Silage additive and a process for preparing silage using it
A technology of silage and additives, which is applied to the preservation method of animal feed raw materials, animal feed, animal feed, etc., can solve problems such as danger, and achieve the effect of improving and stabilizing the quality of silage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
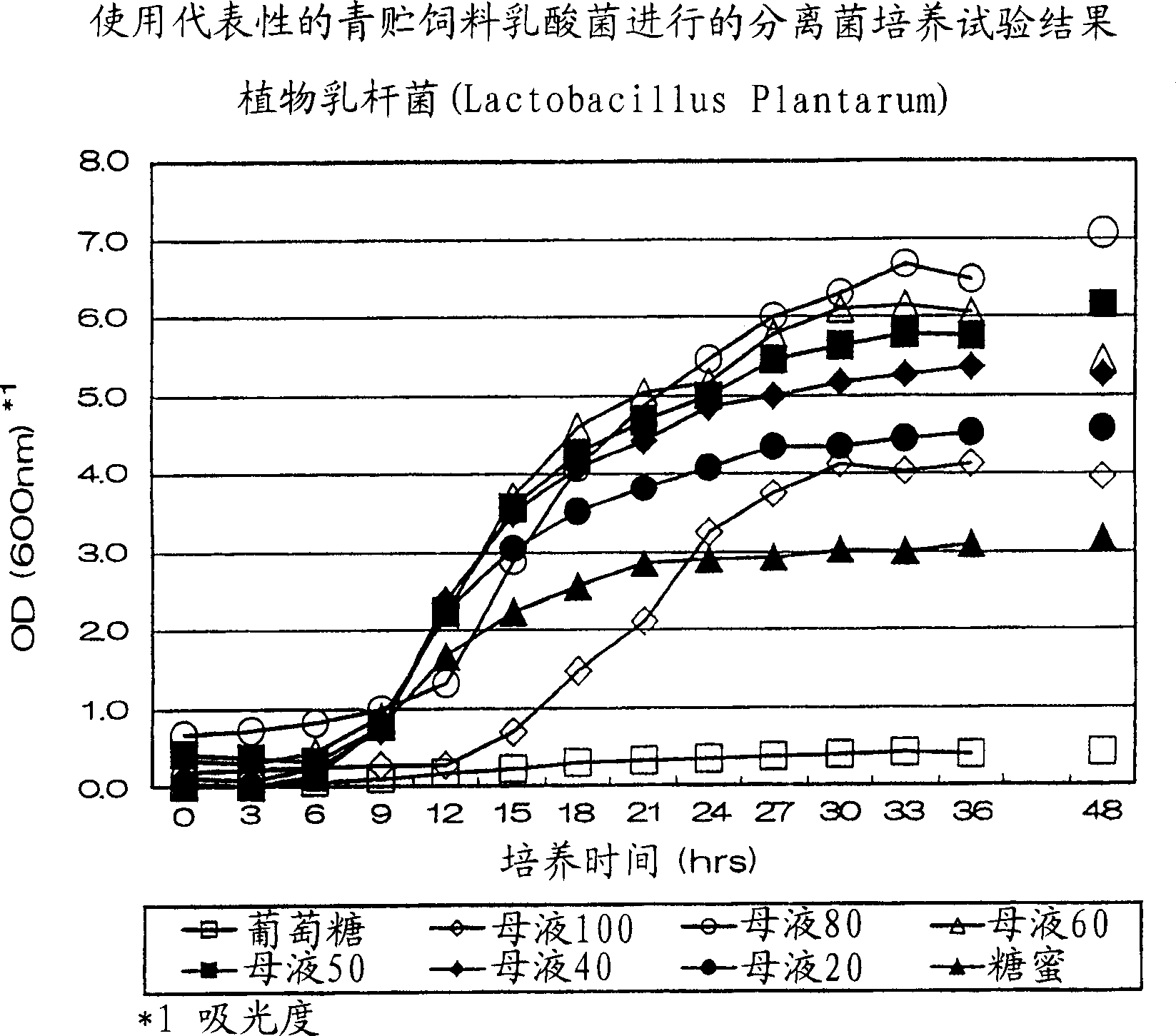
[0040] Example 1: Culture test of isolated bacteria using representative silage lactic acid bacteria
[0041] As a sugar source, prepare a mixture of mother liquor and molasses according to a mixing ratio (weight ratio) of 100:0-0:100, and add the mixture to 804 liquid medium (5g yeast extract, 5g peptone, 0.1g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 (2, 1000 ml of distilled water, pH 7.0), the reducing sugar concentration was adjusted to an amount corresponding to 0.5% by weight, and the lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) was subjected to liquid static culture at 30°C. The molasses used here is a by-product of sugar mills with a moisture content of 25-30% by weight and a sugar content of about 50% by weight.
[0042] As a control area, 804 liquid culture medium with a glucose concentration of 0.5% by weight was set. The details of mixing ratio and abbreviation are shown in Table 1.
[0043] Table 1
[0044] Abbreviation
Mother liquor 100
Mother ...
Embodiment 2
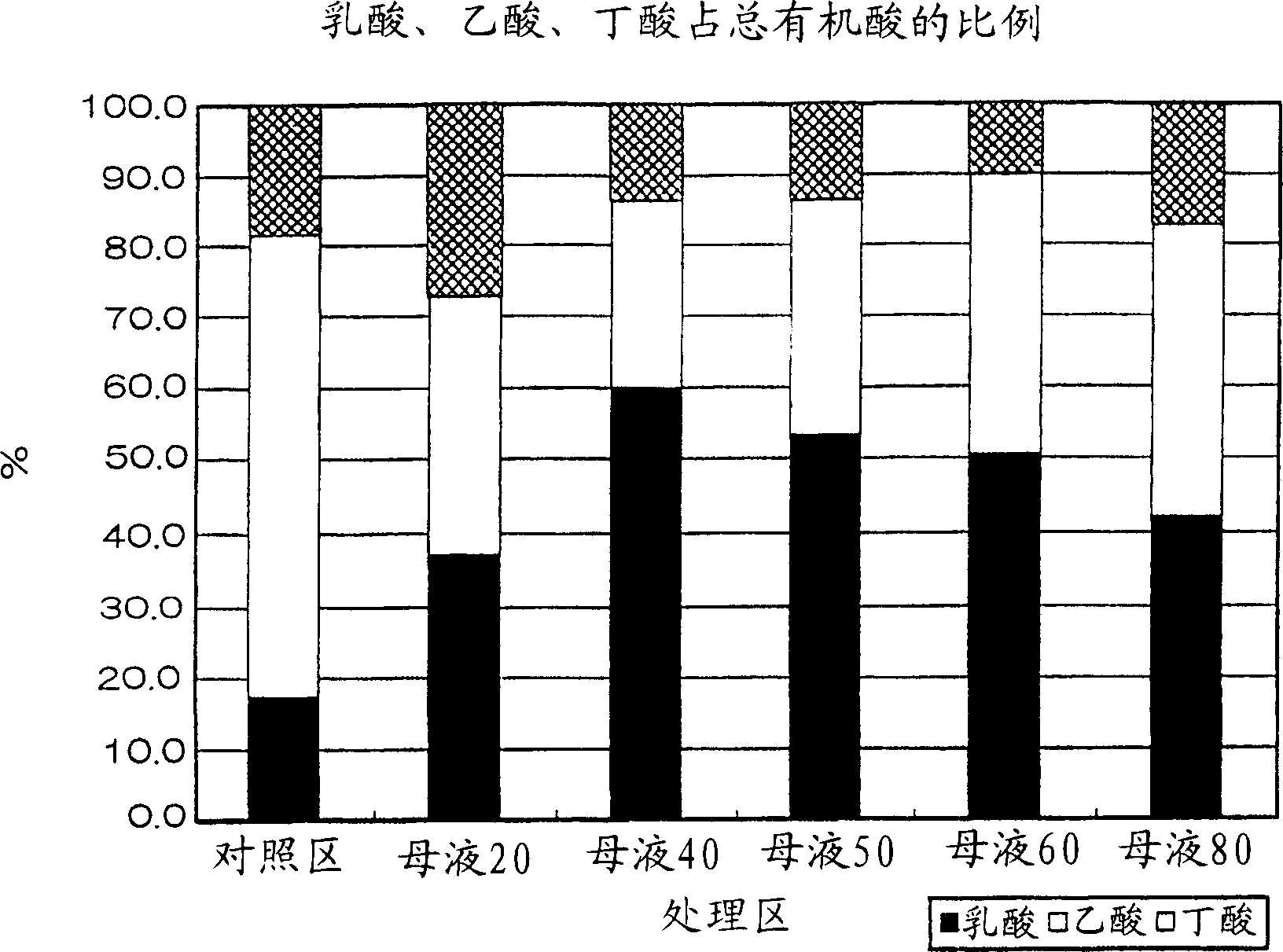
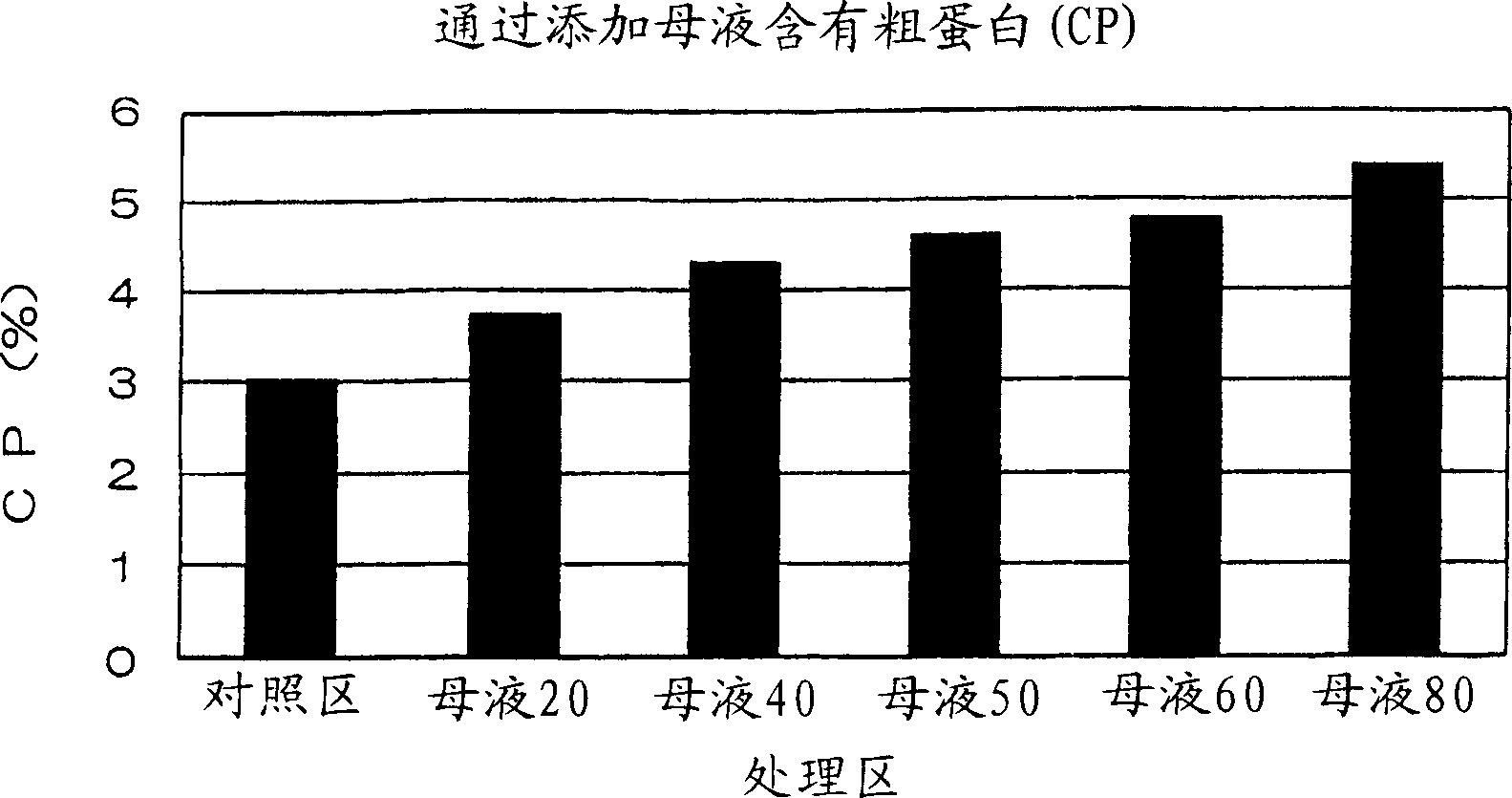
[0050] Embodiment 2: Barley whole plant bottling silage test
[0051] Prepare the mixed solution of mother liquor and molasses according to the mixing ratio (weight ratio) of 80:20-20:80, add it so that it is 3% relative to the fresh weight of the whole barley plant of the material, and pack it into a 1L bottle (packing Bottle density 500g FW / L) carries out silage test.
[0052] Silage without mother liquor was prepared as a control area. The details of mixing ratio and abbreviation are shown in Table 2.
[0053] Table 2
[0054] Abbreviation
Mother liquor 50
Mother liquor 40
Mother liquor 20
Mother Liquor: Molasses
80∶20
60∶40
50∶50
40∶60
20∶80
[0055] Open the package on the 40th day after preparing the silage, take a sample, add 10 times the amount of distilled water, pulverize it with a mixer, and filter it with gauze. The filtrate was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm, ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Embodiment 3: the culture experiment of the yeast that is isolated from silage
[0065] Prepare the mixture of mother liquor and molasses according to the mixing ratio (weight ratio) of 100:0-0:100, and add the mixture to PYG liquid medium (10g peptone, 5g yeast extract, 1000ml distilled water, pH 6.7-6.8) In the method, the reducing sugar concentration was adjusted to an amount corresponding to 0.5% by weight, and the silage yeast was subjected to liquid static culture at 30°C.
[0066] As a control area, a PYG liquid medium with a glucose concentration of 0.5% by weight was set. The details of mixing ratio and abbreviation are shown in Table 4.
[0067] Table 4
[0068] Abbreviation
Mother liquor 100
Mother liquor 80
Mother liquor 60
Mother liquor 50
Mother liquor 40
Mother liquor 20
molasses
Mother Liquor: Molasses
100∶0
80∶20
60∶40
50∶50
40∶60
20∶80
0∶100
[0069] The cul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com