Light wave guide device,light source device and light information processor
A technology of optical waveguide and multiplexing, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, light guide, optics, etc., can solve the problems of increased loss and polarization dependence, and achieve the effect of small light loss and increased productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
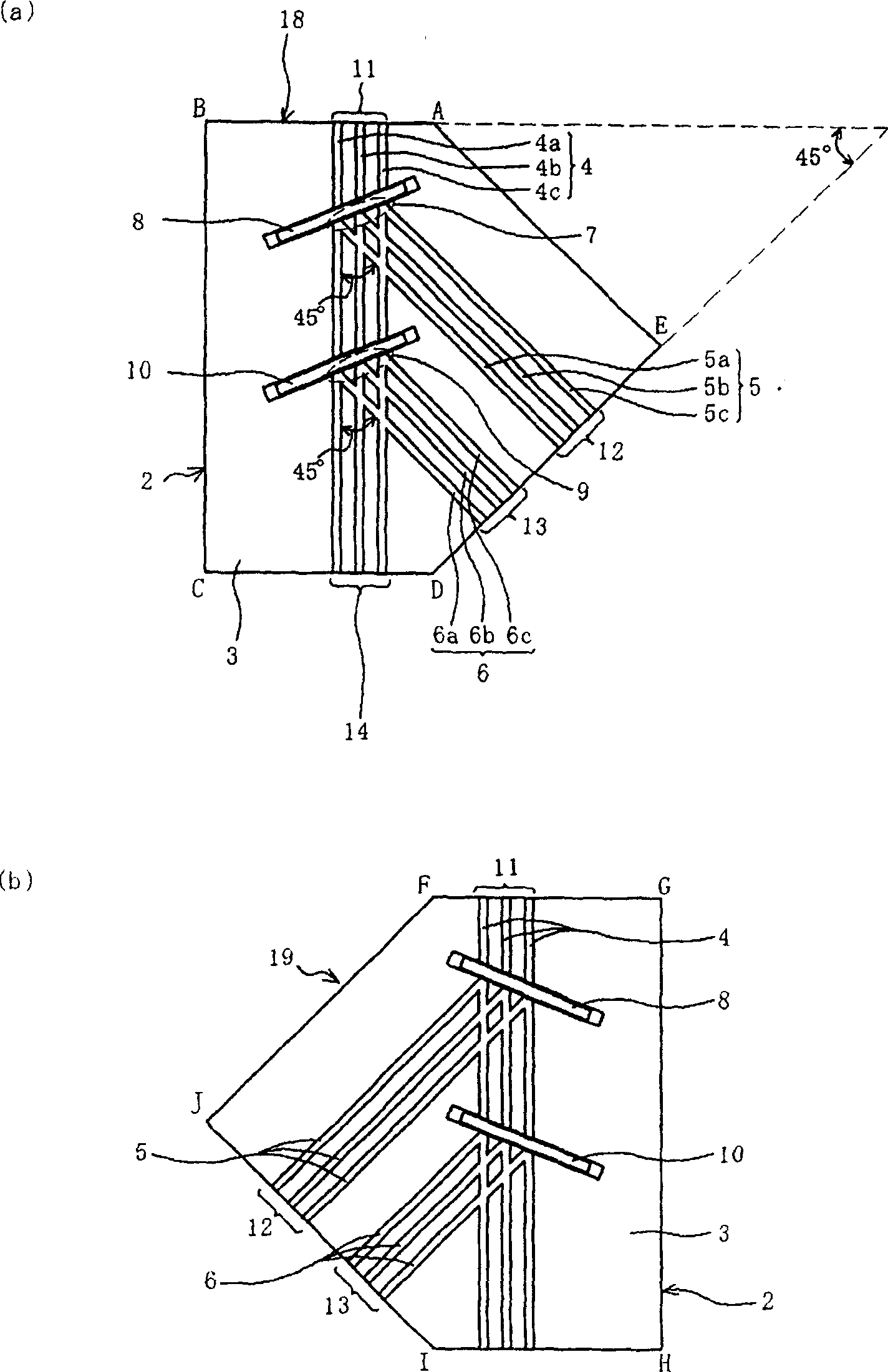
[0109] Embodiment 1 relates to an optical waveguide device having a pentagonal shape as an example of the optical waveguide device of the present invention, and a light source device using the optical waveguide device, and hereby uses Figure 1 to Figure 4 Be explained.
[0110] figure 1 (a) is a plan view of the optical waveguide device 18 according to the first embodiment. In this optical waveguide device 18, an optical waveguide layer 2 composed of a bonded body of a cladding layer 3 and core wires 4 to 6 is formed on a substrate 1 (not shown) such as silicon, and the lower cladding layer and the upper cladding layer A light guiding path, that is, a core wire, is embedded therebetween.
[0111] The optical waveguide layer 2 is made of, for example, an acrylic organic solvent, the refractive index of the cladding 3 is 1.505, the refractive index difference Δn between the core wires 4-6 and the cladding layer 3 is 0.8%, and the cross-section of the core wires 4-6 is 10 μm×...
Embodiment approach 2
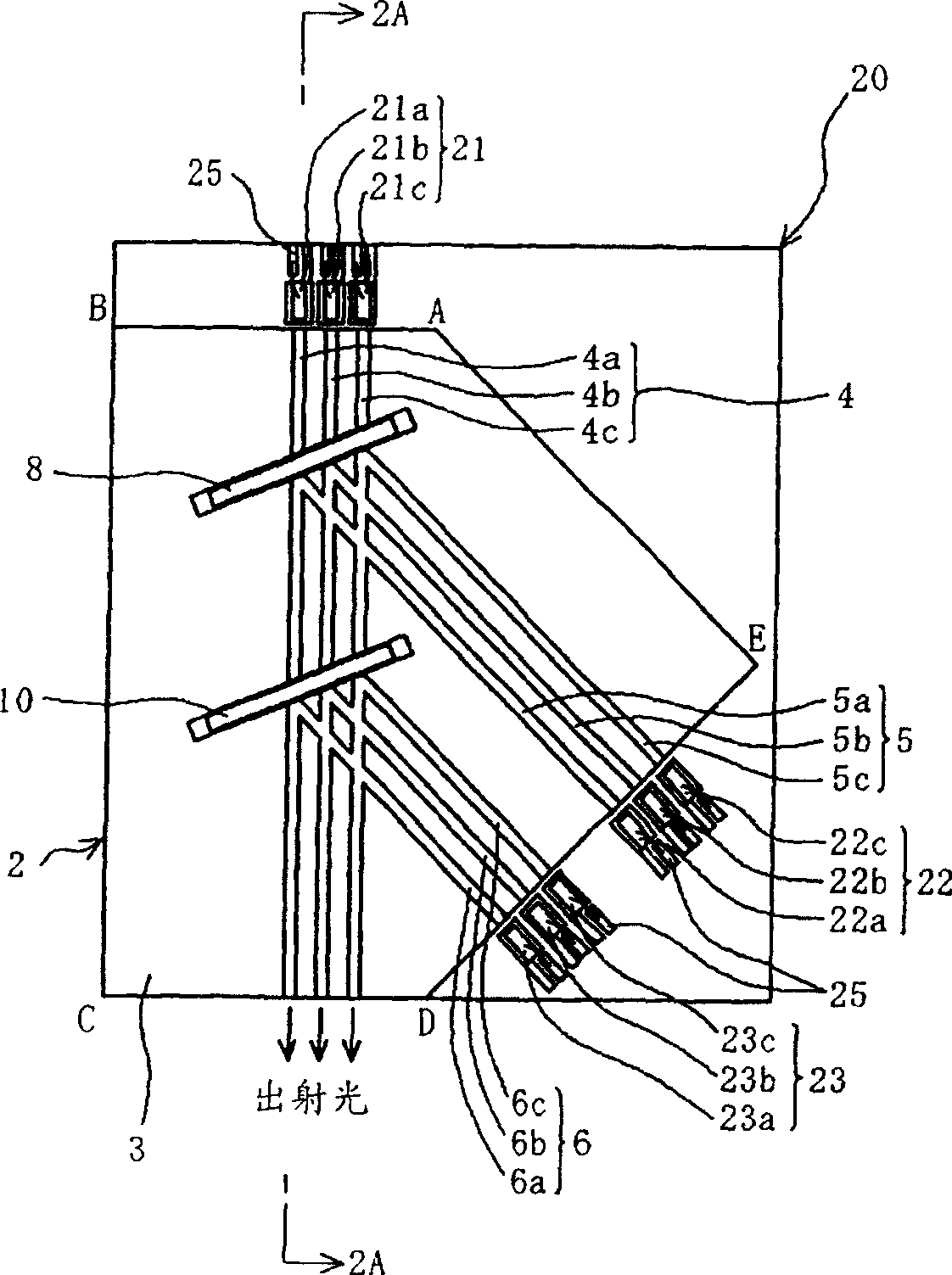
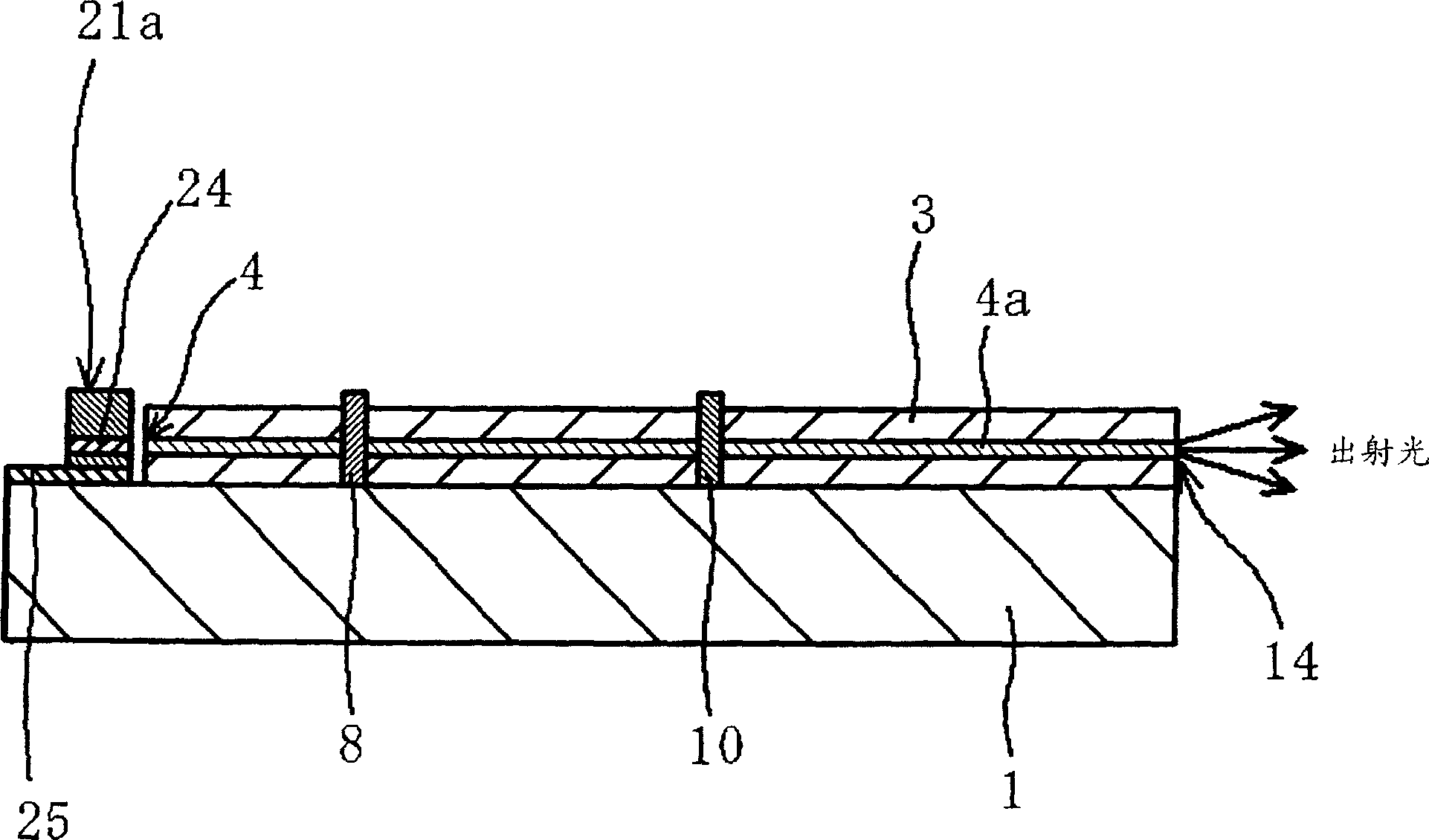
[0131] Embodiment 2 is an example of an optical waveguide device 28 , a light source device using the same, and an optical information processing device. This optical waveguide device 28 is obtained by modifying the optical waveguide device 18 based on Embodiment 1 as follows. The waveguide end faces of the side AB and side DE of the optical waveguide device 18 are subjected to 45-degree inclined processing, and the light incident end faces of the core wires 4 to 6 are formed into inclined reflective end faces, and the light is guided to the inside and outside of each core wire through these reflective end faces. .
[0132] By doing so, it is possible to use a surface-emitting light-emitting element and a surface-receiving light-receiving element. For example, surface-emitting LEDs are easy to manufacture, inexpensive, commercially available in many varieties, excellent in high-frequency characteristics, easy to modulate, and easy to install. In addition, light-receiving elem...
Embodiment approach 3
[0147] Embodiment 3 relates to an optical waveguide device having a square shape as an example of the optical waveguide device of the present invention, and a light source device using the optical waveguide device. Figure 8-10 Let me explain.
[0148] Figure 8 It is a plan view of the optical waveguide device 50 according to the third embodiment. In this optical waveguide device 50, an optical waveguide layer 52 composed of a bonded body of a clad 53 and core wires 54 to 56 is formed on a substrate 1 (not shown) such as silicon, and the lower clad and upper clad The waveguide core wire is buried between the cladding layers.
[0149] The optical waveguide layer 2 is the same as Embodiment 1. For example, it is made of an acrylic organic solvent. The refractive index of the cladding 53 is 1.505. The refractive index difference Δn between the core wires 54-56 and the cladding layer 53 is 0.8%. The cross section of 56 is a square of 10 μm×10 μm.
[0150] The cladding layer 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com