Mycoplasma bovis vaccine and methods of reducing pneumonia in animals
A technology of Mycoplasma bovis and vaccine, which is used in the preparation of Mycoplasma bovis vaccines and kits, the treatment or prevention of diseases or illnesses caused by Mycoplasma bovis infection, and the field of combined vaccines, which can solve problems such as no vaccine available.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Materials and Methods
[0064] animal
[0065] Healthy crossbred heifers of approximately 14 days of age were obtained for immunization. Calves were acclimatized for 7 days before starting the study. All calves received daily concentrated, drug-free food free of any known contaminants or pesticides, and calves had free access to water.
[0066] vaccine
[0067] The bacterin contains BEI-inactivated whole-cell M. bovis bacterin at the appropriate concentration for each dose. In addition, each vaccine formulation contains phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and appropriate adjuvants. Placebo contained PBS or PBS and oil-in-water adjuvant.
[0068] attack method
[0069] Give each calf 10 or 12 ml of a fresh M. bovis culture [approximately 1 x 10 8 ~1×10 10 colony forming unit (CFU / ml)]. The counts (CFU / ml) of the challenge inoculum were determined shortly after completion of each experimental challenge.
[0070] Experimental procedure
[0071] U...
Embodiment 2
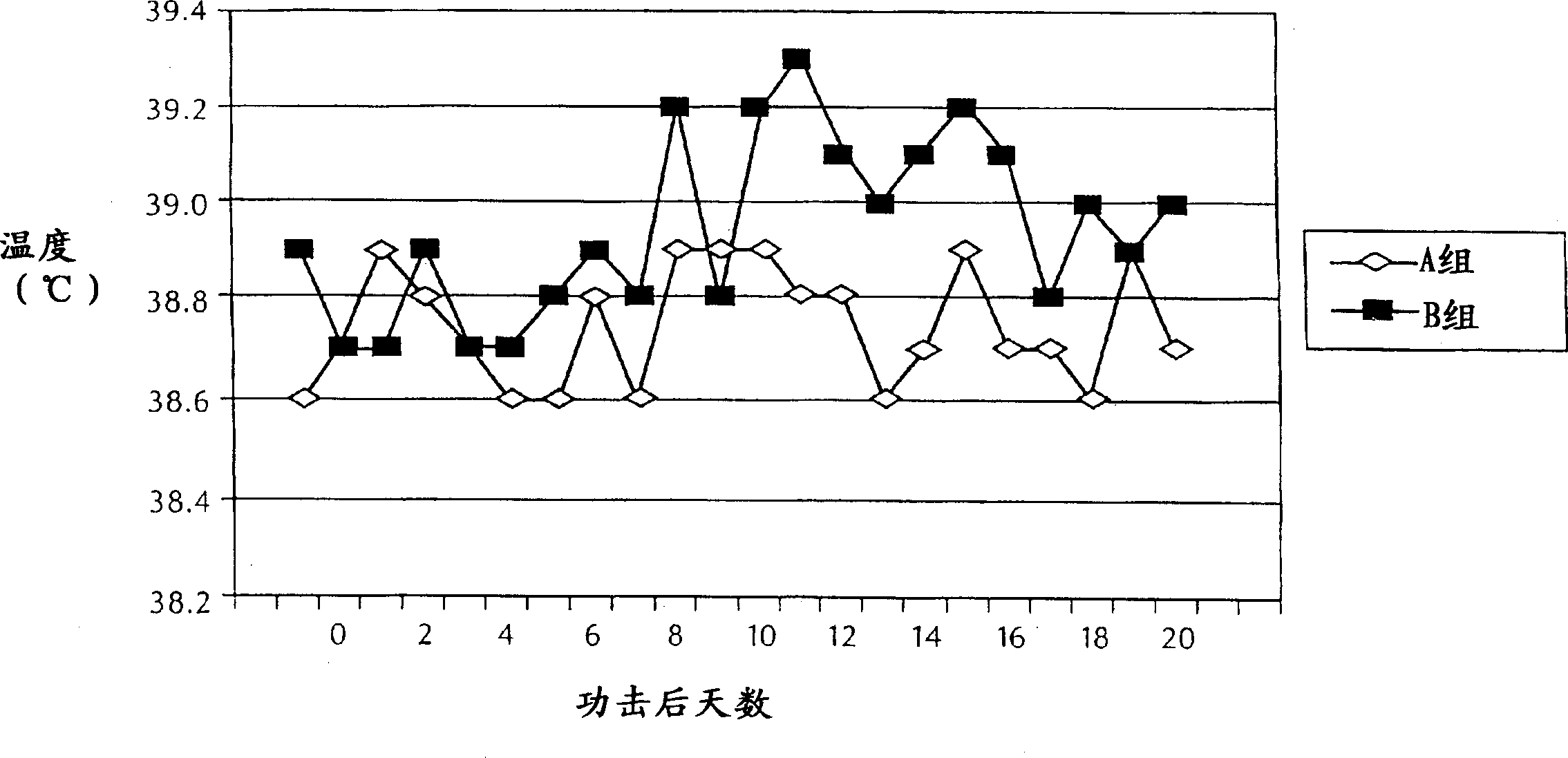
[0083] In this example, the efficacy of the M. bovis bacterin was assessed in young calves. Twenty-four healthy crossbred calves were randomly assigned according to age.
[0084] Animals were immunized by subcutaneous route on day 0 (left neck) and day 21 (right neck) with 2 ml of vaccine or placebo. The experimental treatment groups and the vaccines used are shown in Table 1.
[0085] Table 1
[0086] treatment group
[0087] Calves were challenged 3 weeks after the second immunization as described above. Each calf received 10 ml of fresh M. bovis culture by intranasal route on 3 consecutive days.
[0088] The number of inoculum per challenge (CFU / ml) was determined within 1 hour after completion of the M. bovis experimental challenge. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0089] challenge inoculum
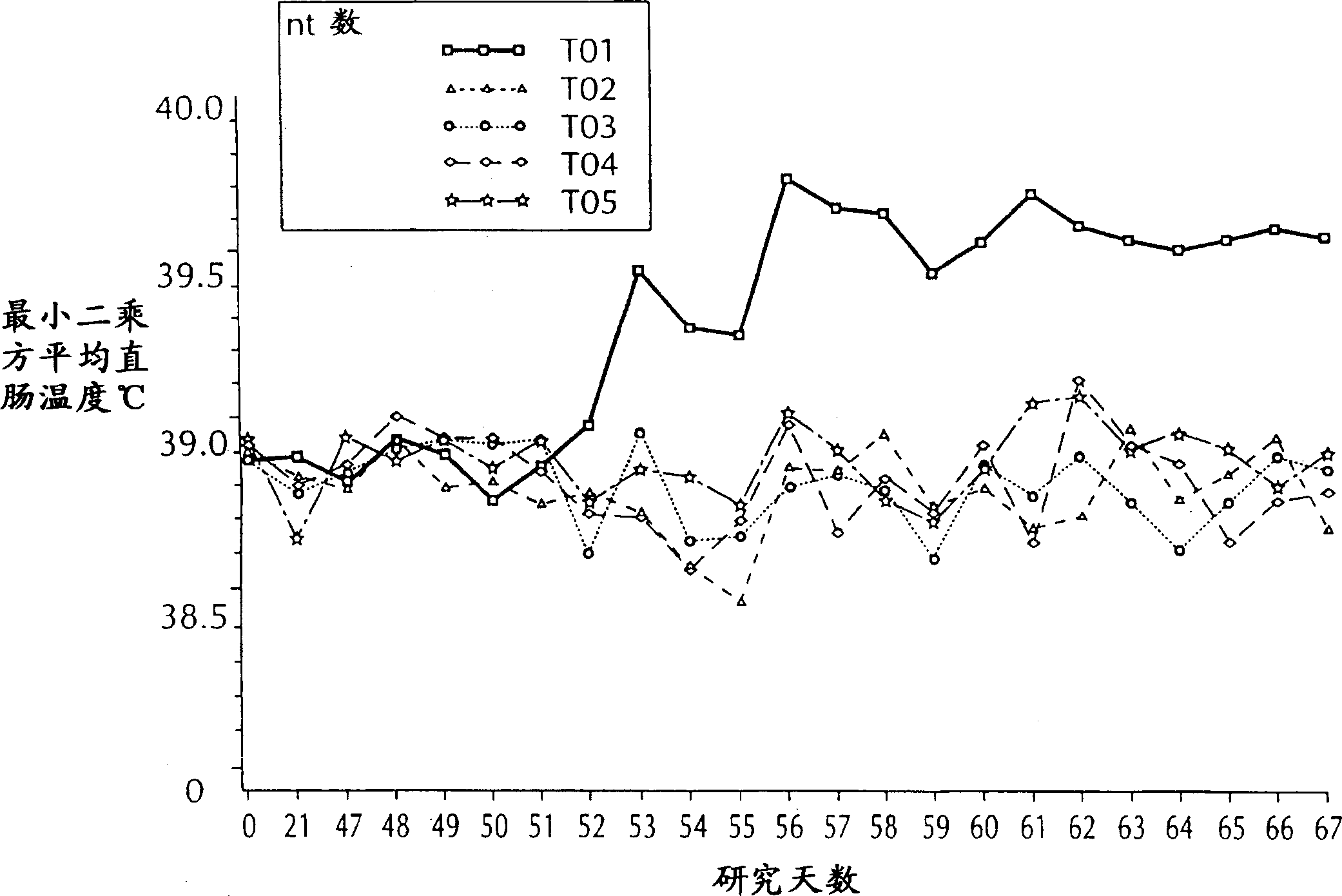
[0090]All animals were weighed 1 day before challenge, 7 days after challenge, 14 days after challenge and approximately 3 weeks af...
Embodiment 3
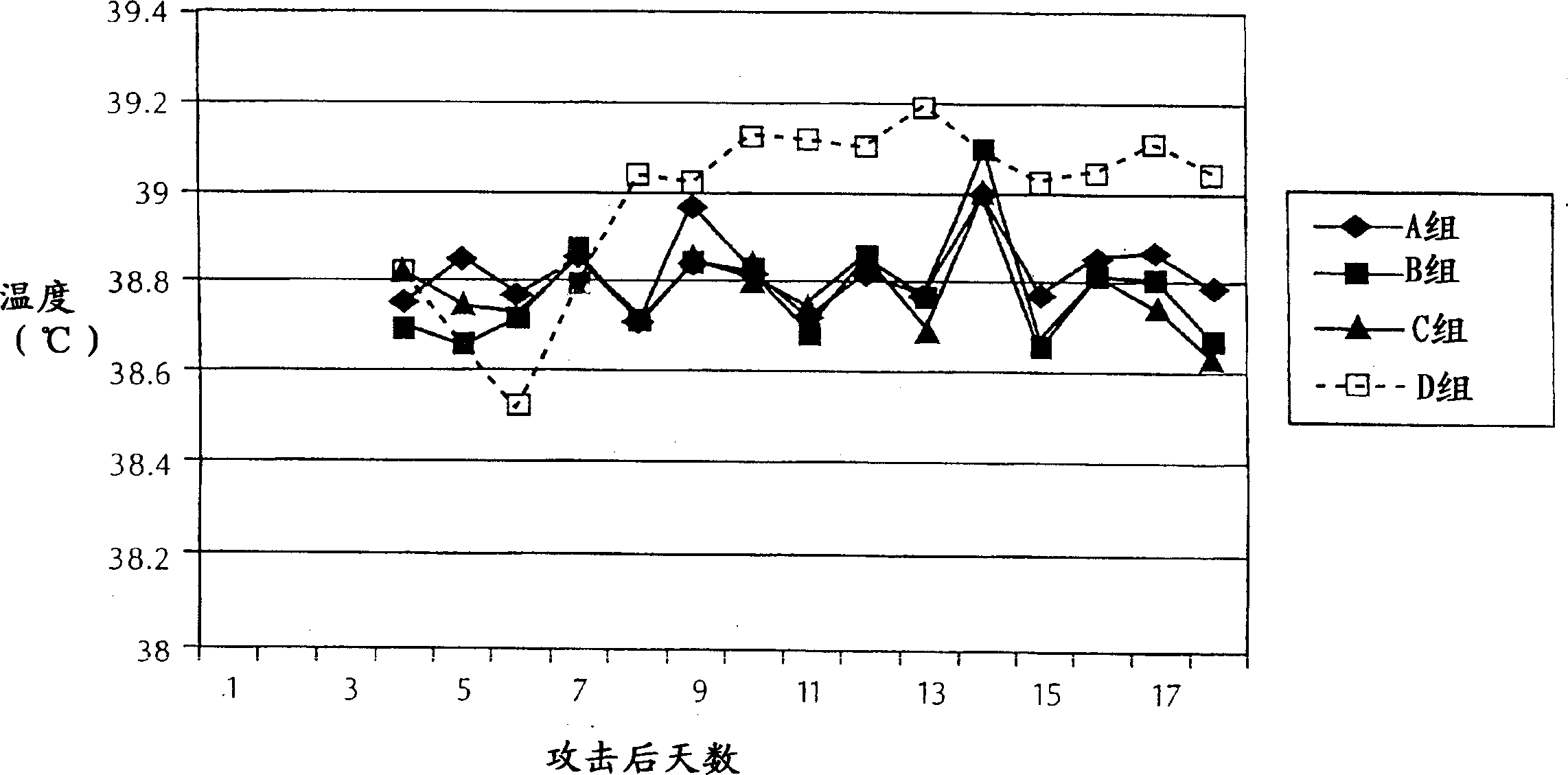
[0108] In this example, the efficacy of various M. bovis bacterins was assessed in young calves. Fifty-eight healthy crossbreed calves were randomly assigned by age.
[0109] Animals were immunized by subcutaneous route on day 0 (left neck) and day 21 (right neck) with 2 ml of the appropriate vaccine or placebo. The experimental treatment groups and the vaccines used are shown in Table 1.
[0110] Table 1
[0111] treatment group
[0112] Calves were challenged 3 weeks after the second immunization as described above. Each calf received 12 ml of fresh M. bovis culture by intranasal route on 3 consecutive days.
[0113] Viable counts (CFU / ml) of each challenge inoculum were determined within 1 hour after completion of the M. bovis experimental challenge. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0114] challenge inoculum
[0115] All animals were weighed 1 day before challenge, 7 days after challenge, 14 days after challenge and appr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com