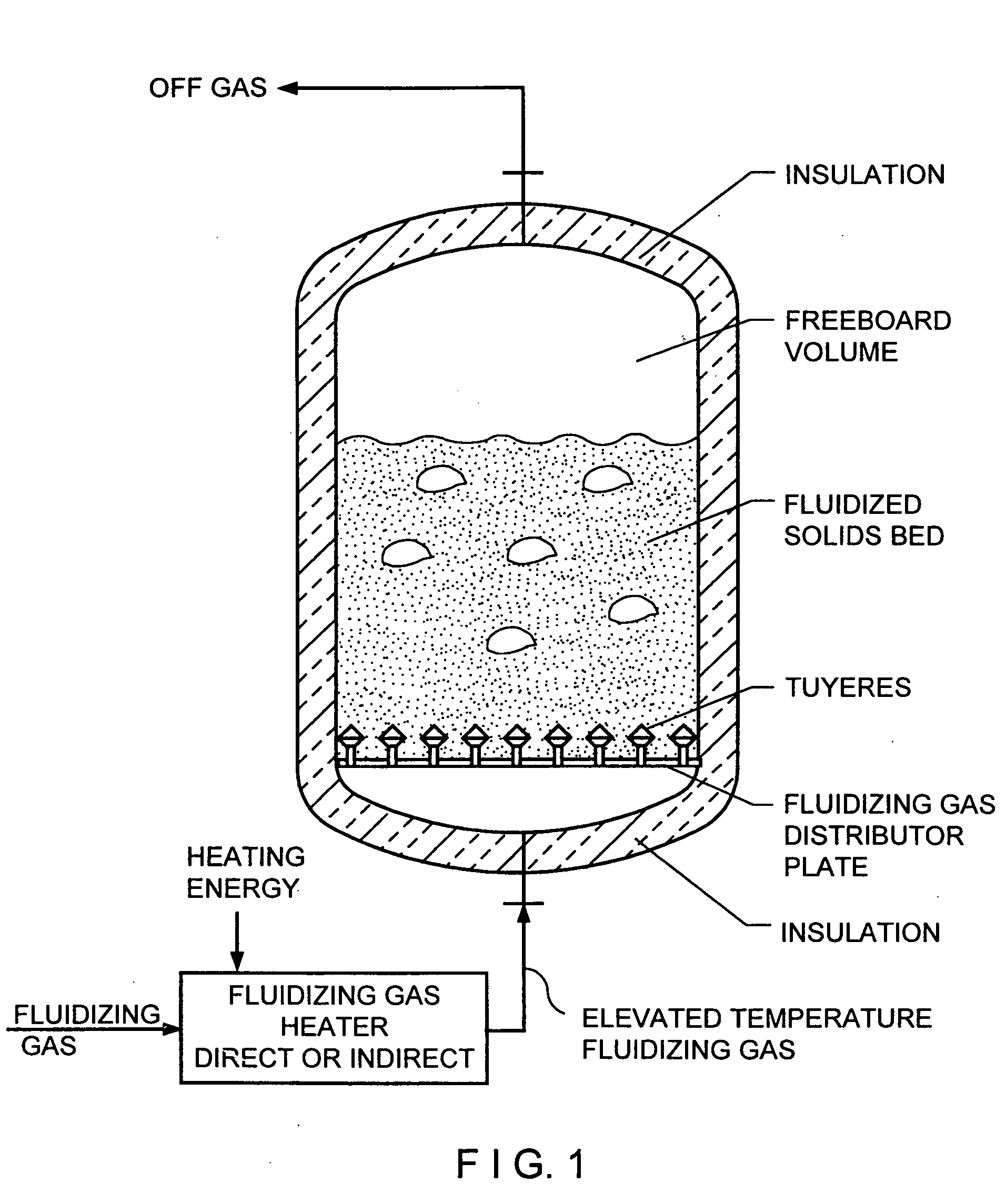
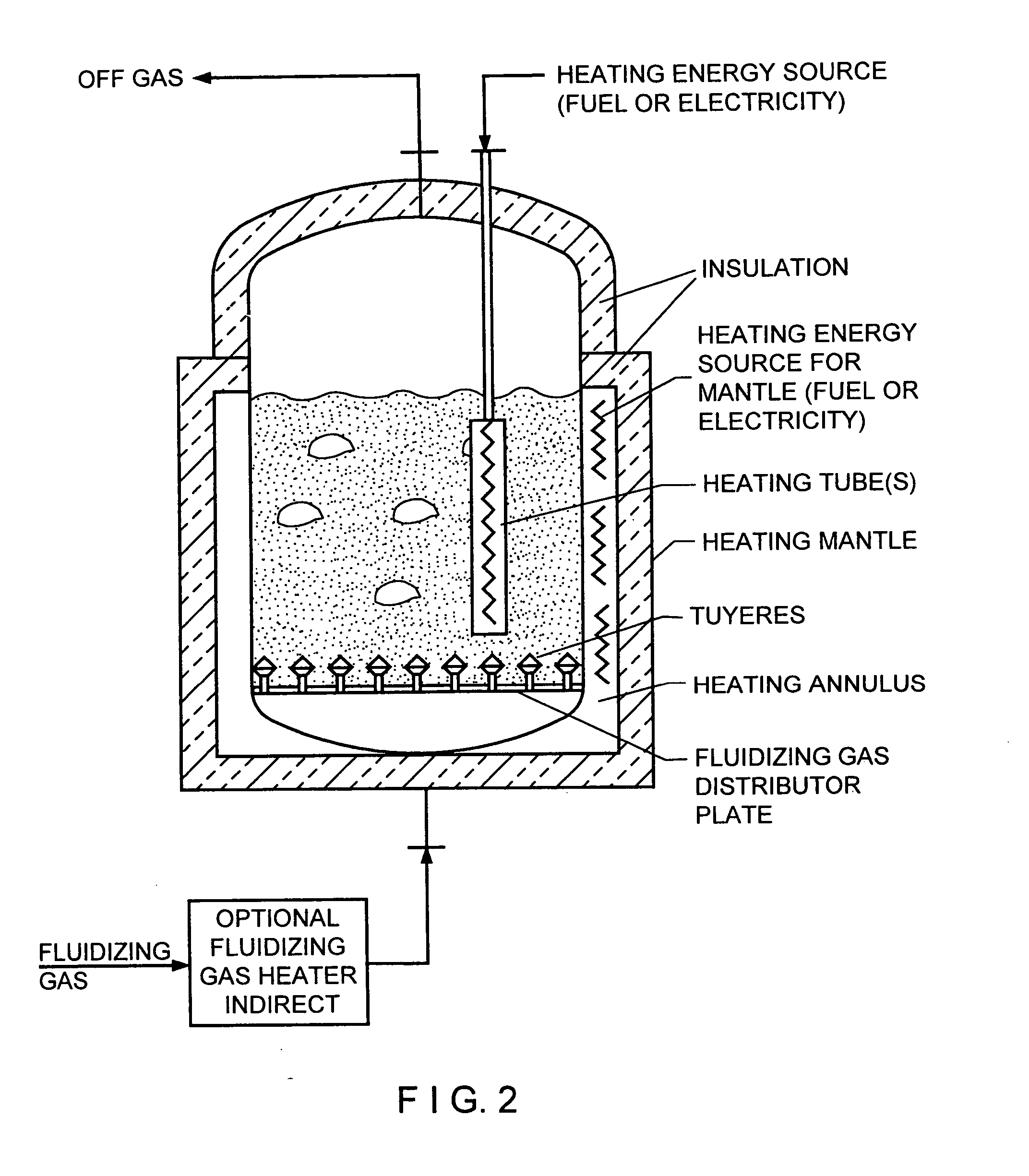
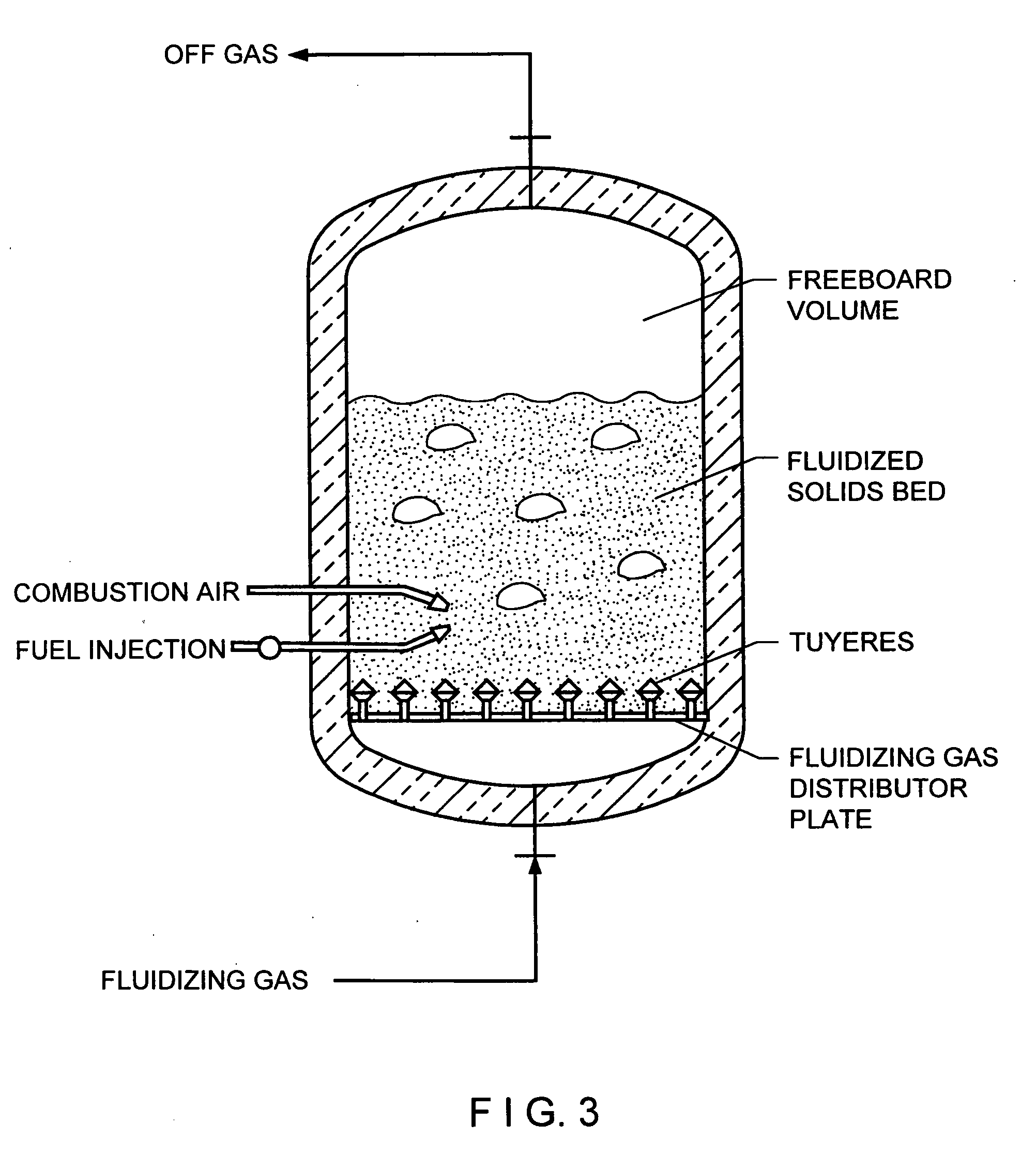
Fluidized bed gas distributor system for elevated temperature operation
a distributor system and fluidized bed technology, applied in lighting and heating apparatus, furnace doors, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of direct injection of fuel into the fluidized bed by mechanism, adverse effect on the quality of products, and inability to be employed, so as to reduce or eliminate the high temperature zones, the effect of favorable heat transfer behavior of fluidized solids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] Turning now to the figures where like parts will be similarly numbered, FIG. 4, shows a high temperature fluidized bed furnace 10 in one typical configuration involving the processing of a major metal part. This furnace is equipped with a fluidized bed gas distributor 12. This gas distributor 12 is shown in more detail in FIG. 5 and the downward discharging tuyere generally designated 14 is shown in FIG. 6.
[0038] In this invention, high temperature fluidizing gas is distributed through the furnace 10 in a horizontal plane by a piping array 16 as shown in FIGS. 4, 5, and 6. With the discharge of the fluidizing gas from the tuyeres 14 located below the distributing piping array 16, the elevation level of initiation of fluidization of the solids is below the piping array 16. Therefore, the piping array 16 has fluidized solids bed 18 all around it, and the heat transfer rate from the piping array 16 to the bed of gas fluidized solids benefits from the typically favorable heat tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com