Paper machine belt
a technology of paper machine and process belt, which is applied in the field of paper machine process belt, can solve the problems of paper sheet misalignment, paper sheet damage, and serious problems for papermakers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
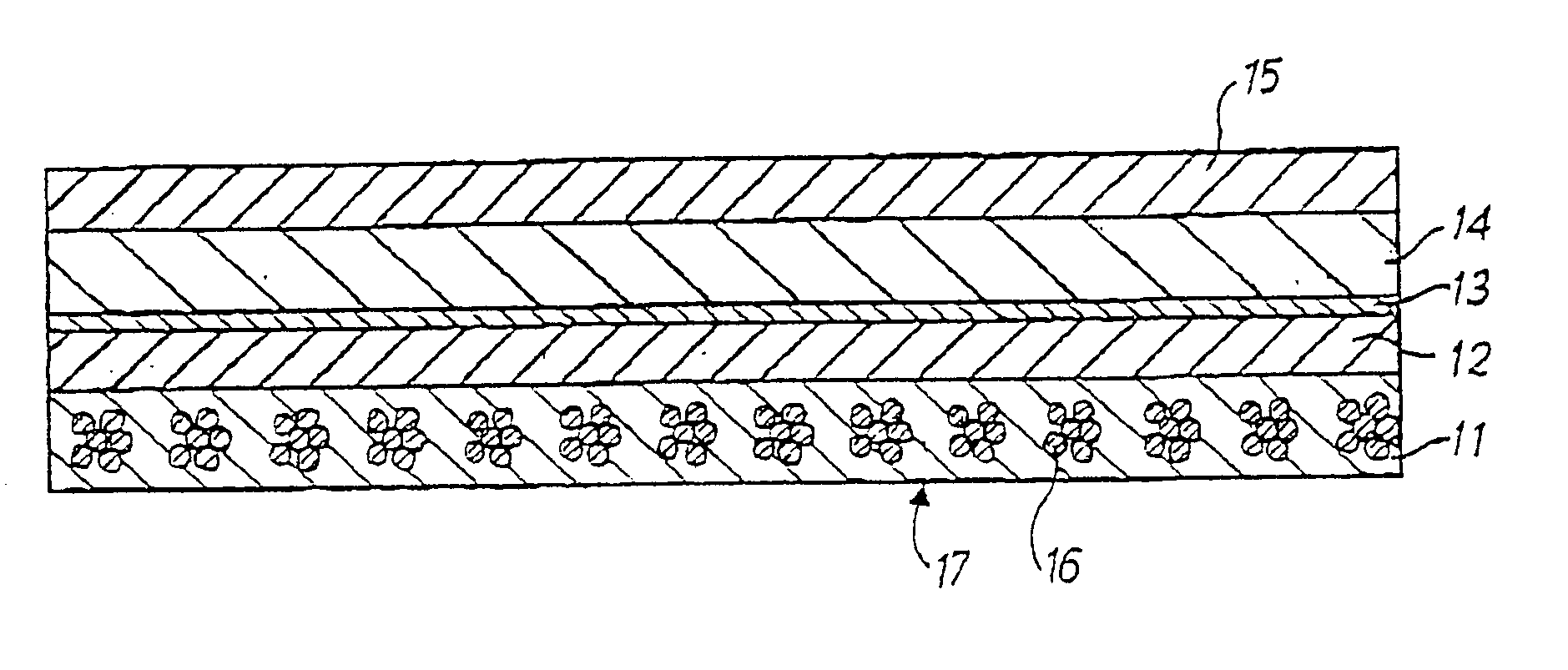
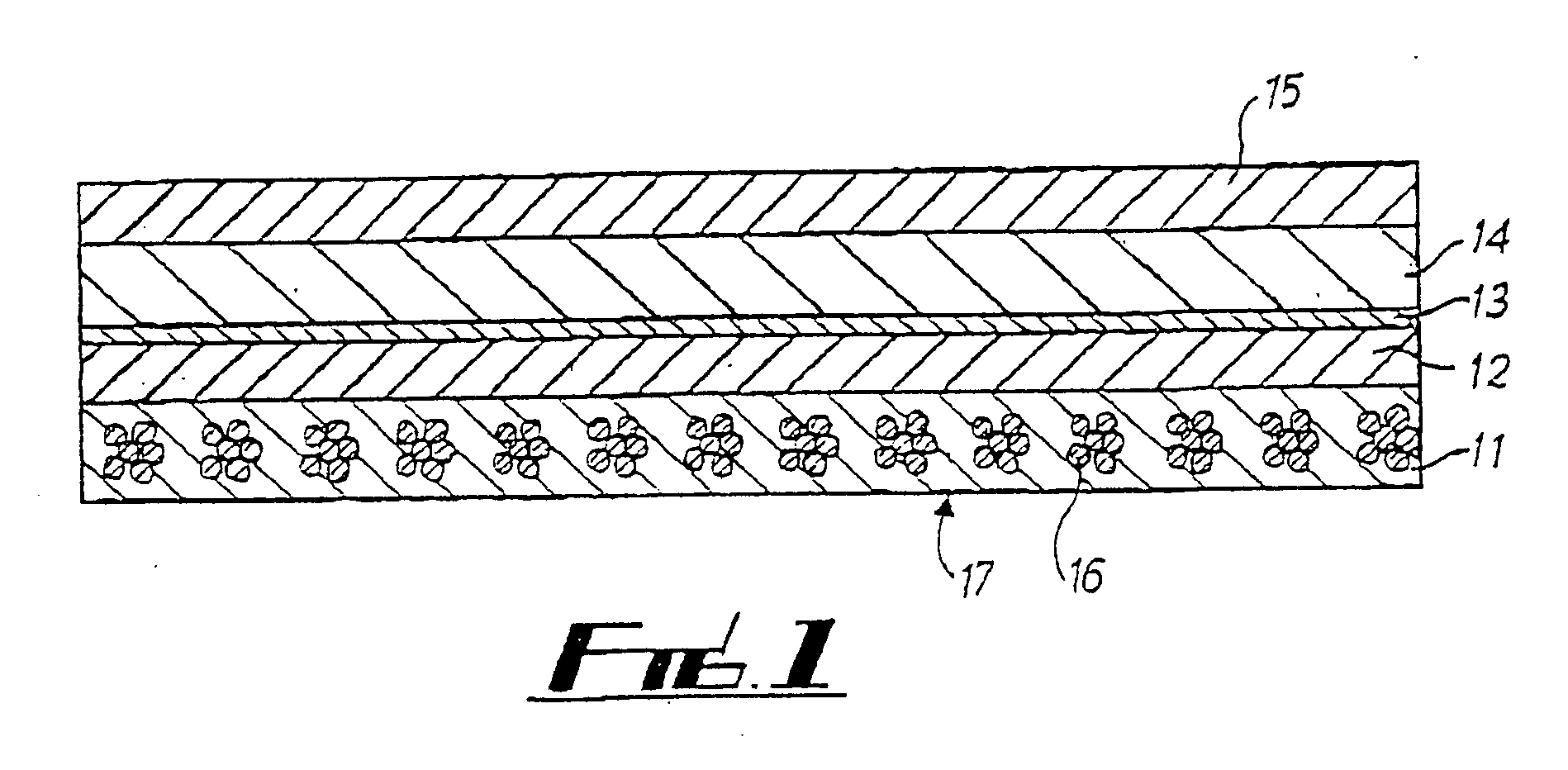
[0046] Referring to FIG. 1, a transfer and smoothing belt 17 for use in the press section of a paper machine includes an endless loop having five layers 11-15.
[0047] The supporting layer 11, includes spirally wound machine direction yarns 16 into which batt has been needled to hold the yarns 16 in position. In this embodiment the machine direction yarns include three pairs of yarns twisted together.
[0048] The second layer 12, located on layer 11, itself includes two individual layers of thermoplastic polyurethane each having a weight of 400 g / m2 and being 0.4 mm thick. On heating these two polyurethane layers, a single homogeneous layer is formed which bonds and partially impregnates the md supporting fabric 11 and the adjacent upper cd supporting layer 13.
[0049] Layer 13 includes a quasi non-woven structure made up of multifilament, cross-machine direction yarns and extremely fine machine direction yarns, for loosely holding the cross-machine direction yarns in position. This la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com