Enzymatic treatment of paper making pulps
A pulp and alkali treatment technology, applied in textile and papermaking, fiber raw material treatment, etc., can solve problems such as excessive consumption of cationic additives and easy blockage of drainage screen filters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0122] Degradation of pectin with pectate lyase and pectinase
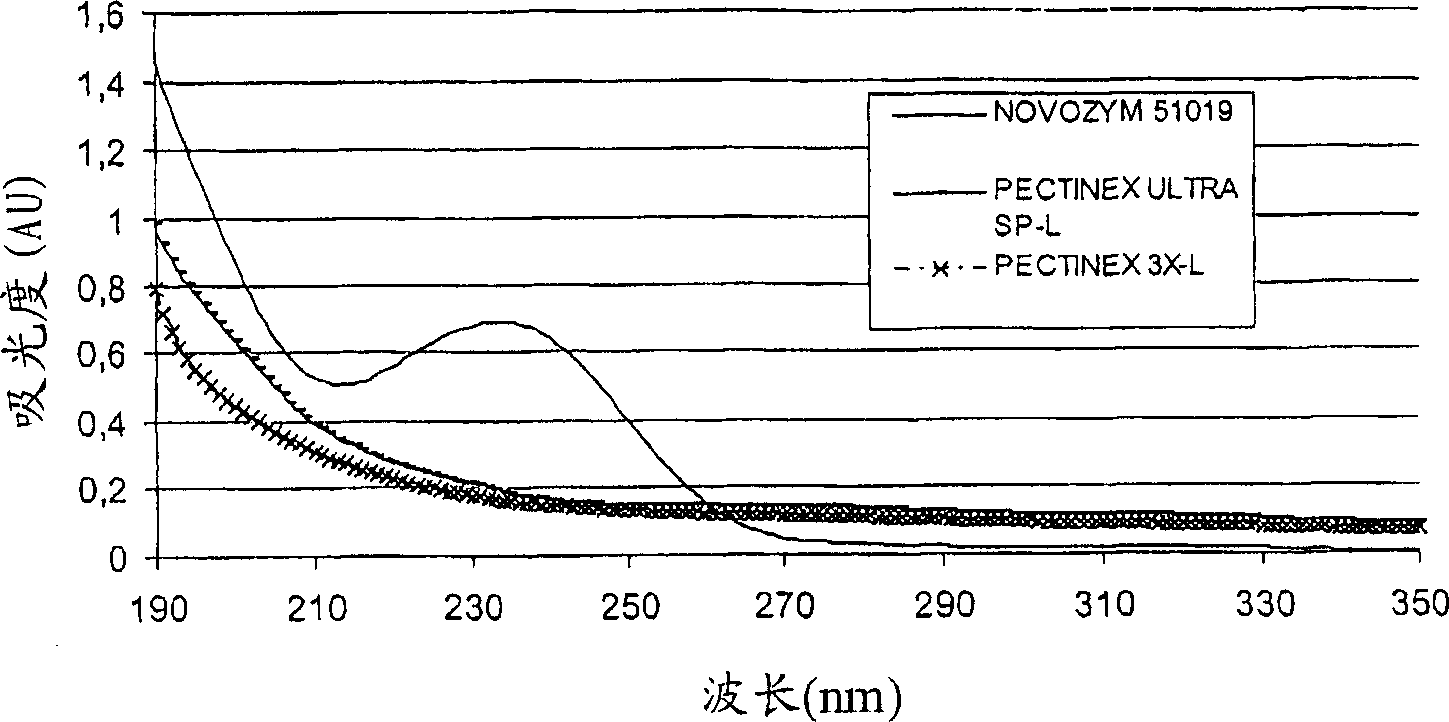
[0123]1 g of polygalacturonic acid sodium salt (Sigma, P3850, minimum purity 85%) was dissolved in 1 L of deionized (DI) water. With NOVOZYM 51019 Pectate lyase, pectinase preparation PECTINEX TM Aliquots of the solution were treated with ULTRA SP-L, and with Pectin ES 3X-L (both available from Novozymes A / S, Krogshoejvej 36, DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark). The treatment was carried out at pH 7.0 and 55°C for 60 min. Enzyme doses were 40 mg / L each of the three enzyme preparations. After the above treatment, the solution was acidified to pH 2.0 with 8% (w / w) phosphoric acid. The solution was diluted 10 times with DI water, and then the UV spectrum was measured by a UV-Vis photometer.
[0124] Such as figure 1 As shown, pectate lyase treatment resulted in different degradation products compared to the two pectinases, as evidenced by strong UV absorption at 235 nm. Pectinase degrades pectin to galacturonic acid, w...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Example 2: Effect of alkaline-treated pectate lyase on cation requirements
[0126] Thermo-mechanical pulp (TMP) samples were treated with 2% NaOH at 60°C for 1 h. The treated pulp was then filtered through a Brit Jar (200 mesh screen) and washed with 0.1 N H 2 SO 4 The filtrate was neutralized to pH7. With different doses of NOVOZYM TM 51019 Pectate lyase treated the filtrate at 55°C for 2 hrs.
[0127] Cation requirements were determined using a Mütek particle charge detector and an automatic titrator. 1.0ml sample was diluted in 20ml DI water, and polydiallyldimethyl-ammonium chloride (polydiallyldimethyl-ammonium chloride) (poly-DADMAC, available from Aldrich ) to titrate the suspension.
[0128] NOVOZYM TM
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3: Enzyme treatment prior to alkaline treatment - effect on cation requirements
[0130] Thermo-mechanical pulp (TMP) samples were treated with different doses of the following enzymes: NOVOZYM TM 51019 Pectate lyase, NOVOZYM TM 51019 Pectate lyase with NOVOSHAPE TM Pectine esterase and pectinase preparation PECTINEX TM A combination of ULTRA SP-L (both available from Novozymes A / S, Krogshoejvej 36, DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark). The pH of the pulp suspension was adjusted to 7.0 before enzyme treatment. Other enzyme treatment conditions are: 55°C, 4% consistency, 2hr. Then, the pulp samples were treated with 2% NaOH at 60 °C for an additional 1 h. Filter the treated pulp through a Brit Jar (200 companion strainer) and wash with 0.1N H 2 SO 4 The filtrate was neutralized to pH 7.
[0131] Cation requirements were determined using a Mütek particle charge monitor and an automated titrator. A 1.0 ml sample was diluted in 20 ml DI water and the suspension w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com