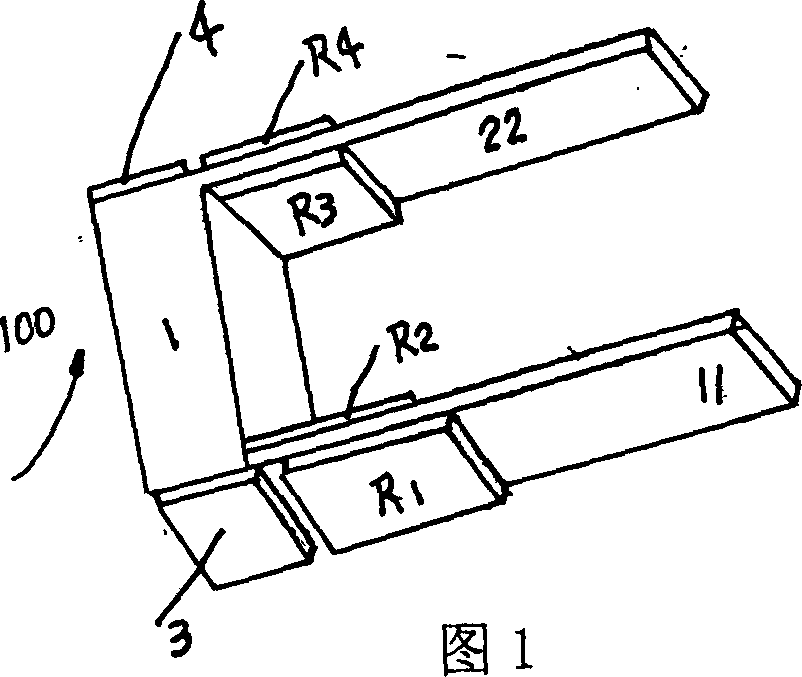
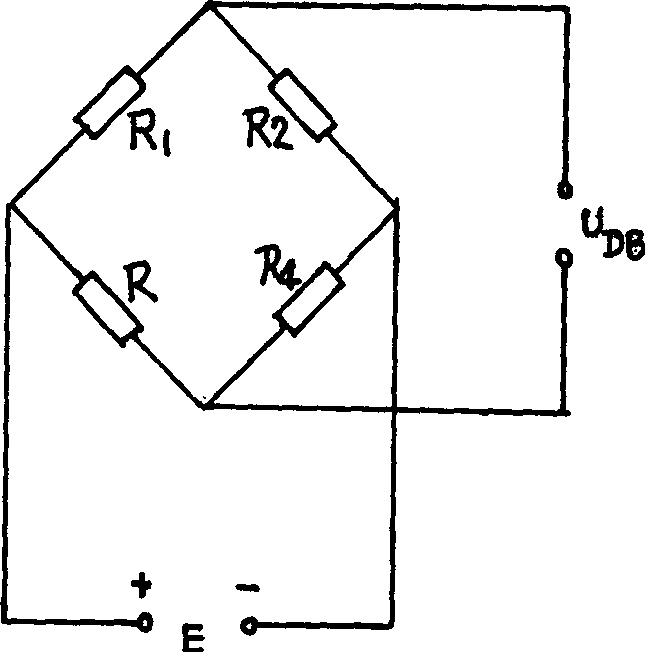
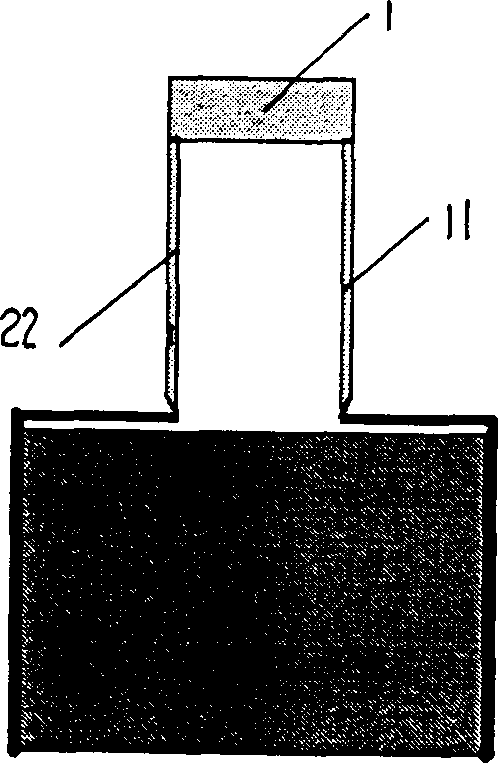
Method for measuring polymer-base foam material linear expansion coefficient by displacement sensor
A displacement sensor, linear expansion coefficient technology, applied in the direction of material thermal expansion coefficient, electromagnetic measurement device, electric/magnetic solid deformation measurement, etc. stability issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 as image 3 As shown, the displacement sensor is used to measure the linear expansion coefficient of a PEI foam from room temperature to liquid hydrogen temperature zone, and the following results are obtained:
[0041] Sample No
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2 Utilizes displacement sensor to measure a kind of PU foam plastics room temperature to the linear expansion coefficient of liquid hydrogen temperature zone, obtains the following results:
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3 Utilize displacement transducer to measure a kind of B type sample foam room temperature to the linear expansion coefficient of liquid hydrogen temperature zone, obtain the following results:
[0045]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com