Wafer probe for measuring plasma and surface characteristics in plasma processing environments
a plasma processing environment and surface characteristics technology, applied in the field of plasma processing environments, can solve the problems of limiting the use of measuring devices for real-time affecting the accuracy of plasma and substrate temperature measurement, and inconvenient operation, so as to reduce or avoid the effect of averaged measurements taken in pulsed plasma environment and limited onboard memory and power resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
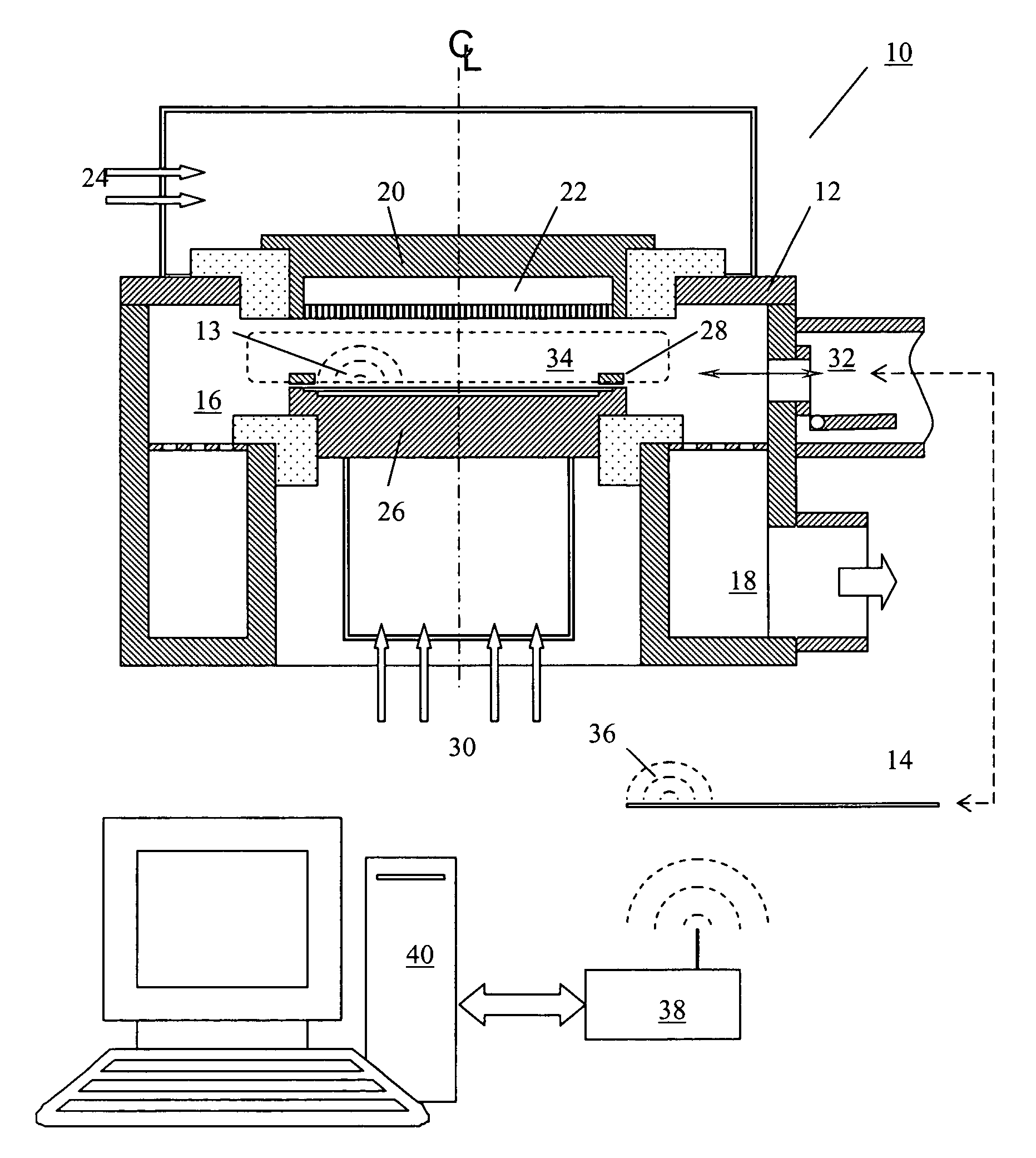
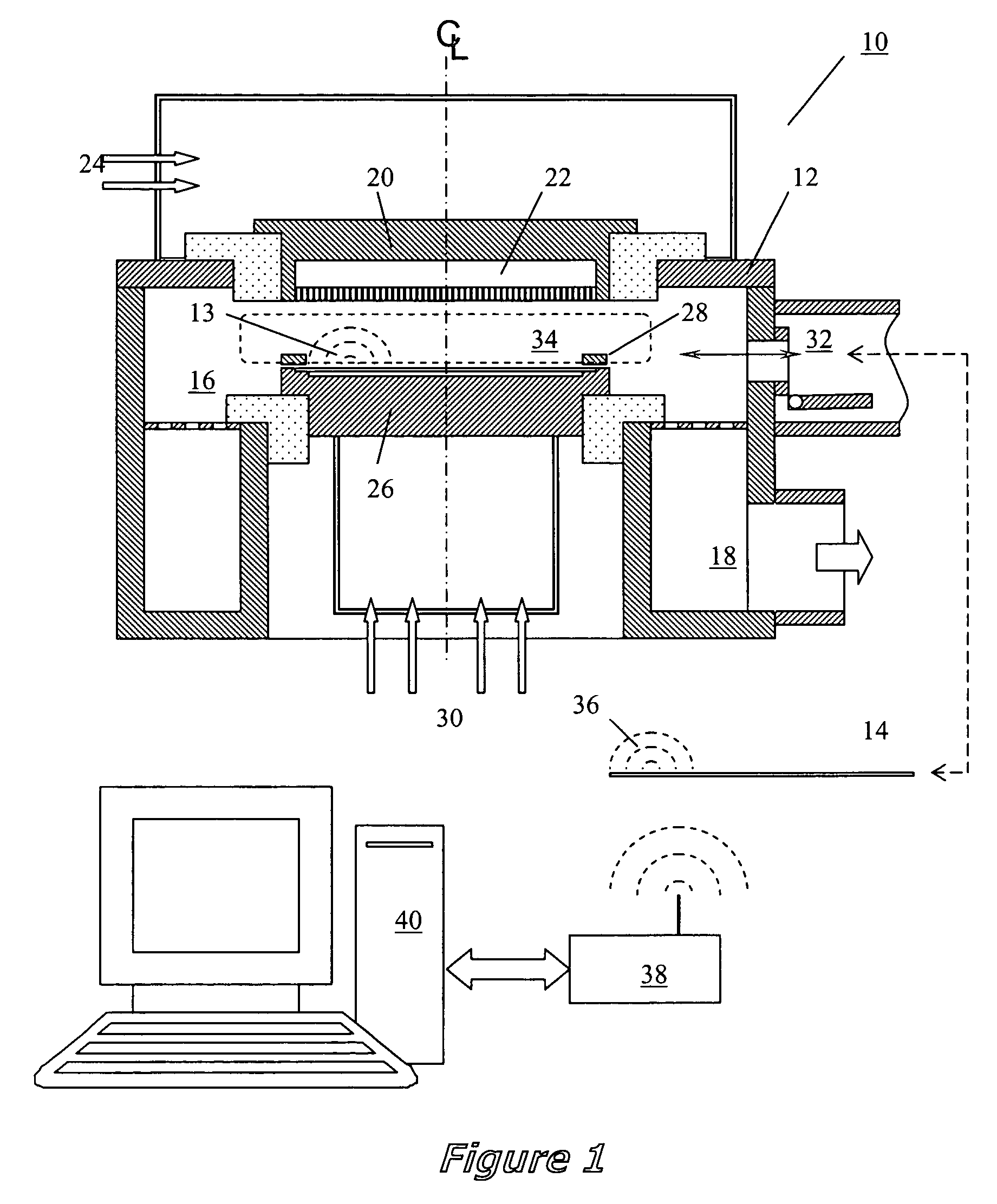
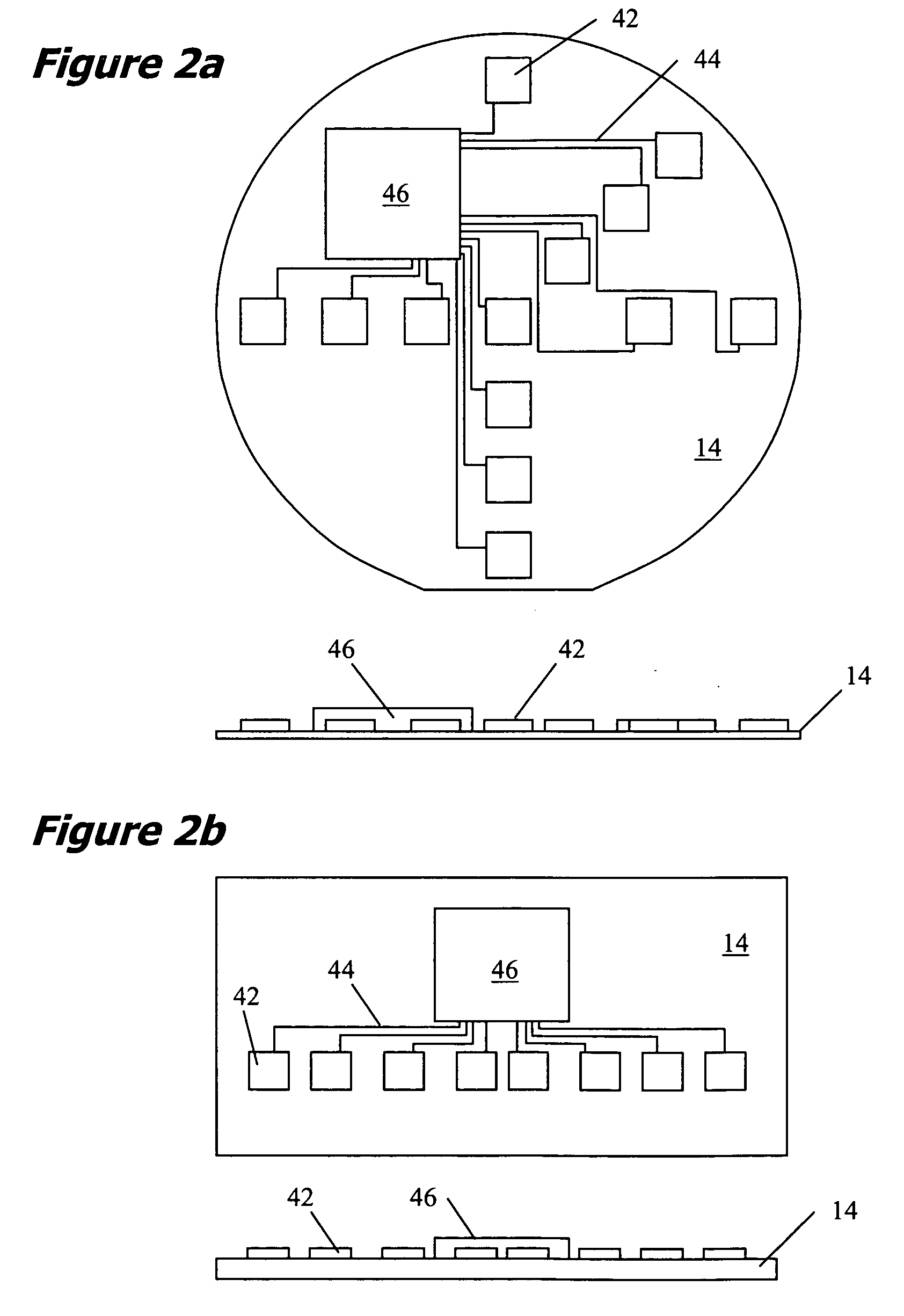
Referring to FIG. 1 there is illustrated an apparatus 10 that is capable of making real-time measurements of incident plasma current flux and surface temperatures of a work piece in a plasma processing system 12. In this particular illustration a diagnostic probe 14 is comprised of a silicon wafer substrate that incorporates plasma probe and surface temperature diagnostic circuitry and wireless communications and a stored power system. In the preferred embodiment, the probe 14 is powered up outside the plasma processing system 12 to enable diagnostic communications prior to use for real-time measurements. The plasma processing system of FIG. 1 is one of many possible plasma processing systems and is presented here to illustrate the function and use of the present invention. The processing system is comprised of a vacuum processing chamber 16, a pumping manifold 18, a plasma source electrode mounted to the top of the chamber 20, a gas delivery manifold or gas shroud 22, gas flow and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| plasma properties | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com