Novel card proteins involved in cell death regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
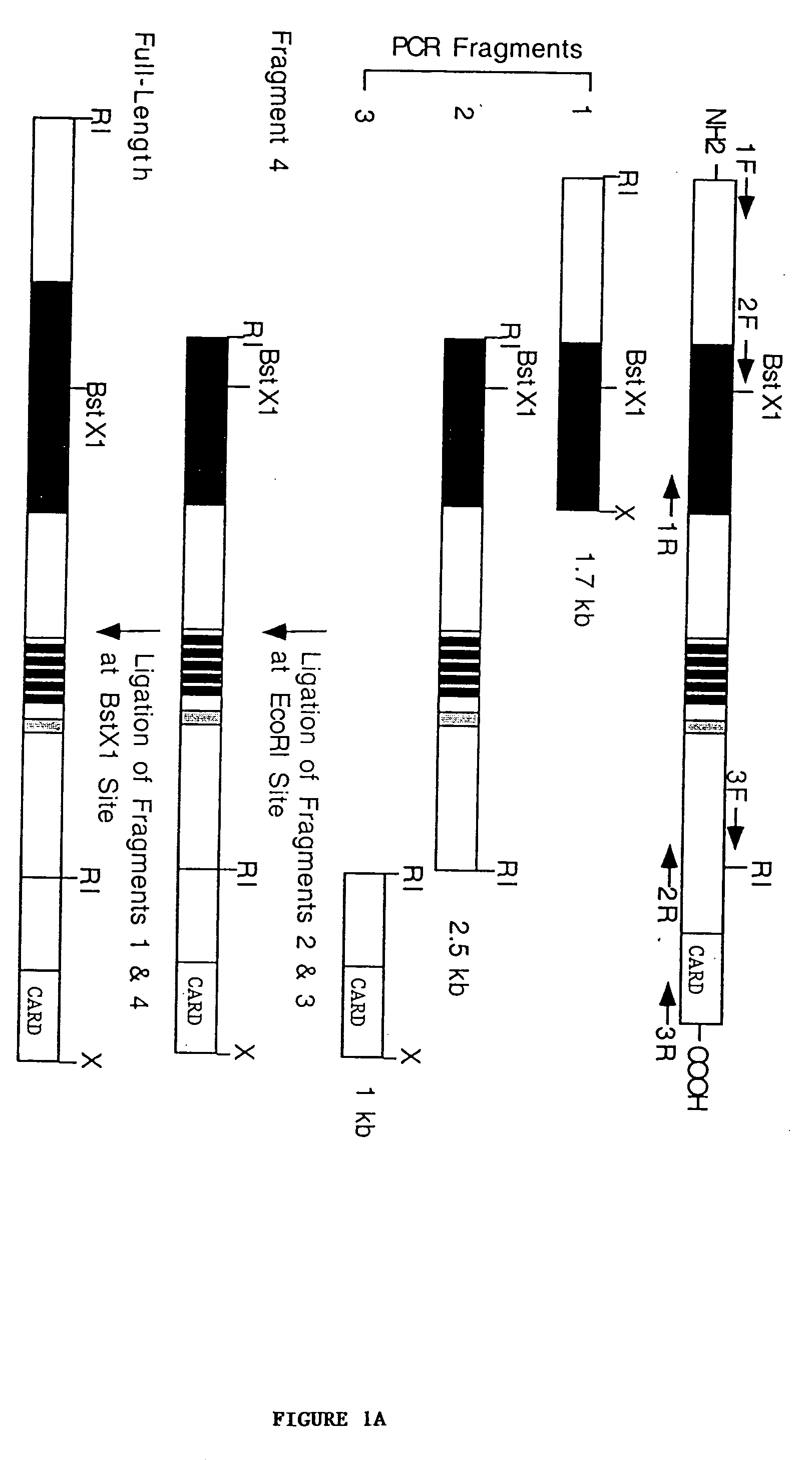
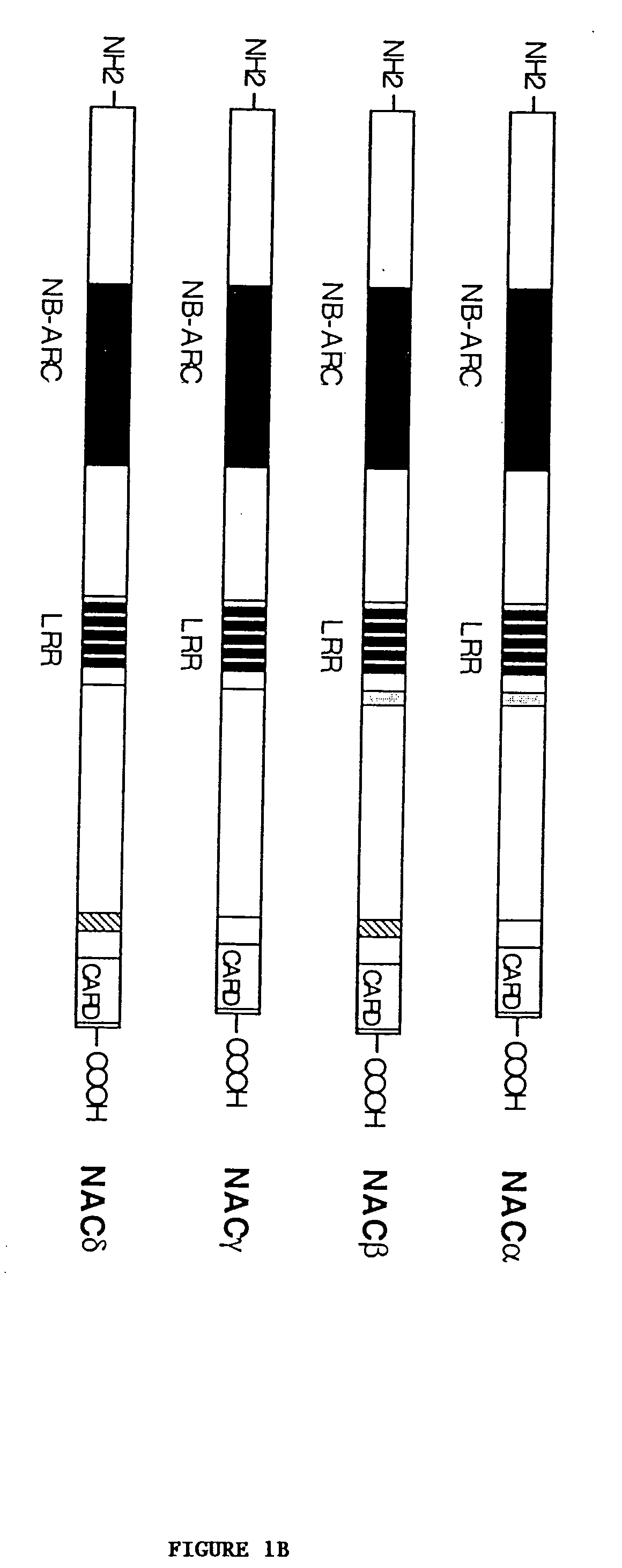
[0181] cDNA Cloning.
[0182] Jurkat total RNA was reverse-transcribed to complementary DNAs using MMLV reverse transcriptase (Stratagene) and random hexanucleotide primers. Three overlapping cDNA fragments of NAC were amplified from the Jurkat complementary DNAs with Turbo P.function.u DNA polymerase (Stratagene) using the following oligonucleotide primer sets: primer set 1; 5'-CCGAATTCACCATGGCTGGCGGAGCCTGGGGC-3' (forward; SEQ ID NO:13) and 5'-CCGCTCGAGTCAACAGAGGGTTGTGGTGGTCTTG-3' (reverse; SEQ ID NO:14), primer set 2; 5'-CCCGAATTCGAACCTCGCATAGTCATACTGC-3' (forward; SEQ ID NO:15) and 5'-GTCCCACAACAGAATTCAATCTCAACGGTC-3' (reverse; SEQ ID NO:16), and primer set 3; 5'-TGTGATGAGAGAAGCGGTGAC-3' (forward; SEQ ID NO:17) and 5'-CCGCTCGAGCAAAGAAGGGTCAGCCAAAGC-3' (reverse; SEQ ID NO:18). The resultant cDNA fragments were ligated into mammalian expression vector pcDNA-myc (Invitrogen, modified as described in Roy et al., EMBO J. 16:6914-6925 (1997)) and assembled to full-length cDNA by ligating ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Reactivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cell proliferation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com