Semiconductor device
A technology of semiconductors and devices applied to the field of erroneous actions caused by erroneous signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
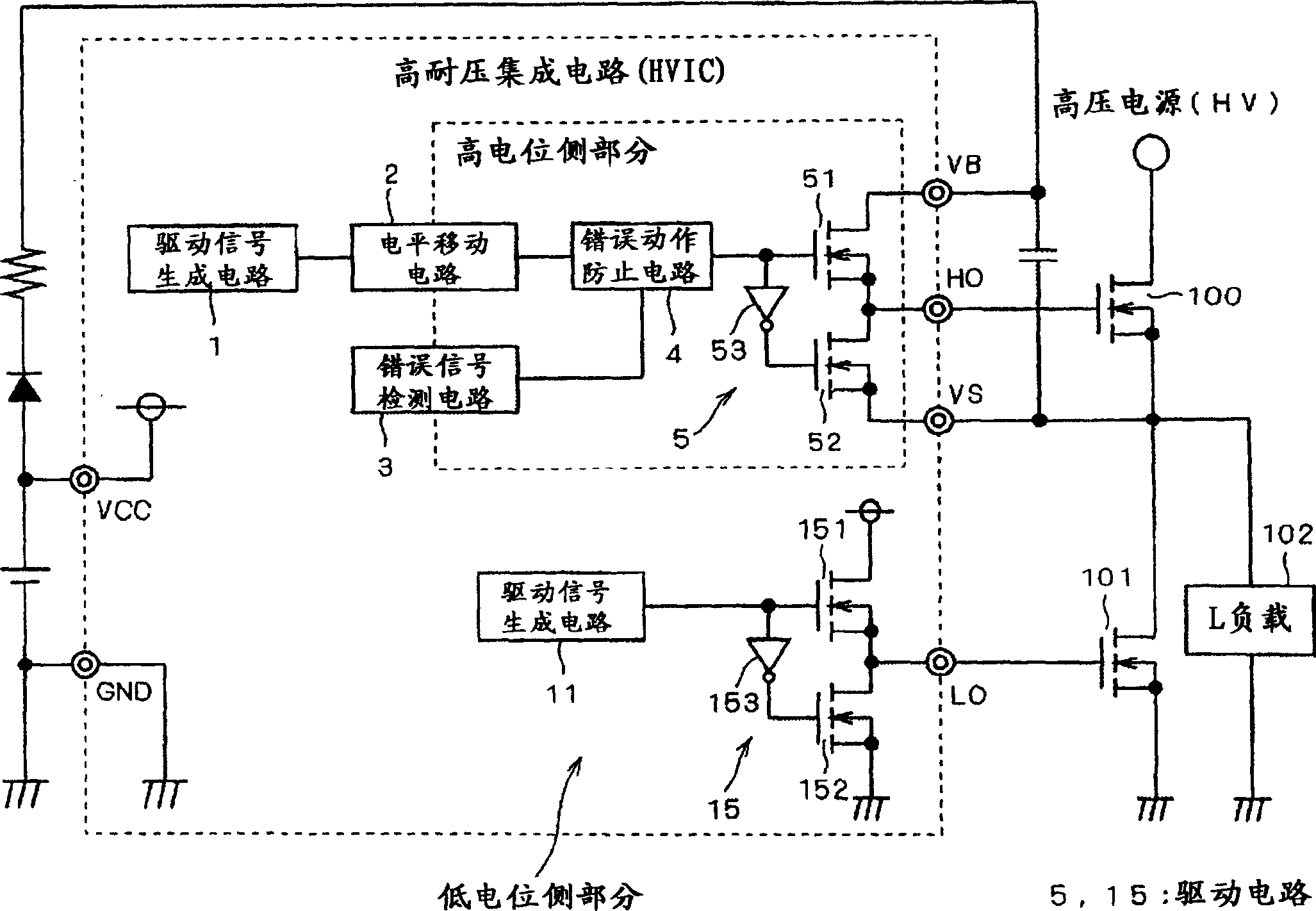
[0028] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the structure of the semiconductor device concerning Example 1, and shows the power device drive apparatus of the bootstrap system using the high withstand voltage integrated circuit (HVIC). In this semiconductor device, power semiconductor elements (MOSFET, IGBT, etc.) 100 and 101 connected in a half-bridge manner between a high-voltage power supply HV and GND are driven by an HVIC. An induction (L) load 102 such as a motor or a fluorescent lamp is connected to the power semiconductor element 101 of the lower arm.
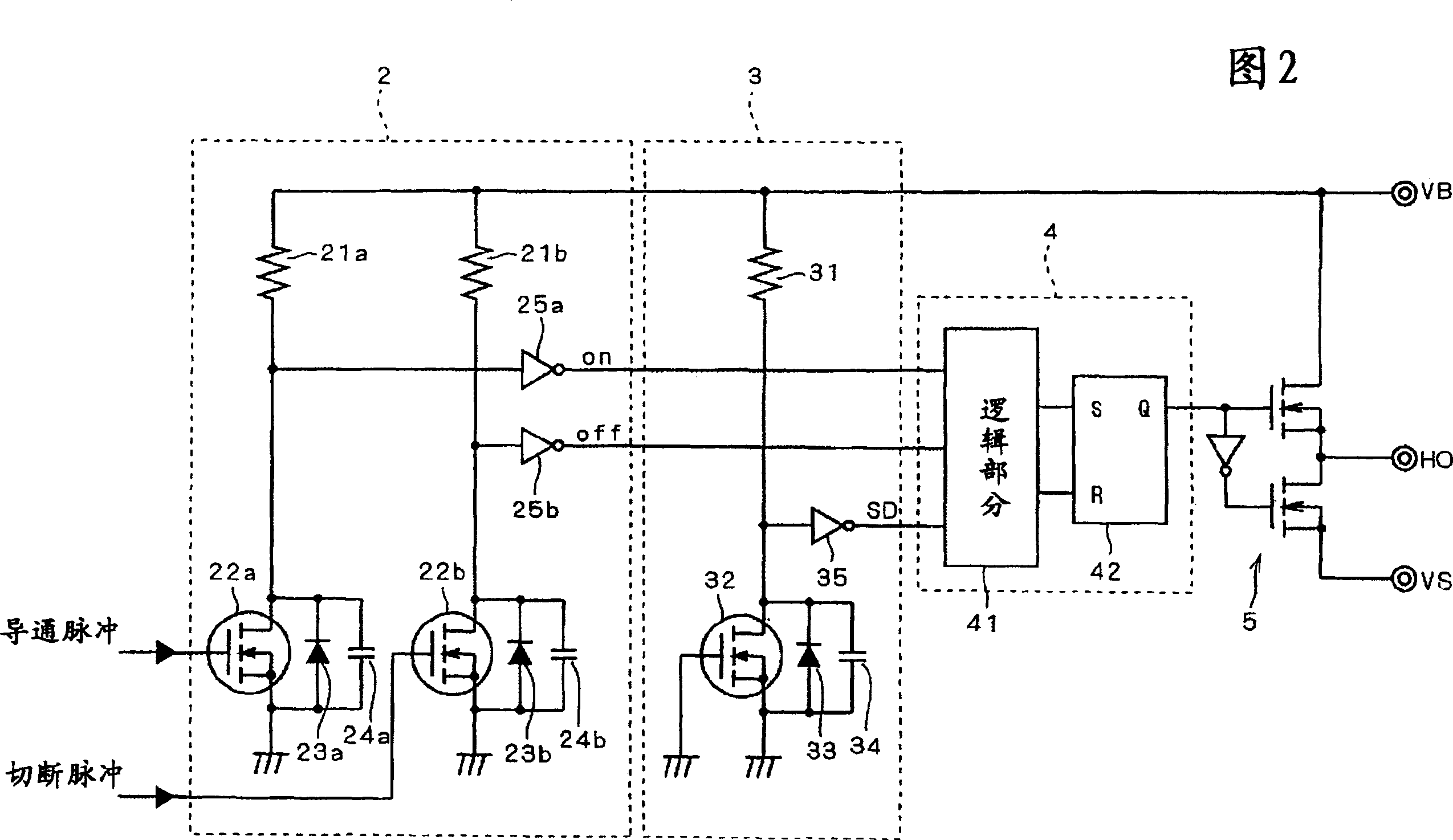
[0029] In this HVIC, the drive signal generating circuit 1 generates drive signals (on pulses and off pulses) as first signals for driving the power semiconductor element 100 of the upper arm. This drive signal is input to the level shift circuit unit 2, where it is converted (level shifted) into a second signal that can be transmitted to each circuit of the high potential side portion. The error signal detection circui...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Figure 4 A portion from the level shift circuit inside the HVIC to the output terminal on the high potential side in the semiconductor device related to Embodiment 2 is shown. This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 only in the configuration of the error signal detection circuit 3, and the configuration of other elements and the overall operation of the semiconductor device are the same as those in Embodiment 1, so the description is omitted here.
[0049] like Figure 4 As shown, in the error signal detection circuit 3 of the second embodiment, the second switching element connected in parallel with the error signal detection resistor 31 is the diode element 36 connected in parallel with the capacitance element 37 . The anode of the diode element 36 is connected to the GND potential, and the cathode is connected to the high potential side power supply potential VB via the error signal detection resistor 31 . That is, the diode element 36 is fixed in the OFF state ...
Embodiment 3
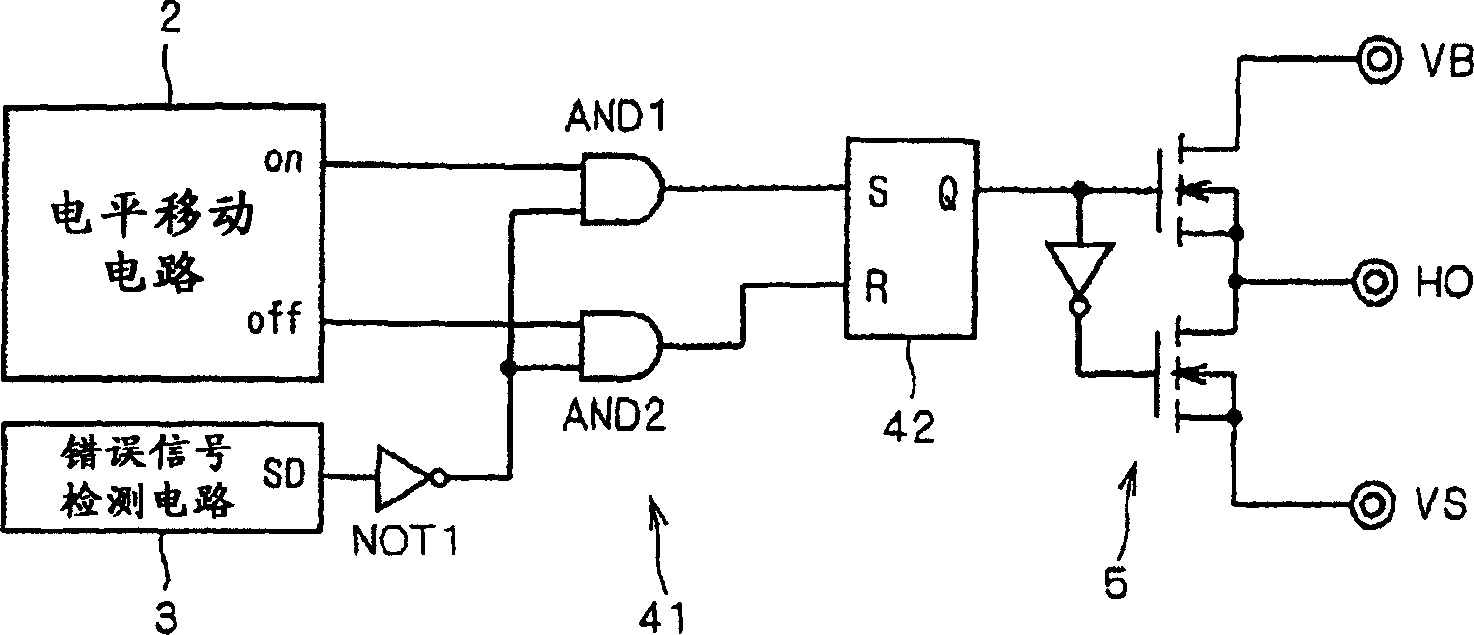
[0053] Figure 5 It is a diagram showing the structure of the malfunction prevention circuit 4 in the third embodiment. As shown in the figure, in this embodiment, the logic gates included in the logic section 41 of the malfunction prevention circuit 4 are AND3 and NOT2. The ON pulse from the level shift circuit 2 is input to one input terminal of AND3, and the OFF pulse is directly input to the R terminal of the RS flip-flop 42 . The error signal generation signal SD from the error signal detection circuit 3 is input to the other input terminal of AND3 through NOT2. Then, the output of AND3 is input to the S terminal of the RS flip-flop 42 .
[0054] Since the error signal generation signal SD is not input from the error signal detection circuit 3 (the error signal generation signal SD is low level) in the normal state where no error signal is generated in the level shift circuit 2, the input to the logic section 41 is The ON pulse and the OFF pulse are respectively input ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com