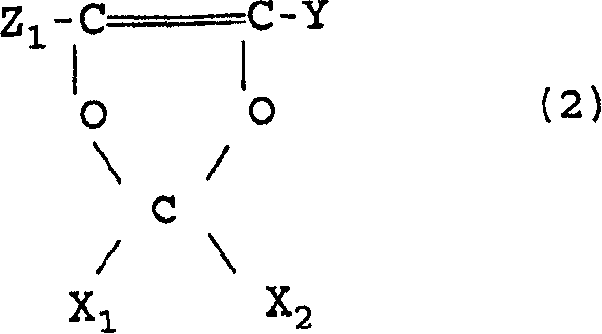
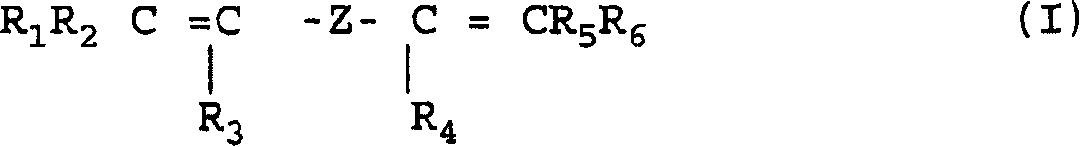Fluoroelastomers
An elastomer, monomer technology, applied in the field of VDF-based fluoroelastomers, can solve problems such as poor productivity, and achieve the effect of improving mechanical and compression set properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0163] The preparation of adducts is described in European patent application EP 684277 in the name of the applicant, which is hereby incorporated by reference.
[0164] The blend for ion curing additionally contains:
[0165] i) One or more inorganic acid acceptors selected from those known in the ionic curing of vinylidene fluoride copolymers, in an amount of 1-40 parts per 100 parts of fluoroelastomer copolymer;
[0166] ii) One or more basic compounds selected from those known in the ionic curing of vinylidene fluoride copolymers, in an amount of 0.5-10 parts per 100 parts of the fluoroelastomer copolymer.
[0167] The basic compound of point ii) is usually selected from Ca(OH) 2 , Sr(OH) 2 , Ba(OH) 2 , Weak acid metal salts, such as carbonates, benzoates, oxalates and phosphites of Ca, Sr, Ba, Na and K, and mixtures of the above-mentioned hydroxides and the above-mentioned metal salts; compounds of type i) MgO can be mentioned in.
[0168] The stated amounts of compounding co...
Embodiment
[0197] Analytical method
[0198] Determination of polymer Tg
[0199] Tg is determined by DSC analysis according to ASTM D 3418 method. The Tg value reported in the examples is the midpoint Tg.
[0200] Determination of intrinsic viscosity
[0201] The intrinsic viscosity was measured in perfluoroheptane at a temperature of 30°C.
[0202] -COF Determination of polar end groups
[0203] At the end of the polymerization, the polymer is separated by coagulation by freezing at -20°C and then defrosting at room temperature until a slurry in which the polymer is deposited at the bottom is obtained; it is washed twice with demineralized water and heated at 90°C in an oven. Dry at ℃ until constant weight (about 12 hours); by using Nicolet Nexus FT-IR device (256 scans, 2cm resolution -1 ) Determination of -COF end groups by FT-IR spectroscopy, in which 4000cm is first carried out on a polymer film with a thickness of 50-300 microns -1 And 400cm -1 Then the film was kept in an en...
Embodiment A
[0213] CF is prepared by thermal reaction at 170℃ in a glass reactor 3 OCOF
[0214] A tubular glass reactor with an inner diameter of 55.6 mm and a length of 510 mm, filled with 6×6 glass Raschig rings (free internal volume 842 ml), and maintained at a constant temperature by electrical resistance was used.
[0215] At the same time, CF synthesized as described in USP 4400872 3 OF gas flow (1.5 liters / hour) and CO flow (1.5 liters / hour) were added to the reactor kept at 170°C for 5 hours. The flow from the reactor is continuously analyzed by on-line gas chromatography analysis.
[0216] The stream from the reactor except CO is condensed in a trap kept at -110°C containing 15gCFCl=CFCl(A 1112), so that residual CF 3 OF reacts with olefin to obtain CF 3 OCFClCF 2 Cl.
[0217] After fractional distillation of the resulting mixture, 33.9 g of 99.8% pure CF was obtained 3 OCOF (for feed CF 3 The molar yield of OF is 76.5%), 12.3g of CF 3 OCFClCF 2 Cl, 3.4g COF 2 .
[0218] Relative fe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mooney viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com