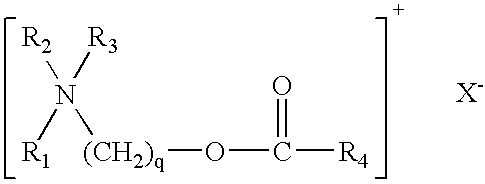
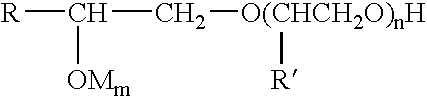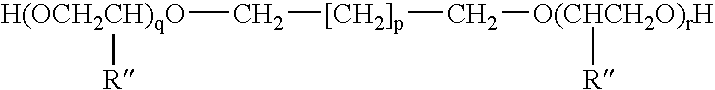Thickened fabric conditioners
a fabric conditioner and thickening technology, applied in the field of thickening fabric conditioners, can solve the problem of marginal perfume carry-over, and achieve the effect of stable ageing, lower stringiness of products, and lower stringiness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example ii
Rate of Dispersion of Extracted Polymers
[0077] This example is carried out to determine if the faster rate of dispersion for the SNF polymer is due to the presence of the co-surfactant or due to a difference in the polymer from BP.
[0078] Procedure: Each Polymer was suspended in hexane to create equal and uniform particle sizes in a 10% solution. 1 ml of this suspension was transferred to a vial containing 10 ml water. Vials were mixed by inverting 3 times and gellation rate was observed.
[0079] Results: The SNF polymer was completely gelled by the end of the inversions. The BP Polymer still showed large lumps of polymer. The sample was allowed to stand overnight and the gel was obtained by morning.
[0080] The data show that the SNF polymer disperses more easily than the BP Polymer in the absence of a co-surfactant. This indicates that there is an inherent difference between the two polymers other than the presence or type of co-surfactant or oil.
example iii
[0081] Three compositions were prepared as described below which differed with respect to the thickening polymer: the first (control) contained no polymer; the second contained P 7050; and the third contained SNF polymer. The formulas are described in the following table:
1 Formula: Percent As Active Ester Quat 8.0% Perfume 0.75% Dequest 2000.sup.(1) 0.10% Lactic / Lactate Buffer 0.063% CaCl.sub.2 (10% sol) 0.050% Polymer* 0 or 0.15% De-ionized H.sub.2O to 100% *= BP 7050 or SNF .sup.(1)Dequest 2000 is a commercial chelating compound comprising aminotri(methylenephosphonic acid). It is referred to as "Dequest" in the remaining Examples.
[0082] Analytical Data: Analysis of Fragrance Deposited onto Fabric by SPME (solid phase micro-extraction) GC / MS. The results are shown in FIG. 2.
[0083] FIG. 2 demonstrates that at 100 ppm water hardness, the softener composition with SNF polymer delivered significantly more fragrance (73% increase) on the fabric surface (dry) as compared to the control ...
example iv
[0085] In this example the swelling kinetic of BP and SNF polymers is compared. A cross-linked polymer, when placed in a suitable solvent, imbibes the solvent and undergoes swelling to an extent determined by the nature of the polymer and the solvent. By swelling is intended the ability of the polymer to thicken the solvent whether it is water or a fabric softening composition.
[0086] De-ionized (DI) water was thickened with 0.5% (% of actives in emulsion) of BP 7050 or SNF polymer. The polymer under emulsion form was rapidly added to DI water through a syringe. The mixing speed was fixed at 250 rpm and dispersion time at 3 minutes. Swelling kinetic was then followed using a Brookfield RVT viscometer (10 rpm, spindle 2). The results are shown in FIG. 6.
[0087] As shown in FIG. 6, the final viscosity (24H) of DI water thickened with SNF polymer is obtained right after making whereas with BP 15 minutes are necessary.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com