Application of non-adenine in preparation of drug for promoting wound healing
A wound healing, non-adenine technology, which is applied in the application field of non-adenine in the preparation of medicines for promoting wound healing, and can solve problems such as wounds that cannot heal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Local application of guanosine to promote skin wound healing in mice
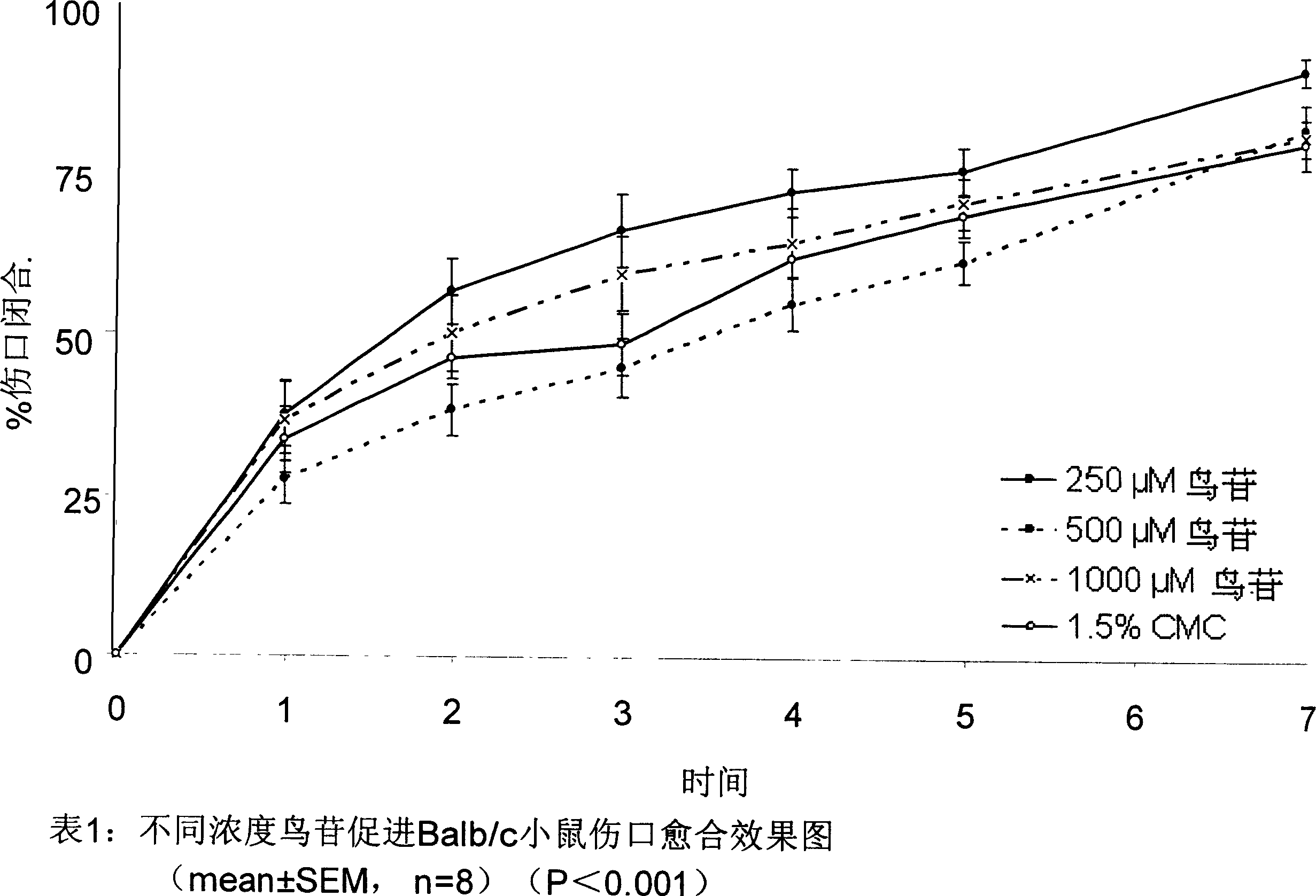
[0054] As can be seen from Table 1, the surgical wounds of Balb / c mice were treated daily with carboxymethylated cellulose at a concentration of guanosine ranging from 50 μM to 5000 μM. Our experiments confirmed that compared with the solvent control group (Graph 1, p<0.001, n=8), topical application of 250 μm guanosine once a day can enhance wound healing, and higher concentrations of guanosine (1000 μm-5000 μm) have no effect on animal wounds. Healing does not produce a stronger boost. Graph 1 also shows that it takes 1.6 days for 50% wound closure in the guanosine treatment group and 3 days in the vehicle control group (p<0.001, n=10).
[0055] The guanosine referred to in this example was topically applied on the skin wounds of Balb / c mice. Wound closure area was measured daily for each mouse as described in the method and expressed as the ratio of the area on the second day to the ar...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Guanosine can promote wound healing in diabetic mice
[0062] Clinical evidence shows that metabolic disturbances in diabetic wounds often lead to difficult wound repair. In order to confirm whether guanosine can promote wound healing in diabetic mice, we studied the effect of topical application of 250um guanosine to the skin wounds of congenital diabetic mice, using experimental mice to simulate type II diabetics. Wounds in diabetic mice healed more slowly than in normal mice (Balb / c). We found that topical application of 250um guanosine once a day accelerated wound healing compared to the solvent control group, as shown in Figure 5.
Embodiment 3
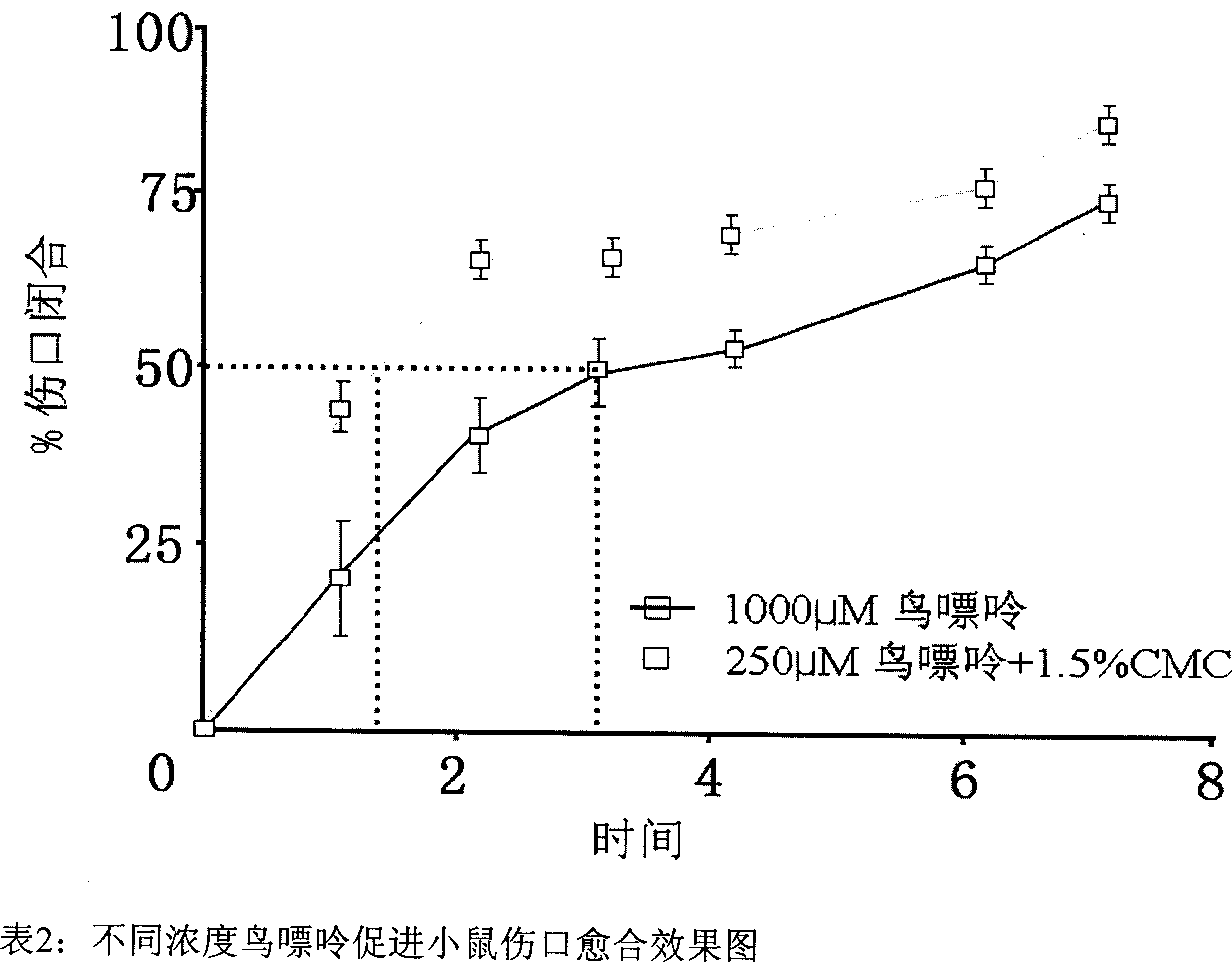
[0063] Example 3 Guanine promotes wound closure in mice
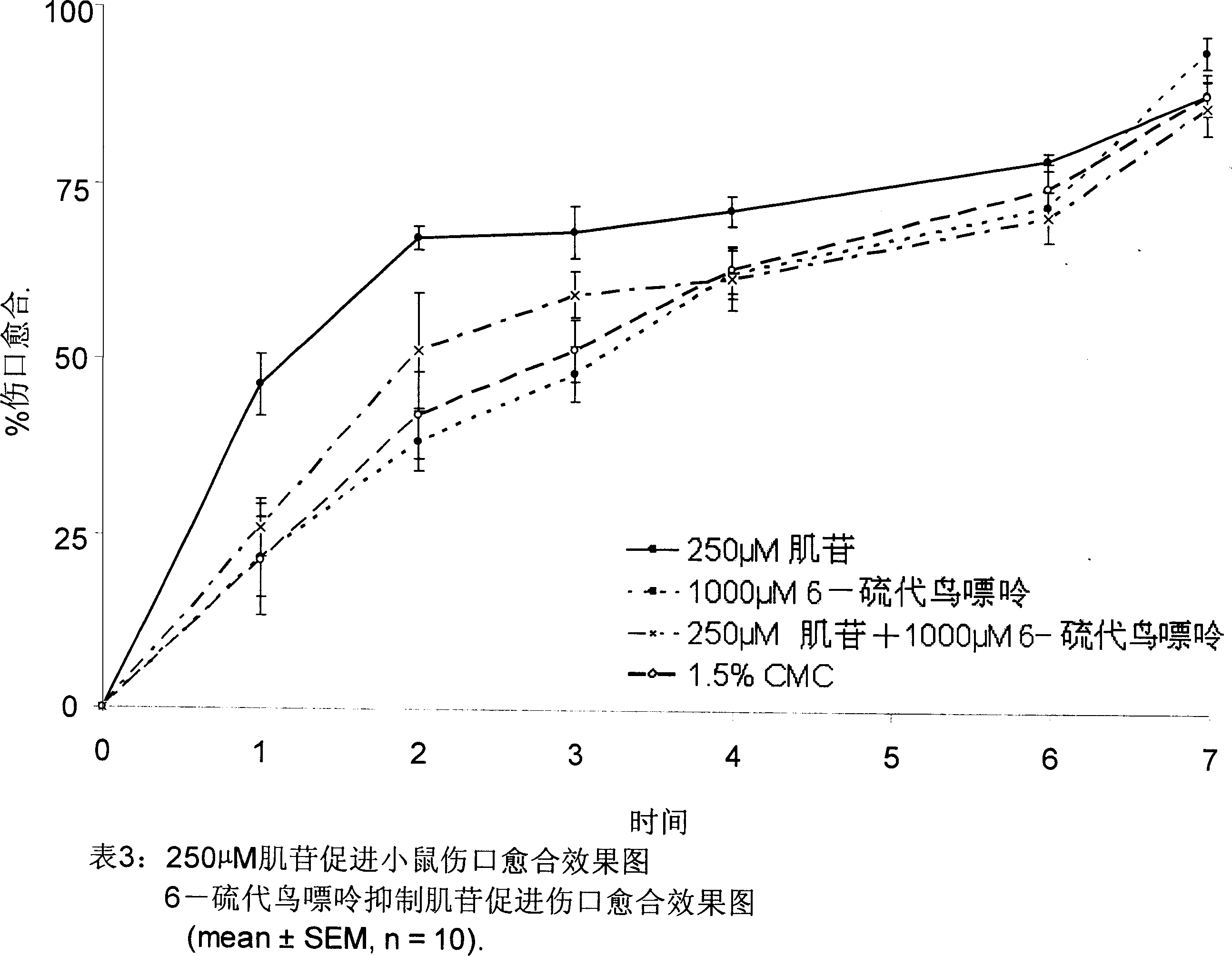
[0064] After confirming that guanosine can promote wound healing in mice, we also want to prove whether other non-adenines, such as guanine and inosine, can also promote skin wound healing in our experiments. The experimental results show that, as shown in Table 2, compared with the solvent control group (p<0.001, n=8), the use of 250 μm and 1000 μm guanine can also effectively promote wound healing. Guanine reduced the wound healing time by 50%, taking 1.6 days in the 250 μm treatment group and 3.1 days in the 1000 μm group.
[0065] The role of guanine in promoting wound healing suggests that ribose molecules are not required for wound healing in vivo.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com