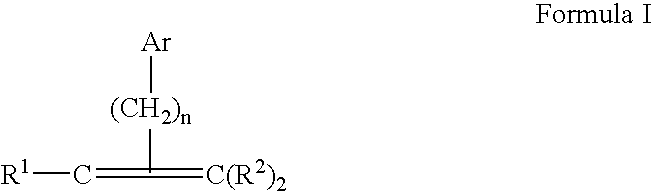Multilayer structures
a multi-layer structure and polyethylene technology, applied in the direction of weaving, pedestrian/occupant safety arrangements, vehicular safety arrangements, etc., can solve the problems of polyethylene films failing in several applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 16 to 24
R
[0148] The coated fabrics of Examples 16 through 24 find use in artificial leather.
example 16
[0149] Example 15 repeated except that the polymer formulation does not contain Silcat R and ATH, but includes 11.4 parts of Perkadox 14S and 5 parts of Perkalink 300. The polymer formulation is applied onto FAB3 as described in Example 15. A standard mat lacquer is applied. Subsequently the polymer coating is foamed in an oven at 200° C. during 2 minutes. The foamed structure is then embossed in a hot platen press at about 100° C.
example 17
[0150] 80 parts of ESI-6 are blended with 20 parts of Affinity HF 1030 polyolefin plastomer. This blend is mixed with 8 parts of ultra fine calcium carbonate, 2 parts of titanium dioxide, 2 parts of Perkadox 14S, 2 parts of Porofor ADC LC2, 0.1 parts of Irganox B225, 0.5 parts of zinc stearate, 0.5 parts of zinc oxide, and I part of stearic acid. This formulation is coated onto FAB3, a mat lacquer is applied to the resulting coating and the coating is foamed as described in Example 15.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Structure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com