Optical modulator
A light modulator and gap technology, applied in the field of light modulators, can solve problems such as hindering the modulation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 2 Embodiment
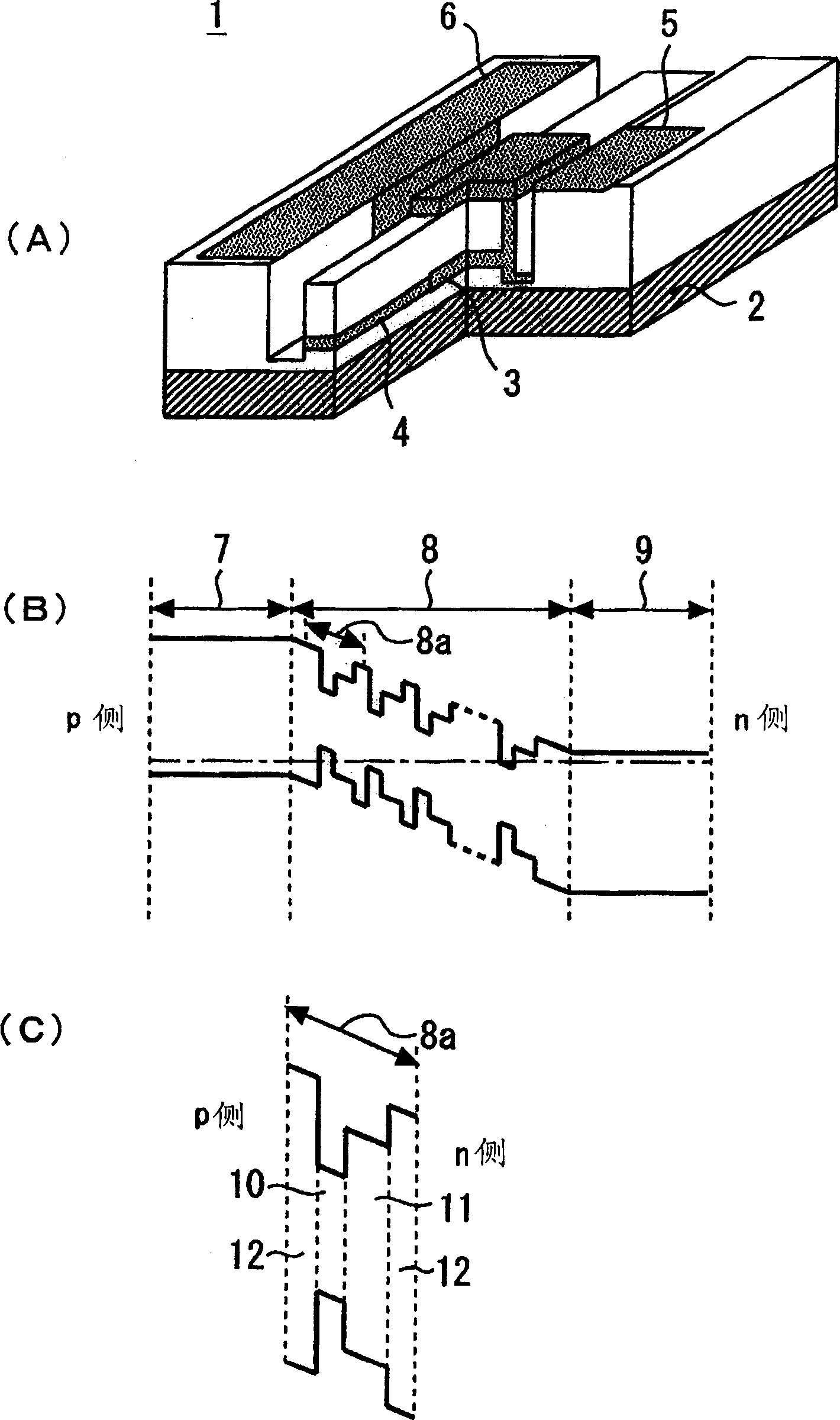
[0036] Figure 5 (A) and (B) are diagrams illustrating the energy bands of the multiple quantum wells of the optical modulator according to the second embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 5 In, due to the use of figure 1 Portions with the same reference numerals denote the same components, and thus their descriptions are omitted. exist Figure 5 In (A), reference numeral 13 denotes a layer having a band gap between the band gap of the well layer 10 and the band gap of the intermediate layer 11 . exist Figure 5 In (B), reference numeral 14 denotes a layer having a gap between the gap of the intermediate layer 11 and the gap of the barrier layer 12 .
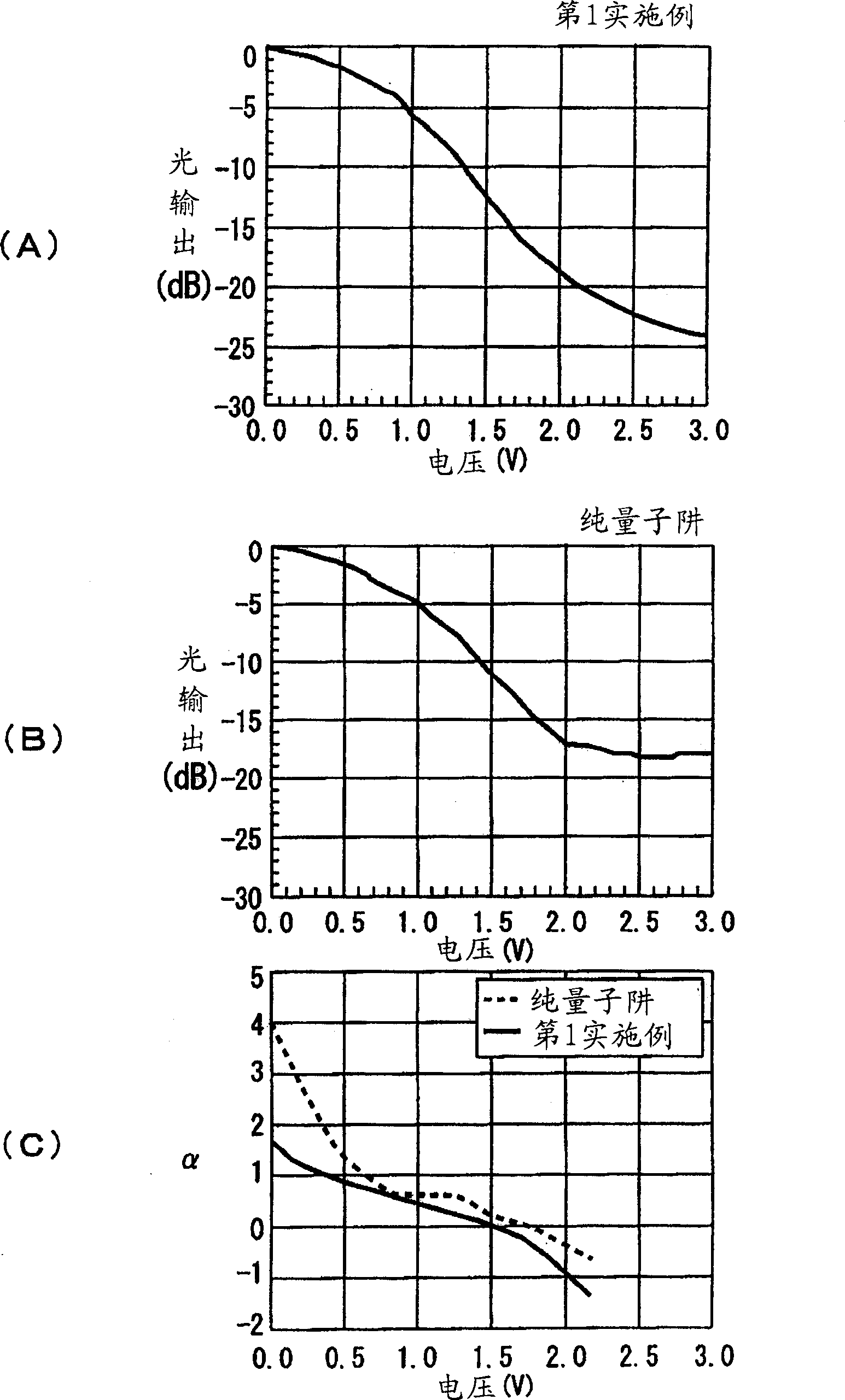
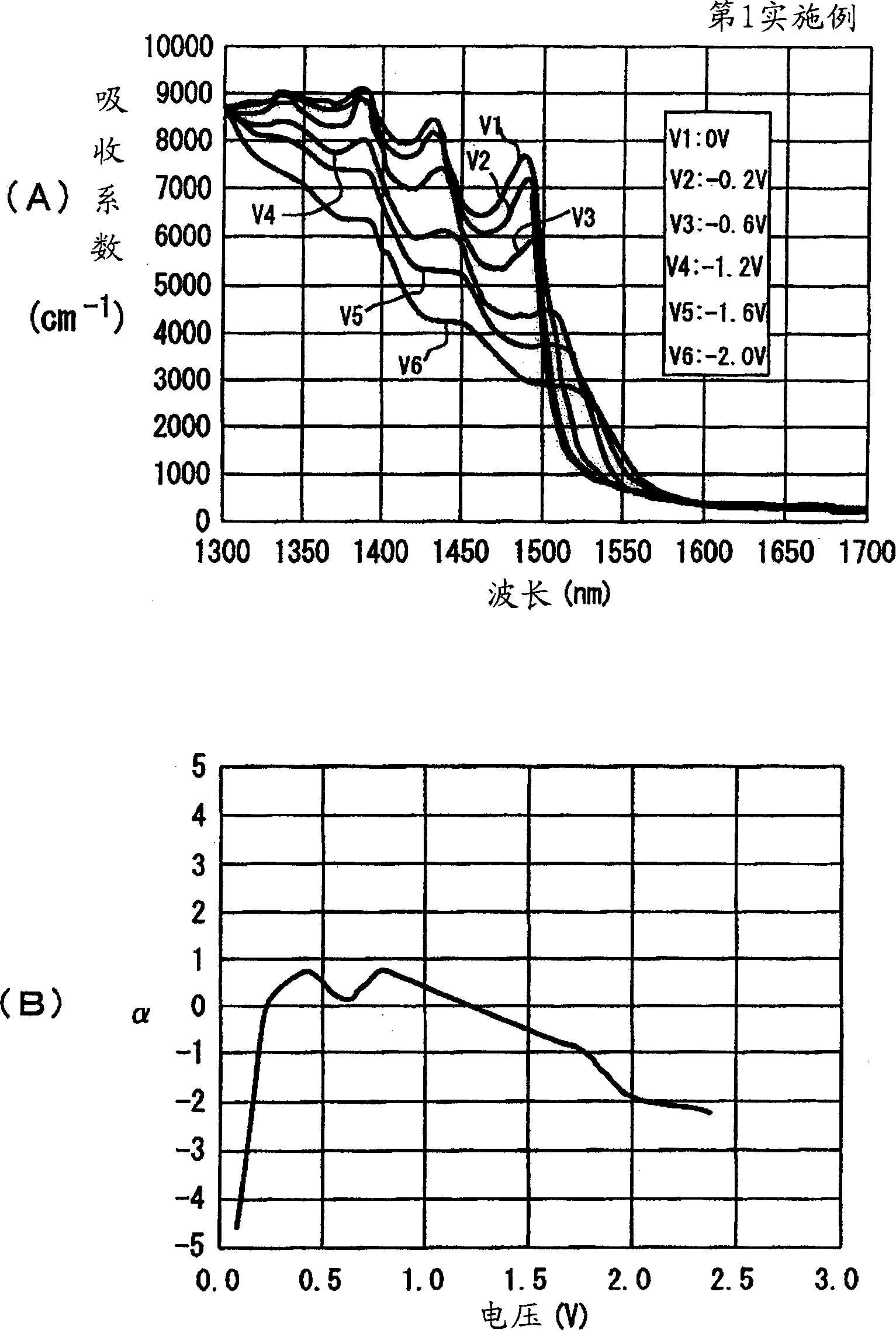
[0037] In the above-mentioned first embodiment, the quantum wells 8a of one period of the multiple quantum wells 8 have three types of layers: the well layer 10, the intermediate layer 11, and the barrier layer 12. In the second embodiment, the quantum well 8 a of one period may have four types of layers in w...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0041] Image 6 It is a diagram showing a semiconductor laser with an optical modulator (modulator-integrated semiconductor laser device) according to a third embodiment of the present invention; Image 6 Among them, the reference numeral 21 represents the optical modulator 1 etc. described in the first embodiment or the second embodiment, the reference numeral 22 represents the isolation (isolasion) region, the reference numeral 23 represents the semiconductor laser, and the reference numeral 24 represents the light modulator absorbing layer, Reference numeral 25 designates a semiconductor laser active layer, reference numeral 26 designates a diffraction grating, reference numeral 27 designates an InP substrate, and reference numeral 28 designates the entirety of a semiconductor laser with an optical modulator.
[0042] In this third embodiment, the optical modulator 1 of the above-mentioned first embodiment or the second embodiment is integrated with the semiconductor laser ...
no. 4 Embodiment
[0045] Figure 7 It is a diagram showing an optical amplifier-integrated optical modulator according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention. exist Figure 7 , due to the Image 6 Portions with the same reference numerals denote the same components, and thus their descriptions are omitted. exist Figure 7 Among them, reference numeral 32 denotes a (semiconductor) optical amplifier, reference numeral 33 denotes an optical amplifier active layer, and reference numeral 31 denotes the entirety of an optical amplifier-integrated optical modulator.
[0046] In this fourth embodiment, the semiconductor optical amplifier 32 can be integrated on the optical modulator 1 of the above-mentioned first embodiment or the second embodiment. The resulting loss is compensated.
[0047] If the fourth embodiment is adopted in the manner described above, by integrating the semiconductor optical amplifier 32 on the optical modulator 1 of the first embodiment or the second embodiment, o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com