Reconstitution medium for protein and peptide formulations
a technology of protein and peptide, which is applied in the direction of peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, pharmaceutical delivery mechanisms, etc., can solve the problems of protein product safety, loss of activity, physical and chemical instability of proteins, etc., and achieve the effects of promoting protein-lipid interaction, preventing physical instability, and stabilizing intermediate structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
We have carried out biophysical studies to determine the effect of ethanol on the secondary and tertiary structure of lysozyme as a function of temperature. Far-UV and near-UV circular dichroism (CD) spectrophotometry was used to investigate ethanol dependent changes in conformation. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) was employed to determine the thermodynamic parameters associated with the unfolding of the protein. ANS (1,8 anilinonaphthalene sulfonate), a fluorescent probe that partitions into hydrophobic domains, was used to detect the exposure of hydrophobic domains that leads to aggregation and precipitation.
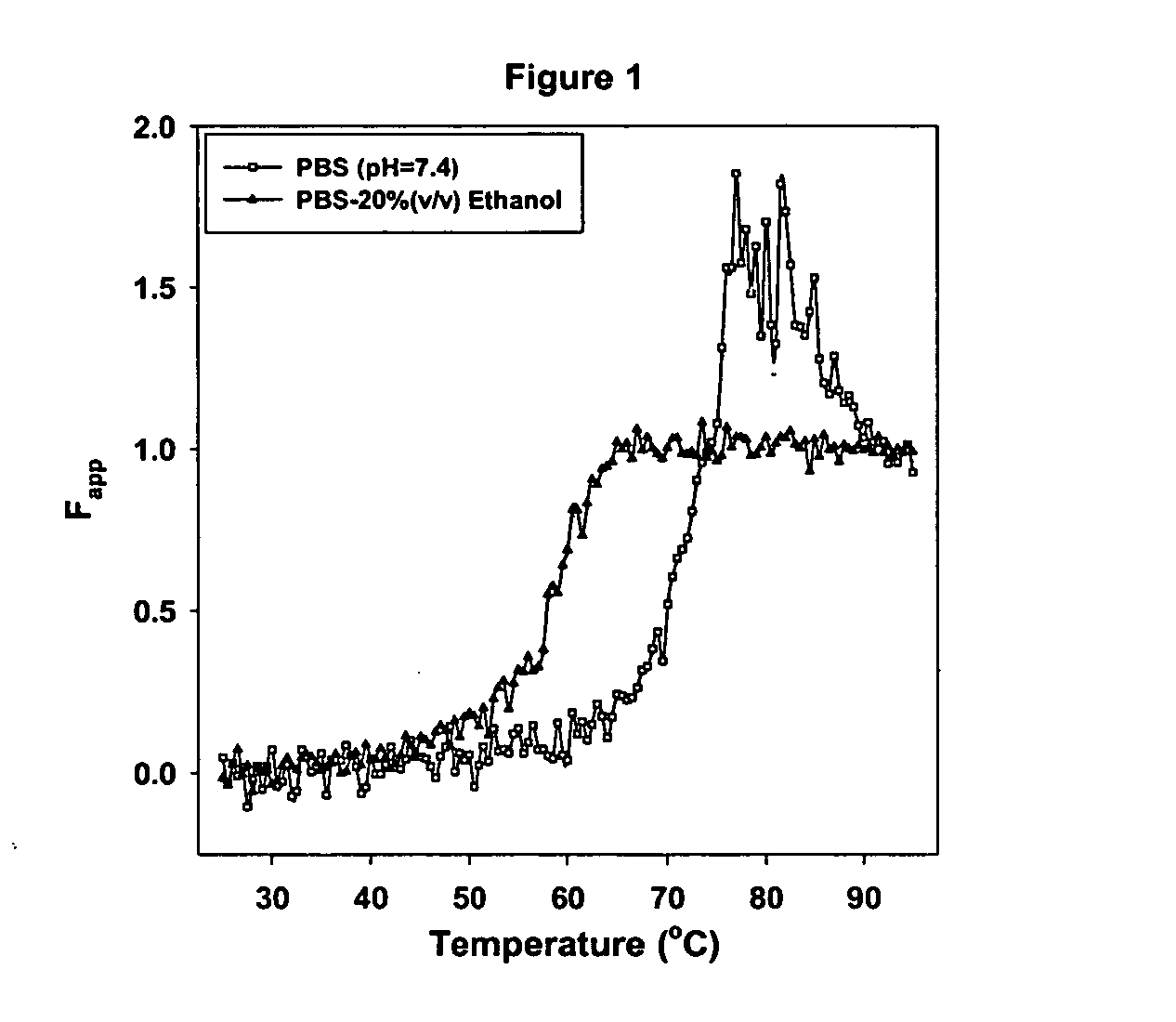
The unfolding of the protein using thermal stress in the presence and in the absence of ethanol is carried out to investigate the thermal stability of the protein in ethanol-buffer mixtures. The lyophilized lysozyme (660 ug / ml) was mixed with (20%) ethanol containing phosphate buffered saline (pH 7.4) and the protein was subjected to thermal stress. The conformatio...
example 2
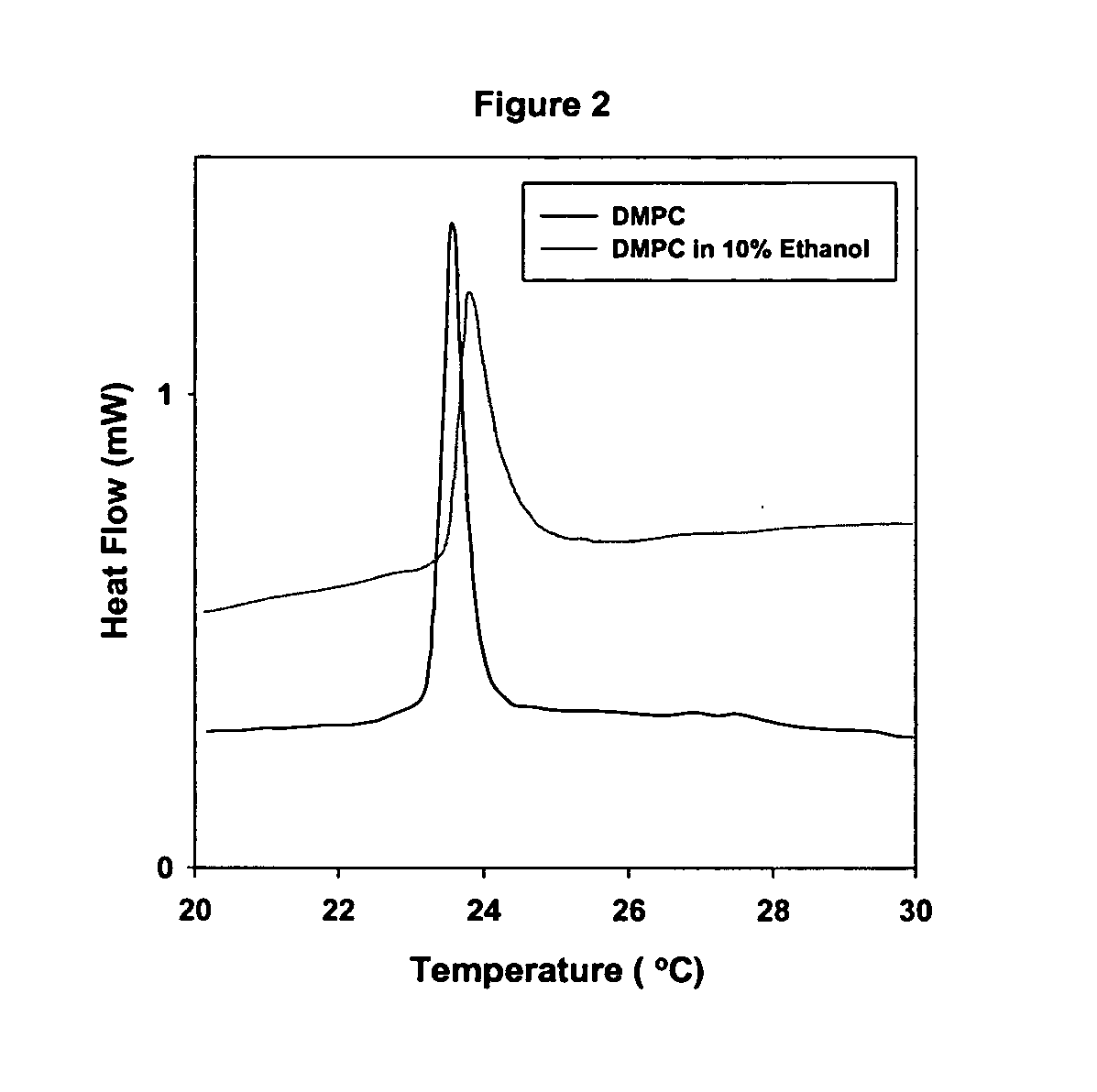
This example describes the effect of ethyl alcohol on tertiary structure. The near-UV CD spectrum is sensitive to the specific orientation of the aromatic groups and tertiary structure. In 100% aqueous, lysozyme displayed three positive bands at 280, 287 and 291 nm; these have been assigned to the transitions of Trp residues. In the presence of lower concentrations of ethanol (≦60% vol / vol), enhancement in the CD bands was observed. In addition, it was also observed that the ratio of the positive peaks at 280 and 287 nm was sensitive to the presence of ethanol. However, further increase in ethanol concentrations resulted in the loss of the CD bands, indicating a lack of any appreciable tertiary structure (data not shown).
Based on the CD results, it is clear that the presence of ethanol at lower concentration has no effect on the secondary structure but displayed a slight increase in the intensity of the near UV bands. Such increase in near UV CD bands may possibly be due to the s...
example 3
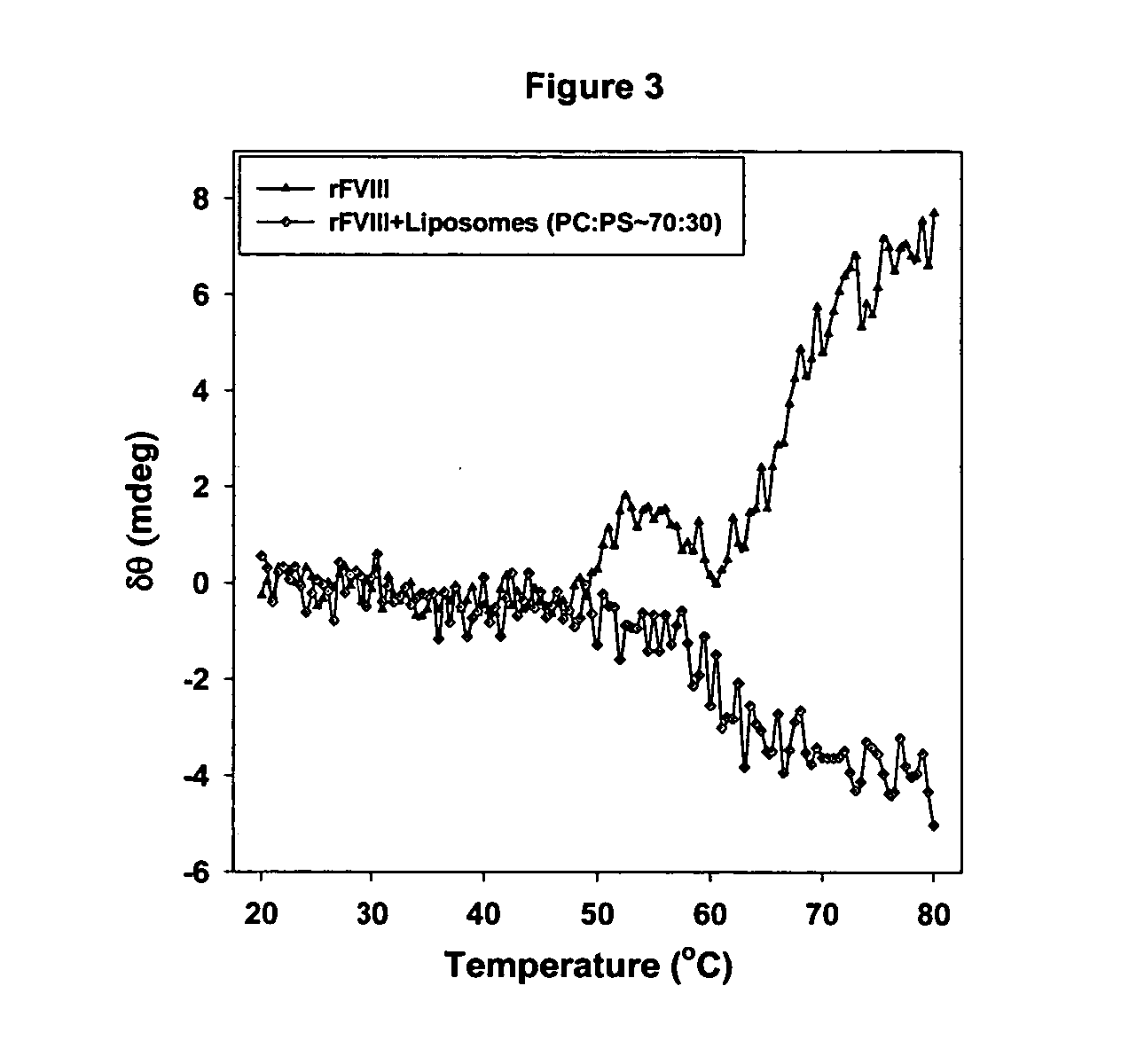
In order to determine the exposure of hydrophobic domains associated with the unfolding of the protein, the binding of fluorescence probes such as 1,8 anilinonaphthalene sulfonate (ANS) was investigated. In aqueous medium, the fluorescence intensity of the probe increased as the protein unfolded indicating the exposure of hydrophobic domains as the protein unfolded. The estimation of the Tm based on such profile was around 74° C. and is consistent with thermal denaturation studies and previously published results. But in the presence of low concentrations of ethanol, the Tm and exposure of hydrophobic domains was found to occur at lower temperature. For example, at 50° C., the fluorescence intensity of the probe bound to protein in aqueous environment increased by 10% over that of the unfolded state, whereas the presence of 20% ethanol the fluorescence intensity of the probe increased by 30%. In order to account for the contribution of solvent enhanced fluorescence, the initial flu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com