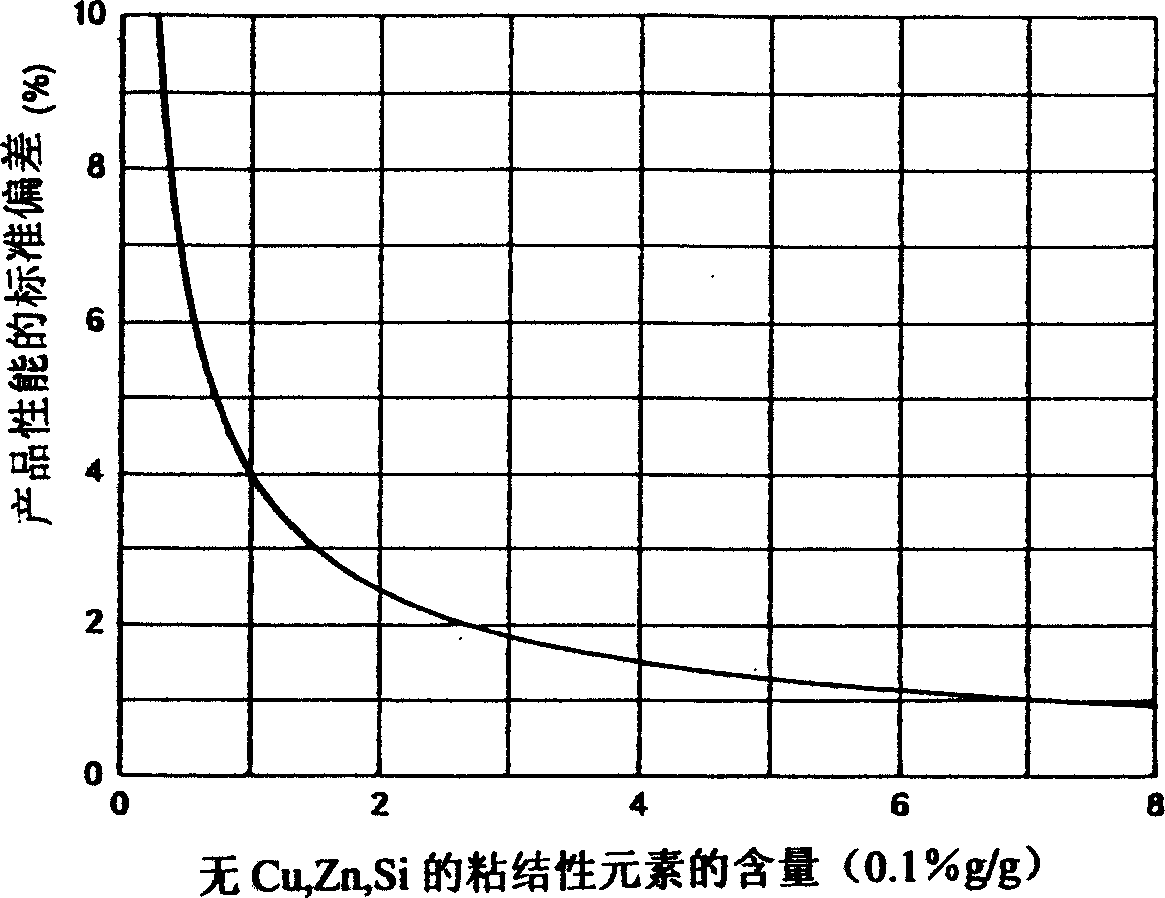
Lead-free copper alloy and a method of manufacture
A technology of copper alloy and alloy, which is applied in the direction of shafts and bearings, anti-centrifugal force rotating parts, bearings, etc., and can solve problems such as stress corrosion cracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] In a preferred embodiment, the copper alloy consists of 60 to 70% Cu, 0.5 to 3.5% Sn, 0.07 to 3% Mg and 0.003 to 0.01% P, with the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities.
[0041] Alternatively in another preferred embodiment the copper alloy consists of 60 to 70% Cu, 0.5 to 3.5% Sn, 0.07 to 3% Mg and 0.03 to 0.1% P, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities .
[0042] Alternatively in another preferred embodiment the copper alloy consists of 60 to 70% Cu, 1.5 to 2.5% Sn, 0.07 to 3% Mg and 0.03 to 0.1% P, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities .
[0043] Alternatively in another preferred embodiment, the copper alloy consists of 60 to 70% Cu, 2.0 to 2.5% Sn, 0.07 to 3% Mg and 0.03 to 0.1% P, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities .
[0044] In all the preferred embodiments described above, phosphorus may be included in order to influence particularly advantageously the formation of the initial cast structure and the corrosion properties. W...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com