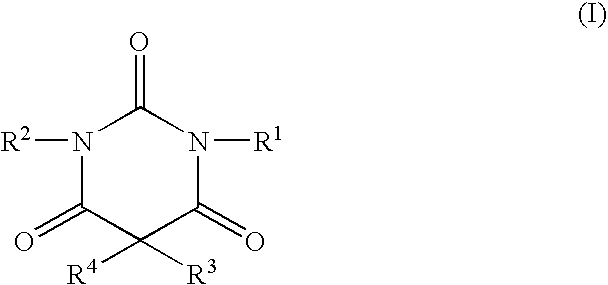
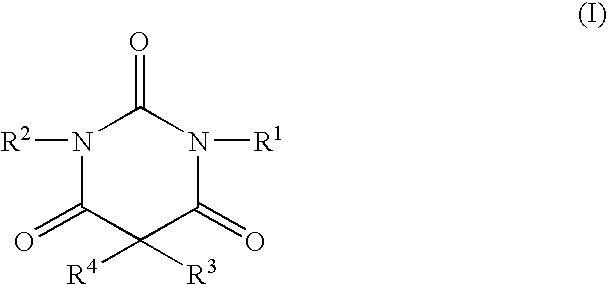
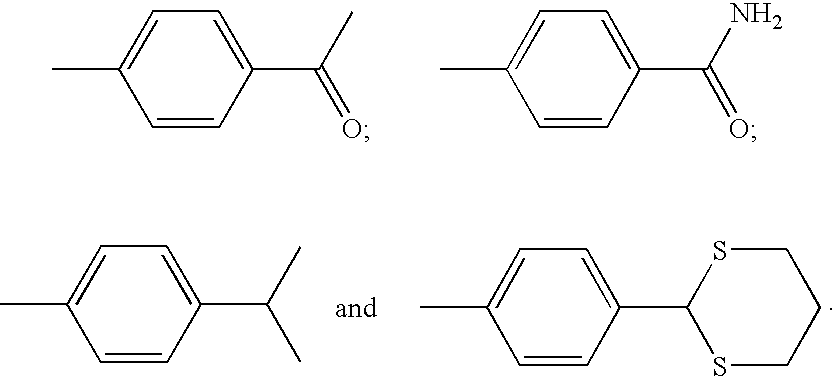
Non-sedating barbituric acid derivatives
a barbituric acid and derivative technology, applied in the field of new drugs, can solve the problems of irreversible damage to neurons and brain infarction, no adequate therapies are yet in practice, and phenobarbital has sedative and hypnotic effects, and achieves long-acting neurological activity, without significant hypnotic and sedative effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0101] The anticonvulsant activity of the barbituric acid derivatives of the invention may be demonstrated or tested by evaluating the protection against a maximal electro shock seizure (MES) in treated rats. MES tests are widely used for the assessment of anticonvulsant properties of chemical compounds, mainly due to the good correlation between the test results and the clinical finding of efficacy in patients suffering from epilepsy. In a typical MES test carried out to evaluate the anticonvulsant properties of barbituric acid derivatives of the invention, corneal electrodes are employed, a current of about 150 milliamperes is used and a 60 hertz stimulus applied for about 200 milliseconds. Rats are tested on the day prior to drug administration so as to eliminate from the study any animals failing to respond with a complete tonic convulsion including tonic hind-limb extension (THE), which serves as the basis for the assessment of the efficacy of the active material employed. Anim...
example 2
[0103] The non-toxicity of barbituric acid derivatives of the invention can be tested by repeated administration of a high dosage, as follows:
[0104] The test compound suspended in warm polyethylene glycol 400 or other suitable solvent is administered in an initial dose of about 1500 mg / kg by gastric tube to, for example, Sprague Dawley rats. A similar dose is administered to same rats after 24 hours and again 48 hours after the first administration. Animals are examined for several hours after administration, again prior to the next dosing, and through an additional 3 days after the last administration. The toxic effects of administration are monitored as well as behavioral effects such as, for example, locomotion, escape behavior, feeding or any other observable effect.
example 3
[0105] The tranquilizing and muscle relaxant properties of the barbituric acid derivatives of the invention can be demonstrated by monitoring the behavioral and motor effects observed with treated mice.
[0106] For example, the test composition in alkalinized saline may be administered intraperitoneally to, for example, Swiss Webster mice. The time required for animals receiving various doses to exhibit particular motor and behavioral effects is noted. Effects monitored may include, for example, muscle hypotonia, motor activity, quietness and escape behavior. Toxic effects are also noted.
[0107] The efficacy of the composition can be evaluated relative to known centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants and / or tranquilizing drugs. The combination of the tranquilizing effect without impairing the capacity of the animal to react to its environment is highly desirable in agents used for the treatment of anxiety. Hypnotic activity or depression of the central nervous system is preferably...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com