Process for preparing titanium odified supported chromium catalyst and its use
A chromium-based catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the field of titanium-modified carrier-type chromium-based catalysts, to achieve high melt index and strong hydrogen tuning ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
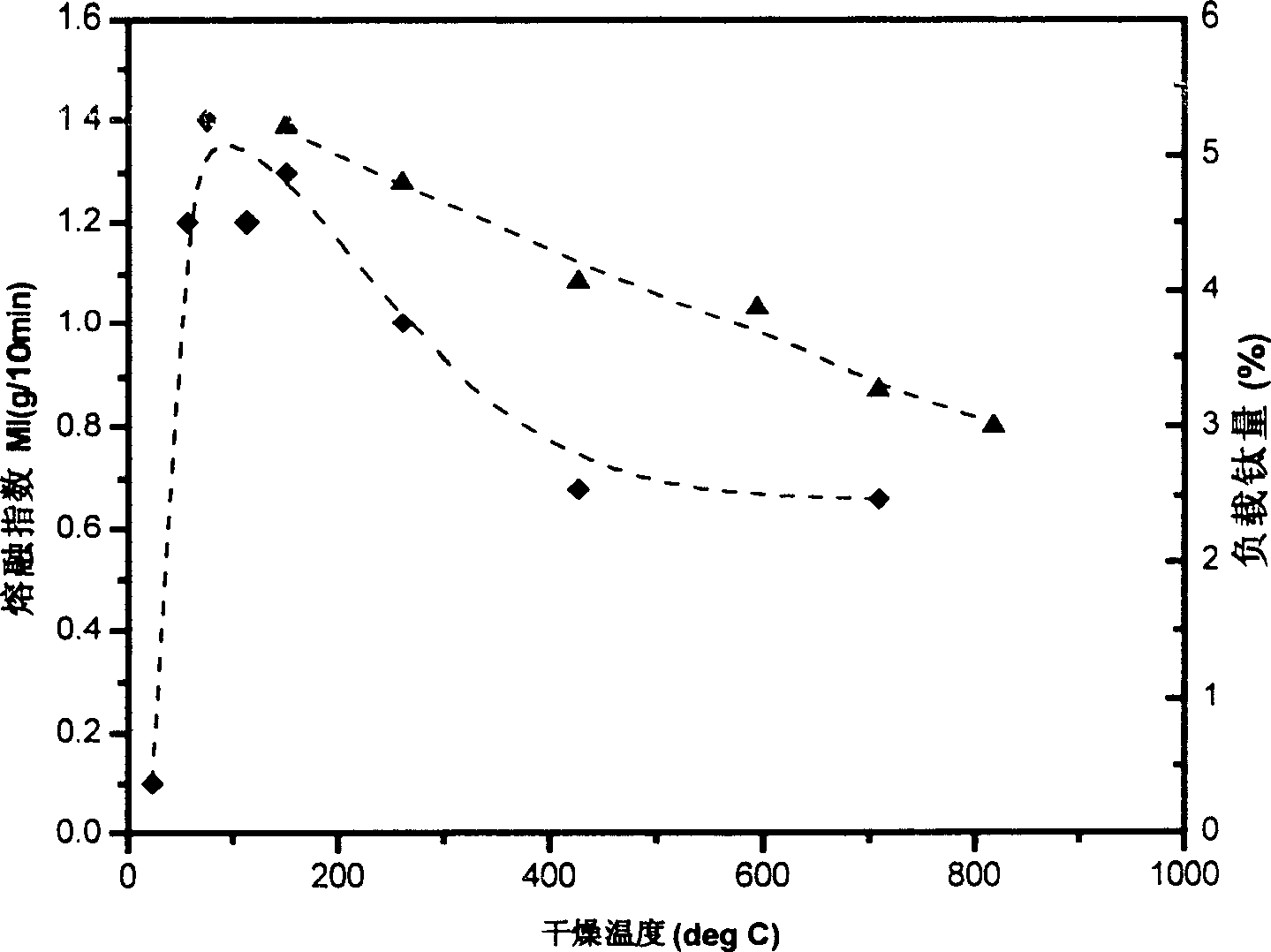
[0060] This example aims to reveal the importance of the contact reaction method and addition sequence of the three raw materials of carrier silica gel, titanium compound and chromium compound in catalyst preparation, which determine the hydrogen adjustment ability of the final catalyst. This example also demonstrates the influence of the pore volume (PV) of the carrier silica gel and the sodium (Na) content in the silica gel on the performance of the final catalyst.
[0061] Three commercially available carrier silica gels were used in the preparation of the catalyst: silica gel A: pore volume 1.92ml / g, specific surface area 539m 2 / g, sodium content 2000ppm; silica gel B: pore volume 1.97ml / g, specific surface area 509m 2 / g, sodium content 1100ppm; silica gel C: pore volume 1.55ml / g, specific surface area 490m 2 / g, sodium content 1000ppm.
[0062] These carrier silica gels are processed by different methods, and the method includes the following 3 steps:
[0063] (1) im...
Embodiment 2
[0070] This example uses another commercially available carrier silica gel with a pore volume of 1.90ml / g and a specific surface area of 510m 2 / g, sodium content 950ppm.
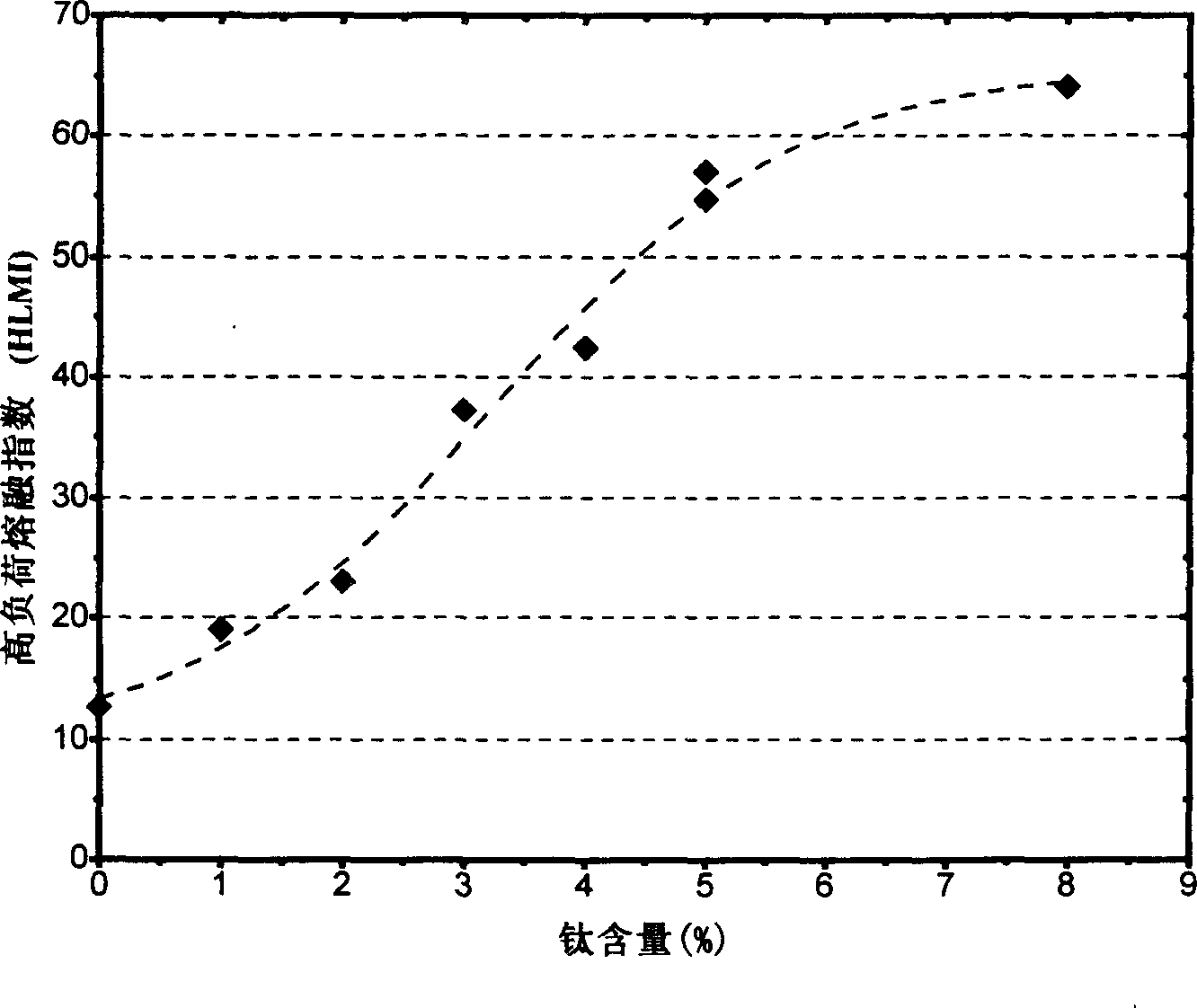
[0071] The carrier silica gel was first impregnated with chromium acetate aqueous solution, and the amount of chromium compound added was based on the chromium content in the final catalyst being 1% by weight. Isopropyl titanate solution in heptane. The addition amount of the titanium compound is different in each preparation example. After distilling off the heptane, the catalysts obtained in each preparation example were activated by calcining at 600° C. according to the method described in Example 1 to obtain final catalysts with different titanium contents. Each catalyst was subjected to polymerization reaction evaluation at 105°C. The test results are listed in Table 2.
[0072] As can be seen from Table 2, as the titanium content in the catalyst increases, the polymer melt index (MI) and the hig...
Embodiment 3
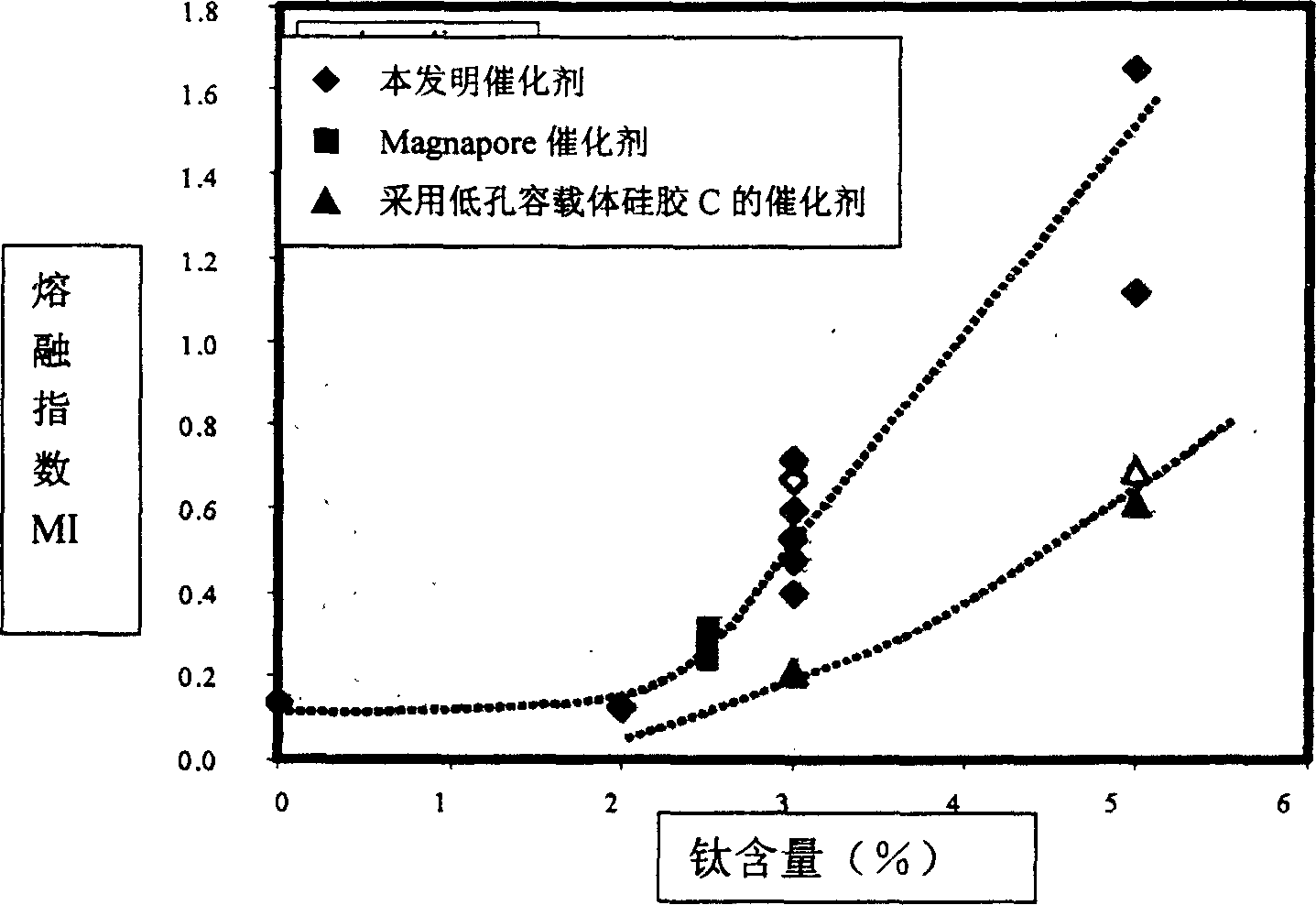
[0075] The purpose of this example is to compare the catalyst of the present invention with currently known commercially available catalysts with better hydrogen adjustment ability, and investigate their hydrogen adjustment ability.
[0076] The "catalyst of the present invention" mentioned in this example was prepared by the method of Example 2 using the carrier silica gel B described in Example 1. That is: first impregnate the carrier silica gel with chromium acetate in isopropanol solution, then dry it at 200° C. according to the method in Example 2, and then impregnate with different amounts of isopropyl titanate heptane solution. Finally, the final catalyst was obtained by calcining and activating at 600°C. Catalysts were evaluated for polymerization at 105°C.
[0077] Produced and sold by W.R Grace under the trademark Magnapore The commercially available catalyst was also calcined and activated at 600° C., and then evaluated for polymerization under the same conditio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com