Method of modulating the activity of calcium channels in cardiac cells and reagents therefor
a technology of calcium channel and activity, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, peptide sources, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of myocardial contractile failure, morbidity and mortality, and contractile failur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
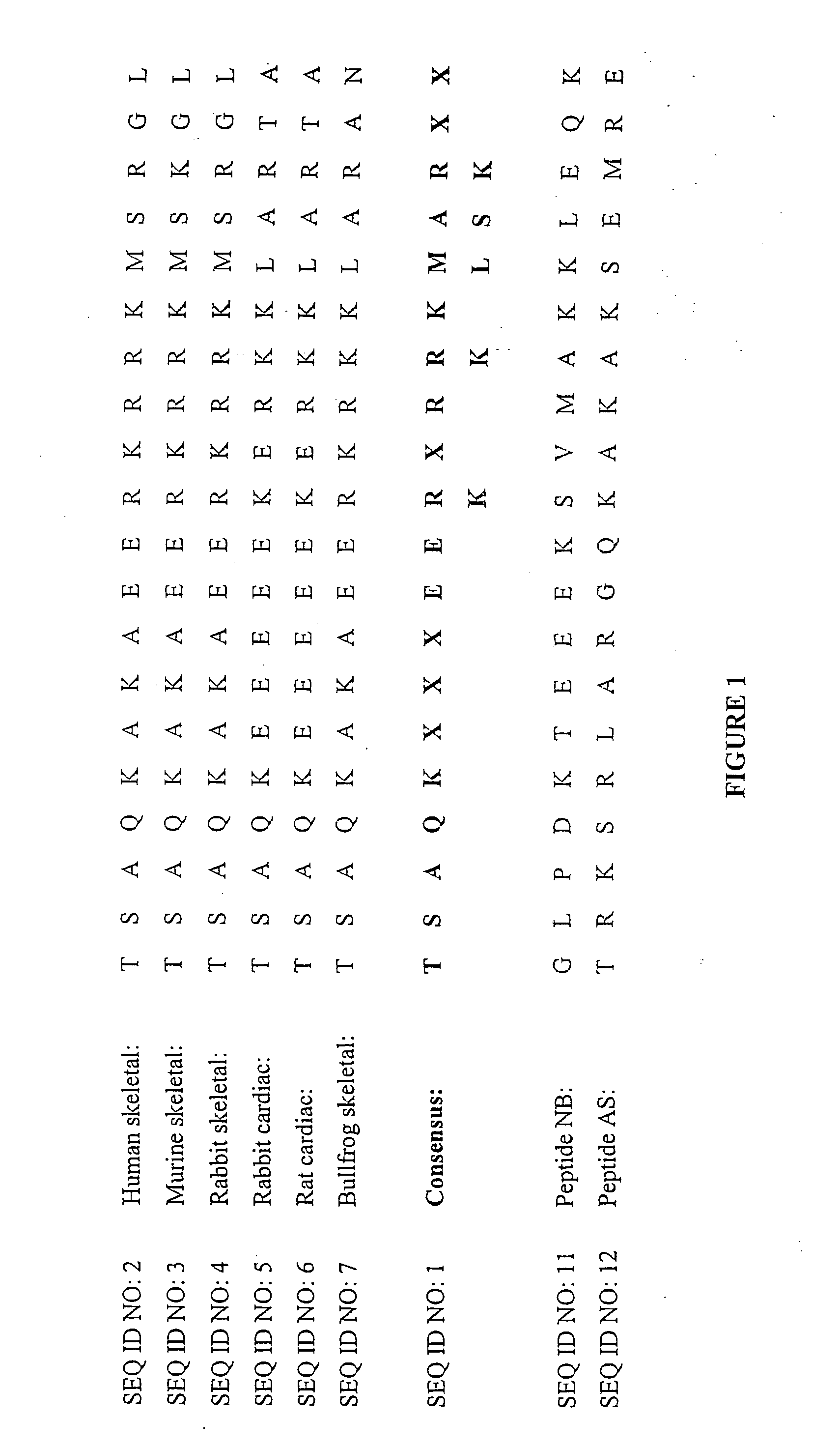
A 20-Mer Peptide that Modulates Cardiac RyR2 Calcium Channel Activity
Results
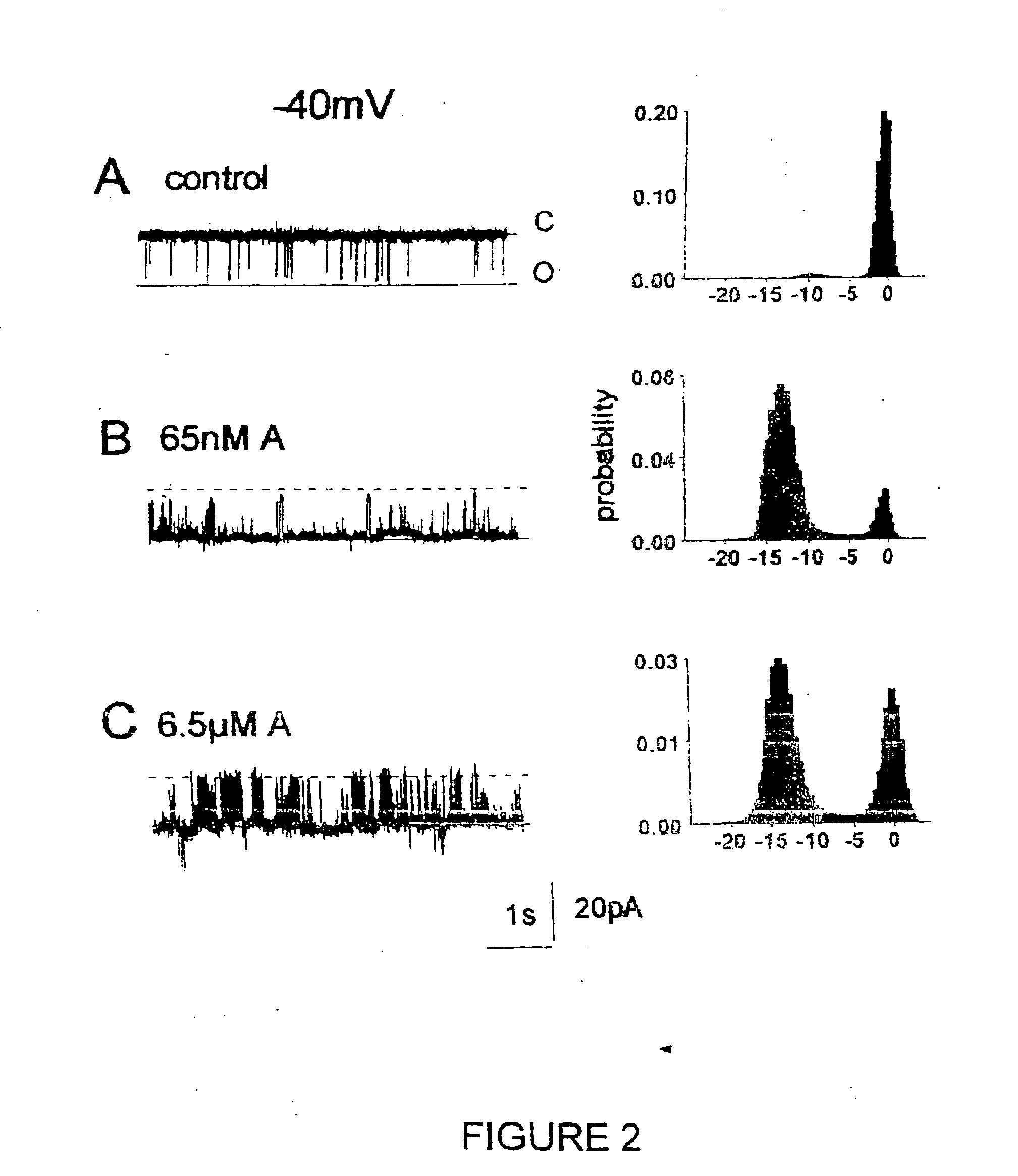
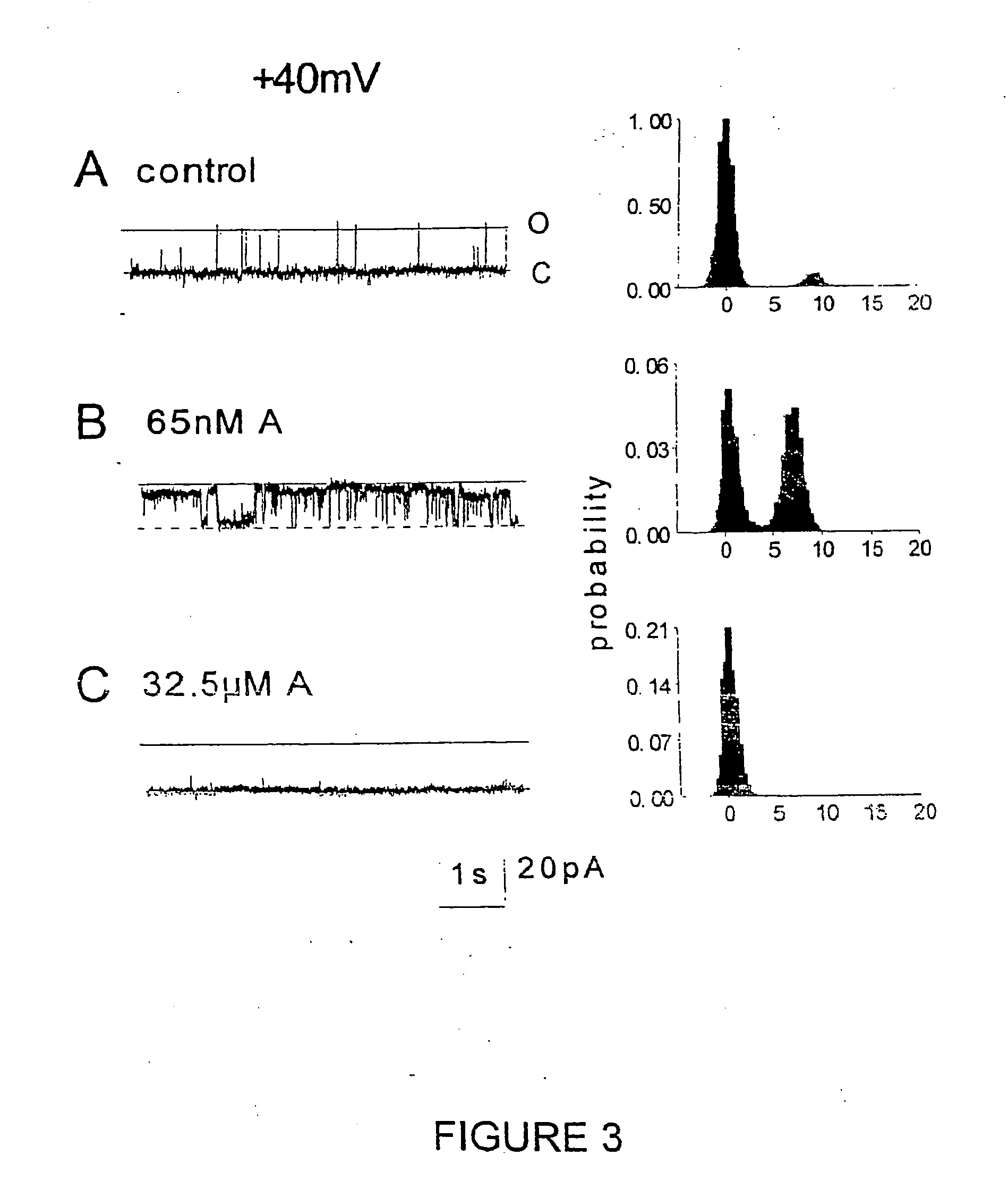
[0174] An increase in the activity of RyRs from cardiac muscle was seen when the 20-mer peptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) was added to the cytoplasmic (cis) side of the channel at a concentration of 10.sup.-7 cis Ca.sup.2+. Single channels were identified as RyRs by their Cs.sup.+ conductance of .about.450 pS with bilayer potentials of +40 mV or -40 mV and by the ability of 30 .mu.M ruthenium red to block the channel at the end of the experiment.
[0175] Records from one experiment in which cardiac RyRs were strongly activated by the 20-mer peptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) are shown in FIG. 2, at -40 mV, and in FIG. 3, at +40 mV. Channel activity before addition of the peptide consisted of brief intermittent openings (FIG. 2, panel A; FIG. 3, panel A). Within 10 s of adding 65 nM peptide (SEQ ID NO: 2), channel openings increased at -40 mV.
[0176] An increase in the frequency of events, and the appearance of very long openings, wer...
example 3
Functional Analysis of DHPR 20-Mer Fragment Derivatives and Analogues
Materials & Methods
[0185] Peptides
[0186] Four peptides were tested in this series of experiments, these being:
[0187] (i) the native DHPR 20-mer peptide (SEQ ID NO: 2);
[0188] (ii) the SEQ ID NO: 2 peptide in which Ser.sup.687 (residue 17) is replaced by an alanine residue to produce SEQ ID NO: 8;
[0189] (iii) the SEQ ID NO: 2 peptide in which Arg.sup.688 (residue 18) is replaced by an D isomer to produce SEQ ID NO: 9; and
[0190] (iv) the SEQ ID NO: 2 peptide in which Ser.sup.687 is mutated to alanine and Arg.sup.688 is replaced by a D isomer to produce SEQ ID NO: 10.
[0191] Measurements of Ca.sup.2+ Release from Cardiac SR
[0192] Cardiac SR vesicles (50 .mu.g of protein) were added to a cuvette, to a final volume of 2 ml of a solution containing (in mM): 100, KH.sub.2PO.sub.4 (pH=7); 4, MgCl.sub.2; 1, Na.sub.2ATP; 0.5, antipyrylazo III. Extravesicular [Ca.sup.2+] was monitored at 710 nm using either a Cary 50 or Cary 10...
example 4
Functional Analysis of DHPR 20-Mer Peptide Fragment Derivatives and Analogues
Results
[0195] Summary
[0196] The example 4 experiments include the testing of all compounds on Ca.sup.2+ release from cardiac SR vesicles. In addition, single cardiac RyR channels were exposed to peptide SEQ ID NO: 9. All peptides significantly enhanced the rates of Ca.sup.+-activated Ca.sup.2+ release or caffeine-activated Ca.sup.2+ release. Peptides SEQ ID NOs: 9 and 10, at high concentrations of >30 .mu.M marginally enhanced the rate of Ca.sup.2+ release in the absence of activating Ca.sup.2+ or caffeine, and also enhanced both Ca.sup.2+-activated Ca.sup.2+ release and caffeine-activated Ca.sup.2+ release. Peptide SEQ ID NO: 9 enhanced cardiac RyR activity in lipid bilayer experiments at low concentrations (1-10 nM), but blocked the channel pore in a voltage- and Ca.sup.2+-dependent manner at +40 mV at high concentrations. Accordingly, under appropriate physiological conditions, the dihydropyridine recept...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com