Use of tyrosine kinase inhibitor to treat diabetes
A tyrosine kinase and inhibitor technology, which is applied to the application of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of diabetes, can solve the problems of shortening average lifespan, affecting blood sugar control, and decreasing quality of life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
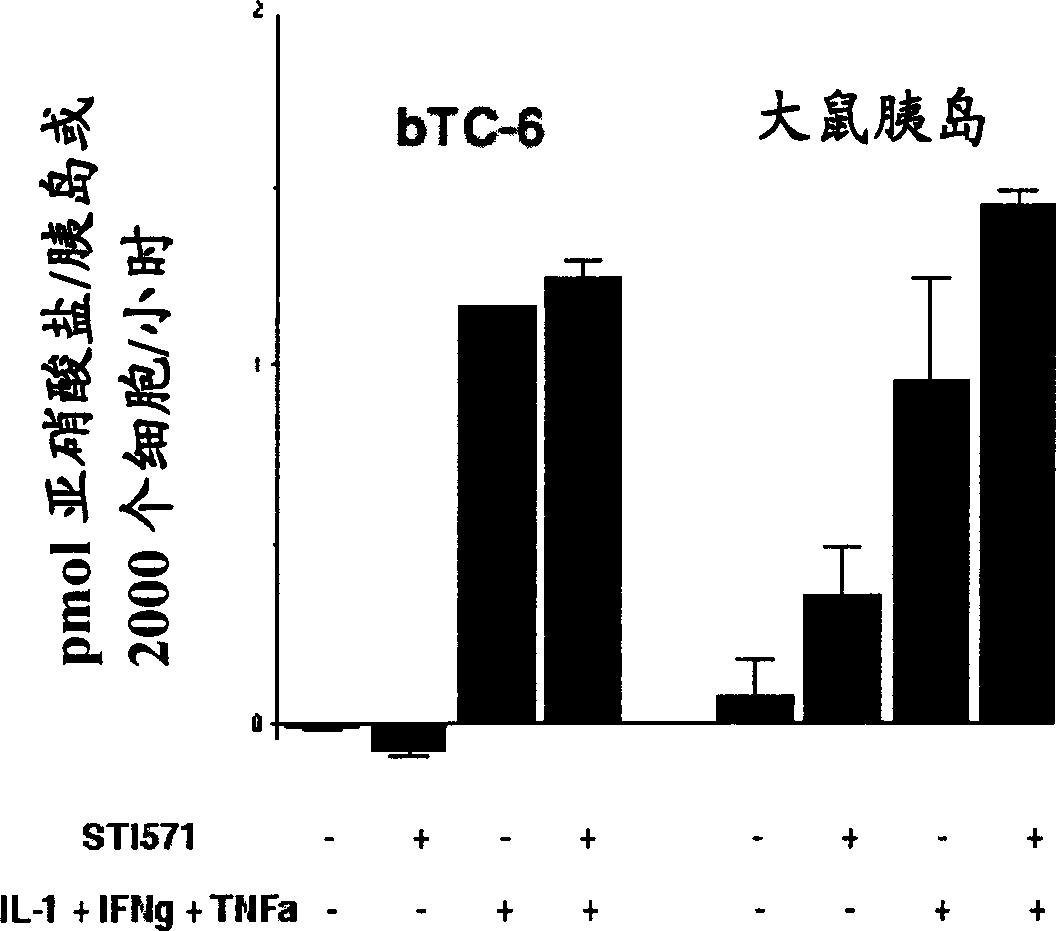
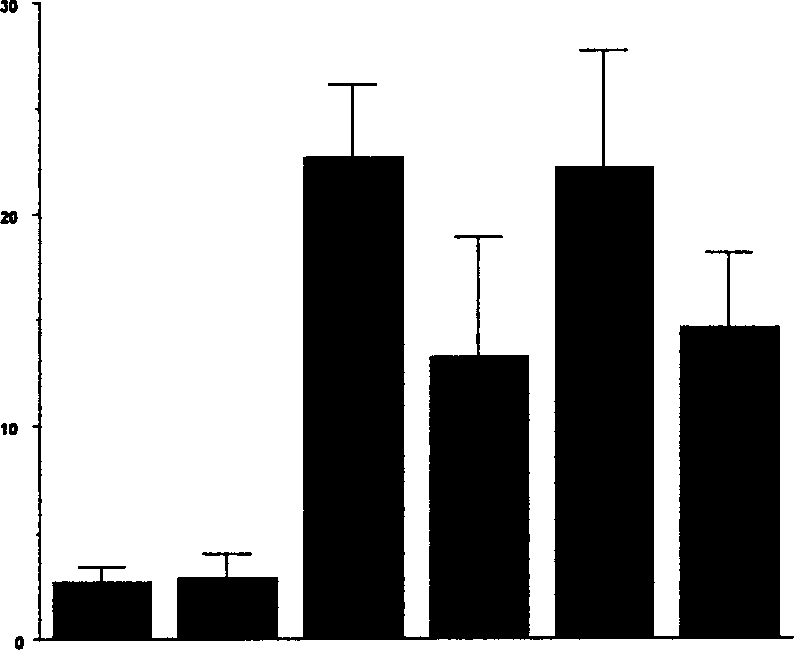
[0045] Example 1: Does compound I such as salt I protect against β-cell death and diabetes?
[0046] In the following examples, β-TC6 cells refer to beta-TC6 cells.
[0047] Insulin-dependent (type I) diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease caused by the specific and progressive destruction of insulin-producing beta cells. The dysfunction and damage of β-cells are thought to be due to their interaction with islet-infiltrating cells (macrophages, CD4 + or CD8 + (NK)T-cells) and / or exposure to cytotoxic mediators produced by these cells, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α, IFN-γ), free radicals, Fas ligand, TRAIL and perforin. Autoimmunity against β-cells can be triggered by environmental factors such as β-cell toxins, nutrients, stress, metabolic overload, viruses, etc. In type I diabetes, it is possible that β-cells actively participate in their own destruction by converting external death signals into internal apoptotic events. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2: 4-[(4-methyl-1-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridine Capsules of pyridyl)-2-pyrimidinyl]amino]phenyl]-benzamide methanesulfonate
[0077] Capsules containing 119.5 mg of Salt I corresponding to 100 mg of Compound I (free base) as active moiety were prepared with the following composition:
[0078] Salt I
[0079] The capsules are prepared by mixing the ingredients and filling the mixture into size 1 hard gelatin capsules.
Embodiment 3
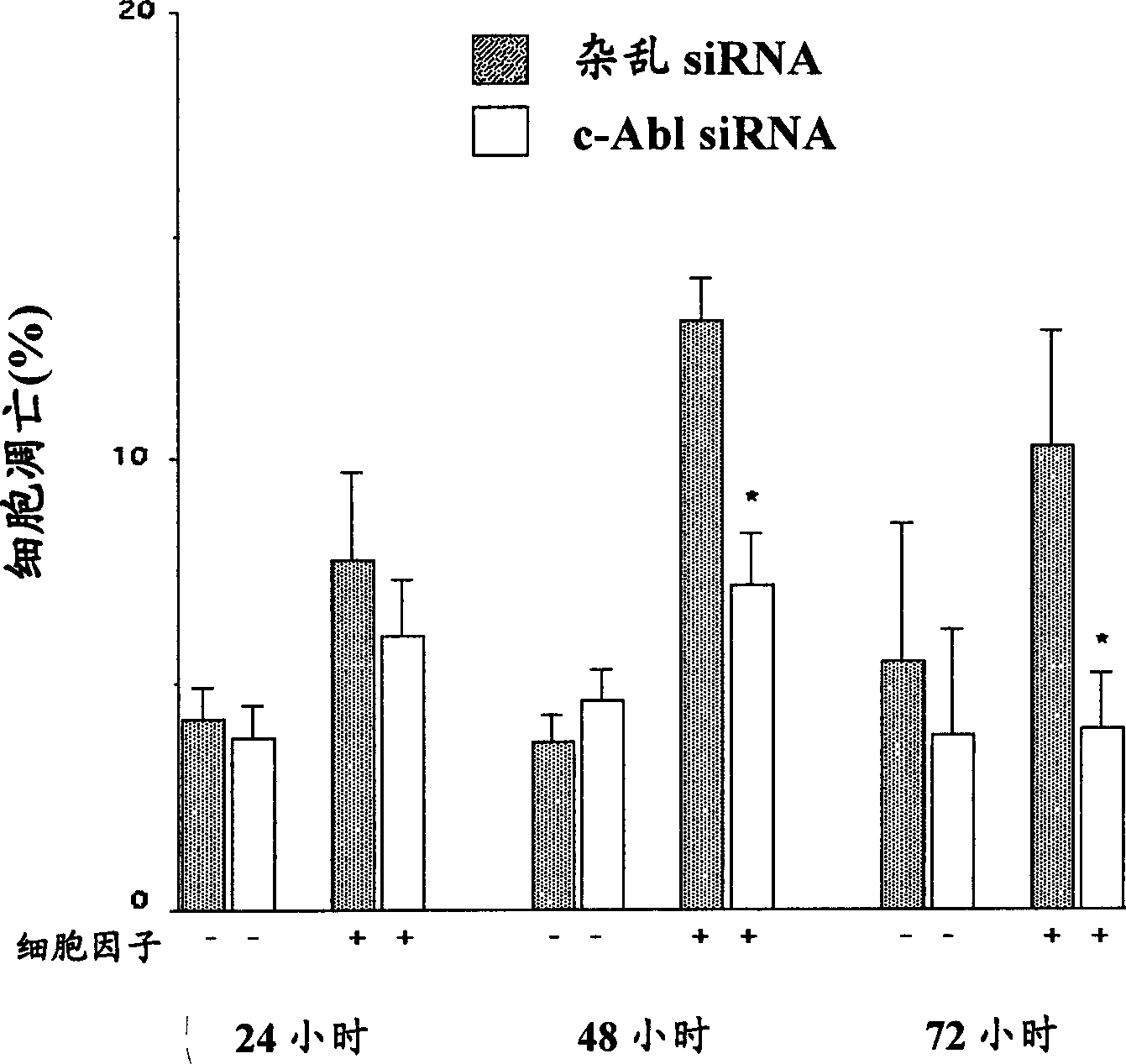
[0080] Example 3: Mechanism of protection against β-cell death and diabetes induced by Compound I in vivo Research
[0081] background: Compound I is known to inhibit c-Abl, a ubiquitously expressed protein tyrosine kinase with a molecular weight of approximately 145 kDa. Under physiological conditions, c-Abl has been shown to be involved in the regulation of cytoskeletal functions such as migration and cell structure as well as cell cycle progression. However, when cells are exposed to different forms of stress, c-Abl becomes hyperactivated, which leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
[0082] Most recently obtained results: C-Abl is expressed in bTC-6 cells and isolated rat islets, and the use of pharmacologically active agent compound I to inhibit c-Abl activity against the expression of streptozotocin, pro-inflammatory cytokines or nitric oxide donors Protection against induced β-cell death. Compound I, such as salt I, is a selective inhibitor clinically used...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com