to those in vehicle-treated controls). This reduction was statistically significant (p<0.05) on days 4 and 6 in rats given 80 mg / kg. The result is shown in Figure 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com