Amino-acid modified chitin nucleophic NO donor and its synthesis method
A synthesis method and amino acid technology, applied in the field of medical engineering, can solve the problems of poor biocompatibility, low loading level, and poor biocompatibility of modified chitosan, so as to promote wound healing, prevent restenosis, improve Effect of antithrombotic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
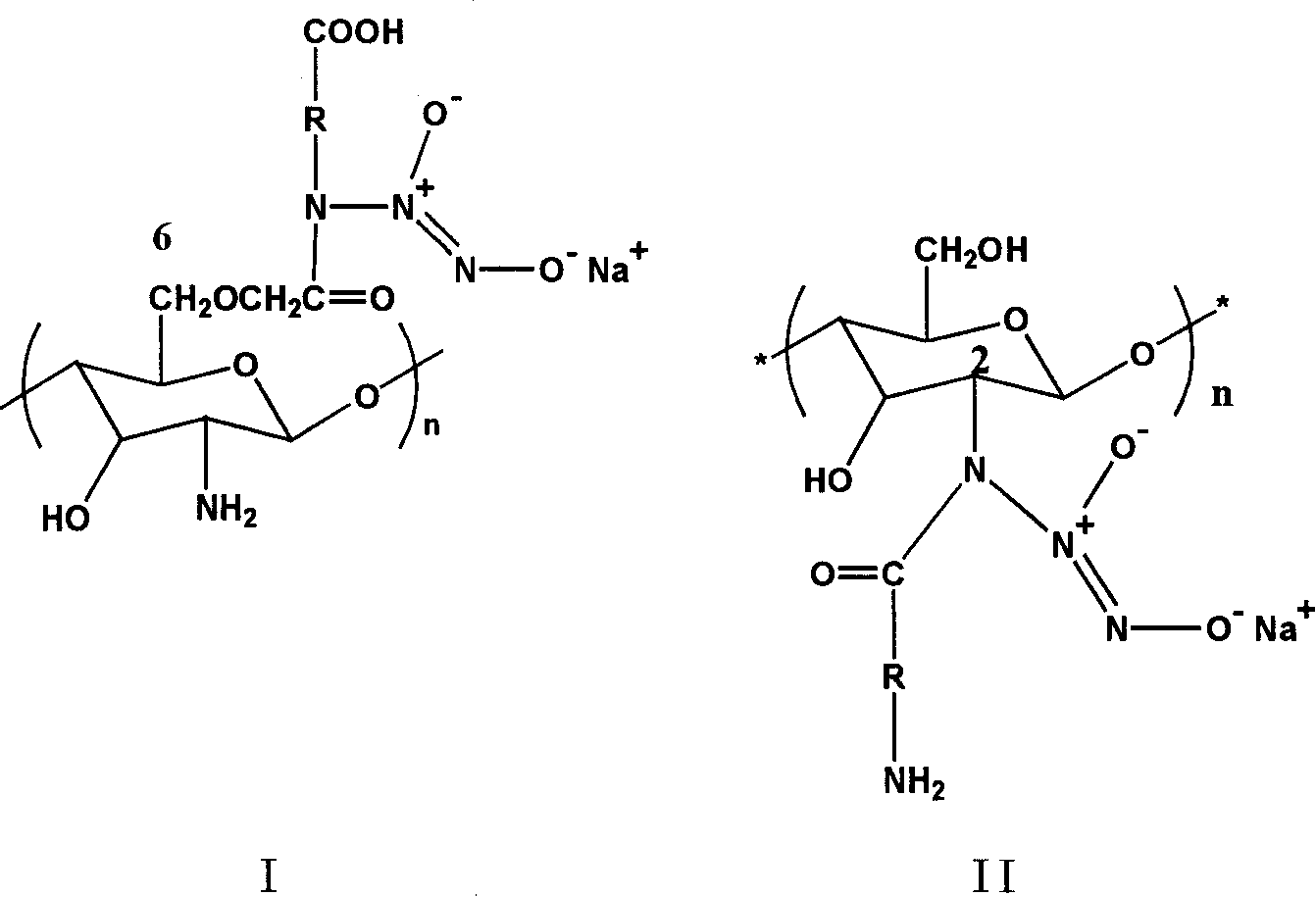
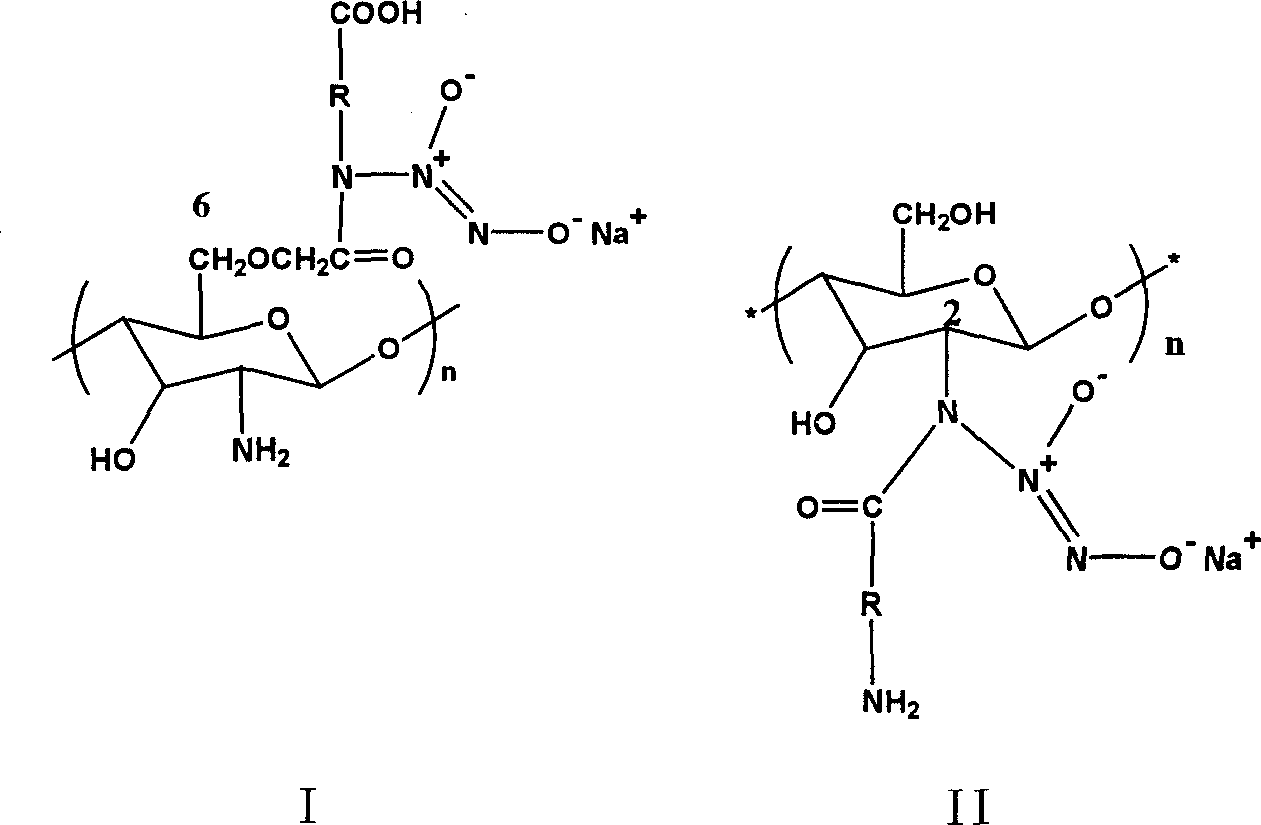
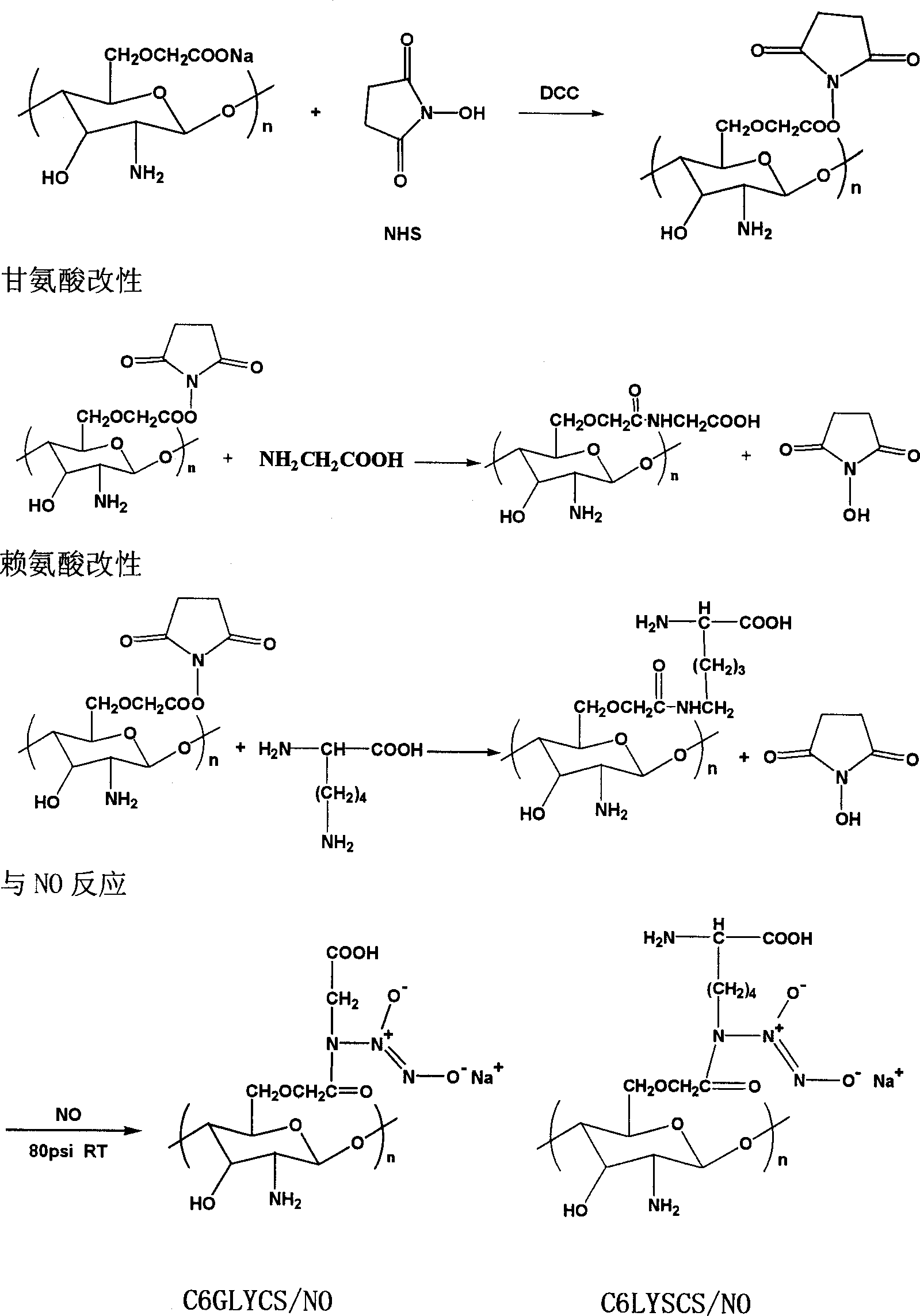
[0028] Example 1: Introduction of glycine at the C6 site
[0029] Preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan
[0030] Add 15g of chitosan and 200ml of isopropanol into a three-neck bottle, stir to disperse chitosan evenly in isopropanol, divide 50ml of 10mol / L NaOH solution into 5 parts, add one part every 30min, and stir at room temperature After 1 hour, a slurry of the reactant was obtained. Dissolve 24g of solid chloroacetic acid in 70ml of isopropanol and add it to the reactant slurry in 4 portions. After the addition, the reactant was heated to 70° C. with a water bath, and the reflux condensing device was turned on under temperature control, and stirred for 2 hours. After stopping, adjust the pH value to 7-8 with glacial acetic acid, and a large amount of light yellow flocculent precipitates precipitated. Vacuum filtration gave a yellow solid, which was washed with methanol three times, and the obtained yellow solid was vacuum-dried for 1 day at 60°C.
[0031] Activation o...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Introduction of lysine at the C6 site
[0037] Take by weighing 1: 1 lysine and the activated carboxymethyl chitosan in embodiment 1 and add the NaHCO of 0.05mol / L 3 In the buffer solution, a pale yellow solution was obtained after stirring for 1 day. After the resulting solution was concentrated, it was dialyzed for three days and freeze-dried to obtain a white fibrous substance.
[0038] Lysine modified chitosan FTIR: 1730cm -1 (-COOH), 1630cm -1 and 1514cm -1 (NH 3 + ), 1415cm -1 (-CH 2 and -CH 3 ), 2928cm -1 (-CH 2 ). 1 H NMR: 4.33(8H), 3.41(9H), 1.05(10H), 0.88(11H), 2.35(12H), 3.60(13H).
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Introduction of amino acids at the C2 site
[0040] Because there are also carboxyl groups in amino acids, first activate the carboxyl groups in amino acids, and then combine with -NH at the 2nd carbon position in chitosan 2 reaction. Dissolve amino acid in 100ml of water alcohol (2:1), add N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), stir for 1 hour, add dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) alcohol solution, and react at room temperature for 24 hours. In the above reaction system, the molar ratio of amino acid:NHS:DCC is 1:1.5:1. Take a quantitative amount of chitosan (amino acid: chitosan molar ratio 1:1) dissolved in 0.1M acetic acid solution, add dropwise to the above solution under stirring, react at room temperature for 24 hours, concentrate the resulting solution, dialyze for three days, freeze-dry A white fibrous substance was obtained.
[0041] FTIR: 1650cm -1 (amide I), 1560cm -1 (Amide II), 1310cm -1 (amide III); 1 H NMR: 3.53 (8H)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com