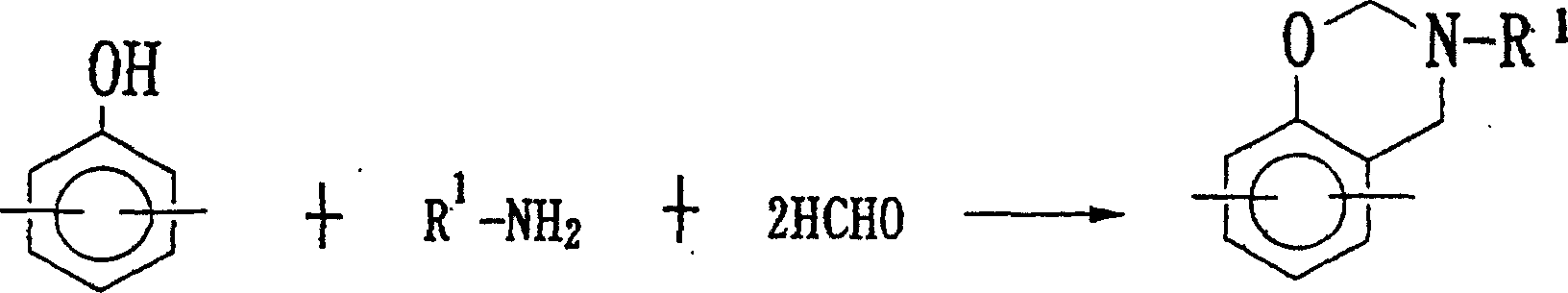Method for producing benzoxazine resin
A technology of benzoxazine and its manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of manufacturing benzoxazine resin, and can solve problems such as laborious waste, lack of solubility, inability to stir, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034]In a 5-liter flask equipped with a thermometer, a stirrer, a cooling tube, and a drop-in device, it is 1040 grams of phenol novolac resin and 1,040 grams of 400 phenol novolac resins that the number average molecular weight (utilizing gel permeation chromatography, using a standard polystyrene calibration curve to measure) is 400. 560 grams of ketones are stirred and dissolved, and then 600 grams of paraformaldehyde are added thereto. While stirring, 931 grams of aniline was added dropwise for 1 hour. At this time, the temperature of the reaction solution was 81°C. Thereafter, the reaction was carried out under reflux (80-82° C.) for 7 hours, and then, under the conditions of heating and 360 mm Hg, concentration under reduced pressure was started. Continue to concentrate while maintaining the reduced pressure, and increase the reduced pressure to 90 mmHg when the temperature of the reaction solution reaches 110°C. When it was confirmed that there was no more effluent (...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Add 140 grams of bisphenol A1 and 900 grams of butanone in a 5-liter flask equipped with a thermometer, a stirrer, a cooling pipe, and a dripping device, stir and dissolve, and add 1622 grams of 37% formalin solution to it, while stirring, 931 grams of aniline were added dropwise in 1 hour. At this time, the temperature of the reaction solution was 81°C. Then, it reacted for 7 hours under reflux (80-82 degreeC). Then, under the conditions of heating and 360 mm Hg, start to carry out concentration under reduced pressure. Continue to concentrate while maintaining the reduced pressure, and increase the reduced pressure to 90 mmHg when the temperature of the reaction solution reaches 85°C. When it was confirmed that there was no more effluent (at this time, the melting temperature of the resin was 100° C.), the resin was taken out and placed on a tray.
[0037] The obtained resin had a softening point of 75°C and a melt viscosity of 2.5 poise (125°C). The temperature of...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Add 1140 grams of bisphenol A1 and 920 grams of methanol into a 5-liter flask equipped with a thermometer, a stirrer, a cooling tube, and a dripping device, and stir to dissolve. Then add paraformaldehyde 652 grams wherein. While stirring, 930 g of aniline was added dropwise for 1 hour. At this time, the temperature of the reaction solution was 79°C. Then, it reacted for 7 hours under reflux (78-80 degreeC). Then, under the conditions of heating and 360 mm Hg, start to concentrate under reduced pressure. Continue to concentrate while maintaining the reduced pressure, and increase the reduced pressure to 90 mmHg when the temperature of the reaction solution reaches 85°C. When it was confirmed that there was no more effluent (at this time, the melting temperature of the resin was 100° C.), the resin was taken out and placed on a tray. The softening point of the resin was 76°C, and the melt viscosity at 125°C was 2.7 poise. At the minimum point (R), the temperature of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com