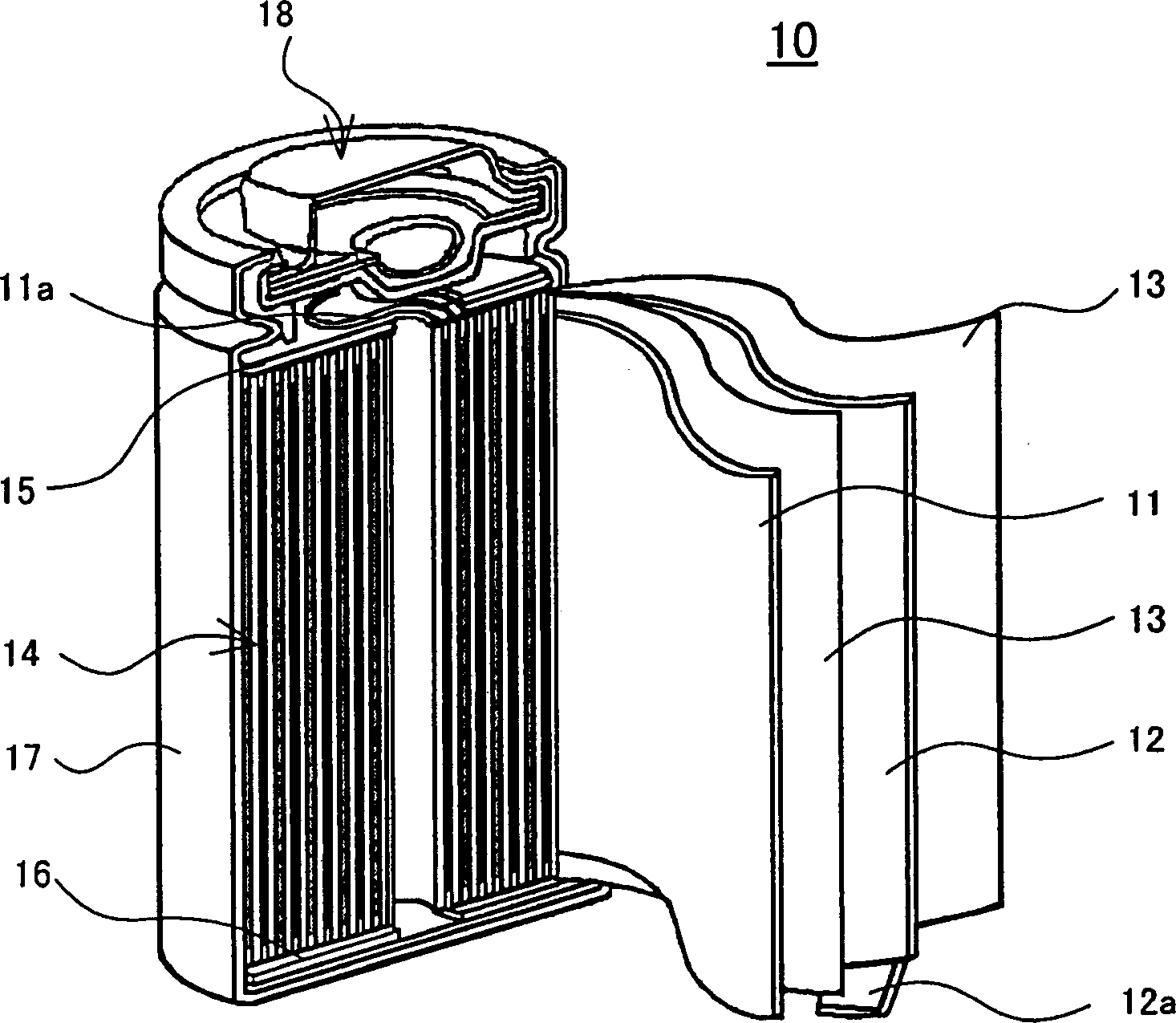
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and charging method thereof
A non-aqueous electrolyte and secondary battery technology, applied in non-aqueous electrolyte storage batteries, secondary battery charging/discharging, secondary batteries, etc., can solve problems such as capacity deterioration, reduction, and failure to show performance, and achieve improved cycle characteristics , high battery voltage, excellent cycle characteristics and thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~11
[0040] First, a specific method of manufacturing a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery common to all of Examples 1 to 11 will be described first.
[0041] [making of positive electrode]
[0042] Lithium cobaltate to which a different element was added was produced as follows. As a starting material, lithium carbonate (Li 2 CO 3 ), as the cobalt source, in the cobalt solution dissolved in the acid, add the zirconium, magnesium, aluminum solution dissolved in the acid in the same way, and then add sodium bicarbonate to make the zirconium, magnesium, aluminum co-precipitate to obtain carbonic acid Cobalt, which is obtained by thermally decomposing cobalt tetroxide (Co 3 o 4 ). After they were weighed so that the molar ratio of the lithium source and the cobalt source reached a given ratio, they were mixed with a mortar, and calcined at 850°C for 20 hours in an air atmosphere to obtain a compound containing zirconium, magnesium, and aluminum lithium cobalt oxide. This...
Embodiment 12、13 and comparative example 13、14
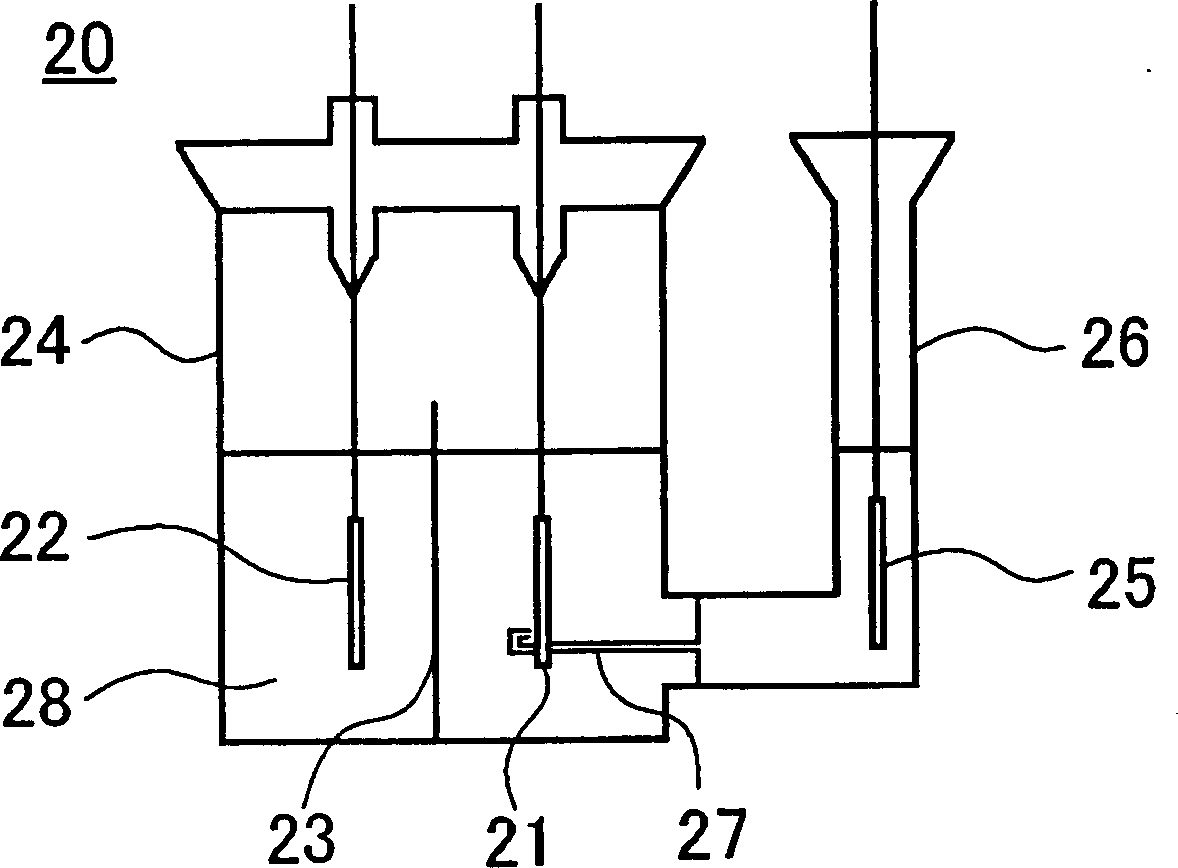
[0086] In addition to changing the molar ratio of lithium and cobalt to 0.98 (Comparative Example 13), 1.03 (Example 12), 1.05 (Example 13) and 1.06 (Comparative Example 14) in the above [Preparation of Positive Electrode], and The positive electrodes of Examples 12 and 13 and Comparative Examples 13 and 14 were produced in the same manner as in Example 3 (the molar ratio of lithium to cobalt = 1.00). The positive electrodes of Examples 12, 13 and Comparative Examples 13, 14, and the five positive electrodes of Example 3 were punched into 8 cm 2 , making figure 2 The simple battery 20 having the configuration shown above was evaluated as a simple battery.
[0087] [Production of positive electrode simple battery]
[0088] Simple battery 20 is made up of the measuring groove 24 of disposing positive pole 21, opposite pole 22 and diaphragm 23, the reference electrode groove 26 of disposing reference electrode 25, and capillary 27 is extended to the surface vicinity of positiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com