Power amplifier having a cascode current-mirror self-bias boosting circuit
A power amplifier, bias circuit technology, applied in power amplifiers, amplifiers, improving amplifiers to reduce temperature/power supply voltage changes, etc., can solve problems such as complex circuits, and achieve the effect of economic structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
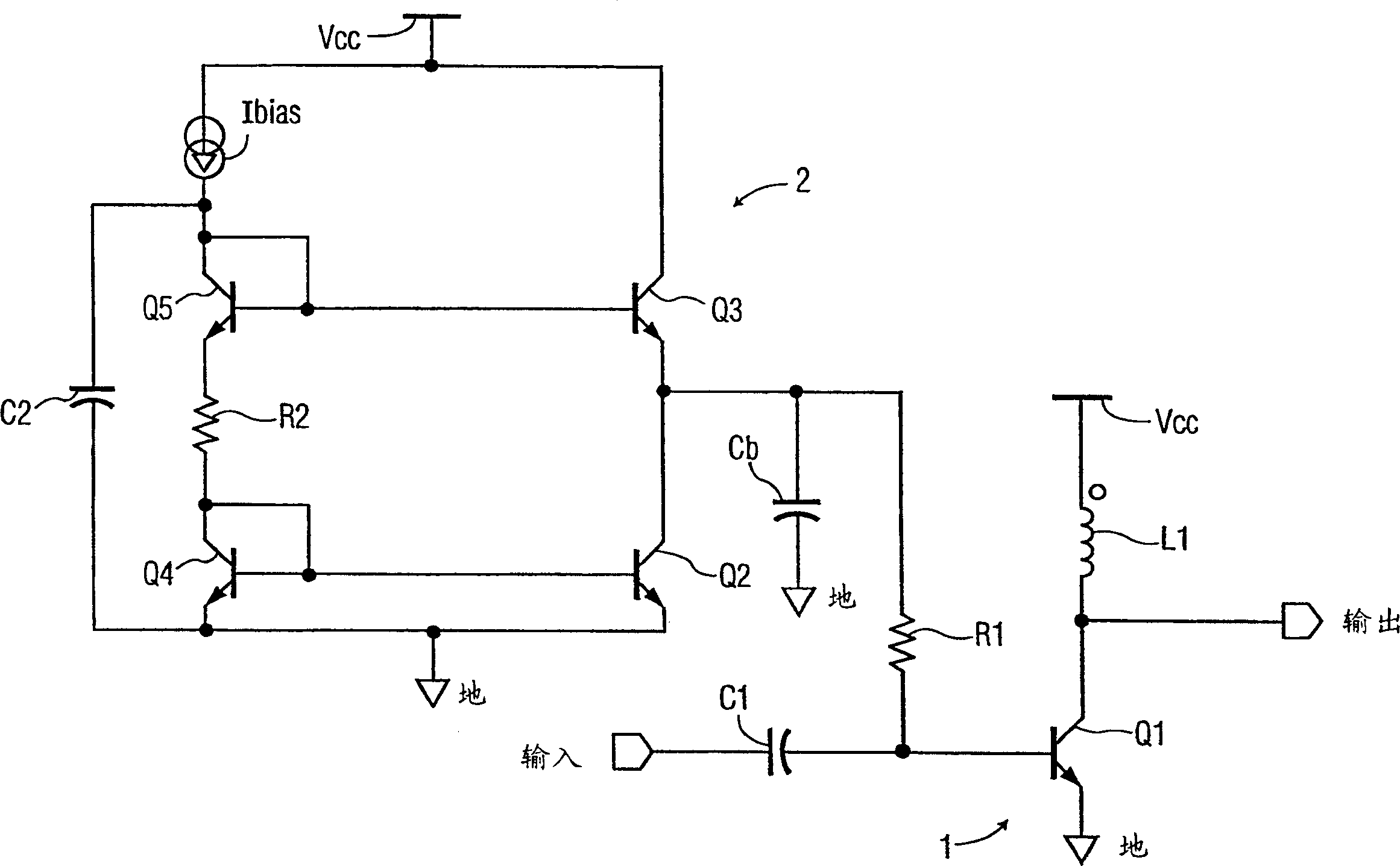
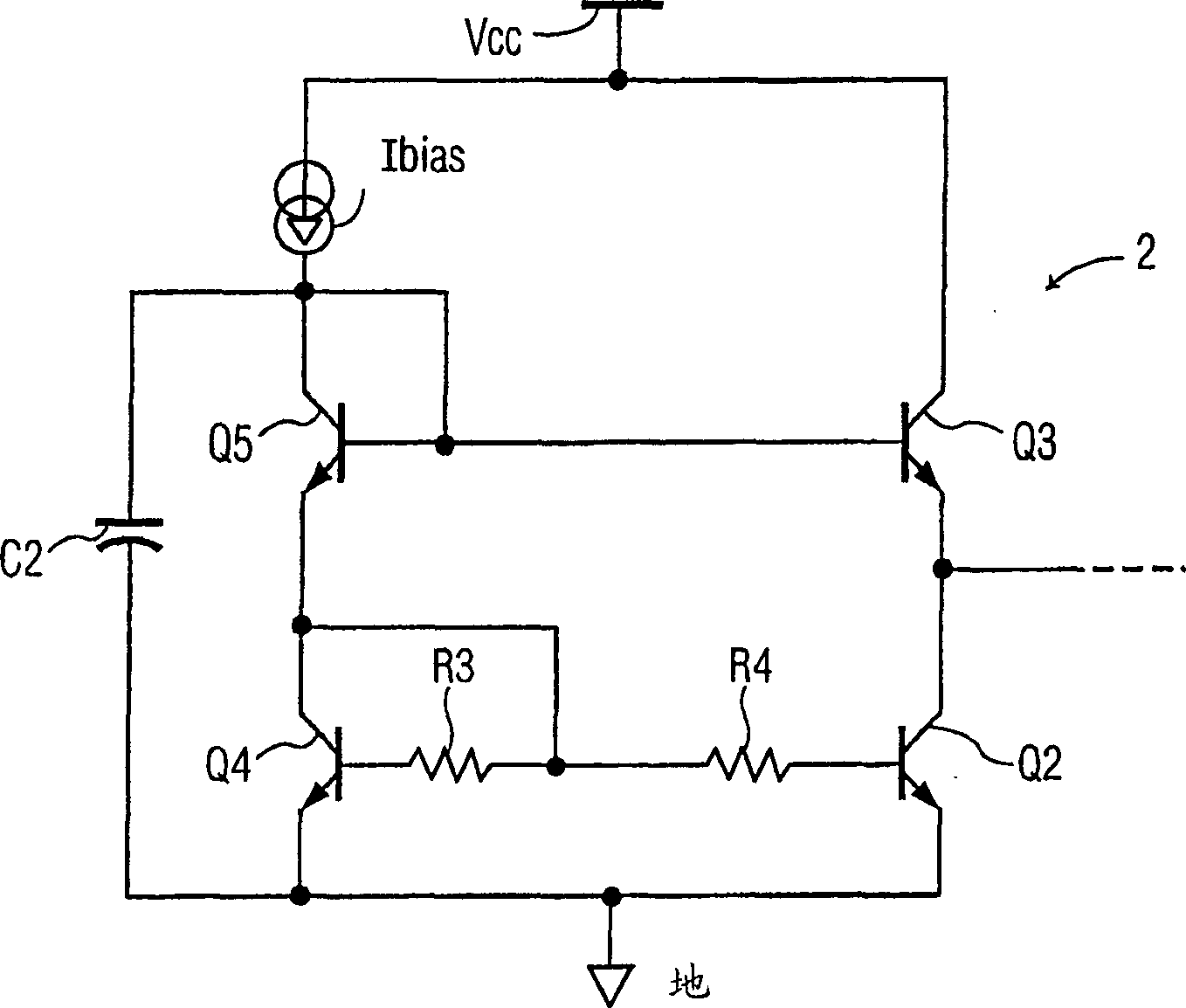
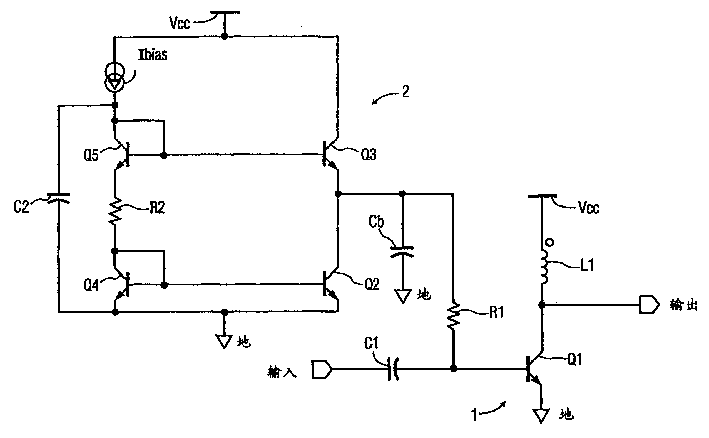
[0017] Attached figure 1 A simplified schematic diagram of the power amplifier circuit 1 is shown in . The amplifier circuit includes an amplifying transistor Q1 and a dc bias circuit 2 coupled to the base of the amplifying transistor Q1 through a resistor R1. The bias circuit 2 includes output bipolar transistors Q2 and Q3 coupled in series between Vcc and a common terminal (ground), the common point of the transistors being coupled to the common terminal via a capacitor Cb and to the transistor Q1 via a resistor R1 base. The basic circuit configuration is completed by an input coupling capacitor C1 for coupling the input signal to the base of amplifying transistor Q1, which is connected in a common-emitter configuration and coupled between Vcc and ground through an inductor L1. The output of the power amplifier circuit 1 is taken from the collector of the transistor Q1.
[0018] In conjunction with the circuit shown, it will be appreciated that although for purposes of il...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com